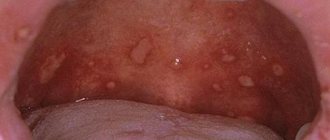
Pulpitis of the tooth
| Dental pulpitis develops in the later stages of caries, when the inflammatory process reaches the soft tissues, which are called pulp. The pulp itself consists of a vascular bundle, connective tissue and nerves. It is the nerves that give pain signals when pathology develops and occurs in the root canal and pulp chamber. The disease is characterized by severe and unpleasant pain, which is especially disturbing at night. Patients also complain of pain reactions that occur when taking hot and cold food or drink. |
Clinical manifestations of acute periodontitis
Acute apical periodontitis is characterized by aching pain, which, as the disease develops, becomes pronounced, becomes sharp and is localized at the site of inflammation. If you do not seek professional help, the pain becomes radiating, and this signals the onset of purulent inflammation.
The process can last from two days to two weeks. Conventionally, it can be divided into two phases:
- The first is characterized by prolonged aching pain with a response when biting on an inflamed tooth. The appearance of the tissues that surround the tooth remains the same, but when lightly tapping the tooth, sensitivity is observed;
- The second stage is characterized by continuous pain, which intensifies when biting, tapping on the tooth, or lightly touching it with the tongue. Often the pain is reflected throughout the entire jaw. There is a feeling as if the tooth does not fit into the dental arch and moves out of it; mobility and swelling of soft tissues are observed.
Symptoms and causes of pulpitis
Depending on the clinical picture, pulpitis can be acute or chronic. The acute form usually develops into a chronic form, and then the sick person simply does not pay attention to periodic pain. This condition is dangerous because periodontitis can begin, in which periodontal inflammation occurs. The reasons for the formation of pulpitis are the following factors:
Caries
The disease leads to the gradual destruction of hard dental tissues and pathogenic microorganisms enter the pulp chamber, leading to pulpitis
Trauma or bruise of a tooth
Trauma or bruise of a tooth can also lead to the development of pulpitis
Complications of certain infectious diseases
When pulpitis forms in the pulp chamber. In such a situation, pathogenic microorganisms enter the pulp from a cyst or periodontal pocket
Due to incorrect previous medical procedures
In particular, pulpitis often appears after incorrectly performed dental canal filling technology.
Prevention
Prevention of periodontitis is not much different from the prevention of caries. To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to pay increased attention to the following factors:
- Proper brushing of teeth. Maintaining oral hygiene helps prevent the appearance of plaque, which is an optimal environment for the development and growth of microorganisms that cause damage to enamel and hard tissues.
- Regular visits to the dental clinic. By detecting periodontitis in a timely manner, it can be cured with minimal surgical intervention. During preventive examinations, the doctor will perform a professional teeth cleaning, removing hard deposits in the form of tartar, which will reduce the risk of developing the disease.
- Your own diet. Sweet foods rich in carbohydrates promote the growth of microorganisms responsible for the appearance of plaque, which provokes the appearance of periodontal disease. An excellent preventive measure would be to include in your diet a large amount of vegetables, fruits, and foods high in calcium, which strengthen tooth enamel.
Following these recommendations does not imply serious costs, but it allows you to avoid serious problems in the future.
Diagnosis and treatment of pulpitis
You can contact the NIKADENT dental clinic and we will provide comprehensive treatment for pulpitis. First of all, an examination of the oral cavity is carried out and an x-ray diagnosis is prescribed. On a targeted X-ray of the tooth, the presence of a pathological focus can be clearly seen. Treatment steps include:
- Anesthesia;
- Elimination of areas of the tooth affected by caries;
- Removal of infected dentin from the dental cavity;
- Nerve removal;
- If necessary, placing antiseptics into the tooth cavity and closing the cavity with a temporary filling;
- Mechanical and medicinal treatment of canals with further filling;
- Installation of a seal.
