Bite disorders in humans are very common. All of them are of a different nature and arise for certain reasons. Sometimes the basis of bite pathology in children is various anomalies in the development of teeth - their size, shape. Today we will talk specifically about size anomalies. Depending on whether they are large or small, a diagnosis of macrodentia or microdentia may be made. Today we will look in detail at these concepts, the causes of anomalies in people and methods of correction.
How to recognize macrodentia
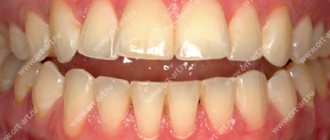
Incorrect development of teeth, namely their excessive growth, is more typical for mixed dentition. It manifests itself before the age of 9 years. It is not difficult to detect pathology; most often the central upper incisors or premolars of the lower jaw grow excessively large. An increase in size is characterized by both a change in width and an excessively high crown height.
Macrodentia is a problem that almost always goes hand in hand with other pathologies, such as crowded teeth. This is due to the fact that large dental units do not leave enough space for the rest in the row. There are also frequent cases of rotation of teeth, that is, rotation around their axis.
The surface of a large tooth may be irregular in shape, the following features are observed:
- pronounced cut-out part in the form of a crescent along the edge;
- areas of hyperdeveloped enamel closer to the gum;
- enamel sagging, protruding areas on the coronal part.
Ask a Question
Symptoms
With this phenomenon, the width of the crowns increases, and the dimensions of the upper central incisors are often disturbed. In addition, symptoms of pathology include:
- Rotations of teeth around the longitudinal axis;
- Offset units in the vertical direction;
- Sometimes individual units may switch places;
- A group of teeth may be closer or further to the midline;
- Eruption of chewing organs from the lingual or palatal side;
- The appearance of a unit outside the row of teeth;
Causes of the anomaly
The main causes of macrodentia include the following:
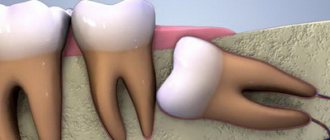
- fusion of the roots of two adjacent teeth during the period of active growth;
- fusion of tooth buds at the stage of their formation (in utero);
- fusion of normal and supernumerary teeth.
This may be due to a whole range of factors - from metabolic disorders to maternal diseases during pregnancy. Genetic predisposition also matters. The causes of the disorder are endocrine diseases and the associated uneven rate of tooth growth.
Types of macrodentia
Macrodentia can manifest itself in different ways. Based on symptoms and clinical forms, five types of anomaly have been identified:
- Localized. There is an increased size of two or more teeth of the same group. As a result, teeth in the same row have different sizes.
- Generalized. The anomaly extends to all teeth of the jaw; their length does not correspond to the size of the jaw arch. In this case, the deviation in the size of each specific tooth can be small - up to 2 mm.
- Isolated. There is an increase in one front incisor, the deviation can be impressive - up to 6 mm.
- Absolute macrodentia. Determined by the total length of the incisors, the length is 35 mm or more for the upper jaw, 28 mm for the lower teeth.
- Relative. With a large form, the length is no more than 35 and 27 mm for the teeth of the upper and lower jaw, respectively.
Classification
It is considered normal if the width of the 4 incisors of the upper row is within 31 millimeters, and the width of the lower ones is within 23 millimeters. When the indicators increase from two to six millimeters, this is already a pathology. Macrodentia is divided into several types. The types of pathology differ from each other. Some people mistakenly believe that therapy is necessary only in cases of severe deviations. But, without timely correction, the anomaly can lead to serious complications.
- Pathological violation of occlusion;
- Delayed eruption of adjacent units, which causes inflammation of periodontal tissues;
- Injury to the mucous membranes, which provokes the appearance of stomatitis;
- Compaction of the chewing organs leads to excessive development of pathogenic bacteria and the appearance of carious cavities;
- Development of neurofibromatosis, deformation of the jaw bones;
- Psychological discomfort, which leads to isolation, aggressiveness, and irritability of the patient;
This problem is dealt with by aesthetic dentistry. It is important to consult a doctor in time. The sooner therapy is prescribed, the easier and faster the treatment will be. Now in more detail about each type of pathology.
Localized
This form of the disease differs in that the pathological process extends to single crowns, possibly to a small group of masticatory organs. Anomalous dimensional deviations are clearly visible in the general row.
Generalized
Macrodentia of this type of teeth is characterized by the fact that each unit on the jaw bone is increased slightly, that is, by one or two millimeters. The distribution zone is the entire row on one jaw. Its total length differs from the size of the jaw arch.
Isolated
This type of anomaly is characterized by abnormal development of only one incisor. Isolated pathology is distinguished by the fact that the incisor exceeds the norm significantly - from 5 to 6 millimeters.
Absolute
Absolute and relative macrodentia are pathologies that are opposite in clinical picture. With an absolute anomaly, the entire width of the crowns of the four incisors of the upper row is 35 millimeters, even more. As for the lower incisors, the sum of the width of their crowns is 27 millimeters or more. The front units are located closely. Most often there is no room for two or more organs. About '/2 the width of the existing crowns is missing. These patients have a narrow face.
