Tooth extraction is carried out plannedly, as well as for emergency indications.
The main indications for planned tooth extraction: complete or severe destruction of the tooth crown and the inability to use it for prosthetics, chronic periodontitis that is not amenable to conservative treatment, grade III tooth mobility in periodontal diseases, and others.
Urgent tooth extraction is indicated for purulent periodontitis, acute osteomyelitis, periostitis, sinusitis, lymphadenitis (if the source is a diseased tooth), fracture of the tooth crown exposing the pulp and some other diseases and conditions.
Removing various teeth has some of its own characteristics, for example, removing teeth with a crown is somewhat simpler than removing tooth roots. The extraction technique for the teeth of the upper and lower jaws, incisors and molars is also slightly different.
Features of the procedure
The canines on the upper jaw have one root located laterally. In cross section, part of the element resembles the outline of a triangle. In 30% of cases, the apex of the canine root has a curved structure. The outer part of the root is thicker than the inner one, but both sides of the alveoli are thicker in width than the incisors. Due to the listed features of the structure of the fangs, some difficulties arise when removing them from the socket.
Removing a maxillary canine requires certain specialist skills. The method involves complex, atypical extraction.
The patient’s further condition depends on how correctly the procedure is performed.
If the rules are not followed, infection of the wound cannot be ruled out, which may be accompanied by complications such as alveolitis, nerve injury, cyst, odontogenic phlegmon, periostitis, dry socket syndrome.
During the operation, the doctor should place the fingers of the left hand in the same way as when removing incisors on the upper jaw. When removing an element from the right side, the patient's head should be slightly turned to the left and vice versa. This position of the patient will be more comfortable at the time of surgery.
Removal of the maxillary canine is indicated for children whose baby tooth has not fallen out, but whose permanent tooth has already begun to grow.
Without surgical intervention, a pathology such as a double canine will develop: the baby and permanent teeth will grow in the same vertical plane.The cause of the pathology is ankylosis of the root of a baby tooth (fusion with the jaw bone).
Dentist
Novikova Olga Alexandrovna
8 years of experience
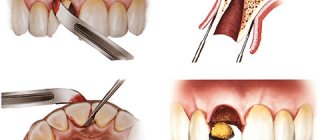
The canines on the upper jaw are removed from the socket using wide forceps. During the operation, the element swings alternately towards the lips and palate with rotation around the longitudinal plane of the fang. The doctor makes the first movement of the instrument towards the outer wall of the alveoli, since it has a thinner structure.
The next dislocation is performed towards the palatine alveolus, and then the specialist performs rotations. The procedure consists of successive rocking and rotation of the element until the nerve fibers and tissues surrounding it are completely ruptured.
Due to the anatomical features of the canines on the upper jaw, when extracting them, a specialist has to make a lot of effort.
Tooth extraction under sedation
Tooth extraction under sedation is used when several teeth need to be removed at once, especially if they are wisdom teeth, in complex operations. Sedation can also be used when removing one tooth, if the patient is prone to panic attacks, increased blood pressure due to stress and anxiety, etc.
This operation to remove an impacted tooth went according to plan. The duration of the complex operation was 3 hours. During the operation under sedation, the patient's condition was constantly monitored by an anesthesiologist, monitoring pulse, blood pressure, and respiration.
When Removal is Required
Indications for the removal of fangs on the upper jaw are divided into local and general. The last group of prescriptions includes chronic endogenous intoxication of the body due to rheumatism, sepsis, endocarditis and connective tissue pathologies.
Tooth extraction under anesthesia
The main task of all dentists is to ensure the safety of teeth using all possible methods.
Local recommendations for canine removal are divided into relative and absolute. Tooth extraction can be performed urgently if there are special indications for the procedure:
- suppuration of periodontitis;
- acute osteomyelitis;
- periostitis;
- phlegmon;
- other dental pathologies that cannot be treated with medication.
Fangs with a longitudinal fracture, severe damage to the coronal part and exposure of the pulp are urgently removed.
Elements of bone tissue are removed as planned in the following cases:
- if treatment of the inflammatory process in periodontitis and bone structures is unsuccessful
- in case of improper treatment, causing damage to the tooth root or its cavity;
- in case of complete destruction of the crown of the element and the impossibility of using its remaining part for prosthetic purposes;
- with significant mobility of the canine and its protrusion relative to the remaining elements of the row;
- with incorrect anatomical location of the tooth, as a result of which permanent damage to the mucous membranes of the oral cavity occurs;
- in the presence of unerupted or partially manifested elements that cause inflammation of the soft tissues.
In addition to the indications for surgery, the doctor must establish any restrictions on the procedure. Tooth extraction may be delayed due to chronic diseases or poor health of the patient.
Simple removal of the top eight
Simple is the removal of the upper wisdom tooth, which does not require preliminary dissection of the gums. This is how molars are removed that have erupted without pathologies and have small, even roots. Simple removal is carried out in 4 stages.
