Unfortunately, now a fairly small part of people can boast of a beautiful snow-white smile. An even smaller proportion do not have hidden problems and diseases of the oral cavity. Teeth deteriorate, and sometimes quite quickly. What could be the reason, and therefore how to avoid such problems? We will try to figure it out with you together.
The first thing you need to understand is how the tooth itself works. The basis of the tooth is dentin, which is covered with enamel in the crown part and in the root part with dental cement. Inside the tooth there is a cavity filled with pulp. Through the pulp, teeth receive nutrition from the blood vessels of the body. The main protection of tooth integrity is enamel. Almost entirely tooth enamel consists of mineral salts, the lack of which is one of the reasons for the onset of destruction of the integrity of the tooth. Harmful bacteria that enter the mouth through food can remain on the teeth and multiply there. If food remains between the teeth after eating, these are ideal conditions for the development of harmful bacteria. If the tooth enamel does not have enough minerals or is damaged by mechanical stress, bacteria begin to attack the dentin. This is how caries and other dental diseases appear.
Chronic diseases
The main disease is caries. If left untreated, the tooth will collapse, as the superficial lesion gradually penetrates deeper, reaching the nerve. They can also get sick and deteriorate in the presence of certain chronic diseases:
- Diabetes mellitus provokes the development of periodontitis, which causes premature tooth loss and destruction of the jaw system. In diabetes, mineral metabolism in the body is disrupted, fluoride and calcium are washed out of it, and their deficiency leads to thinning of the enamel. As a result, bacteria quickly penetrate inside the tooth, destroying it.
- Osteoporosis affects not only the spine, but also the jaw bones on which the teeth are attached. The disease develops due to a lack of calcium, which is the main element in the structure of the skeletal system. Osteoporosis destroys periodontal tissue, causing gum disease, making gums soft and exposing tooth roots where bacteria can easily penetrate.
- Hypertension, for the treatment of which drugs that cause dry mouth are often prescribed. As a result, pathogenic microorganisms are not washed off by saliva, actively multiply, penetrating microcracks in the enamel, and increase the risk of caries.
- Gastritis with high acidity, changing the qualitative composition of gastric secretions and disrupting the absorption of phosphorus and calcium from it. Their deficiency leads to a decrease in the strength of the enamel.
The curvature of the spine also has a negative impact, which can provoke improper closing of the jaws, which leads to loosening and wear of teeth. It negatively affects the condition of the oral cavity and impaired metabolism, due to which the body does not receive the required amount of vitamins and microelements.
Why do teeth deteriorate?
Reason #1 - bacteria
They are tightly attached to the surface of the tooth, accumulate, form dental plaque and secrete enzymes. As a result, organic acids are formed - pyruvic, lactic, butyric, etc. Under the dental plaque, the enamel becomes softer, and then a defect forms on it. Moreover, the superficial layers of enamel are damaged less than the deep ones. At first glance it looks like minor damage. In fact, half of the tooth is already missing inside.
Reason #2 - pH
The more acidic the environment in the mouth, the more comfortable it is for bacteria. An acidic environment is the result of eating habits. Do you like sweets, baked goods, soda? Can't imagine yourself without smoked sausage? Are vegetables and herbs rare “guests” on your table? This is fraught with chronic acidosis - “acidification” of the body. And this is a direct path to caries. As well as chronic fatigue, osteoporosis and other “diseases of civilization.”
Poor nutrition
Proper nutrition affects both the entire body as a whole and its individual systems, including preventing the development of dental diseases. The most dangerous is the unreasonable consumption of carbohydrates, namely sugar-containing products, and their significant predominance in the diet.
To maintain dental health, it is recommended to include foods rich in:
- protein (meat, fish, eggs, milk), since its deficiency has an unsatisfactory effect on the accumulation of calcium;
- fluoride (seafood, fish, buckwheat, radishes, carrots), the optimal amount of which increases the resistance of tooth enamel to pathological factors;
- calcium (cabbage, nuts, fruits, dairy products), which has a positive effect on the crystal lattice of teeth.
