From this article you will learn:
- features of the development of childhood caries,
- reasons for appearance, photos,
- how caries is treated in children under 3 years of age and after.
Bottle caries is one of the terms used in dentistry to refer to carious lesions in primary teeth (in young children). This term seems to emphasize the importance of poor nutrition in the development of dental caries in a child. And the main factors here are: firstly, the consumption of large amounts of sugar-containing foods and drinks, and secondly, a violation of the diet (for example, feeding on demand).
The most adverse effect on the development of bottle caries in children is caused by frequent night feedings of sweet and sour foods. This can be sweet porridge, sweet tea, juice, dairy products, etc. The fact is that at night salivation is very reduced, and therefore the possibility of self-cleaning of teeth is reduced (due to washing off with saliva and swallowing food particles), and also the remineralization of dental tissue is reduced. enamel with calcium contained in saliva.
Bottle caries: photo
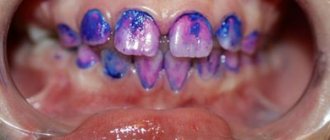
Caries of baby teeth in children can occur not only after their eruption has finished, but also when the crown of the baby tooth is only partially visible above the mucous membrane. The upper incisors and first molars are usually affected first, often all the teeth as they erupt. In young children, the development of caries is aggressive in nature, which is associated with weak mineralization of the enamel of primary teeth (its saturation with calcium, phosphates, fluoride). If we add to this poor nutrition and irregular care of the baby’s oral cavity on the part of the parents, we get a “circular form of caries” (Fig. 1.9).
Childhood caries in children under 3 years of age is usually asymptomatic. This is due not only to the characteristics of the nervous system of children, but also to the immaturity of the nerve endings in the pulp of temporary teeth. When caries occurs, children usually do not show any concern, and only a few of them refuse to eat sour fruits and vegetables and solid foods. All this leads to parents bringing their child to the dentist too late. But there is one more feature...
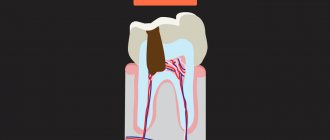
Important: children under 3 years of age have a very small thickness of hard tooth tissue, and therefore the appearance of even a shallow carious cavity immediately leads to the development of pulpitis (inflammation of the nerve in the tooth). At first, pulpitis can be asymptomatic, or with the appearance of paroxysmal pain in response to taking hot or cold. Pulpitis quickly turns into periodontitis, which leads to the formation of a purulent abscess in the area of the roots of a baby tooth, which can be manifested by swelling of the gums and the formation of a fistula.
Interesting point -
Often, a dark pigment plaque forms on a child’s teeth in the form of black spots, which can be mistaken for caries. The integrity of the enamel is not compromised, and such pigmentation is a deposition of iron salts on the surface of the enamel - due to the activity of anaerobic bacteria (actinomycetes). This type of staining is called chromogenic (Fig. 4).
This dark plaque is formed as a result of the interaction of hydrogen sulfite (a waste product of actinomycetes) with iron contained in saliva or with iron in red blood cells that can enter the oral cavity, for example, when gums bleed due to inflammation.
Forms of caries of primary teeth in children -
As we said above, caries can occur in children as early as 1 year of life, starting from the moment the primary teeth erupt. Caries of permanent teeth also begins in children from the moment they erupt, i.e. at the age of 5-6 years. And if in preschoolers and schoolchildren the resulting carious defect can exist for quite a long time (until the transition of caries to pulpitis and periodontitis), then in children under 2-3 years of age, a rapid development of caries and its complications is usually observed. The reasons for this are the following factors:
- weak enamel mineralization,
- a very thin layer of tooth enamel,
- a very thin layer of dentin (only 1-2 mm) that separates the enamel from the pulp of the tooth.
Therefore, even from shallow carious defects, bacteria very quickly enter the pulp (the neurovascular bundle located in the center of the tooth) and first cause the development of inflammation and then the death of the pulp. Therefore, parents should pay attention not only to the appearance of already typical carious defects. The initial form of caries in children is manifested in the formation on the surface of the enamel - white chalky spots (foci of demineralization), the appearance of which precedes the occurrence of carious defects themselves.
