Palate cancer is a malignant neoplasm that forms from the mucous membrane of the hard and soft palate. This is a fairly rare disease. It is more common between the ages of 40 and 60 years. Men get sick 4 times more often than women.
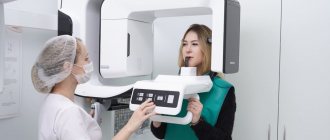
Diagnosis of cancer of the soft and hard palate at the Yusupov Hospital is carried out using modern research methods. The oncology clinic is equipped with modern equipment from leading American and European manufacturers, which allows you to quickly establish an accurate diagnosis. To treat malignant tumors of the palate, surgical interventions, chemotherapy drugs and innovative methods of radiation therapy are used.
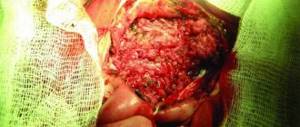
The most malignant tumor of the palate occurs due to metastases of cancer of the nasopharynx and nose. The neoplasm affects the periosteum of the hard palate, lower and upper jaws, muscles and tissue of the oral cavity, and tongue. Atypical cells spread to the submandibular, mental and cervical lymph nodes.
Structure of the palate
The upper palate (palatum durum) is a dome-shaped vault of the mouth, which is divided into 2 “floors” - the oral and nasal cavities - and also delimits them from the pharynx. There are two sections of this organ: the soft and hard palate.
In front there is a hard bone part. It is built from processes of the bones of the upper jaw in the form of plates that have a concave shape and are located horizontally. From below it is covered with a delicate mucous membrane, gradually turning into the soft palate or the velum palate. It is located in the back above the root of the tongue and is adjacent to the tonsils.
The soft has a muscular base, covered with fibrous tissue and mucous membrane. This uvula divides the nasopharynx into 2 entrances: one of them is the beginning of the larynx, the other is the pharynx and leads to the trachea and esophagus, respectively.
If there are pathologies in the oral cavity, both parts hurt, and discomfort is present both at rest and when talking or swallowing. This always causes a person a lot of problems. What to do in such cases? First you need to visit a dentist, only he will determine the cause of the disease and prescribe treatment.
Structure of the palate
The video describes the structure of the oral cavity and palate:
Diagnostics
To find out the factors that provoked inflammation of the palate, the patient needs to undergo a comprehensive examination:
- Examination of the oral cavity by a dentist and, if necessary, an otolaryngologist.
- Laboratory research. General and biochemical blood test, scraping (for seals on the palate).
- Ultrasound, computed tomography – for immune pathologies and diseases of the digestive system.
A blood test is done to identify the causes of inflammation of the palate.
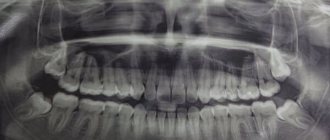
If inflammation and pain are caused by dental disorders, you need to undergo an x-ray of the jaw to rule out purulent processes in the bone tissue.
Only after making a diagnosis can the doctor choose a special treatment that will be aimed at eliminating the source of the problem and improving the patient’s well-being.
Main causes of pain
There are many different causes for pain in the palate: internal pathologies, infections and functional disorders. Discomfort may be associated with increased tissue sensitivity, a reaction to too hot or cold food, or poor oral hygiene. Even a small scratch can develop into a serious pathology due to a favorable environment for this.
Dentists identify ten main reasons why their patients complain of pain in the palate:
- Bacterial infection. It becomes hyperemic, swells, a dirty gray coating appears on it, and ulcers and erosions appear on the mucous membrane.
- Sore throat and inflammation of the tonsils. Has similar symptoms to a bacterial infection. Neglected cases are fraught with severe complications in the form of myocarditis and polyarthritis.
- Stomatitis. Depending on the type of disease, ulcers, a dense yellowish coating, or herpes formations may appear in the mouth.
- Leukoplakia is a pathology of the oral mucosa that develops with constant temperature changes from food and drinks, and can also appear due to injuries to the mucous membrane. It is considered a precancerous condition.
- The consequence of smoking is that the mucous membrane is constantly exposed to the high temperature of smoke and its components. Smokers often develop Tappeiner's leukoplakia.