In order to avoid negative effects on the jaw system, you should limit the consumption of sticky, viscous foods - toffee, chocolate bars, liquid caramel.
Such food sticks to the teeth, is poorly washed off by saliva, and contributes to the development of caries. You should not abuse sweet carbonated drinks and packaged juices, due to the high sugar content in them.
What does a tooth consist of?
The tooth is an independent organ, has a unique structure and its own blood supply.
Dentin, pulp and enamel form the basis of the tooth
The base of the tooth is represented by dentin, the outside is covered with enamel, and inside the dentin there is soft connective tissue - pulp. The root of the tooth also consists of dentin, but is covered on the outside with cement.
Enamel is the strongest tissue in the body, far exceeding the strength of ordinary bones. 96% consists of inorganic compounds, the basis of which is crystals of calcium hydroxyapatite. The remaining 4% comes from organic compounds and water.
This fabric is strong, but fragile, so if there are significant temperature changes, cracks may appear in it.
Dentin is a tissue consisting of an organic component and an inorganic matrix. The organic component is represented by connective tissue, namely collagen fibers. The inorganic matrix consists of calcium hydroxyapatite crystals. The production of organic substances is carried out by dentin cells - odontoblasts. It is dentin that reacts to temperature and chemical stimuli when the enamel is destroyed.
Pulp is loose connective tissue, covered with dentin, penetrated by vessels and nerves. Performs the function of nourishing the tooth and also ensures its sensitivity.
Improper hygiene
To maintain dental health, daily oral hygiene is necessary. The main thing that is taught from early childhood is to clean them twice a day, morning and evening, preferably after eating for at least 3 minutes.
In addition, proper hygiene includes:
- optimal selection of toothbrush and toothpaste, depending on the condition of the gums and teeth;
- replacing the old brush with a new one at least once every three months;
- cleansing the tongue and cheeks.
People who maintain proper hygiene are less likely to develop gingivitis and periodontal disease.
In addition to a toothbrush and paste, it is recommended to use special rinses and floss, the diameter of which is selected depending on the distance between the teeth, to clean the oral cavity. You should not use one paste for more than 3 months to avoid addiction.
An electric toothbrush cleans better than a regular toothbrush.
Not true
I call these brushes brushes for the lazy. If you have an electric brush with a spinning head, I suggest throwing it away. She is not able to clean plaque. There is not enough power to rotate the head enough times. The trajectory of movement of such brushes only contributes to the fact that plaque ends up in the interdental space. If your electric toothbrush has a head that looks like a regular one, you can safely use this one. But still, it cannot be said that it cleans better than usual. They work the same way.
Genetic predisposition
The quality of teeth depends on what kind of teeth the parents had. Dental heredity can manifest itself both in children, during the formation of teeth, and in adults. It is not the specific disease that depends on genes, but the predisposition to it.
Heredity affects:
- tooth structure;
- jaw shape;
- metabolism in the body, which influences the occurrence of caries.
Studies have shown that if both parents had the first manifestations of caries on their lower teeth, then the same row will be weaker in the child. Scientists also found that if mothers had bad teeth, then 90% of children subsequently developed various dental diseases.
Chewing gum is good for your teeth
Is it true. But with reservations
Chewing gum works like an apple - it cleans your teeth. But you can snack on an apple, but not on chewing gum. In addition, it is important when you chew gum and how long you do it. If the gum does not contain sugar and you chew it for two or three minutes after eating, then yes, it is rather useful, it will clean your teeth and promote digestion. If you chew gum often, for a long time, or instead of eating, you can cause great harm to the stomach; in this case, the benefits for teeth are in doubt.
Lifestyle and micronutrient deficiencies
To a certain extent, a person’s lifestyle affects the condition of their teeth. Thus, in people involved in certain sports (boxing, hockey), they are often injured, their integrity is compromised, a crack forms, and a crown or root fracture occurs. Because of this, the tooth becomes loose and its position in relation to the rest of the jaw changes.
