Causes of dental diseases in humans
The main cause of dental diseases is the activity of bacteria, which results in caries. But there are other factors that affect oral health:
- heredity and genetic pathologies;
- quality of drinking water;
- ecology of the urban environment;
- nutritional features;
- professional activity.
In most cases, it is impossible to change anything from this list. Therefore, it is important to at least be able to promptly recognize the symptoms of dental disease and consult a doctor as soon as possible to avoid complications.
Causes of development of diseases of the teeth and oral cavity
Dental diseases can occur due to the harmful effects of one factor or a combination of several. Most dental diseases develop for the following reasons:
- Violation of hygiene rules. We are talking not only about complete disregard for hygiene, but also about irregular or improper brushing of teeth. The accumulation and hardening of soft plaque ensures the rapid development of bacteria in the oral cavity, the waste products of which destroy even the hardest tissue in the body - enamel.
- Infectious diseases. Pathogens can enter dental tissues from the oral cavity, where inflammation occurs, through cracks in the crowns. In addition, bacteria can be introduced into them through the bloodstream from any diseased, infected organ.
- Insufficient supply of dental tissues with nutrients due to improper nutrition.
- Excessive intake of certain elements into the body, for example, fluoride.
- Taking medications.
- Metabolic disorder or hormonal shift.
- Low immunity.
- Hereditary predisposition to dental diseases and congenital anomalies.
- The effect of radiation and chemicals in contaminated places of residence or hazardous production.
- Injuries.
The main reasons for the development of dental diseases in children are the use of pacifiers and bottles with pacifiers, the habit of thumb sucking and putting dirty objects into their mouths.
Classification of dental diseases
Pathologies of teeth eruption and formation
Early detection of dental anomalies makes it easier to carry out subsequent bite correction. Irregularities in the sequence of eruption or asymmetry of opposing teeth should be a reason to contact an orthodontist. Diagnostic accuracy is ensured through x-ray examination.
Edentia
Characterized by partial or complete absence of teeth. The disease can be hereditary or develop throughout life. Sometimes the rudiments of teeth are completely absent from birth.
Supernumerary teeth (hyperdontia)
There are too many teeth in the mouth, and the extra ones can be located both in the dentition, disturbing the arrangement of the remaining teeth, and in atypical places - on the palate or on the front surface of the gums. The anomaly occurs in 5% of the population.
Impacted teeth
The teeth remain in the bone tissue of the jaw and do not erupt completely. In most cases, this is a disease of the molars - eights.
Dystopian teeth
The teeth are located in the wrong places in the jaw, at an angle, and only partially erupt. Pathology refers to diseases of wisdom teeth.
Macrodentia/Microdentia
An increase (or decrease) in the size of teeth compared to the standard norm.
Tooth enamel diseases
There are many chemical processes going on in the mouth that wear down the enamel. Under the influence of food containing dyes or acids, as well as cleaning products, the normal mineralization of teeth is disrupted. Pathologies of the endocrine system and work in hazardous industries are additional unfavorable factors.
Fluorosis
Damage caused by an excess of fluoride in consumed water or food. Fluorosis is commonly referred to as yellow tooth disease.
Enamel hypoplasia
A disease associated with impaired formation of the enamel structure. In most cases, it develops in the first nine months of a child's life.
Wedge-shaped defect
Formation of a “protrusion” at the neck of the tooth on the front side. A disease of the front teeth that can lead to chipping of the entire crown part.
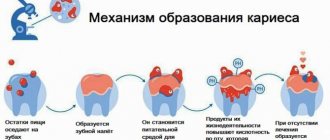
Dental disease caries and its complications
Dental caries occurs in places where microbial plaque lingers and accumulates. The likelihood of developing the disease depends on the individual resistance of both dental tissues and the body as a whole. Resistance to caries is determined by the structure and composition of the enamel, the degree of its mineralization, as well as the characteristics of the dental system - the structure of the facial skeleton, jaws, bite and location of the teeth.
Caries
A pathology that develops in the hard tissues of the tooth, accompanied by demineralization of the enamel and the formation of a cavity. If left untreated, it provokes the development of inflammation in the pulp and periodontal tissues.
