A strange creature is a man. He is always looking for answers to the questions he asks himself. He is looking for a way out of situations that he himself gets himself into. Curiosity by nature is a good gift if used to the point and in moderation, because there are a number of questions to which everyone should know the answers. For example, why do people need teeth and why is it so important to take care of them? Most of us know that the main task of teeth is to chew food so that it is convenient to eat it. But teeth actually perform a number of functions that affect not only the health of the smile, but the entire body as a whole.
If sugar had teeth it would eat itself *
To begin with, let’s define what is the benefit of mechanoenzymatic hydrolysis of natural polymers - proteins and carbohydrates? It is known that in the spatial organization of the structure of such molecules several levels can be distinguished: from a simple chain of sequentially connected monomers to complex aggregates of several macromolecules. In some cases, polymers of different natures can even interact with each other, forming complex supramolecular complexes.
Let's take, for example, plant cells, which, unlike animal cells, are covered with a special durable membrane. The plant wall is made of a kind of lignin-hemicellulose "concrete" reinforced with cellulose fibers. Sometimes such a structure is further strengthened with silicon dioxide, especially in integumentary and conductive tissues. The supramolecular architecture of the cell walls of yeast, already classified as fungi, is composed of a branched network of mannoproteins and chitin attached to a high-molecular-weight polysaccharide - β-1,3-glucan.
Such a supramolecular structure of biological structures helps cells perform their functions, but makes it much more difficult for researchers to solve problems in processing natural raw materials.
For example, in the process of producing bioethanol from cellulose, it is necessary to obtain carbohydrate monomers, which is not an easy task. For these purposes, enzymatic hydrolysis is used, which will proceed better with an increase in the surface area on which hydrolyzing enzymes can be sorbed. In addition, the supramolecular structure of the cell walls should be disrupted, and this should be done in such a way that there is as much cellulose on the surface as possible and less lignin, which inhibits enzymes (Sinitsyn et al.
, 1995).
Returning to our “digestive” analogy, we note that even protein molecules isolated from peas, due to their complex polymer structure, may not be fully absorbed by people with certain disorders in the gastrointestinal tract.
Thus, to intensify the processes of processing plant raw materials, it is necessary to disorder the structure of cell walls using one of the currently known methods, such as treatment with superheated steam, extraction with organic solvents, chemical treatment and, finally, mechanochemical methods. And it must be said that the latter method has a number of undeniable advantages: environmental friendliness, apparent simplicity of operations and a relatively rapid transition from laboratory developments to industrial technologies.
I would eat turnips, but my teeth are rare
As is known, the original plant raw materials most often cannot be processed without preliminary grinding. For this function in animals, the front teeth - incisors - are used; for technological purposes, there is a wide range of special equipment: knife, hammer, roller and jaw mills, chippers, etc. Some of these devices are designed for brittle, and some for fibrous materials. Some are representatives of laboratory equipment with a productivity of several kilograms per hour, while others are capable of crushing tree trunks into chips in seconds.
The reactivity of the product obtained after processing in such mills, as a rule, does not differ much from the reactivity of the original raw material: the main purpose of grinding is to obtain material with particle sizes of 0.5-5.0 mm, suitable for further disordering of the supramolecular structure of cell walls at with the help of other devices - energy-intensive activators, these “molars” of mechanochemistry.
It is known that the reactivity of lignocellulosic material, the main “participant” of enzymatic hydrolysis, depends on many parameters: chemical composition (mainly lignin content), specific surface area, degree of crystallinity of cellulose polymerization. These characteristics can be changed by properly selected mechanical action implemented in activators.
We should not forget about the second participant in enzymatic hydrolysis - a complex of cellulolytic enzymes, which must somehow be distributed over the substrate. Of course, a pre-prepared enzyme solution can be added to the activated lignocellulosic material. However, this is not at all necessary.
It turned out that there is a narrow optimum of mechanical action conditions under which the enzyme (a substance of protein nature) does not change its structure and retains catalytic activity (Bychkov et al.
, 2011). As a result of such processing, a product is obtained in which the particles of the enzyme preparation are fairly evenly distributed among the particles of the substrate. After this, to start hydrolysis, all that remains is to add water and set the desired temperature.
It would seem that everything is simple, but it should be noted that the above-mentioned optimum is indeed very narrow: in most cases, mechanical action leads to irreversible denaturation of enzymes. To avoid this, it is necessary to strictly control the energy supplied to the substance during processing and prepare the substrate itself accordingly.
The situation is like in agricultural technology: you can scatter as many seeds as you like on the surface of dense, unprepared soil - and only a few will sprout from them, but as soon as the same soil is properly plowed, loosened and fertilized - a wonderful harvest will result from fewer seeds.