A lack of vitamins and microelements causes hypovitaminosis, which is manifested by bleeding gums during the cleaning process. Most often, this happens in the winter-spring period, due to a lack of fresh fruits and vegetables.
To eliminate vitamin deficiency, you should take synthetic preparations that contain the required amount of all trace elements and minerals.
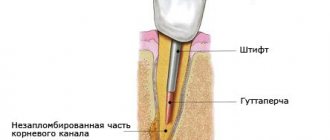
If you take several x-rays in a row, you can get high levels of radiation
Reality: According to one of the leading specialists in dental radiology, D.V. Rogatskin, one intraoral photograph of a tooth corresponds to approximately one microsievert.
The radiation dose when taking one three-dimensional image on a dental tomograph is approximately equal to the radiation dose from a panoramic image and is about 20-50 microsieverts. What to do?
You should not apply to a peaceful dental office the same concepts that are used at a nuclear test site. During the treatment process, you can and should take as many x-rays as your doctor needs, and if necessary, do not be afraid to do 1-2 studies per year on a dental tomograph. It is necessary to understand that your attending physician takes a picture, or a series of pictures, so that the quality of treatment is at the proper level and the tooth will serve you for many more years. And such a modern method as tomography of the maxillofacial area goes beyond the boundaries of conventional x-ray examination and often allows the doctor to see in volumetric form the pathology that cannot be determined on ordinary photographs.
Malocclusion
Malocclusion is diagnosed in the majority of the population. But, people go to the clinic for its correction only in case of a pronounced anomaly, although due to malocclusion the following occurs:
- Uneven load on teeth when chewing food. For some of them it is double the amount, while others are inactive. Due to excessive pressure, dental tissue is destroyed, leading to tooth loss.
- Reduced chewing activity, since not every tooth can participate in the process. To chew food well, you need to close your jaws tightly, but if you want to do this, discomfort and pain often occur. As a result, the composition of bone and soft tissue is disrupted.
An incorrect bite provokes the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the gums - periodontitis. In some people, due to an abnormal bite, involuntary grinding of teeth occurs - bruxism, which causes tooth wear and loosening.
Tooth decay during pregnancy
During pregnancy, teeth bear increased stress and can quickly deteriorate. This is due to the growing fetus.
The body's reserves of calcium, phosphorus and magnesium during pregnancy are spent on fetal development.
For the formation and growth of its skeletal system, a large amount of calcium, phosphorus and magnesium is required. If there is insufficient supply of these elements with food, they are borrowed from the body of the expectant mother. Calcium is contained in teeth in an easily accessible form, so it is primarily deposited from there. This leads to enamel fragility and reduced resistance to external influences. As a result of hormonal changes, the composition of saliva changes to the acidic side, which also negatively affects the teeth.
Important! When preparing for pregnancy, special attention should be paid to oral health by treating all teeth. This will reduce their destruction during pregnancy.
Bad habits
Bad habits have an important impact on the condition of the oral cavity. These include:
- Drinking alcohol and smoking. Alcohol and nicotine contained in drinks and cigarettes change the composition of saliva, increasing the acid content. This negatively affects the composition of tooth enamel, and pores form in hard tissues.
- Chewing laziness. Dentists use a similar term to describe reluctance to eat solid foods that require thorough chewing. As a result, there are no processes of self-cleaning of the oral cavity; dental plaque accumulates in large quantities, causing caries and damage to periodontal tissue.
The habit of constantly gnawing nuts and seeds, opening the lids of cans and bottles with your teeth, and using toothpicks also negatively affects the condition of your teeth and provokes their damage.
Maintaining oral hygiene, a balanced diet, including raw vegetables and fruits, enriched with essential vitamins and microelements, will have a beneficial effect on the condition of teeth and gums.
You should also minimize the consumption of sweet drinks and sugar-containing foods and get rid of bad habits. But, first of all, even excluding all the negative aspects, it is necessary to regularly (at least once a year) undergo a preventive examination with a dentist.