Forms of dental caries in children:
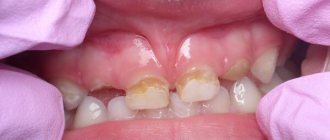
- The initial form of caries (Fig. 5-6) - with irregular oral hygiene, microbial plaque accumulates at the necks of the teeth. Plaque bacteria produce acid, which begins to dissolve the already weakly mineralized enamel, which leads to the formation of foci of demineralization on the surface of the tooth enamel. The latter look like white chalky spots, slightly rough to the touch.
Parents often do not notice the appearance of such spots in time, because... they are hidden under a layer of soft plaque. Or the parents do not see anything serious in their appearance. If during this period there is no normalization of the child’s oral hygiene, as well as his diet, the white spots on the surface of the enamel very quickly turn into superficial carious defects.
- Superficial caries (Fig. 7) - at this stage of caries development, only the tooth enamel is affected, i.e. The carious process does not yet affect the layer of dentin located under the enamel. Superficial carious defects usually appear directly on the site of previous foci of demineralization (white chalky spots). By the way, this is clearly visible in Fig. 2.
- Middle caries (Fig. 8-9) - at this stage of development, the bottom of the carious cavity is localized already below the enamel-dentin border, i.e. located in the middle layers of dentin. If initial and superficial caries remain, as a rule, unnoticed by parents, then intermediate caries is clearly visible on the surface of the tooth. In addition, children may already experience short-term pain when eating cold or sweet foods, but young children are not able to express their feelings.
Moreover, in children under 2 years of age, tooth damage by medium caries most often tends to unlimited planar and circular distribution. Those. A carious lesion can occupy several entire tooth surfaces at once. And only after 2 years of age, the carious lesion will have its usual appearance - a limited carious cavity (saucer-shaped). - Deep caries (Fig. 10) is the next stage in the development of the carious process, but in children under 3 years of age this form of caries practically does not occur. The latter is due, among other things, to the fact that in children of this age group the thickness of dentin is only 1-2 mm, and therefore, even with a shallow carious cavity, infection of the pulp (neurovascular bundle) quickly occurs - with the subsequent development of pulpitis and periodontitis.
The dangers of early absence of baby teeth
The dentition in children consists of a certain number of teeth, and if it is disrupted ahead of time, this can disrupt the formation of a correct bite. This happens because nearby milk teeth may shift to the place of the missing one, which means that the permanent teeth will begin to grow unevenly .
The absence of baby teeth complicates the process of chewing and biting food, and also makes it difficult for a child to develop correct sound production and diction.
In addition, the absence of a tooth does not look aesthetically pleasing and can lead to psychological problems for the child and low self-esteem.
Treatment of caries of primary teeth –
Treatment of caries in children under 3 years of age differs from treatment in older children. The choice of technique will primarily depend on 1) the age of the child and his behavior in the doctor’s chair, 2) the depth of the carious lesion, 3) as well as the behavior of the child’s parents. Typical inadequate demands of parents are “not to paint your teeth black”, “not to give an anesthetic injection”, “not to drill your teeth”, etc. All this makes it difficult to choose the optimal treatment method for a particular child.
1) Treatment of caries in children under 3 years of age –
In children of this age (depending on the depth of the carious process, as well as on behavior in the dentist’s chair), the following treatment methods can be used:
- remineralizing therapy,
- silvering (Fig. 11),
- deep fluoridation (Fig. 12),
- gentle filling of teeth (Fig. 13).
The method of tooth remineralization - remineralization of tooth enamel (saturation of it with calcium and phosphates) is carried out for the initial and superficial forms of caries of primary teeth. The course ranges from 5 to 10 procedures. As therapeutic agents, drugs such as, for example, calcium phosphate gel “GC Tooth Mousse” containing the complex “CPP-ACP” (casein-phospho-peptide-amorphous calcium phosphate) are used. An example of another product is “ROCS-mineral” based on calcium glycerophosphate and xylitol.
