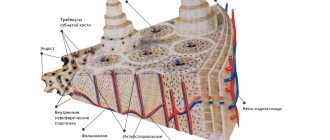
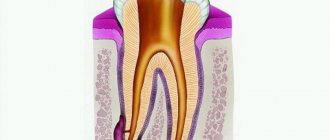
What is cementoma
This is a type of benign tumor that forms in the area of the tooth root. It consists of fibrous cement-like tissue and at first does not manifest itself in any way - only a specialist can diagnose the problem. The development of the pathological process is accompanied by the gradual destruction of bone and epithelial tissue in the oral cavity. When the tumor reaches a large size, deformation of the jaw occurs. In some cases, the disease can lead to a fracture of the jaw bone. Women, as well as persons under the age of 20, are more susceptible to pathology.
Only a specialist can diagnose the problem
Most often, cementoma forms in the area of the central teeth of the lower jaw. In other cases, the tumor may be localized in the upper jaw, but this situation is especially dangerous, since here the pathological process can affect the maxillary sinuses. According to ICD-10, cementoma belongs to category D16 - benign neoplasm of bones and articular cartilage, subtype D16.4 - bones of the skull and face.
Reasons for the development of pathology
Experts in the field of dentistry still cannot identify specific reasons that are guaranteed to lead to the formation of a benign tumor on the jaw bone. Today, experts identify several factors that can provoke the development of pathology:
- chronic course of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity - osteomyelitis, actinomycosis, fibrous periodontitis and others,
- severe injury to the jaw bone due to a blow, bruise,
- systematic mechanical damage to hard or soft tissues of the oral cavity - incorrectly installed fillings, dentures, orthodontic apparatus (brackets).
The photo shows osteomyelitis.
Genetic predisposition can also be added to possible predispositions. Negative external influences, such as smoking or radiation therapy, can also contribute to the development of pathology.
Reviews
Benign tumors of this type are not uncommon. Young people who have had experience in treating and detecting them can share it by leaving a comment below on this article.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags cementoma jaw
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
Plastic crowns for front teeth: reviews, pros and cons, cost
Next article
Metal braces – price issue
Characteristic symptoms
One of the most dangerous characteristics of cementoma is its asymptomatic course. In the first stages of development of the pathology, the patient does not experience any discomfort or pain. Therefore, most often the tumor can only be detected at a dentist’s appointment.
“Dangerous disease! I noticed it already at the last stage, when I went to the dentist to treat a tooth, I just wanted to put a filling and remove one. As a result, they discovered cementoma... And indeed, there was no pain at all, I didn’t feel anything. I’m sure that I’m still very lucky that everything coincided like that...”
Nataly, from correspondence on the forum www.32top.ru
The tumor can be identified by x-ray.
As the size of the tumor increases, the thickness of the cortical plate decreases, which creates unnecessary pressure on the periosteum. At this stage of pathology development, the patient may experience the following symptoms:
- discomfort and moderate pain when eating or talking,
- unpleasant sensations at the moment of mechanical impact on the causative area,
- slight deformation of the enamel structure, change in its color.
When the tumor reaches a large size, it can lead to rupture of the mucous membrane and soft tissues in the oral cavity. In the most advanced cases, there is a risk of deformation of facial features and even fracture of the jaw bone.
Characteristics of varieties
Each of the histological types of this group of formations should be described in more detail.
Periapical fibrous dysplasia
Photo: mandibular cementoma on CT
In this case, there is a defect in the formation of cement
. In addition to the roots, the process of destruction also affects the bone of the jaw itself. However, despite this, the prognosis is usually favorable.
Detection, as in other cases, usually occurs by accident. Most often this is associated with the treatment of a tooth when its root is fractured, since the neoplasm can make it more fragile.
The main distinguishing characteristic of this species is the absence of a periodontal fissure, although changes occur near the apex (or apexes) of the root. In the affected areas of the bone there may not be clear boundaries of newly formed dense tissue.
The degree of mineralization of these areas can be different, so the consistency also changes - from soft to very dense.
The best way to diagnose is an x-ray examination of the desired area with four or five times magnification.
Cement-forming fibroma
As in other cases, this formation is not classified as malignant. Diagnosis is carried out in the same way. However, the picture during X-ray examination and histology is somewhat different.
First of all, the growth of this tumor is determined by the processes occurring in the bone. More precisely, it is the process of mineralization.
In the image you will be able to see an area where the bone tissue is somewhat sparse. This is the source of the lesion. It has smooth outlines.
The sparseness is explained by the fact that this type of formation has rather weak mineralization. Histology shows a fibroplastic structure.
A cement-like structure can only become in the last stages of the disease, if it has not been identified and treated earlier.