Relative
This category of disease is also called individual. The entire width of the incisors of the maxillary bone is 33 to 34 millimeters. On the lower jaw, this parameter ranges from 26 to 27 millimeters. Such patients require correction of the shape of their teeth. Their face is elongated, narrow, and there is not enough space on each jaw for the lateral incisors.
Consequences of macrodentia
An increase in the size of a tooth or all units of the dentition is an anomaly that does not cause acute symptoms (pain, inflammatory reaction, etc.). Therefore, some patients believe that it is not necessary to see a dentist about this, especially with a slight increase in the size of the teeth. Despite the fact that the defect seems harmless, it not only spoils the aesthetics of the smile. The consequences of macrodontia can manifest themselves in the form of serious complications:
- malocclusions, including crowding, rotation, displacement of teeth in a row;
- disturbances in the eruption of teeth located next to large ones, pericoronaritis, inflammatory processes in the gums;
- trauma to the mucous membranes and, as a consequence, stomatitis;
- high risks of developing multiple caries due to the close fit of the lateral surfaces of the teeth.
Macrodentia may be one of the manifestations of neurofibromatosis, which, as it progresses, leads to deformation of bone tissue. An unaesthetic smile often leads to difficulties in communication, embarrassment, irritability, and withdrawal. Sometimes enlarged incisors affect diction and speech defects occur. That is why macrodentia is a problem that needs to be addressed. Fortunately, there are now methods to get rid of the anomaly and maintain oral health.
Prevention
To prevent pathology, it is important to teach the patient how to properly care for the oral cavity. You should choose the right hygiene products. The main role is played by regular visits to the dental office at least once every 6 months. Proper use of modern means of therapy, surgery, implantation, orthodontics, orthopedics will minimize risks, correct deviations, aesthetic indicators, and normalize the functioning of the dentofacial apparatus.
A preventive measure is to take care of the intrauterine development of the fetus and the postnatal development of the baby. The child must eat rationally and get rid of endocrine disorders in a timely manner.
Diagnostic methods
Anomalies in tooth size are visible to the naked eye. But it is important not only to detect an enlarged tooth crown, but also to evaluate the root system. Therefore, the first appointment begins with a visual examination and questioning, and later the dentist will direct you to a number of examinations:
- measuring the jaw incisors using a ruler with grips - carried out as part of the initial examination by the dentist;
- radiography - to determine the condition and structure of the root system, detect impacted teeth, root fusion, etc.;
- other methods according to indications - OPG, targeted X-ray of a suspicious tooth, etc.
Based on the data obtained, the specialist selects the appropriate correction method.
What to do in case of pathological enlargement of teeth
Tactics depend on the degree of violation of the position of individual teeth and bite. In some cases, the lateral surfaces of enlarged teeth are ground and coated with fluoride varnish.
In case of serious pathologies, removal of individual teeth (for example, first premolars) is indicated, followed by orthodontic treatment to restore the shape of the dentition and the position of individual teeth. The Hotz method is the most popular today.
We advise you to read: In what cases are early erupted teeth removed?
Features of treatment
The treatment method depends on how severe the deviations are. There are several effective methods, each of which has its own indications.
Separation
This is a way to reduce volume by grinding down the enamel. Unlike a regular tooth, an enlarged one may have a thicker layer of enamel - its volume may be one and a half to two times greater than normal. Therefore, if the excess is slight, sanding off excess enamel is a safe, simple and effective method. With the help of separation, it is possible to remove up to 6 mm of the crown width. There are no nerve endings in the tooth enamel, so the procedure does not require pain relief with injections; topical anesthesia is sufficient.
The main indications for separation are crowding and slight rotation of teeth. This method of treating macrodentia avoids surgical intervention.
Grinding large amounts of enamel usually requires several sessions. After each procedure, remineralizing therapy is carried out, which helps restore hard tissue and prevent the development of caries.
Composite restoration
The method involves not only grinding down part of the tooth, but also further restoration using composite materials. This is necessary if you want to restore the aesthetic shape of the tooth. The direct method involves layer-by-layer application of material to the tooth after grinding, with each layer treated with a special lamp for rapid hardening. The indirect method involves the application of composite plates made in advance in a dental laboratory according to the patient’s own impressions and individual parameters of the jaw. This saves time, but is somewhat more expensive.
Installation of veneers
Ceramic onlays made from porcelain are the most expensive type of composite restoration. The method involves preliminary preparation, after which ceramic plates that meet high aesthetic requirements are applied to the teeth.
Surgery
Tooth extraction is often necessary in cases of severe crowding or the presence of supernumerary large teeth. Restoring the correct position may require the removal of one or more teeth.
Orthopedic treatment
Prosthetics are used to eliminate the included defect. Crowns or bridges are widely used.
Orthodontic treatment
Curvature, changes in the position of teeth, malocclusion - in all these cases, the installation of corrective structures is indicated - plates, braces, devices for increasing the rate of jaw growth, trainers, etc. The choice of design depends on age and the severity of the defect. Sometimes a combination of several means is required.
The treatment of macrodentia and its consequences is carried out by the dentists of the STOMA clinics. With us you will receive help from a dentist of any profile, undergo a quick and accurate diagnosis, and find out answers to your questions. We offer cutting-edge treatments to give you a flawless smile. Make an appointment by calling the specified phone number or using a special form on the website.