Pulpitis
Inflammation of the dental nerve. Characterized by acute pain radiating to the temples. May lead to tooth loss or exacerbation of periodontitis.
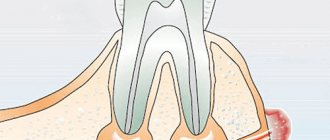
Periodontitis
The inflammatory process covers the apex of the tooth root. Without treatment, there is a risk of developing a cyst or abscess. The main manifestations are swelling of the gums, increased temperature.
Periostitis (flux)
Inflammation of the periosteum due to untreated periodontitis. Accompanied by swelling of the gums and severe pain.
Granuloma
Proliferation of inflammatory tissue in the area of the tooth root. Symptoms are redness and swelling of the gums, tooth pain. Ignoring the disease leads to the appearance of a cyst on the root of the tooth, fistula and diseases of the roots of the teeth.
Tooth cyst
A formation in the form of a capsule with pus at the apex of the tooth root, resulting from the penetration of infection into the root canals. The disease is asymptomatic, in some cases there is pain when chewing. The cyst is usually noticed on x-rays.
If you find signs of dental disease presented in the table, you must go to a dental clinic as soon as possible and consult a doctor. The specialist will examine the oral cavity, prescribe diagnostic procedures and draw up an optimal treatment plan for dental diseases to restore the health and beauty of your smile.
Types, signs and symptoms of periodontitis
According to the Russian classification, there are several forms of inflammatory processes developing in the periodontium.
- Spicy.
- Chronic.
- Separately, it is customary to highlight exacerbations of chronic inflammation of the tooth root.
Signs and symptoms of acute periodontitis
The main symptom of this form of the disease is sharp, aching, sometimes unbearable pain. In this case, the pain is clearly localized in the area of the diseased tooth and is permanent. If the patient did not receive dental care on time, the pain quickly intensifies, becomes tearing and pulsating, which in most cases indicates that the primary inflammation has turned purulent.
The period during which an acute form of tooth root inflammation can last is from several days to 2 weeks. In this case, two successive stages are distinguished.
- 1st (phase of periodontal intoxication). Severe, persistent aching pain is the main sign indicating the beginning of the development of the inflammatory process. Often the patient feels heaviness in the area of the affected tooth and complains of a dull pain, which sharply intensifies when trying to bite.
- 2nd (exudative). In this phase, inflammation of the tooth root is characterized by very strong pain that does not subside without the use of analgesics for almost a minute. Unbearable pain is now caused not only by biting, but even by a slight touch of the tip of the tongue to the affected tooth. Most patients complain of the feeling that the diseased tooth is “pushing out”, which to some extent corresponds to reality, since it acquires increased mobility. In the exudative stage, the adjacent soft tissues may swell and the lymph nodes may become inflamed.
Chronic inflammation of the tooth root
Diagnosing the chronic form in a timely manner is difficult for two reasons. First, many patients do not have the signs and symptoms characteristic of acute apical periodontitis, and complaints may be misleading. Secondly, the clinical picture of chronic periodontal inflammation is in many ways similar to other diseases, for example, some complex types of pulpitis.
The following signs and symptoms may indicate the development of chronic tooth root inflammation.
- There is usually no constant or prolonged pain, but severe discomfort is often felt when pressing and biting on the affected tooth.
- A weak, intermittent feeling of heaviness and fullness, intensifying from time to time.
- Bad breath.
- Change in tooth color (not to be confused with carious stains).
- The occurrence of fistulas.
- Enlargement of regional lymph nodes, their pain.
- Unpleasant sensations when pressing on the gums.
During a diagnostic examination, the dentist usually identifies a deep cavity, the probing of which causes severe pain in the patient. The diagnosis is made based on the X-ray obtained.
Prevention of dental diseases
Some people are not even aware of what dental diseases with inflammatory processes and pathologies are provoked in other vital organs. For those who are not in the know, we inform you: these are gastritis, ulcers, tonsillitis, thrombosis, heart attack and stroke! And the pathogenic bacteria are to blame for everything, which, multiplying in the oral cavity, enter the throat, stomach, blood vessels and even the heart.