After all procedures, X-ray control is performed. We guarantee that we will provide the most effective treatment of pulpitis with subsequent tooth filling. How to prevent the appearance of pulpitis? First of all, you need to carefully monitor the condition of your teeth, carry out daily oral hygiene by cleaning your teeth with floss, irrigators, rinses, toothbrushes and pastes.
Features of diagnosis during pregnancy -
At the very beginning of communication with a pregnant woman, the dentist must collect a thorough medical history, which will allow him to develop dental treatment tactics in order to minimize the risk of adverse effects on the fetus. It is especially important to find out the gestational age, history of previous pregnancies and pregnancy-related diseases - such as diabetes, hypertension, preeclampsia, eclampsia. Sometimes an obstetrician-gynecologist is involved to assess the risks.
Can pregnant women have x-rays taken?
During pregnancy, X-ray examinations are not carried out only if during the examination the X-rays pass through or in close proximity to the fetus. In addition, dentistry now uses highly sensitive X-ray films and sensors, which require an 8-10 times lower dose of X-ray radiation than before. Therefore, the use of x-ray examination together with special protective equipment (lead apron) is absolutely safe for the fetus, even if you take several targeted x-rays.
The radiation dose from 1 image taken on a modern radiovisiograph is almost equal to the radiation dose of any person to natural background radiation in 1 day (2-5 μSv). In addition, numerous studies have estimated that the dose to the fetus is only approximately 1/50,000 of the dose that a woman would receive during an X-ray (assuming a standard lead apron was used). In the article at the link above you will find what dosages of radiation a person receives during an X-ray examination of the upper and lower teeth.
Therefore, the only thing you should avoid is regular radiographs, and, probably, the period from 1 to 8 weeks inclusive (the first trimester) is more dangerous than others. Since it is during this period that the fetus is most sensitive to the effects of teratogenic factors. In other words – dental x-rays should not be a cause for concern at this time. This is confirmed by many studies, for example, a British clinical study of a group of 7375 mothers (who had X-rays taken during pregnancy) did not reveal any increased risks to the fetus. And there are a lot of such studies.
Prices for services
| Name | Price |
| Consultation | For free |
| Treatment of pulpitis and periodontitis | |
| Mechanical and medicinal treatment of one canal | 1,100 rub. |
| Repeated mechanical and medicinal treatment of one canal | 500 rub. |
| Unsealing one root canal | 1,100 rub. |
| Filling one canal using vertical condensation method | 1,300 rub. |
| Filling one canal using lateral condensation method | 1,150 rub. |
| Temporary filling of one canal with medicinal paste | 500 rub. |
| Installation of intrachannel fiberglass pin | 1,450 rub. |
| Temporary chemical filling | 400 rub. |
| Light temporary filling | 450 rub. |
Inspection and primary treatment of dental canal cavities
Treatment of periodontitis begins with a thorough examination of the patient by a dentist, after which the specialist prescribes an x-ray for the patient. The image will help make the diagnosis as accurately as possible, as well as study in detail the number of dental canals, their length and shape. Next, an anesthetic injection is made into the area of the diseased tooth, without which treatment of periodontitis can be a very painful and uncomfortable process for the patient.
After the drug takes effect, the doctor will perform the following manipulations:
- It will remove from the diseased dental unit all tissues damaged by the carious process, as well as some healthy enamel and dentin. This is necessary to gain access to the mouths of the dental canals;
- If the tooth has not been treated before, the doctor will remove the inflamed pulp from it. If treatment of the unit with the removal of nerves has previously been carried out, the tooth canals are unfilled;
- Expand the tooth canals manually, using specialized instruments for this purpose. After expansion, the tooth canals are thoroughly washed with an antibacterial solution;
- Place a medicine with enhanced antiseptic action into the channels.
After applying the antiseptic to the dental unit, a temporary filling is installed, and the specialist thoroughly advises the patient on oral care, prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs and medications that reduce the risk of allergic reactions. The next time you will need to visit the doctor approximately three days after completing the first stage of periodontitis treatment.