Gigantoform cementoma
It has been reliably revealed that this variety is a hereditary pathology
. In this regard, most often it can be observed in several family members.
The image will show that large areas of spongy bone are dense and dark. In most of the described cases, pathological changes occur symmetrically on the jaw.
Types of dental cementoma - classification
Experts identify several forms of cementoma. Each variety is characterized by its own characteristics and symptoms. Let's look at each type in a little more detail.
Benign cementoblastoma
We are talking about a true cementoma, which is understood as a neoplasm of coarse fibrous tissue with varying degrees of mineralization. The tumor is covered with a kind of film - this capsule separates it from healthy cells. This form is characterized by a rather slow course, but the tumor itself can grow to unlimited sizes. The initial stages of this process are not accompanied by any symptoms, but over time there is pronounced resorption of the cortical plate. As a result, the patient experiences discomfort and unpleasant sensations during mechanical action on the causative area, for example, when brushing teeth or eating.
The tumor is covered by a peculiar capsule
An advanced stage can lead to deformation of the jaw bone and the eruption of a tumor, which is fraught with infection and the development of inflammatory processes. Typically, the tumor occurs on the lower jaw in the premolar area.
Cement-forming fibroma
The tumor grows slowly, and the process of its development is usually accompanied by mild symptoms. A lesion with weak mineralization of the neoplasm is formed in the bone tissue, which is due to its fibroblastic structure. In this case, cement-like tissue is formed already at an advanced stage of the pathology, when tumor growth stops. This form of cementoma is especially dangerous when localized in the upper jaw, where its spread is fraught with damage to the maxillary sinus1.
Periapical cement dysplasia
The pathological process occurs in dental cement and bone tissue, which leads to thinning of the walls of the root system of molars. This situation is dangerous due to root fracture. Cement dysplasia usually has many pathological foci, but all of them, as a rule, do not exceed 1 cm in diameter. Tumor formation is also asymptomatic. In this case, there is no deformation of the jaw. Most often, the neoplasm is localized in the anterior parts of the lower dentition.
Periapical cemental dysplasia is often localized in the mandible
Gigantoform cementoma
This form of cementoma is characterized by intensive development, namely the rapid transformation of connective tissue into cementum. The x-ray image clearly shows oval-shaped pathological foci located in close proximity to the root system of the tooth. In this case, the localization can be very different, but usually tumors arise in places that are symmetrical relative to each other. Many experts agree that giganoform cementoma has genetic background, so often a similar diagnosis is given to several members of the same family.
This variety has oval-shaped lesions
Symptoms of dysplasia
The main manifestations of dentin and enamel dysplasia are observed in such dental diseases as:
- dentinogenesis imperfecta;
- Stanton-Capdepont syndrome;
- imperfect amelogenesis.
Stanton-Capdepont syndrome
Stanton-Capdepont disease or syndrome is a hereditary disorder of the formation of enamel and dentin tissue. The main symptoms of this pathology are:
- eruption of teeth having a natural shade and shape, and the subsequent change in the color of their enamel to gray;
- gradual destruction and chipping of tooth enamel;
- early, rapidly progressing abrasion of dentin;
- illumination of the contours of the dental cavity through dentin defects;
- decreased sensitivity of the pulp.
Molars with Stanton-Capdepont disease are subject to destruction and abrasion to a lesser extent than milk teeth. In some cases, the disease is completely asymptomatic, while the teeth are in excellent condition and look practically healthy.
Dentinogenesis imperfecta
Dentinogenesis imperfecta is a pathology characterized by a disruption in the formation of a layer of hard dental tissue located under the enamel (dentin). According to statistics, this disease is found in one out of 8,000 babies, with girls being diagnosed more often.
Depending on the symptoms, there are 4 forms of dentinogenesis imperfecta:
- Type I (the disease acts as one of the symptoms of a congenital disorder of bone formation, and its main signs, in addition to dental dysplasia, are bone fragility, changes in the shape of the middle ear and blue coloring of the eye sclera);
- Type II (the main signs of pathology are opalescence (translucency) of the teeth, a change in the natural color of the enamel to dull gray, increased abrasion of the teeth in the zone of closure of the dentition);
- root dysplasia (underdevelopment or complete blockage of dental roots, early loosening and loss of teeth, minimal difference in the shade of dental crowns from the natural one);
- coronal dysplasia (translucency of tooth enamel, frequent injury to the blood vessels of the pulp, accompanied by minor local bleeding, staining of teeth an amber or brownish-gray color by blood breakdown products).
Amelogenesis imperfecta
In turn, amelogenesis imperfecta is a disorder of the enamel formation process, leading to a change in shade and complete or partial loss of dental tissue.