To prevent dental diseases, follow simple rules that will help significantly improve your oral health and overall well-being.
- Stop smoking.
A bad habit provokes vasoconstriction and deterioration of blood supply to the mucous membrane, which results in a lack of nutrients necessary for teeth and gums. - Eat a balanced diet.
The abundance of flour and sweet foods in the diet contributes to an excessive increase in microorganisms and inevitably leads to caries and its complications. Take care of strengthening your enamel by taking vitamin complexes. Then the disease when “teeth crumble”, which occurs due to a lack of calcium in the body, will not be scary for you. - Brush your teeth 2 times a day.
Regular hygiene is one of the most effective ways to keep your teeth safe and sound. In addition to the traditional use of brushes and pastes, you should not neglect dental floss. Flosses effectively remove food debris between the teeth, preventing the development of many diseases. - Get preventive examinations once every six months.
It is easier to cure any disease if it is detected at the beginning of its development. Some dental diseases in dentistry have symptoms that cannot be identified on their own. For example, caries at the junction of teeth is visible only on an x-ray.
A person is not able to influence factors that cause various types of dental diseases, such as poor ecology, heredity, and stress. However, with a responsible attitude towards hygiene and prevention, the risk of dental diseases can be significantly reduced or, at least, their treatment can be facilitated.
Treatment methods
As already noted, in modern dentistry, preference is given to conservative treatment. However, it is often impossible to fully treat tooth root inflammation without surgical intervention.
Conservative treatment
This is a complex methodology that includes several types of activities:
- mechanical cleaning of channels
- disinfection of canals using medications
- Temporary filling with medication
Conservative therapy includes the prescription of antibiotics for inflammation of the tooth root.
Surgery
Involves the operation:
- removal of 1/3 of the root tip
- removal of part of the root (hemisection)
- removal of a tooth from the dental socket
Important: Doctors try to save teeth using all conservative treatment methods available today, since they are successful in 70-90% of cases.
3.Treatment of tooth infection
Treatment of a tooth abscess is aimed at fighting the infection, preserving the tooth, and preventing complications. You may need to do a root canal drainage
or even
surgical root canal treatment
. During the mini-surgery, root tissue damaged due to infection is removed. And a crown can be placed on the tooth. In more serious cases, the tooth will need to be removed. And only after this is drainage done. The third way to drain and clean the affected area is through an incision in the gum.
To treat the infection, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics. And to relieve toothache and discomfort due to a tooth abscess, you can rinse your mouth with warm salt water or take a pain reliever (for example, ibuprofen).
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Clinical researches
During clinical trials using a series of Asepta products, conducted in the department of periodontology of the Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery of Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow, the high effectiveness of Asepta products for moderate periodontitis was proven. The use of Asepta mouth rinse turned out to be quite effective. In addition, no phenomena of mucosal irritation or brown staining of fillings were recorded. This indicates that the use of this rinse for a two-week period provides an obvious clinical effect in the absence of negative side effects.
Sources:
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: Asepta toothpaste used in combination with Asepta mouthwash and Asepta gum balm Head. Department of PFS Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor S.B. Ulitovsky St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova. Faculty of Dentistry. Department of Preventive Dentistry.
- Clinical experience in using the Asepta series of products Fuchs Elena Ivanovna Assistant of the Department of Therapeutic and Pediatric Dentistry State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education Ryazan State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (GBOU VPO RyazSMU Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia)
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
Computer method for dental diagnostics
Computer dental diagnostics plays a vital role in making a diagnosis. If identifying caries in the early stages does not require the connection of serious devices, then an erroneous diagnosis of a form of pulpitis can lead to incorrectly prescribed treatment.
Average price in Moscow 300 ₽
Diagnosis of caries
Early diagnosis of caries is a primary task for a dentist. To detect caries, clinical examination, transillumination, electroodontometry, X-ray and laser methods are used. Read more about each of them.
More details