What is pulpitis?
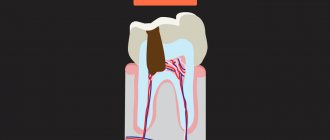
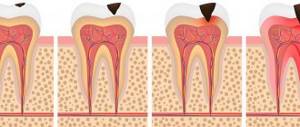
Pulpitis is a process of inflammation in the tissues inside the tooth, where the nerves and blood vessels are located. In children, this process is recorded much more often than in adults. This is especially true for temporary teeth.
The baby teeth
themselves are smaller in size, so both the dentin layer and the enamel layer are thinner, through which infection penetrates more easily.
The body's defenses in childhood are not yet fully developed and weakly fight infection. As a result, the rapid development of caries and pulpitis.
How much does pulpitis treatment cost?
In St. Petersburg, prices for services to eliminate pulpitis vary in different clinics. The cost of the procedure starts from 2500 rubles and can reach 6 thousand rubles. and more. Pricing is formed taking into account a number of factors:
- type and severity of pathology;
- treatment method;
- number of affected units;
- medications, filling materials and equipment used;
- status of the clinic and qualifications of the doctor.
The longer parents delay visiting a pediatric dentist, the more difficult and expensive the treatment will be.
Our clinic employs experienced pediatric dentists who can efficiently and painlessly eliminate any problems with children’s teeth. The cost is calculated in each case individually and depends on the complexity of the problem. Average prices for the treatment of pulpitis of primary teeth are indicated in the form below.
Symptoms of pulpitis of temporary teeth
Symptoms of pulpitis
milk teeth, according to dentists, are quite varied and even blurred. They may be clearly expressed, or they may be completely absent. However, on average they can be reduced to the following list:
- High body temperature.
- Pain of varying degrees, which can radiate to the temple, around the eye area and the back of the head.
- Inflammatory processes in the lymph node system.
- Swelling of the soft tissues around the diseased tooth.
- Inflammatory processes in the periosteum area.
Additional challenges in identifying symptoms
are related to the age of the baby. In the first years of life, he still cannot say what exactly is bothering him, and after a few years he can hide the symptoms “until the last” because he is afraid or does not want to go to see a doctor.
What is pulpitis of a baby tooth and treatment features?
Pulpitis of baby teeth in children is a rather dangerous disease.
If treatment is not carried out, this may negatively affect the condition of permanent units. Immediately below the milk teeth are the rudiments of permanent teeth. If an infection gets into them, then the permanent teeth will no longer be healthy as soon as they grow. Inflammation of the pulp in children can occur in two forms: chronic and acute. Chronic pulpitis
Occurs with superficial caries.
It occurs without pronounced symptoms, since, unlike adults, the child’s body reacts more mildly to infection. There are also cases where the disease developed with deep carious tissue damage, and even under fillings. Due to food getting into the interdental spaces or when exposed to hot and cold drinks, the baby feels a nagging pain, so he tries to eat only on the “healthy” side, which is already an alarming symptom and the reason for a visit to the doctor. Acute pulpitis
The acute form is observed in children from 1.5 years of age, when the pulp is already forming. Initially, the disease occurs in the serous stage, while serous fluid is formed in the canals due to inflammation. For the first time, the pain occurs at night, but soon the child complains of discomfort and pain when chewing. In a matter of hours, the disease can progress to a purulent stage, during which swelling of the cheek occurs and the body temperature rises sharply.
Types of pulpitis
Pulpitis of temporary and permanent teeth
dentists divide the disease into different types of disease.
Acute pulpitis
can be
focal
, usually with mild symptoms, and
general
(diffuse), which is difficult to miss.
There is a reaction to cold and hot. Chronic pulpitis
, with periodic attacks of pain, dentists divide according to the degree of inflammation into
fibrous, hypertrophic and gangrenous.
Chronic pulpitis can also worsen.
Treatment methods
Depending on the complexity, the disease can be treated in several ways:
- conservative, in which the pulp is preserved;
- surgical, which involves removing the infected pulp;
- tooth extraction if it cannot be saved by other methods.