Depending on the clinical picture, there are 4 subtypes of this pathology:
- type 1 (the enamel acquires a brown or yellow tint immediately after the teeth appear, unevenness of the dentin-enamel junction is observed);
- type 2 (1-3 years after the appearance of the first teeth, the enamel acquires a brown tint, becomes rough, matte, and becomes covered with cracks);
- type 3 (at the moment of teething, the teeth are covered with thin white enamel, which quickly disappears, exposing dentin);
- Type 4 (when teething, teeth are covered with matte, chalky enamel, which is easily separated from dentin under mechanical stress).
The sensitivity of the pulp with dental dysplasia is usually significantly reduced. Therefore, pain in people suffering from this disease is mainly caused not by increased sensitivity of the teeth, but by injury to the gums from the sharp edges of damaged crowns.
How is diagnostics carried out?
Diagnosis of cementoma is possible only in a dental clinic. It is often possible to identify it after the patient contacts him, but for a different purpose, for example, for the treatment of caries or standard prevention. If, during a visual examination, a specialist develops appropriate suspicions or characteristic symptoms occur, the patient will be sent for an x-ray.
Histology helps to conduct a thorough study of the structure and structure of deformed tissues. The sample is placed on a microslide (slide for the object being studied), after which it is carefully examined in a multiply enlarged format, that is, under a microscope. This allows you to accurately determine the specific form of the tumor and make a final diagnosis. Histological examination also makes it possible to differentiate cementoma from other types of tumors, including malignant ones.
Histological examination is also performed for diagnosis
What treatment is required
The choice of direction of therapy directly depends on the form of the pathology. Thus, benign cementoblastoma and cementing fibroma are treated by surgical removal, including partial excision of the affected area of bone tissue. In this case, the causative tooth has to be removed.
In the case of periapical cement dysplasia, the growth of the tumor does not occur as intensively. The surgical method is practically not used, since such an intervention can create a threat of tissue necrosis. If there are no symptoms, therapy is based on regular observation by a specialist, enhanced oral hygiene, and careful monitoring of the periapical lesion area.
In the presence of pronounced symptoms and the development of the inflammatory process, rejection of the sclerotic masses occurs. This process may take an impressive period of time, but upon completion, complete recovery will be achieved. To speed it up, a specialist can create a small depression in the area of the affected bone.
Conservative methods of therapy are also used to treat gigantoform cementoma. The doctor will definitely prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs and put the patient on regular monitoring.
Possible complications
Complications most often arise when cementoma is localized in the anterior part of the upper jaw. As the tumor grows, there is a serious risk of its spreading to the nasal sinuses, which can subsequently lead to the development of nasopharyngeal pathologies.
Another possible complication of cementoma may be a breakthrough of the oral mucosa with the tumor coming to the surface. Perforation leads to the appearance of a hole in the bone tissue and mucous membrane. As a result, the risk of infection of the affected tissues, the development of inflammation and the spread of pathological processes to adjacent areas of the jaw increases.
Preventive measures
To minimize the risk of developing cementoma, it is important to ensure proper and complete oral hygiene, and also, if possible, eliminate the risks of accidental injury to the teeth and jawbone. Experts provide a number of specific recommendations in this regard:
- brush your teeth twice a day, rinse your mouth after every meal, use floss and preventative rinses, visit a dental hygienist twice a year to remove plaque and dental deposits,
- promptly seek dental care for injuries to the teeth and mucous membranes,
- do not postpone a visit to the doctor if there is a traumatic factor in the oral cavity, for example, an incorrectly installed filling, crown or prosthesis.
It is worth having professional teeth cleaning twice a year.
Late detection of cementoma can lead to disruption of the integrity of bone tissue, spread of the tumor to healthy parts of the jaw, and the appearance of perforation in the jaw bone and mucous membrane. To avoid all these complications, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of your teeth and oral cavity, as well as regularly visit the dentist’s office for preventive maintenance - at least twice a year.
- Trigolos N.N., Makedonova Yu.A., Firsova I.V., Starikova I.V., Piterskaya N.V., Marymova E.B., Poroyskaya A.V. Cement-bone dysplasia of the jaws, 2015.
Prevention
Key methods for preventing cementoma are aimed at preventing damage to the teeth and jaw, as well as regular oral care.
Experts recommend following these tips:
- brush your teeth at least twice a day and rinse them after each meal;
- in addition to a toothbrush, use floss or irrigator;
- promptly seek help in case of mechanical injury to the teeth, mucous membrane or temporomandibular joint;
- do not delay treatment of dental diseases;
- undergo regular dental examinations and oral hygiene.