What is periodontitis?
| Periodontitis, like pulpitis, is a complication that accompanies the development of caries. The disease may appear due to injury or improper dental treatment. With periodontitis, the inflammatory process moves to the periodontal area, which is a narrow space of connective tissue between the bone socket and the tooth itself. According to the clinical course, the disease can be acute or chronic. Acute periodontitis is characterized by sharp pain, sensitivity to cold or hot, and swelling of the gums. Flux forms in the area where gum tissue is damaged. The chronic form is often asymptomatic, but this is where the danger lies, since the inflammatory process begins to actively develop deep in the tissues. |
There are the following forms of chronic periodontitis:
- Granulomatous periodontitis;
- Fibrous;
- Granulating.
It is important to note that periodontitis is a dangerous disease for health and cannot be cured on its own. You should definitely contact your dentist in order to diagnose and eliminate it on time.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is made on the basis of the wedge, pictures, and also using radiography. Roentgenol, the method occupies a leading place in diagnosis and assessment wedge. course and results of treatment P. Intraoral contact radiography is more often used. In cases of increased gag reflex, trismus, and also in pediatric practice, intraoral bitewing radiography is used. If it is impossible to perform intraoral radiography, use extraoral radiography or pantomography (see).
X-ray, P.'s picture is characterized by the following signs: an increase in the width and deformation of the periodontal fissure, destruction or sclerosis of the compact substance of the wall of the dental alveolus, changes in the structure of the bone tissue of the dental alveolus, uneven contours and hypercementosis of the tooth root.
Acute apical P., despite the pronounced wedge, picture, is poor in radiographs, signs. Only in some cases, with a significant accumulation of exudate in the periodontal fissure, its expansion in the area of the apex of the tooth root is noticeable on the radiograph.
Rice. 5. Intraoral radiographs of the lower lateral teeth in chronic periodontitis: a - the compact substance of the dental alveolus of the sixth tooth is sclerosed (1), its root (2) is thickened - hypercementosis (signs of chronic fibrous periodontitis); at the apex of the root of the fifth tooth there is a focus of destruction (3) of the bone substance with unclear boundaries (chronic granulating periodontitis), the apex of the interalveolar septum (4) between the fifth and sixth teeth is destroyed; b—at the apex of the root of the fifth tooth there is a focus of destruction (indicated by an arrow) with smooth contours (granuloma).
Hron, forms of apical P. have characteristic features rentgenol, pictures. Granulating P. is radiologically manifested as a focus of destruction of bone tissue at the apex of the tooth root (Fig. 5, a). The compact substance of the wall of the dental alveolus in this place is destroyed. The contours of the lesion are uneven and unclear. As a result of resorption of cement and dentin at the apex of the tooth root, its contours become uneven. With granulomatous P. (dental granuloma), a rounded focus of clearing with smooth, clear, sometimes sclerotic contours is determined in the periapical region (Fig. 5, b). In children and adolescents, dental granuloma should not be mixed with the tooth growth zone in the area of the apex of the formed root (in the growth zone, the periodontal fissure remains uniform in width, the compact substance of the dental alveolus wall is preserved, the tooth has a wide root canal).
Fibrous P. is recognized by the expansion of the periodontal fissure at the apex of the tooth root. The compact substance of the wall of the dental alveolus is preserved; sclerosis is sometimes noted.
The apex of the tooth root is thickened due to hypercementosis (Fig. 5, a). With exacerbation of chronic P., the x-ray picture does not change significantly.
X-ray manifestations of acute regional P. are usually absent. Chron, regional P. on radiographs is manifested by osteoporosis of the apex of the interalveolar septum, which subsequently turns into its gradual destruction with its partial or almost complete disappearance.