- Inflammation of the salivary glands - submandibular, sublingual or minor salivary glands - due to an infection in the mouth.
- Consequence of poor-quality prosthetics or unsuccessful treatment, tooth extraction.
- Pathologies of jaw joints, neuralgia. In this case, pain occurs not only in the palate, but also on the face, teeth and gums.
- Sialometaplasia is the appearance of a small benign tumor on the mucosa that causes pain. It grows to a certain size, then the bubble opens and a small wound forms.
- Domestic thermal and chemical burns of the mucous membrane that occurred due to negligence.
Inflammation of the salivary glands is one of the reasons
Yellow palate in the mouth of an adult
If the sky has turned yellow, you should see a dentist. During the examination, the specialist will determine whether the yellowness of the mucous membrane is a sign of any disease, or indicates a lack of proper oral hygiene.
The patient’s attitude towards bad habits is also taken into account. Yellowness with a pronounced network of veins is often formed as a result of regular smoking.
When conducting diagnostics, the patient's age is taken into account. In people over 50 years of age, the appearance of yellow plaque on the palate is considered a physiological process, so serious health problems are not always detected.
Read also: How to get kindergarten at 2 years old
The child has
A yellowed sky appears not only in adults, but also in children. In addition to dental problems, this sign may indicate other diseases, so the child should be shown to a gastroenterologist, ENT specialist, pediatrician, infectious disease specialist, or hepatologist.
Often, young patients with this symptom are diagnosed with thrush. If there is any doubt in determining the problem, it is recommended to undergo a full examination, including donating blood to check bilirubin levels.
The main symptoms of palate diseases and methods of their treatment
Each disease has its own specific symptoms. Not only doctors, but also patients need to know them. At least in order to determine which specialist to go to with your illness.
The appearance of ulcers on the oral mucosa indicates the development of candidiasis or thrush. Canker sores may have a cheesy appearance and are usually itchy and painful. Often they affect the entire tongue. Treatment of the disease is usually carried out with antimycotics and local treatment.
Candidiasis
With angina, the palate is hyperemic, swollen, the tonsils are enlarged and inflamed. Constant pain when swallowing increases sharply, and the patient's temperature rises. Sore throat can be different: catarrhal, follicular, etc. Effective treatment is only antibacterial, and it should last at least 10 days. This is necessary in order to avoid complications.
Angina
Pulpitis and periodontitis lead to tooth decay. They are accompanied by inflammation of the nerve bundles and severe throbbing pain. For treatment, the doctor must clean the dental canals and seal them. Periodontitis and other periodontal tissue diseases are treated by a dental hygienist. He will clean your teeth of plaque and tartar, rinse out the gum pockets and prescribe a course of antibiotics.
Signs of inflammation, redness of the gums and pain in the roof of the mouth may appear after tooth extraction. In this case, alveolitis can be suspected. This is suppuration and inflammation of the walls of the hole in which the tooth sits. This phenomenon occurs due to insufficient hygiene after surgery, when a protective blood clot falls out of the socket, or with reduced immunity. With alveolitis, the temperature rises, the face and gums swell. For treatment, the hole is completely cleaned, an antibiotic is added, and local treatment is prescribed.
Alveolitis
Leukoplakia is accompanied by a grayish coating on the palate and inner surface of the cheeks, and their swelling. There is roughness, tightness of the mucous membrane, moderate pain in the palate, burning in the mouth, decreased saliva production, and thirst. The pathology is sluggish, lasts for years, but has no reverse development. The plaque is replaced by keratinized areas raised above the level of the mucosa. They also have a white coating that is easily scraped off. Vitamins and immunomodulators are taken for treatment. In severe cases, you will need the help of an oncologist.
Leukoplakia on the palate in the initial stage
With benign tumors in the oral cavity, the palate does not hurt. They grow slowly and usually do not bother the patient until he accidentally notices them. However, any tumor must be shown to a doctor and removed as prescribed. There are many methods for painless removal: electrocoagulation, laser removal, radio waves, freezing with liquid nitrogen, sclerotherapy and others.
