Rogatskin D. V. Radiologist, Ortos LLC (Smolensk)
Until recently, radiation diagnostics in dentistry was considered as an additional examination method, that is, optional, without which, in principle, full treatment could be carried out. However, in the 21st century the situation has changed dramatically, new technologies, new specialties and new requirements for the examination and treatment of patients have appeared. Currently, not a single civilized dental appointment is complete without a detailed radiodiagnostic examination of the patient, and it can be argued that radiodiagnostics in dentistry is now one of the main and most popular research methods.
The main difference between digital radiography (radiovisiography) and traditional one is that in this case, instead of film, the image receiver is a sensor that perceives radiation and transmits information to a computer. The equipment required for radiovisiography consists in sequence of a radiation source, a device for reading information, a device for digitizing information, and a device for reproducing and processing images.
Modern low-dose generators with a minimum timer value, designed to work as part of a visualization complex, are used as a radiation source. The visual imager itself consists of a sensor, which is a sensor based on a CCD or CIMOS matrix, an analog-to-digital converter and a computer program designed to optimize and store images.
At first glance, the original digital photographs may differ slightly from the usual film ones, and therefore require processing using software options. The highest quality image is the one that is closest in visual perception to analogue, therefore, even despite the highest technical characteristics of the visiograph, the quality of the final image largely depends on the capabilities of the program and the ability of a specialist to work with it.
Popular methods of radiation diagnostics
Today, the most common and popular method of radiation examination in outpatient practice is intraoral radiography of teeth, or intraoral photograph of the tooth. Sometimes intraoral photographs of teeth are called targeted, which is incorrect. A targeted photograph is a photograph taken outside the standard positioning, and standardized studies are named according to the positioning method.
At a therapeutic appointment during endodontic treatment, at least three intraoral photographs of each tooth under examination must be taken:
- A diagnostic image is necessary to assess the condition of periodontal tissues at the time of examination, make a diagnosis, determine the number and shape of roots, the direction of canals, and choose treatment tactics.
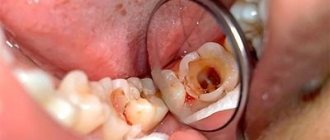
- measuring photograph - a photograph of a tooth at the treatment stage with endodontic instruments inserted into the canals with a fixed stopper length of the working part or verifiers after instrumental treatment of the canals. If the orthogonal projection is performed correctly, provided that the visiograph program is accurately calibrated and there is no projection distortion for incisors and premolars, some measurements can be taken from the diagnostic radiogram. For multi-rooted teeth, it is preferable to measure the length of the canals using endodontic instruments (Fig. 1), an apex locator or from a three-dimensional photograph.
- a control photograph is taken immediately after the end of endodontic treatment in order to determine how well the root canals are filled, as well as after a certain specified time, in order to verify the absence or detect the presence of complications (Fig. 2). When examining multi-rooted teeth and in cases where there is an additional canal, in an image taken with the orthoradial direction of the beam (direct projection), the root canals often overlap each other, which significantly complicates diagnosis and can lead to errors in the treatment process. To obtain a separate image of the root canals, radiography with an oblique (eccentric) direction of the central beam is used (Fig. 1). For each specific case, the mesial or distal inclination (angulation) of the tube in the horizontal plane is selected (for more details, see: Rogatskin D.V., Ginali N.V. The Art of Dental Radiography, 2007).
Ideally, maximum information about the topography of the roots and the condition of periodontal tissues can be obtained by performing polypositional radiography. In this case, for diagnostic purposes, three photographs are taken - one in a straight line, with an orthoradial direction of the beam, and two in an oblique projection - with a distal-eccentric (Fig. 1) and mesial-eccentric direction of the beam (respectively, straight, posterior oblique and anterior oblique projections).
The most important aspects of successful intraoral radiography are standardization and consistent manipulation. Standardization of manipulations means the ability of a specialist conducting a radiation examination to choose the optimal method for each case and take a series of identical images, regardless of the position, condition of the patient and the time separating one examination from another. That is, if a diagnostic or measurement image is considered to be of high quality, each subsequent clarifying and control image must be made with the same spatial and technical settings, and each subsequent image must be identical to the previous one (Fig. 1, 2).
Rice. 1. Diagnostic and measuring images of tooth 36, taken in direct (a) and distal-eccentric projection (b). 36 - chronic apical periodontitis (K04.5) with characteristic changes on the mesial root.
Rice. 2. A control image immediately after treatment of teeth 21, 22 (chronic periapical abscess in a state of suppuration) (a) and a delayed control image 5 months after filling the canal (b), the state of repair at the treatment stage.
Radiology and computed tomography
The role of correct diagnosis in dental treatment is difficult to overestimate. Both the success of treatment and the ability to save the patient from unnecessary inconveniences that accompany the dental treatment process fully depend on the accuracy and completeness of the diagnostic picture of the disease.
Diagnosis of the oral cavity
In our clinic, diagnostics are carried out using an ultra-modern panoramic X-ray machine Sirona, manufactured in Germany. When examining patients using a new orthopantomograph, the dose of ionizing radiation is 80% (!) less than when examining using traditional devices. It achieves excellent image quality through the use of panoramic dental X-ray equipment, which has a number of excellent features. This device has the ability to scan jaws layer-by-layer for the purpose of performing dental implantation operations.
Our doctors can instantly receive an accurate image of the patient’s teeth (panoramic image, etc.) on a computer monitor and can quickly process it - increase its size, enhance the contrast. The use of this device allows you to obtain high-quality and informative images of the upper and lower jaw in real time, and also allows you to perform 3D reconstruction of the image. This allows the doctor to detect the presence of a pathological focus at the earliest stages of the disease, monitor the quality of treatment, providing the patient with the most comfortable and effective treatment.