A personal treatment plan is drawn up for each child. If you ignore visiting a doctor, then the risks of developing periodontitis, sepsis, gumboil and other pathologies increase to the maximum.
Treatment of pulpitis in children
When does the dentist treat pulpitis
, its main goal is
to relieve the inflammatory process
while the surrounding soft and bone structures are not affected. At the same time, in children’s teeth it is important to maintain the tedious vector during the formation of permanent ones. Treatment is divided into surgical and medical.
With conservative
(medical method) the dentist tries to keep part of the pulp alive. This can happen at the partial acute and fibrous stage of pulpitis. Using a bur machine, the cavity of the inflamed tooth is cleaned of affected tissue, disinfected, and a filling paste with a therapeutic effect is placed there. Treatment takes one visit to the doctor.
Surgical treatment of pulpitis
– this is the removal of the affected pulp and filling of the canals.
Performed using different methods. Vital removal
is used in children with incompletely formed roots.
The pulpous tissue is not removed at the root, but only the crown is treated and filled. Vital extirpation
is the method of choice for patency of root canals.
It is used extremely rarely in children, as it is long and painful. Devital pulp removal
is most often used in children. Dental arsenic is placed into the affected cavity. After a day or two, the already dead, non-sensitive pulp is removed, and in its place a medicinal paste is placed, which prevents the processes of tissue decomposition. However, this method makes it difficult for permanent teeth to erupt. Therefore, by the time they appear, the healed milk teeth are removed.
Treatment of temporary teeth
As a rule, a child’s first teeth appear before reaching the age of one, and at three years the baby has a full set of milk teeth (20 in total). The enamel of primary teeth is thinner and the connective tissue is looser, so they are much more susceptible to the influence of bacteria and the external environment. Considering the anatomy and structure of baby teeth, the treatment of young children has its own characteristics. Let's talk about them:
Treatment/prevention of teeth for children under one year old
At the time of teething (especially the first incisors), the gums often swell, the temperature may even rise, so the child experiences discomfort and stress. In this case, our pediatric dentists can prescribe medications to alleviate discomfort. And dental hygienists will help you choose hygiene products (brushes, fingertips and special toothpaste).
Dental treatment for a child aged 1-2 years
At 2 years old, most of the baby teeth erupt, and it is at this age that the first signs of caries often appear. At the initial stages of the disease, our pediatric dentists apply various medications to the teeth that stop the spread of caries. For the same purpose, our specialists can offer remineralizing therapy.
Dental treatment for a 3 year old child
At 3 years of age, all baby teeth usually erupt. At this time, the child often develops a craving for sweet foods and drinks, so carious lesions are not uncommon. However, if the child’s carious lesions are extensive and multiple, our dentists treat the teeth under local anesthesia. Fissure sealing (grooves on the chewing teeth) is often done.
Dental treatment for a child aged 4 and 5 years
Upon reaching 4-5 years of age, the risk of pulpitis increases in children (especially in the absence of timely treatment). It is very important to preserve the root part of the pulp, so our specialists carefully treat such teeth. Unfortunately, in advanced cases, the child is sent to our adult for tooth extraction, and this is extremely undesirable. The ideal option is when by the age of five the child has completely preserved all his milk teeth.
Therefore, it is very important for parents to follow these rules:
- regularly bring your child to the pediatric dentist for a medical examination (at least once every 3 months);
- regularly bring your child to professional hygiene (at least once every 6 months);
- Correctly plan and monitor the child’s diet.
Children's Dental – Prevention is better than cure!
Benefits of the “Smile Factor”
The clinic has created all the conditions for comfortable and painless treatment of the youngest patients. Regardless of whether you need to conduct a preventive examination, cure caries or pulpitis in children, in each case you will receive high-quality help from us.
Our doctors know how to treat children and have knowledge of child psychology, the child quickly makes contact, feels calm and at ease.
Contact us and your children will receive:
- accurate diagnostics using modern equipment;
- comfortable treatment in a playful way;
- high-quality and safe anesthesia.