Pain also appears with pathologies of the temporomandibular joint. Inflammation of the bone structure causes sharp sharp pains in the palate, which intensify when opening the mouth and chewing. The soft tissues turn red and swell, a feeling of fullness appears in the joint area, and the temperature may rise. For this pathology, the doctor prescribes symptomatic treatment.
There are a number of symptoms, in the presence of which you need to see a doctor as soon as possible:
- decreased taste sensitivity;
- it became painful to chew and swallow;
- there was a feeling as if there was something in the mouth;
- mucous membrane is swollen;
- teeth are crumbling
- gums hurt and become very inflamed;
- ulcers or lumps on the roof of the mouth.
Popular drugs for treatment
If the mucous membrane is slightly damaged, use warm herbal rinses with calendula, chamomile and sage. You can also use antiseptics - Chlorhexidine, Rotocan, Chlorophyllipt.
Combined dental gels are suitable for pain relief - Cholisal, Kalgel, Kamistad.
Of the antimycotics for candidiasis, the most often recommended are Candide, Pimafucin, Nizoral, Clotrimazole and the like.
For aphthous stomatitis of bacterial origin, sea buckthorn and rosehip oils are used, and for rinsing - propolis tincture, Romazulan, Miramistin, Stomatidin, Lugol. These agents accelerate the healing of mucous tissues.
For neuralgia, novocaine blockades, lidocaine, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and analgesics are prescribed.
In the video, Alexander Myasnikov talks about the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia:
For inflammation of the temporomandibular joints - anti-inflammatory treatment. Antibiotics and physiotherapy are used.
For burns, rinsing with lukewarm water and applications with Metrogil-Dent gel for pain relief are prescribed. To speed up healing, the palate is lubricated with sea buckthorn or rosehip oil and treated with tincture of calendula, Kalanchoe and other herbs.
Prevention of palate diseases
Basic prevention includes the following actions:
- balanced diet;
- correct and sufficient oral hygiene;
- rinsing your mouth after eating;
- cleaning the spaces between teeth with floss and dental brushes;
- giving up any type of smoking.
Now you know what to do if the roof of your mouth hurts. It is important not to forget that every six months a preventive examination by a dentist is necessary for timely treatment of oral diseases.
Mammals, when chewing food, form a food bolus in their mouth. They manipulate the food bolus using their teeth and tongue, pressing it to the palate. In order to fix the bolus of food in certain positions, the palate must be non-smooth. And when the lump moves to different ends, there is a certain number of clamps, which is why nature created transverse ridges in the palate.
All about your body Do tattoos increase the risk of skin cancer? Why do only Russians have a vaccine mark on their shoulder? What architectural and common sense mistakes have been made in the structure of the human body? Find out more
Inflammatory and infectious pathologies of the throat, gums, dental diseases, mechanical damage to the mucous membrane - all these are reasons that can provoke inflammation of the palate (palatinitis). As a result, pain occurs, the timbre of the voice is disrupted, and the pitch of the sound changes. The goal of treatment is to eliminate provoking factors and prevent serious complications with the help of medications and traditional recipes.
Inflammation on the palate
Causes of inflammation of the palate
Components of the palate:
- hard palate or upper palate - bone tissue, has an arched shape;
- soft or lower - consists of the mucous membrane.
Components of the palate
The main function of the organ is to prevent food from entering the nasal passage from the mouth. Additional responsibilities include participation in articulation through superficial receptors that are associated with the larynx.
The functioning of the palate can be affected by an inflammatory process that affects mucous tissues due to exposure to external irritants or dysfunction of internal organs.