- The doctor conducts a diagnosis
- takes an X-ray or CT scan, assessing the position of the tooth and the structure of the root system. - The patient receives pain relief.
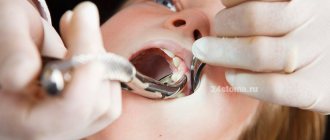
Removal of the upper “eight” is usually performed under local anesthesia. - The doctor places forceps on the crown of the tooth and performs luxation and traction
- he rocks the tooth and pulls it out of the socket. - The hole is treated with an antiseptic and, if necessary, sutured.
Read more about the operation in a separate article.
Contraindications to the procedure
The list of contraindications for removing a fang on the upper jaw includes:
- Cardiovascular pathologies – myocardial infarction (suffered earlier six months ago), bacterial endocarditis, hypertension.
- Diseases of the urinary system - pyelonephritis in the acute stage, glomerulonephritis, renal failure.
- Diseases of an infectious and viral nature - hepatitis, acute respiratory infections, influenza and other pathologies transmitted by airborne droplets.
- Exacerbation of psychological problems - manic psychosis, epilepsy.
- Pregnancy at 1, 2 and 9 months.
- Poor clotting .
- Cancer – acute leukemia.
- Malignant tumors located in the maxillotemporal zone.
Main indications and contraindications
Complex removal is required in a number of complex clinical cases when it is not possible to perform surgical intervention using standard techniques and instruments. Very often it is carried out in relation to the last painters (“eights”). As a rule, they do not have enough space, against which they begin to grow incorrectly (for example, erupt towards the cheek, injuring the mucous membrane), slowly erupt, accompanied by painful sensations. The last molars do not participate in the chewing process, so most often the dental surgeon decides to remove them in such situations.
Complex surgical procedures are resorted to in the presence of a chronic inflammatory process, against the background of which the bone tissue and the molar or premolar itself have fused. A complex operation cannot be avoided if the molar has several roots or its area is severely curved. Benign neoplasms (for example, granulomas or cysts) are often an indication for removal if the tooth is destroyed and there is no point in trying to restore it. Sometimes a complex extraction of a previously treated tooth is performed several times. This is due to the fact that it is not durable, its density is weakened, and it is capable of cracking.
As with any surgical intervention, there are a number of absolute and temporary contraindications to complex removal of molars or premolars. Among them:
- diseases of viral etiology;
- serious deviations from the cardiovascular system;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- blood diseases (anemia, poor clotting, leukemia);
- chronic pathologies during exacerbation;
- recent strokes and heart attacks;
- serious mental disorders (schizophrenia);
- long-term use of medications that affect blood clotting.
Progress of the operation
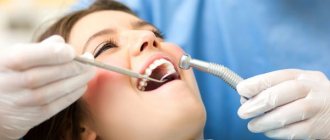
Before removing a fang on the upper jaw, local anesthesia of the treated area is mandatory. Dentistry offers a wide selection of anesthetics and methods of their administration, after which the patient will not feel severe pain during surgery.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Elements of bone tissue located on the upper jaw are often removed using bilateral infiltration anesthesia, less often using palatal, tuberal or infraorbital anesthesia.
It should be remembered that the therapeutic effect of the drugs used is reduced if there is inflammation at the location of the canine. Therefore, if the doctor advises urgent removal of an element, you should not refuse the operation and postpone it to a later date.
Extraction of the maxillary canine from the socket is performed using special tools - forceps and elevators. The equipment used has various designs.
Removal of dystopic and impacted teeth
Impacted teeth, as well as dystopic teeth, bring discomfort to a person.
When removing elements on the upper jaw, bayonet-shaped forceps are used. Elevators are used when extracting the roots of fangs or if forceps cannot be used to grasp the tooth tightly.
The operation can be performed according to two schemes: it all depends on the condition of the root. When saving the tooth crown, the procedure is performed according to the following algorithm:
- Peeling off the canine ligaments for better grip with forceps.
- Perform swinging movements.
- Fixing an element.
- Dislocation.
- Extracting a tooth from its socket.
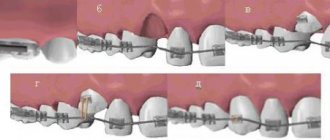
This type of canine removal is called simple because it is performed using one instrument. The tactics of the operation change if the coronal part is preserved and only the root needs to be extracted from the socket. This procedure is considered complex because the doctor uses several tools - elevators to dislocate the roots and forceps to remove fragments from the hole.
Removing fangs using elevators requires certain skills and abilities from the doctor. The basic rule when working with a tool is to correctly find the fulcrum for its working part.
If the alveolar wall is thick, the doctor tries to place the equipment between the root of the canine and the wall of the socket, while performing rotational movements. Such manipulations can loosen the tooth.
Sometimes during the process of removing a fang, the doctor needs to make an additional soft tissue incision. This type of operation is called atypical. The technique is used to remove unerupted fangs or those that have not completely appeared above the surface of the gum.