Even in difficult situations, dentists strive to find a solution in favor of saving the tooth, regardless of whether pulpitis is diagnosed - acute or chronic. Make an appointment and we will do everything possible to ensure that your baby proudly shows off his treated tooth to the delight of the whole family.
Chapter 6. CRITERIA FOR SELECTION OF TREATMENT METHOD OF PULPITIS OF TEMPORARY AND PERMANENT IMFORMED TEETH
Questions to control the initial level of knowledge
► List the layers of pulp, what are their characteristics?
► What are the features of the blood supply and innervation of the pulp?
► What are the features of diagnosing pulpitis in children?
► List what main drugs are used for pulpotomy in children?
► What materials are used for obturation of the canals of temporary teeth?
► What types of calcium hydroxide based materials do you know?
CHOICE OF TREATMENT METHOD DEPENDING ON THE FORM OF PULPTIS
The main content of the topic is presented in Fig. 6.1-6.2 and in table. 6.1.
Desensitization
- stage of treatment of pulpitis, aimed at relieving the symptoms of acute inflammation in the pulp before performing pulpotomy or pulpectomy (Fig. 6.3). Preparations used - Rockle's solution (Septodont), septomixineρ (Septodont), pulpomixineρ (Septodont), ledermixρ (Riemser), Cresophene Dental materials for treating canals before filling♠ [Septodont] (only before using formocresol or pulpotec ).
Rice. 6.1.
Criteria for choosing a treatment method for pulpitis in children
Rice. 6.2.
Treatment methods for pulpitis in children
Table 6.1.
Correlation of causative factors and symptoms with the recommended treatment method for pulpitis
| Cause | Symptoms | Pulp condition | Dental treatment | |
| Temporary | Permanent unformed | |||
| Tooth trauma with exposure of the pulp of single-rooted teeth | No | Mechanical damage to the area adjacent to the fracture line | Pulpotomy | Partial pulpotomy |
| Accidental opening of the tooth cavity during preparation | If detected immediately - visual signs only | Mechanical damage to the area adjacent to the opening zone | Pulpotomy | Direct pulp capping, partial pulpotomy |
| Caries - deep cavity without autopsies cavities tooth | Only when the cavity is localized according to Black class I and V | Primary (not bacterial) inflammation coronal pulp | Indirect pulp capping | Indirect pulp capping |
| Caries - deep cavity with autopsy cavities tooth | Short-term pain when exposed to irritants | Inflammation in the coronal pulp, vitality of the root pulp | Pulpotomy | Pulpotomy |
| No pathological mobility | ||||
| No changes were detected on the x-ray | ||||
| Spontaneous pain | Irreversible pulpitis | Desensitization* + pulpotomy/pulp-ectomy | Desensitization + pulpotomy | |
| Pathological mobility | ||||
| Swelling and hyperemia along the transitional fold | ||||
| Prolonged bleeding from the ostial pulp during pulpotomy | Irreversible pulpitis with destruction of the root pulp | Pulpectomia | High pulpotomy | |
| Diffuse severe pain, collateral edema, reaction of lymph nodes, increased body temperature, signs of intoxication | Irreversible pulpitis | Removal of a tooth | Prescription of anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drugs. Local – desensitization + high pulpotomy | |
End of table. 6.1
| Cause | Symptoms | Pulp condition | Dental treatment | |
| Temporary | Permanent unformed | |||
| Significant carious destruction of the coronal part of the tooth | Impossibility of therapeutic recovery | Irreversible pulpitis | Removal of a tooth | High pulpotomy, temporary restoration, pulpectomy after completion of apexogenesis, restoration of the coronal part using pin structures or inlays |
Rice. 6.3.
Carrying out the desensitization method
Indications:
► exacerbation of chronic pulpitis;
► low cooperation of the child at the first visit;
► hypersensitivity of the pulp - the inability to provide adequate pain relief during a prolonged course of the inflammatory process.
Method algorithm
First visit
► Local anesthesia.
► Isolation of the working field.
► Removal of carious tissues.
► Apply the drug on a small cotton ball to the exposed pulp.
► Hermetically sealing the cavity with a temporary filling.
Second visit
(after 7-14 days as signs of inflammation subside).