All these products can be used not only in the dentist’s office, but also at home. The main requirements are regular oral hygiene and a complete absence of plaque (plus the exclusion of the consumption of easily digestible carbohydrates, including sugary drinks). Treatment will not be effective if these requirements are not met. The drug “GC Tooth Mousse” will be more effective; it is easy to buy online and easy to use at home.
Deep fluoridation method (Fig. 12) - this method is also carried out in the presence of initial caries in the white spot stage, as well as in superficial caries. It is best to apply it in the second stage, i.e. immediately after the remineralization course. In total, a fluoridation course consists of 3-5 procedures, which consist of applying preparations based on sodium fluoride, tin fluoride, amino fluoride (optimally in the form of a varnish, which after application hardens on the enamel surface) to the surface of the tooth enamel.
The effectiveness of the fluoridation process greatly depends on the composition of the product used. It is important to choose an effective and at the same time safe concentration of fluoride for the child. You can read more about optimal medications at the link above. In addition, there is the drug “Enamel-sealing liquid Tiefenfluorid” (Germany), which is two-component and allows you to combine both remineralization and fluoridation at once.
Teeth silvering method (Fig. 11) - this method is used to treat initial caries in the white spot stage, superficial and medium caries. The silvering method is used only for the treatment of baby teeth, because... it causes areas of the tooth affected by caries to turn black. It is usually indicated in children no older than 3 years, because After 3-3.5 years of age, in most cases it is already possible to agree with the child on the traditional option of dental treatment (here, everything basically depends on the ability and desire of the dentist to find an approach to the child).
Of course, it is not entirely optimal to use it for the treatment of foci of demineralization in the form of white spots, as well as superficial caries, because Ideally, in these cases, it is advisable to conduct courses of remineralization and fluoridation. But with average caries (circular and planar forms), this method is not so bad, because In some children, it may be the only opportunity to survive until the physiological change of teeth, i.e. will allow you to do without their premature removal.
The optimal drug is Saforide (based on 38% silver diaminofluoride). According to the recommendations of the Russian Dental Association, silvering of teeth should be carried out not just once, but from 3 to 5 times. Only in this case is it possible to achieve stabilization of the process, but further maintenance repeated courses will be necessary, the period between which can be 1-3-6 months. The duration between repeated courses will depend on a number of factors, for example, the level of oral hygiene, the rate of caries progression, etc.
Gentle filling of teeth in children under 3 years of age - this method is carried out for superficial and medium caries. Don’t worry, filling teeth in children of this age is quite possible, and many dentists treat even 1.5-year-old children in this way. The most important thing here is the approach, and that the child is not scared from the very beginning. For example, it is very important not to cause any unpleasant sensations to the child during 1 visit, and therefore the child first only has his teeth brushed with polishing brushes and a tasty paste, and enamel strengthening agents are also applied to the teeth.
On the second visit, you can begin gentle filling. First, it is necessary to remove the sharp edges of the enamel and softened dentin. This can be done not only with a drill, but also with the help of scraping with hand tools specially designed for this. This is possible because the enamel and dentin in children of this age are much softer than in adults. It is also very important that in young children pain sensitivity in the teeth is reduced, and usually everything is painless.
There is another way to facilitate the removal of enamel and dentin affected by caries. This method involves first applying a special gel (for example, Carisolv, Switzerland), which softens tissues affected by caries and does not affect healthy enamel and dentin. After this, all that remains is to carry out very light scraping with hand tools. Nevertheless, it must be recognized that in some cases, high-quality filling can be carried out only after preparing the carious cavity with a drill, and in this case, only small carious cavities can be cured without anesthesia.
Important points that parents need to know before getting a filling -
- It is very important that the dentist has a “caries marker” drug, which helps the dentist determine whether he has completely removed the dentin affected by caries. In children of this age, this can be very difficult to determine. If the dentist leaves even a little bit of carious dentin, caries will occur under the filling, which will very quickly turn into pulpitis and acute pain. Those. If the doctor doesn’t have such a drug initially, I wouldn’t even sign up for treatment if I were you.
