Antibiotics for periodontitis often prescribed for acute inflammatory processes that occur in periodontal tissues. The drugs effectively eliminate inflammation and destroy pathogenic microflora. However, they may have contraindications and side effects.
Important! Only a doctor should prescribe antibiotics; self-medication leads to serious complications and bacterial resistance to drug components in the future.
Prices for periodontitis treatment
| Name | Price |
| Treatment of a single-canal tooth | from 10,000 rub. |
| Treatment of a two-channel tooth | from 14,000 rub. |
| Treatment of a three-channel tooth | from 18,000 rub. |
| Tooth restoration after treatment | from 4,600 rub. |
| Aesthetic tooth restoration | from 6,800 rub. |
| In-canal whitening | from 2,900 rub. |
Contraindications and side effects of antibiotics for periodontitis
Depending on the type of drug, contraindications for use are as follows:
- pregnancy and lactation;
- liver and kidney failure;
- epilepsy, lymphocytic leukemia, leukopenia;
- intolerance to the components of the drug;
- severe heart pathologies;
- age (certain products should not be taken by children or elderly people);
- porphyrin disease;
- Infectious mononucleosis.
Contraindications and side effects
Any antibiotics for periodontitis should be taken with caution by those who have problems with the gastrointestinal tract, as well as when using anticoagulants at the same time.
During the course you should not drink alcohol, since many drugs that are incompatible with alcohol can cause a severe reaction. Important !
Before treating periodontitis with antimicrobial agents, the patient must inform the doctor about his state of health. In general, antibacterial medications for periodontitis are well tolerated. However, you should stop using it and consult a doctor if the following signs appear:
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea;
- dizziness or headache;
- soreness in the stomach;
- itching and skin rashes like urticaria;
- overexcitation, insomnia, anxiety;
- swelling of the face, lips, eyelids;
- shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat.
In severe cases, convulsions, loss of consciousness or fainting, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and hematuria may occur. You also need to warn the doctor if the patient is taking other medications, since not all are compatible with antibiotics.
If antibiotic therapy is prescribed, the medications must be taken carefully, at the same time, in the strict dosage prescribed by the doctor. It is prohibited to independently increase or decrease the dose or replace the drug - this leads to resistance of microorganisms to the drug. You should also carefully observe oral hygiene, and after treatment, undergo a preventive examination by a dentist.
0
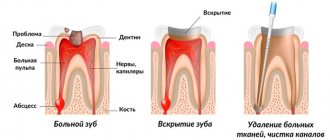
What is periodontitis
Periodontitis is an inflammation of the tissues surrounding the root of the tooth. Factors that contribute to the occurrence of periodontitis:
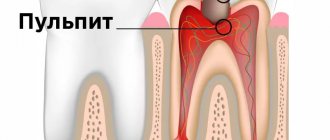
- Untreated caries, pulpitis;
- Chronic foci of infection in the oral cavity;
- Periodontal diseases;
- Chronic dental injuries.
Spicy
For acute periodontitis, a distinctive feature is the patient’s precise indication of the diseased tooth, as a feeling of “an overgrown tooth” appears, and only after a while unexpressed pain occurs. If the patient does not consult a doctor in a timely manner, general intoxication of the body, swelling of the gums and face may occur.
Chronic
The chronic process differs from the acute process in the absence of pronounced pain, and diagnosing such a tooth is sometimes only possible at an appointment with a dentist and during an X-ray examination.
Granulating
This type is determined only by x-ray examination, which determines the growth of granulation tissue in the area of the root apex.
When is antibiotic therapy necessary?
With periodontitis, the tooth root and surrounding structures become inflamed. Most often it develops due to caries, pulpitis, and jaw injuries. The causative agents are streptococci, staphylococci, actinomycetes, lactobacilli, and yeast-like fungi. From the primary source of destruction, pathogenic microflora enters the root canal, from where it spreads to surrounding tissues and provokes inflammation. Therefore, indications for the use of antibiotics for periodontitis are a combination of the following factors:
- increase in body temperature to 38 degrees and above;
- the appearance of pus from the affected tooth;
- deterioration of health, weakness, drowsiness;
- swelling and redness of the gums;
- progression of epithelial tissue degeneration;
- abscess formation;
- treatment after surgery.
are especially effective for periodontitis if it is impossible to eliminate bacteria through professional teeth cleaning or removal of deposits in hard-to-reach places.
Important! For periodontitis, local and systemic agents are used.
How to treat periodontitis
Stages
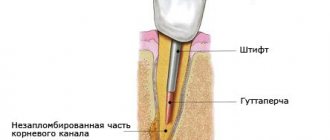
- On the first visit, it is necessary to take an x-ray to assess the stage of the disease and determine the form of periodontitis. Next comes the treatment of the tooth, providing access to the canals, actually working with the canals, and administering medications. Treatment of the canal in this disease is carried out repeatedly, at certain time intervals and under X-ray control. Permanent canal filling is carried out only if the doctor is completely confident that there are no pathological processes or complaints from the patient in the given tooth. Sometimes the terms last up to six months,
- During subsequent visits, permanent filling of the canals is performed.
- The final stage of periodontitis treatment is restoration of the anatomical shape of the tooth.
Each stage of periodontitis treatment is accompanied by diagnostic images! The number of visits depends on the anatomical structure of the tooth and the general condition of the body as a whole. And it is important to carry out an x-ray examination after 8-10 months to ensure the restoration of bone tissue.