Diagnosis and treatment of periodontitis
| Our dental clinic "NIKADENT" provides modern and effective treatment of periodontitis. First of all, when visiting a doctor, the oral cavity is examined and a diagnosis is prescribed. An accurate diagnosis can be obtained through the use of X-ray examination. Based on the image obtained, the doctor determines the type and nature of the pathology, the area of formation of the lesion, and the condition of the tooth. The treatment is complex and consists of the following medical procedures: |
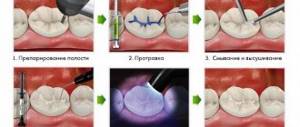
1. Preparation of tooth tissues and unfilling of the dental canal. The doctor uses a bur to open the tooth cavity and, if there is a history of caries, removes the affected dentin;
2. Obturation of all canals in the tooth. It is impossible to do without thorough cleansing and antiseptic treatment of the root, so our dentists use special antiseptic pastes for this purpose;
3. Installation of a temporary filling. After obturation, the dental canals are processed and antibacterial substances are placed in them, which kill all pathogenic microorganisms;
4. Installation of a permanent filling, which is placed after eliminating the pathological focus. At the last stage, the tooth is restored and, if necessary, roots are pinned.
Treatment of periodontitis and pulpitis cannot be delayed. Be sure to contact your dentist on time. Our NIKADENT clinic guarantees its patients the highest quality of dental services.
Clinical manifestations of chronic periodontitis
Different types of chronic periodontitis have different clinical manifestations:
- Fibrous periodontitis can be difficult to diagnose because it is practically asymptomatic and resembles gangrenous pulpitis. During a visual examination, the dentist notes a change in tooth color, a painful reaction to percussion, the presence of a carious cavity and a lack of response to thermal stimuli. There is dead pulp in the dental cavity, which emits a putrid odor;
- Granulating periodontitis has symptoms in the form of mild pain, a feeling of tooth swelling, slight pain when biting, the appearance of a fistula from which pus flows;
- Granulomatous periodontitis is practically asymptomatic. There may be slight pain when biting. The color of the crown of a diseased tooth is changed, but it may not always have a carious cavity. Tapping on a tooth causes pain. In the absence of timely treatment, acute apical granulomatous periodontitis can outgrow cystogranuloma or dental cyst.
Temporary filling
During a second visit to a dentist-therapist during the course of treatment of chronic periodontitis, the area of manipulation is examined. The specialist will also clarify whether the patient has any complaints of pain, swelling in the gum area or other discomfort. If such negative phenomena are not observed, temporary filling of the dental canals is performed.
For this purpose, the temporary filling is initially removed, as well as the antiseptic placed in the tooth canals. The canal openings are thoroughly washed with an antiseptic and then filled with a special type of composite material used for temporary filling. This composite contains calcium hydroxide, a substance that destroys pathogenic microflora and also catalyzes the process of bone tissue regeneration in the area of the upper zone of the tooth root. Temporary filling of canal cavities is done for a fairly long period - from two to three months. The dentist then places a temporary filling in the crown of the tooth.
Causes
Complications of oral diseases
As a consequence of untreated gingivitis, periodontal disease, tooth root cysts and pulpitis.
Infection
Bacteria penetrate the gums through the bloodstream during inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx and upper respiratory tract (sore throat, sinusitis, etc.).
Deep caries
As a rule, it leads to the occurrence of granulosa or fibrous forms of periodontitis due to decay products that accumulate daily in the dental canals of severely damaged teeth.
Dentist mistakes
Poorly performed treatment of tooth canals, when fragments of dental instruments, etc. accidentally remain there.
Injuries
The bad habit of constantly pressing on the tooth with a ballpoint pen, a smoking pipe, or a filling that is too high and injures the periodontium can also provoke non-infectious periodontitis.
Professional factor
In professions such as a brass musician or a tailor, pathological pressure on the tooth occurs on a regular basis: in the first case when playing an instrument, and in the second due to the habit of biting off the thread with teeth instead of cutting with scissors.
Attention!!
Patients with reduced immunity and chronic diseases of the endocrine system are also at risk.