Table “Causes of inflammation of the palate”
| External factors | Consuming hot foods or drinks, which can cause a burn to the mucous membrane (blue, swollen palate, bruising) |
| Negative effects of metals (braces, crowns) on a healthy oral environment | |
| The use of prostheses (friction of a foreign body on the mucous membrane over time can provoke wounds or ulcerative processes) | |
| Abuse of tobacco products | |
| Ignoring oral hygiene. If you do not brush your teeth or rinse your mouth for a long time, any mechanical damage (scratches, bruises) can allow infection to enter the body. | |
| Wounds, ulcers due to injury or an injection of anesthesia during tooth extraction (treatment). As a result, vascular spasm or ischemia occurs, which leads to a benign compaction - sialometaplasia | |
| Pathological conditions of the oral cavity | Fungal or bacterial infections, viral pathologies provoke a rash on the mucous membrane - enanthema (in a child it is expressed in the form of hyperemia of the mucous membrane, small pimples, ulcerations) |
| Development of infection in the bone tissue of the jaw (osteomyelitis) | |
| Seals of oncological etiology. Often found in adults with pathological immune disorders | |
| Damage to the joints of the jaw (upper or lower) due to the development of neurological abnormalities | |
| Upper respiratory tract infections (tonsillitis, sore throat, pharyngitis, rhinitis) | |
| Dental diseases (caries, periodontitis, stomatitis, pulpitis) | |
| Allergic manifestations to drugs | |
| Temporomandibular joint dysfunction |
Inflammation of the palate does not occur hidden. Usually the pain is pronounced, which makes chewing food very difficult and becomes acute when swallowing. Depending on the reasons that led to this condition, there are many symptoms of the disease.
- With fungi and bacteria (often happens in children under 1 year of age due to the fact that the child puts everything in his mouth) - a white coating and small ulcerations appear on the palate. The mucous membrane burns, hurts (especially while eating), and a putrid odor appears from the mouth. In adults, infection can develop after poor-quality tooth extraction, be a consequence of dental pathologies, or result from injuries.
- In case of throat diseases (tonsillitis, sore throat), the upper palate is red, there is swelling, the mucous membrane is loose. Swallowing is accompanied by pain and tingling, and severe irritation of the mucous membrane develops.
- With malignant tumors, the patient's palate hurts inside, with aching discomfort.
- After tooth extraction, bruising and swelling are observed closer to the teeth near the gums.
- In case of liver dysfunction, there is a yellow coating on the soft and hard palate, slight swelling and redness are possible.
- When you have a cold, the upper part of the oral cavity stings, cramps, and the mucous membrane is rough.
Inflammation of the palate often affects other parts of the oral cavity. A rash and swelling may appear under the tongue and behind the arches, on the inside of the cheeks, and behind the front teeth. In acute cases, the body temperature rises, hyperemia develops (intensive filling of blood vessels at the site of inflammation), and the mucous membrane dries out.
The photo shows what a healthy palate looks like and one affected by foci of inflammation.
Palate without deviations
Inflammatory process on the palate
Which doctor should I contact?
Negative processes in the oral cavity are treated by a dentist. If necessary, he can prescribe a consultation with a therapist and otolaryngologist, sometimes an oncologist (if there are tumors on the palate).
Diagnostics
To find out the factors that provoked inflammation of the palate, the patient needs to undergo a comprehensive examination:
- Examination of the oral cavity by a dentist and, if necessary, an otolaryngologist.
- Laboratory research. General and biochemical blood test, scraping (for seals on the palate).
- Ultrasound, computed tomography – for immune pathologies and diseases of the digestive system.
A blood test is done to identify the causes of inflammation of the palate.
If inflammation and pain are caused by dental disorders, you need to undergo an x-ray of the jaw to rule out purulent processes in the bone tissue.
Only after making a diagnosis can the doctor choose a special treatment that will be aimed at eliminating the source of the problem and improving the patient’s well-being.
Treatment at home
Pain and discomfort inside the oral cavity due to inflammation of the palate greatly worsens the patient’s normal life. Pharmacy medications and folk remedies as auxiliary therapy help alleviate the condition and cope with the disease.
Medicines
The main treatment depends on the original disease:
- For fungi and bacterial pathologies, it is recommended to use local preparations for rinsing the mouth and lubricating the mucous membrane - Chlorhexidine solution and gel, Rotokan, Stomatofit.
- For severe pain of various etiologies, local anesthetics are prescribed - Kalgel, Cholisal-gel.
- For purulent lesions, antibiotics are needed for oral use - Flemoxin, Sumamed.
Sumamed is an antibiotic agent
Important!
It is important not to delay treatment, but to immediately take the prescribed medications, strictly following the doctor’s instructions. Otherwise, there is a risk of serious complications.