- Selection of material for filling - after removing all tissues affected by caries and appropriate antiseptic treatment, the actual filling begins. The second important point is the choice of filling material. Children of this age can and should have their teeth filled only with “glass ionomer cements” (GIC), for example, “Ketak-molar”, “Ionofil”, “Fuji IX”, “Cemion”, etc. In addition, even with average caries in children, a therapeutic pad made of calcium-containing material is always placed under such a filling.
2) Treatment of caries in children from 3 to 6 years old –
If your child has an initial form of caries (in the form of white chalky spots), then the treatment will be the same as for children under 3 years of age - remineralizing therapy, deep fluoridation, and in the worst case - silvering. We provided a link to these methods just above. For superficial, medium and deep caries in children of this age, it is optimal to use the technique of filling teeth with glass ionomer cements (GIC).
Before filling, carious tissues should preferably be drilled out with a drill, and only as a last resort can scraping of carious tissues with curettage spoons or smoothers be used. Under the glass ionomer filling (if the caries is medium or deep), a spacer made of calcium-containing material must also be placed.
Only if the child is emotionally unbalanced, is very afraid of the sound of the drill, in children who do not allow anesthesia or have a contraindication for it, in children with diseases of the central nervous system, it is preferable to use not a drill, but alternative methods of removing tissue affected by caries. It is also worth considering that if we are talking about a child’s very first visit to the dentist, then no invasive procedures should be performed during this visit (you should limit yourself to only polishing the teeth and applying fluoride varnish). This will allow the child to have a more positive attitude towards the dentist in the future.
Complications of caries in children -
As we said above, in children under 3 years of age, newly appeared caries can turn into pulpitis (inflammation of the nerve in the tooth) in just 2-3 months, which is also due to the too small thickness of enamel and dentin.
The resulting pulpitis can have either an acute or chronic course. The acute course of pulpitis in primary teeth is characterized by the occurrence of spontaneous paroxysmal pain, especially at night and in the evening. The pain is usually provoked by hot or cold food, and after eliminating the irritant it can last from 15 minutes to several hours. In the chronic course of pulpitis of primary teeth, pain symptoms may either be completely absent, or pain may occur during meals (due to irritation of the receptors in the area of the bottom of the carious cavity by the food lump). This form of pulpitis can be very difficult to distinguish from average caries, which often leads to medical errors. Mistaking pulpitis for average caries, the doctor traditionally treats it with silvering or filling, which inevitably leads to the development of periodontitis (24stoma.ru).
But in the absence of treatment, pulpitis in any case sooner or later transforms into periodontitis (purulent inflammation at the apex of the root). The following symptoms are characteristic of periodontitis in primary teeth: 1) an abscess periodically appears on the gum in the form of a lump filled with pus, 2) fistulas with purulent discharge periodically open in the projection of the root of the diseased tooth on the gum. What purulent inflammation looks like during periodontitis (Fig. 15-16).
The occurrence of fistulas and purulent lumps on the gums is an absolute indication for tooth extraction (regardless of how much time is left before its physiological change). The fact is that purulent inflammation at the apex of the root of a baby tooth can most likely cause inflammation of the germ of a permanent tooth, which is located only 1-2 mm from the tops of the roots of a baby tooth. In addition, bacteria and toxins will constantly enter the blood, leading to deterioration of immunity and the development of a number of chronic diseases (for example, diseases of the ENT organs, bronchial asthma, allergies, etc.).
You can read about what needs to be done if your child has a fistula or purulent abscess on his gum in the article at the link above.
What is bottle caries?
There is another type of childhood caries - bottle caries. It occurs in children after the eruption of baby teeth, when the baby is breastfed or bottle-fed. This disease usually occurs as a result of feeding a child before bedtime. While he sleeps, bacteria begin to multiply in his mouth.
Often this form of carious process affects the cervical area. Gradually, caries spreads along the entire circumference of the crown. First, white spots appear, then they darken and destroy dentin. The child constantly cries, especially during meals, sleeps poorly and tries to refuse food. This indicates increased sensitivity of the enamel. Left untreated, it can lead to premature loss of baby teeth.