Features of the structure of wisdom teeth
The structure of a wisdom tooth is no different from other molars and consists of a neck, a root system (4–5 pieces) and a crown. In some cases, root development is disrupted and a single conglomerate is formed, that is, a tooth grows with one root.
Its only difference from its neighbors is that recent studies recognize the wisdom tooth as a rudiment that has lost its functional purpose during the evolutionary development of man. Scientists do not consider it as a full-fledged organ, since some part of humanity does not grow it at all.
However, the wisdom tooth has several parameters that distinguish it from the same “seven”:
- lack of milk precursors, which ultimately complicates eruption and impedes growth. There is no room left for it on the dental arch, which is why various developmental pathologies arise;
- the number of roots is greater than that of other molars - up to 5 pieces. In this regard, problems often arise when removing a wisdom tooth;
- significantly curved roots of the “eights” make cleaning and treatment of root canals very difficult;
- poor blood supply compared to other teeth leads to rapid aging, accompanied by fragility and susceptibility of tissues to caries, despite minimal load;
- many pathological conditions, for example, pathologies of the masticatory muscles, malocclusion, pericoronitis, are associated with the growth of “eights”.
Thus, the appearance of third molars has many more negative consequences than positive ones. Many patients are forced to see a dentist even before they can be seen in person.
Possible complications
After removing the fang from the socket, various complications may develop, which in the vast majority develop due to infection of the wound.
Dry socket syndrome
The problem arises due to the patient’s failure to comply with the doctor’s recommendations or too active treatment of the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions. The actions lead to the fact that a blood clot does not have time to form in the wound, protecting the soft tissues from the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms.
The condition is not life-threatening, but can cause a number of consequences, for example, inflammation of a postoperative wound.
Alveolitis
The disease is an inflammatory process that spreads to the mucous membranes of the socket. Alveolitis causes infection to spread to bone structures. Pathology rarely develops after the removal of fangs on the upper jaw; more often, this condition appears after the extraction of molars located in the lower row.
Nerve injury
If the canine is positioned incorrectly or has a curved root, then during surgery damage to its nerve endings may occur. Characteristic symptoms of this condition are loss of sensitivity in the operated area, numbness of the cheek, and the appearance of “running goosebumps.”
Alveolar exposure
Even with a normal course of the postoperative period, problems with wound regeneration may occur. If pain occurs at the site of the hole when consuming hot or cold food, this indicates that the area of the bone is not covered with soft tissue.
Cyst on a tooth
The development of a pathological formation after canine removal is a rare consequence. A cyst is a growth filled with fluid. In this way, the human body independently separates infected soft tissue from healthy areas.
The tumor, increasing in size, can spread to neighboring areas and therefore requires immediate surgical intervention.
The occurrence of odontogenic phlegmon
The pathology develops against the background of osteomyelitis of the jaw structures. The problem manifests itself as pain and swelling of the cheek in the upper jaw area. It becomes difficult for a person to open his mouth and consume food. The pathology is accompanied by a deterioration in health and a rise in temperature.
Odontogenic periostitis
It develops against the background of alveolitis or osteomyelitis and is an inflammation of the periosteum. The condition is manifested by a number of the following symptoms:
- rise in temperature;
- toothache ;
- swelling on one side of the cheek.
Removal of the maxillary canine is carried out taking into account the structure of this element of bone tissue. The tooth has only one root, which in 30% is located in the wrong position. The stages of surgery for this type of intervention are no different from removing the remaining elements located in the top row. Depending on the location of the canine and the condition of its crown, the doctor performs simple, complex or atypical tooth extraction.
Recovery period
How long does recovery take after removal of upper wisdom teeth and what limitations does it impose? In most cases, after 1-2 days the patient returns to normal life, but sometimes recovery takes longer. To prevent the rehabilitation period from being prolonged, it is very important to follow the doctor’s recommendations:
- take prescribed antibiotics, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- do not visit the bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool, or take a bath;
- follow a diet, if possible, eat only soft foods;
- refrain from smoking.
If the doctor did not make mistakes during removal, and the patient carefully followed all the doctor’s recommendations, then the recovery period will pass quickly, and the problem of the upper “eights” can be forgotten forever.
Why do you need to remove a cyst?
Patients sometimes do not want to resort to surgery, claiming that the tumor does not cause discomfort. Yes, the development of a cyst is asymptomatic. But it begins to destroy the root of the adjacent tooth, and then the surrounding tissue. And instead of timely basic surgery, you have to perform complex manipulations that threaten complications.
Another point:
If you do not remove the dental cyst while it is still forming (the cost will be determined by the attending physician), then there is a possibility of its degeneration into a malignant tumor.
Come for a consultation, and we will decide what steps you need to take specifically in your situation, whether you can save the tooth or need to remove it, we will take pictures to identify a cyst or granuloma. Fast, comfortable, pain-free.