Types of toothache and relief strategies
We will provide a list of warning signs that, due to the presence of nerves, can let us know that there are problems with our teeth and we should not hesitate to go to the dentist.
Slight sensitivity, unpleasant sensations close to pain
Symptom: Sensitivity to hot or cold foods and drinks.
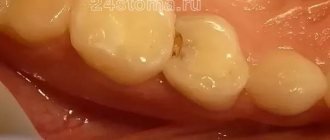
This may be caused by: incipient caries on one of the teeth, the use of a hard toothbrush and whitening pastes, or a recent teeth whitening procedure. In addition, this may also be an individual feature determined genetically.
What to do: If your tooth enamel is too sensitive, keep it clean and prevent stubborn plaque and tartar from forming. Use an extra soft toothbrush, but no more than twice a day. If more frequent hygiene is required, then use soft rinses. Also try using a fluoride toothpaste designed for sensitive teeth. You can use the remineralizing gel as a compress, rubbing it into the surface of the tooth. If after all these steps the sensitivity does not go away, make an appointment at the dental clinic.
He who chews as he lives lives as he does.
How should lignocellulosic materials be prepared for enzymatic hydrolysis? An important assistant in this matter is a set of physicochemical methods that make it possible to describe the process of mechanical activation and determine the degree and quality of grinding, including microscopy.
As a result of mechanical activation, a homogeneous product with an average particle size of about 16 microns is obtained. As the particle size decreases, the specific surface area naturally increases. This is a particularly important parameter, since first endo-glucanase enzymes must be sorbed on the surface of polymeric carbohydrates and catalyze the depolymerization reaction, and only then the resulting oligomeric carbohydrates will react with exo-glucanases in solution. Using the method of thermal desorption of nitrogen, it was possible to show that mechanical activation leads to an almost fivefold increase in the specific surface area of the material!
The next important factor influencing the efficiency of enzymatic hydrolysis is the degree of crystallinity of cellulose. Mechanical activation leads to a twofold decrease in the proportion of crystalline regions of cellulose, which are little susceptible to the action of enzymes. Amorphization of these non-reactive regions is a direct consequence of disorder of the supramolecular structure of the cell wall (Bychkov et al.
, 2012). An additional increase in the proportion of amorphous regions allows enzymatic hydrolysis to be carried out with high yields of the final product.
Another successful example of the influence of mechanical activation on subsequent enzymatic hydrolysis is the technology for producing mannanoligosaccharide antibiotic substitutes for livestock from yeast biomass (Bychkov et al.
, 2012).
The cell walls of yeast consist of several layers, so in order for the mannanoligosaccharides in mannoproteins to interact with pathogenic microorganisms, it is necessary to partially hydrolyze the β-glucan with which they are associated into a single supramolecular ensemble. Mechanical action disrupts the structure of β-glucan, allowing the enzymatic process to proceed.
The example with yeast shows how the results of work begun ten years ago at the Institute of Chemical Technology and Technology of the SB RAS to solve the fundamental problems of “mechanochemical disassembly” of supramolecular structures formed the basis for the technology for producing environmentally friendly antibiotics for agriculture. Today, this technology is being tested at the Sibbiopharm Production Association (Berdsk), the leading biotechnological production enterprise in Russia.
The use of preliminary mechanical activation makes it possible to effectively carry out enzymatic hydrolysis of the proteins that make up peas, obtaining a new product in which the content of free amino acids increases tens of times compared to the original (Samoshkin et al., 2013). Puree soups based on this hydrolyzate can be used for therapeutic and prophylactic nutrition of people with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as nutrition for athletes who need a large amount of quickly digestible protein.
Why remove wisdom teeth?
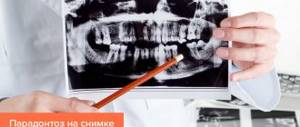
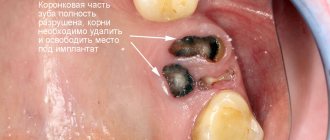
Although wisdom teeth are a vestigial organ, they may well be useful to modern people, but their growth often becomes a real problem, causing severe pain and inflammation, destruction of adjacent teeth, deformation of the dentition, as well as other serious complications and pathologies. In this case, based on x-rays, examination and medical history, the dentist can decide on the need to remove teeth that promise to pose a threat to oral health. Typically, the need for extraction arises due to the incorrect position of the tooth, as a result of which it injures the soft tissues of the oral cavity and interferes with the normal growth of neighboring teeth.
When wisdom teeth are coming in, we recommend drinking the Asepta vitamin and mineral complex. Otherwise, molars may grow with weak enamel, which will subsequently lead to carious processes. The complex provides the body with calcium and other minerals and is well absorbed by the body.