Caffeine
Drinks containing caffeine (any type of coffee, cola, energy drinks) provoke dehydration and slow down the absorption of vitamins and minerals (including calcium). They stain teeth, change the color of enamel, making it darker. Therefore, dentists at the Dentospas clinic do not recommend drinking coffee in large quantities.
Caffeine also has beneficial properties: it contains fluoride and has an antibacterial effect, but coffee drinks do more harm to teeth than good. You can replace coffee with chicory. For those who are used to drinking a lot of green tea, it is better to switch to herbal teas.
You have questions?
We will call you back within 30 seconds
+7
What vitamins and elements are needed for dental health?
Vitamin A
Many people have heard that in order to maintain good vision, a sufficient intake of vitamin A is necessary in the body. But it also plays a huge role in maintaining oral health. Vitamin A helps increase the resistance of mucous membranes to damage, strengthens gums, prevents loosening of teeth, and has a positive effect on the condition of tooth enamel. With a deficiency of this vitamin, the gums become inflamed, which is accompanied by the appearance of swelling. Wounds in the mouth heal very slowly, the enamel loses its smoothness, and the teeth become loose, which can lead to the development of deep caries and a number of other dental diseases.
The causes of caries are food debris and various types of bacteria. It is vitamin A that stimulates the production of saliva, which provides natural cleaning of the oral cavity. Vitamin A is found in foods of plant and animal origin. A sufficient amount of this element is present in the liver of mammals, marine fish and eggs. Don't forget about carotenes, the largest amount of which is found in carrots. Excellent sources include cabbage, green onions, pumpkin, red peppers, and spinach. Beta carotene is found in many fruits and legumes. Children under five years of age are more susceptible to vitamin A deficiency. To make up for the deficiency, give children enough fruits, vegetables and dairy products. This will avoid a number of problems with teeth and gums.
Vitamin B3
Vitamin B3 (or niacin) is an essential participant in most chemical processes and reactions in the human body. An insufficient amount of this substance over time leads to the appearance of ulcers in the mouth, stale breath and the development of dental caries. Among food products, good suppliers of B3 are fish and its derivatives, and chicken.
Vitamins B12 and B2
A lack of these vitamins leads to inflammation of the tissues, gums, and tongue, and the result of a more complex deficiency of vitamins B12 and B2 will be gingivitis and inflammatory processes in the gums. Foods that provide the body with vitamin B12: almonds, greens (spinach), whole grain pasta. The body receives vitamin B2 from foods such as meat, fish, and milk.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C helps maintain healthy gums. Its deficiency leads to serious consequences: the gums begin to bleed, the teeth become mobile, which, in turn, causes caries. A sufficient amount of vitamin C reduces the likelihood of plaque and increases the risk of developing caries. Vitamin C is found in all citrus fruits, broccoli, strawberries, bell peppers, and sweet potatoes.
Signs of vitamin C deficiency in the body:
- sensitivity and bleeding gums;
- the appearance of ulcers in the mouth;
- tooth mobility;
- tendency to frequent caries
Vitamin E
Vitamin E effectively removes harmful substances from the body and promotes tissue restoration in the mouth. This vitamin is useful for babies with toothache and during teething. By eating sunflower seeds, nuts, avocados, fish and green vegetables, you can ensure that you receive the optimal amount of vitamin E.
Vitamin D
The lack of which important microelement contributes to the development of dental caries? One of the leaders in the list of useful vitamins for preventing caries is vitamin D. It helps to absorb calcium, which is a key element of dental health. Often the main causes of caries are a deficiency of calcium and vitamin D. With a deficiency of vitamin D, a person experiences a burning sensation in the mouth. Dryness and a metallic taste also appear, taste sensations change, certain parts of the mouth become numb, and caries develops. Vitamin D deficiency can be compensated for by adding eggs, fish, cod liver and dairy products to your diet. It is also useful to spend more time in the sun - at least 15 minutes a day.