The equipment of the RuDenta clinic allows you to obtain complete diagnostic information of the highest quality, however, for successful treatment and further monitoring of patients, the quality of storage, recording and cataloging of the obtained diagnostic data is equally important. In the special computer patient registration system of the RuDenta clinic, a personal folder is created for each of them, where the entire history of treatment and diagnosis is stored, including all x-rays taken. Any of these images is available for viewing by specialists directly at their workplace.
We carefully collect anamnesis, which allows us to trace the history of the development of the disease, stages of development, and identify factors contributing to the progression of the process. Many systemic diseases are both triggering and supporting factors in the development and course of oral pathology. Timely identification of aggravating factors greatly contributes to the correct choice of treatment method.
What additional diagnostics can the dentist prescribe?
- Apex locator
With its help, the doctor can determine the length of the dental root canal as accurately as possible. Due to the complex anatomy, it is difficult to do this in other ways. Selecting the right tools is essential to effectively treating root infections.
- Biopsy
This procedure is carried out if a dental cyst or other neoplasm has been diagnosed. A biopsy is necessary to ensure that the suspicious object is benign. The dentist takes a sample of fluid or tissue using a biopsy needle and sends the finished sample to a laboratory for analysis.
The diagnostic methods used in our clinic are safe and do not cause any discomfort. Thanks to them, the doctor will be able to start treatment on time and keep your smile healthy and beautiful!
Sight image of a tooth –
A targeted photograph of a tooth can be recorded either on photographic film or using a special intraoral sensor that detects X-ray radiation and transmits the image to a computer screen (such a device is called a radiovisiograph or simply a visiograph - Fig. 5). In both cases, an X-ray machine is used as a radiation source (Fig. 4), i.e. the only difference is in the way the image is captured - either on X-ray film or using a digital sensor.
Taking an image using a visiograph -
Digital vs Film Photography: Pros and Cons
Targeted dental x-rays using film were once the only examination option in clinics. It must be said that film photographs have a number of disadvantages that have significantly reduced their use. They require expensive consumables (film, reagents), time to develop photographs, there are difficulties with storing photographs, and over time they fade and are lost. There are also differences in patient safety.
Even modern X-ray films require 4-8 times the radiation dose compared to digital X-ray sensors. For example, the radiation dose to a patient for 1 film image is 10-15 μSv (microsieverts), and for a picture on a visiograph it is on average 1-3 μSv (this dose corresponds to the background natural radiation received by each person in 1 day).
The patient's exposure time when using film X-ray is 0.5-1.2 seconds, and using a digital visiograph sensor - 0.05-0.3 seconds. It is precisely by reducing the required exposure time when using a radiovisiograph that the radiation dose is significantly reduced. Thus, in one day of treatment at the dentist you can take no more than 3 film photographs and 5-6 digital photographs. And as you will see below, the use of a visiograph in some cases even allows you to take an X-ray of a tooth during pregnancy, but in compliance with all safety rules and for urgent indications.
How to take a picture of a tooth using a visiograph: video
Important: always try to take digital photos and inform them in advance that you want them saved to a flash drive. Firstly, then you will always have the pictures at hand, and you can always show them to another doctor. Secondly, the photographs taken for control after treatment will be your guarantee that if you received poor-quality treatment, you will always be able to prove it (the clinic will no longer be able to lose your photographs and rewrite the medical record).
Thirdly, if a digital image is printed on a printer, then the quality of the image will depend not only on the quality of the digital image, but on the resolution of the printer (rare clinics have printers that print in high resolution). Therefore, a photo in digital format will have better quality than a photo printed on paper.
Dental X-ray – price for 2021
The cost of one digital X-ray in Moscow will average from 250 to 350 rubles in different clinics. In addition, this price may only apply to a diagnostic initial image, while all other images taken during the treatment phase may cost less (about 150 rubles per image). Therefore, you should carefully read the clinic’s price list.
It should also be noted that there are a large number of clinics in which the cost of dental treatment is indicated on an all-inclusive basis. Accordingly, the cost of treating your tooth will already include the required number of x-rays (usually 2-4 pictures), for which you will no longer pay anything extra.
What else you need to pay attention to is that the price list of some clinics may state that the cost of a targeted x-ray indicated on the clinic’s website applies only if you are a patient of this clinic. Therefore, if an image is taken to be submitted to another clinic, its cost may be 100 rubles higher).
In addition, if you need a printout of a digital image, some clinics may also charge you about 50 rubles for this. The same applies to the description of the x-ray image: if you want to receive a written description of the image taken by a radiologist, then in some clinics they may additionally ask you for about 100-150 rubles.
Orthopantomogram, panoramic image
When you have some kind of local problem, of course, you can and should take a targeted photo. But since all the teeth and nerve endings in the mouth are connected, you may think that one tooth hurts, but the problem is actually somewhere nearby. That is why all professional doctors take a panoramic photograph of the teeth during the initial diagnosis in dentistry. And this “panorama” represents your entire dentition and allows you to see the existing problems in their entirety.
The panoramic image clearly shows both jaws, it is possible to draw conclusions about the condition of the teeth and roots, skeletal system and paranasal sinuses, and diagnose defects in bite, location and shape of teeth. Having received an orthopantomogram, the doctor will see caries at any stage, periodontal pockets, fibromas, granulomas and cysts, latent inflammation, possible changes in the condition of the temporomandibular joint, unerupted wisdom teeth, and sinusitis. A panoramic photograph is necessary before implantation, prosthetics, orthodontic treatment, surgery (complicated removal of wisdom teeth), complex treatment of periodontitis and periodontal disease.