Folk remedies
If wounds in the mouth do not heal for a long time, traditional medicine will help relieve inflammation in the oral cavity and relieve pain. Effective recipes help well in complex drug therapy.
Sage decoction
Brew 1 tsp in 250 ml of boiling water. herbs, simmer over low heat for 3 minutes, cool. Rinse your mouth with the strained solution 4–6 times a day. The course of treatment is until the unpleasant symptoms are completely eliminated.
Gargling with sage decoction will help relieve inflammation.
Oak bark decoction
Grind the raw materials and pour 2 tbsp into an enamel pan. l., pour 500 ml of boiling water. Boil in a water bath for 5-7 minutes, leave to infuse. Strain and rinse your mouth with warm broth every 2 hours.
Rinse your mouth with oak bark decoction every two hours
Raspberry leaf infusion
Finely chop raspberry leaves (2 tbsp) and pour a glass of boiling water. Rinse your mouth with the cooled liquid at least 5 times a day. For each manipulation it is necessary to prepare a glass of fresh infusion.
An infusion of raspberry leaves effectively relieves inflammation
St. John's wort tincture
Dry grass (150 g) pour 0.5 liters of vodka, leave for a week in a dark place. Take the medicine 35 drops with water. The product is also suitable for external use. Dilute 20 drops of solution in 50 ml of water and moisten a cotton pad and wipe the ulcerations on the palate.
St. John's wort tincture can be used for internal and external use
Viburnum berry decoction
Place dried berries (100 g) in boiling water (1 l) and boil for 15 minutes. Rinse your mouth with the cooled broth 3-4 times a day.
A decoction of viburnum berries is a good remedy for treating inflammation of the palate.
Chamomile and calendula infusion
Combine chamomile and calendula inflorescences in equal parts (1 tsp each). Pour two cups of boiling water over the vegetable mixture and leave to steep for 50 minutes. Thoroughly rinse your mouth and throat with herbal tea in the morning and evening.
Rinse your mouth with chamomile and calendula infusion morning and evening.
Propolis tincture
Dilute the pharmaceutical product in water at the rate of 10 drops per 200 ml of warm water. Rinse your mouth with the solution for 5–7 minutes every 2–3 hours.
To relieve inflammation on the palate, use propolis tincture
Folk recipes for inflammation of the palate are aimed at relieving swelling, redness and burning sensation. Herbal decoctions, infusions and tinctures produce antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, soothing and antimicrobial effects.
Possible complications
In most cases, inflammation of the palate is a consequence of external irritants or internal diseases.
Ignoring this condition can provoke undesirable consequences:
- destruction of bone tissue;
- tooth loss;
- purulent lesions of the gums;
- deformation of the upper part of the oral cavity;
- disturbances in voice timbre and changes in sound quality.
In severe cases, advanced stages can transform into malignant pathologies.
Ignoring palatal inflammation can lead to tooth loss
Prevention of inflammation of the palate
To avoid discomfort and pain that accompany inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, you need to follow simple rules of prevention.
- Brushing your teeth should be done in the morning and before going to bed at night.
- It is recommended to rinse your mouth after every meal.
- Avoiding very hot foods and drinks.
- Limit smoking and alcohol consumption.
- Eat a balanced diet. There are foods rich in microelements and vitamins (vegetables, fruits, fish, meat, beans and soy).
Rinse your mouth after eating
Prevention helps strengthen local immunity, establish metabolic processes in the body, maintain a healthy environment in the oral cavity and strengthen the body as a whole.
Inflammation of the upper and lower palate can be caused by dental diseases, infectious pathologies of the throat, gums, bad habits and poor oral hygiene. The disease causes severe pain and worsens a person’s quality of life, as it interferes with chewing food, speaking, and swallowing. To prevent the disease from worsening, it is important to consult a doctor on time and receive proper treatment.
Teeth and mouth
Rate the article (ratings, average of 5)
Many people experience painful sensations if the roof of their mouth is inflamed, and do not know how to treat this condition; its possible causes, photos and methods of struggle can be found in this article.