Calcium
Which element is the most important for teeth? Many dentists will agree that calcium. If a person has enough calcium in his body, his teeth will always be healthy. Regular consumption of calcium helps strengthen tooth enamel. With its deficiency, not only teeth, but also bones deteriorate, because the deficiency of this microelement is replenished from the bones. Calcium is quickly absorbed into the blood, so it should be consumed regularly. To avoid tooth decay, you should enrich your diet with foods that are rich in calcium. A lot of this element is found in dairy products, green leafy vegetables, broccoli, beans, soy milk, nuts, and fish.
Signs of calcium deficiency:
- the mouth feels dry and painful lumps appear;
- teeth react to cold and hot foods with increased sensitivity (which can lead to the development of caries).
Phosphorus
It is difficult to overestimate the importance of phosphorus in the formation, integrity and health of teeth. Scientists were able to prove the need to take phosphorus-containing foods for more efficient absorption of calcium in the body. Phosphorus is found in sufficient quantities in foods such as milk, kefir, yogurt, lentils, legumes, red meat, various nuts, cereals, and cheeses.
Iron
The lack of this element in the body provokes inflammatory processes in the tongue and causes ulcers in the oral cavity. This is explained by the ability of iron to control the balance of red blood cells, effectively resist infections and diseases, and strengthen the immune system. Chicken eggs, fish and seafood, beef and pork, wholemeal bran, beans, and buckwheat will help you get the missing nutrients.
Possible signs and consequences of iron deficiency:
- anemia;
- joint problems;
- rupture of capillaries under the skin;
- acute inflammation of the gums.
Potassium
Potassium is an essential element in the construction and restoration of bone tissue, and therefore jaw bones. Sufficient potassium content in the body prevents the formation of osteoporosis. This microelement ensures optimal blood clotting, which helps wounds in the oral cavity heal faster.
The leader in potassium content is wheat bran. There is also a lot of this element in legumes, various vegetables and fruits, some types of meat, seafood and fish, dairy products, green tea and mushrooms.
Fluoride
Fluoride is used in dentistry to combat the destruction of enamel. It is a common ingredient in many toothpastes. It effectively fights caries and also protects tooth enamel from negative influences. If there is a deficiency of fluoride, gums may bleed and dental caries may develop. Foods rich in fluoride: seafood, nuts, green and black tea.
Iodine
Iodine is a trace element that is involved in almost all biological processes actively occurring in the human body. This element helps calcium to be absorbed into the tissues, which contributes to the growth of teeth and maintaining them in a healthy condition. Iodine deficiency can be replenished by eating seaweed, garlic and sesame seeds.
Magnesium
Magnesium is a trace element that can prevent the thinning of enamel and its further destruction. With a lack of magnesium, caries develops very quickly. Magnesium is present in cabbage, spinach and chocolate.
Zinc
This trace element is responsible for controlling the growth of bacteria in the mouth. With a lack of zinc, there are too many bacteria, and this already leads to the development of serious caries. Zinc is found in sufficient quantities in pork, beef and lamb, as well as in cheese products, beans and peas, and in large quantities in morels and shiitake mushrooms, pumpkin seeds and dark chocolate.
Folic acid
Folic acid (folacin or vitamin B9) is involved in the body's redox reactions. If there is a deficiency in the oral cavity, ulcers may appear on the mucous membrane and tongue, as well as bad breath. In this case, focal inflammation of the oral cavity or aphthous stomatitis appears. This trace element is found in spinach and lettuce leaves, cabbage, onions, potatoes, and meat (liver and kidneys).
Heredity is to blame for bad teeth
Reality : The role of heredity in the health of our teeth is extremely small and is manifested in the structure and properties of tooth tissue: enamel and dentin. In fact, a person even with not very good heredity has every chance of keeping his teeth healthy.
What to do?
Take proper care of your teeth throughout your life and make regular visits to your dentist.
Fact: Today, there is an opposite theory that lesions of specific teeth may indicate a predisposition to the pathology of a particular organ or an already existing disease.
Correlation of teeth affected by caries with pathology of internal organs