The palate has an important functional significance for the body: it separates the nasal cavity from the oral cavity, helps to chew and swallow food without choking, clearly reproduces speech sounds, and participates in the formation of the voice. Anatomically, the palate is divided into two parts: hard, located closer to the teeth, and soft, smoothly passing into the pharynx. Both of these sections can become inflamed, but these conditions will manifest themselves in different ways.
Preventive measures
As a preventative measure, it is recommended to periodically undergo dental examinations.
This will help identify the disease at an early stage and begin a course of treatment in a timely manner, thereby preventing the development of complications.
It is also necessary to carry out daily oral hygiene procedures to remove food debris and remove plaque from the mucous membrane.
The main defense of any person is, first of all, immunity. To strengthen it, you should maintain physical fitness, radically review your diet, and enrich the body with valuable minerals and vitamins.
The following recommendations are also preventive measures:
- You should not overuse spicy, salty foods, or foods with a hard structure;
- after eating, you need to rinse your mouth with a special balm or at least clean water;
- If you experience unpleasant sensations in your mouth, rinse for several days using decoctions of propolis, chamomile, oak bark or sage.
Quitting bad habits, in particular smoking, can prevent the formation of yellow plaque on the palate.
Causes of inflammation of the palate
Why do the palatal structures become inflamed? Patients can often themselves indicate the factor that caused this problem: injury, scratch, burn. However, in some cases, the mucous membrane becomes inflamed for no apparent reason and it can be difficult to prescribe treatment without first establishing the origin (etiology) of the disease.
The most common causes of inflammatory changes in the palate:
- Viral, bacterial, fungal infections. The palatal mucosa can be affected by the herpes virus, Candida fungus, and various bacteria. The spread of infection to the palate is facilitated by insufficient oral hygiene, microtrauma of the mucous membrane of the upper oral cavity, and reduced immunity. The latter especially concerns fungal and bacterial diseases caused by opportunistic microbes. These are microorganisms that constantly live in the mouth, but do not cause disease. If the immune response is suppressed, they begin to actively multiply and lead to inflammation.
- Injuries to the palate from hard objects (pencils and pens, nut shells, candies), thermal burns from eating too hot food. Both the hard and soft palates can be affected.
- Dental diseases of the oral cavity: stomatitis, periodontitis, periodontitis, pulpitis, caries. Often, symptoms of inflammation appear after a visit to the dentist and complex dental procedures. This is due to the possible traumatization of the mucous membrane of the hard palate by instruments directly behind the front teeth or on the lateral surface. The soft palate is much less likely to be injured in dentistry. In addition, the palate is often damaged by dentures, especially if they are installed incorrectly.
- Tumors of the oral cavity, leukoplakia (changes in the mucous membrane with frequent damage), long-term smoking can also contribute to the development of an inflammatory reaction of the palate mucosa under unfavorable conditions.
Diagnostics
The initial examination should be entrusted to the dentist; problems with the oral cavity are within his competence. The specialist studies not only the oral mucosa, but also the condition of the gums, teeth and the gaps between them.
This is where signs of thrush or stomatitis may appear. Based on the visual examination, the doctor outlines the following stages of diagnosis.
Changed color of the palate may be an independent condition or indicate the development of other diseases.
To clarify the diagnosis, the dentist refers the patient to the following specialists:
Diagnostics also includes laboratory tests of biological samples: blood, urine, feces.
If an allergy is suspected, the patient is referred to undergo:
- Ultrasound;
- CT;
- MRI;
- x-ray.
The doctor examines the oral cavity
Does your throat also hurt?
In the case when the soft palate is inflamed, but the throat is also bothering you: there is a soreness, a cough, it hurts to swallow food - the cause should be sought in the primary inflammation of the pharynx (pharyngitis) or tonsils (tonsillitis, sore throat).
The soft palate directly passes into the tissues of the pharynx, so the inflammatory process spreads unhindered from one area of the mucosa to another. Often such symptoms develop against the background of colds, are accompanied by a runny nose, fever and require treatment by an otolaryngologist.
Primary and secondary inflammation
There are two stages of inflammation:
- Primary inflammation is associated with the direct impact of a damaging agent, it develops only under the direct influence of this factor and is associated with the destruction of cellular structures, the release of substances called inflammatory mediators, which cause all inflammatory symptoms: redness, swelling, pain. Due to these mechanisms, the local blood supply to the tissues is disrupted, small nerve fibers are damaged, and the process moves into the second stage.
- Secondary inflammation causes the greatest damage: it continues even after the elimination of the causative factor and is associated with tissue destruction against the background of reduced blood supply and damage by enzymes isolated from already decayed cells. At this stage, the vascular wall is damaged, which is manifested by tissue bleeding. Without adequate treatment, this vicious circle can persist for a long time and cover an increasingly larger area of the mucous membrane.
Stages of palate cancer
Palate cancer is staged according to principles common to most malignant tumors - according to the TNM system, which involves assessing the size and extent of the primary tumor, the involvement of regional lymph nodes and the presence of distant metastases, and according to these parameters the following stages are distinguished:
- Stage 0 - cancer in situ. Only the superficial layers of the mucous membrane are affected without spreading to the underlying layers.
- Stage I - tumor up to 2 cm in greatest dimension, without damage to regional lymph nodes and distant metastases.
- Stage II - tumor from 2 to 4 cm in greatest dimension, without involvement of regional lymph nodes and isolated metastases.
- Stage III - a tumor more than 4 cm in greatest dimension, or a tumor node up to 4 cm with a metastasis less than 3 cm in size in one regional lymph node on the affected side.
- Stage IV - tumor spreading to nearby structures (for example, cortical bone, masticatory apparatus, pterygoid processes of the main bone or skull base); or metastases larger than 3 cm in size and/or in several lymph nodes, both on one side of the neck and on both; or the presence of distant metastases.
Symptoms
- Pain in the area of the palatal structures, constant, aggravated by swallowing or chewing food that touches the damaged area. If the cause of inflammation is high temperatures, then the palate burns severely.
- Swelling of the mucous membrane of the palate: it increases in volume and begins to “interfere” in the mouth like a foreign body, sometimes it can even make breathing difficult. As a rule, this happens with serious purulent processes affecting the soft palate.
- Changes in the appearance of the palatal surface: it turns red, ulcers and erosions form, with a fungal infection a white coating appears, with the herpes virus - vesicular rashes on the palate, on the inner surface of the cheeks, under the tongue. The clinical picture of a bacterial infection often manifests itself as purulent inflammation. Signs of the presence of pus: yellow plaque, the appearance of a lump, a bump on the roof of the mouth, sometimes with a white “head”.
- Other symptoms: bleeding of the oral mucosa at the slightest damage, enlargement, swelling and redness of the tonsils, pharynx, excessive salivation, decreased taste perception, increased body temperature with extensive inflammation.
Long-term absence of necessary treatment for inflammation of the palate can be complicated by the following conditions:
- abscesses of surrounding tissues (limited purulent inflammation);
- phlegmon (unlimited purulent inflammation) of the cellular spaces of the neck, mediastinum - mediastinitis;
- formation of deep ulcers of the mucous membrane;
- leukoplakia can lead to the formation of malignant neoplasms, this condition is called “precancer”;
- complications from teeth and surrounding tissues (periodontitis).
These situations are often life-threatening and require immediate medical attention; phlegmon, which can spread to vital organs, is especially dangerous.
What should parents of a child with such an anomaly do?
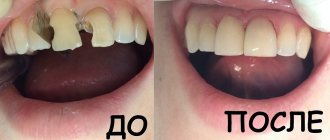
The main thing is not to panic at the thought, my child has a cleft palate, and not to try to terminate the pregnancy. You shouldn’t risk the mother’s health by postponing the birth of a baby because of a defect that can be successfully treated with modern surgery. Abortion is too high a price, especially if the cause of the defect is hereditary, and it may appear during the next pregnancy. Timely surgical treatment of congenital cleft palate makes this anomaly safe for the life and health of children.
It is important to seek qualified medical help from specialists in time to correct the defect and prevent the development of numerous complications, including:
- respiratory failure leading to hypoxia (lack of oxygen);
- frequent infectious and colds that weaken the immune system;
- speech and hearing disorders;
- delayed growth and development of the jaw.