Methods
- The therapeutic method consists of treating the canals using medicinal and mechanical methods. The main goal of this treatment is to preserve the tooth for many years. The success of such treatment largely depends on the patient’s timely visit to the doctor, the state of the immune system, and the availability of a qualified specialist.
- The surgical method is used when therapeutic treatment does not bring positive results. The most radical method is tooth extraction, but there are also a number of tooth-preserving procedures, which include resection of the apex of the tooth root, hismisection, cystotomy, and cystectomy.
What antibiotics are used?
What antibiotics are used?
To suppress pathogenic microorganisms, the following drugs are prescribed:
- "Lincomycin", "Doxycycline";
- "Tetracycline", "Amoxiclav";
- "Ciprofloxacin", "Azithromycin";
- "Erythromycin", "Metronidazole";
- "Ofloxacin", "Cifrofloxan".
Also, antiseptics “Biseptol”, “Chlorhexidine”, “Biomycin”, “Povidone-iodine”, sodium hypochloride, penicillin group drugs “Clavulanate”, “Sulbactam” have a negative effect on bacteria.
During the treatment process, local antibacterial agents are used, which are placed into the affected cavity after cleaning. Often, along with antibiotics, the doctor prescribes antihistamines to reduce reactions from the immune system. The course of administration is 5-7 days, it cannot be interrupted, otherwise the drugs will stop working. Important! Tetracycline group drugs do not enter the bloodstream, so they can only have a local effect on microorganisms.
Reasons for appearance
As already mentioned, the cause of the development of periodontitis in primary and permanent teeth is periodontal infection. The routes of entry of the pathogen can be:
- intradental - the disease is a complication of pulpitis that is not cured in time;
- extradental - the disease spread from infected surrounding tissues in diseases such as sinusitis, osteomyelitis.
Sometimes periodontitis occurs after incorrect treatment of pulpitis. In this case, it is provoked by chemicals (phenol, farmalin, arsenic paste) that fall into the periodontium.
Treatment methods
Dental periodontitis can be treated conservatively or surgically. A combination of techniques is possible: physiotherapy, medications, surgery.
The therapy consists of mechanical and antiseptic treatment of the root canal, application of medicinal paste and subsequent filling. If the disease occurs under the crown, it is removed. A permanent filling is placed at least after 2 - 4 weeks if the inflammatory processes are successfully relieved. During this period, the doctor prescribes antibiotics and rinses to the patient. It is possible to carry out UHF therapy, laser therapy, magnetic therapy, and paraffin applications.
During surgery, the following is performed:
- resection of the apex (part of the root);
- cystomy (remove the cyst);
- coronoradicular separation (multi-root is dissected);
- cystectomy (the affected periodontium and root apex are cut out);
- complete removal of the infected tooth.
The patient is prescribed medications and physical therapy.
How to get rid of toothache?
If the pain after dental treatment is not pathological, effective traditional methods will help eliminate it. Recipes for the 3 most popular folk remedies will be described below.
It is important to know!
Before using one or another folk remedy to treat toothache, it is recommended to find out if you are allergic to the components that make up it.
Recipe No. 1 Garlic compress
The wrist opposite the side where the causative tooth is located should be rubbed with half a clove of garlic cut in half. After this, another clove needs to be crushed and applied to the surface of the wrist. To avoid burns, before applying garlic pulp, it is recommended to wrap the surface of the skin with gauze folded in half. Next you need to bandage your wrist. The tighter the compress is applied, the more effective its therapeutic effect will be. You need to keep the bandage on for at least an hour.
Recipe No. 2 Herbal decoction
St. John's wort flowers, chamomile, elderberry and strawberry leaves (10 g of each component) must be poured with water (450 ml) and brought to a boil. Boil for 40 minutes. Then strain the broth and rinse your mouth with it. The more often the procedures are performed, the faster the toothache will disappear.
Quality of service in our clinic
FamilySmile has modern equipment and safe drugs for high-quality treatment of periodontitis. Our staff includes dentists and therapists with extensive experience working in Moscow clinics. They do everything possible to save the tooth.
We carry out cleaning and filling of canals under a microscope. It allows you to see the slightest changes and perform dental procedures with pinpoint precision. If a patient suffers from dental phobia, experiences stress when visiting the clinic, or simply has a strong fear of treatment or removal, we provide general anesthesia or sedation.
What are the risks?
Antibiotics are potent medications, so their use is justified only as prescribed by a doctor. Most of these drugs have many contraindications, and their use is always associated with the likelihood of side effects. To reduce all risks, you must strictly follow the instructions of your doctor. In some cases, skin rashes, disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system, and acute allergic reactions are possible.
If the patient knows that he has hypersensitivity to certain drugs, he must inform the doctor about this. If adverse reactions develop while taking antibiotics, you should contact your dentist to prescribe another remedy.
- Tsarev, V.N. Transcanal use of new generation antibiotics in the treatment of chronic periodontitis, and assessment of their effectiveness using gene diagnostics, 2004.
Stages and forms of the disease
Periodontitis is divided according to the general principle into chronic and acute. Chronic cannot be completely cured. It is only possible to eliminate local inflammation and stop further exacerbation of the disease. Chronic periodontitis is asymptomatic and does not bother the carrier, but in case of exacerbation of the disease, symptoms begin to appear. In a calm state, a small fistula may appear on the gum from time to time, and slight discomfort may occur when chewing food or mechanical impact on the area of inflammation. If left untreated for a long time, the risk of tooth loss is high.
Treatment of acute periodontitis has an end result. But even after complete recovery, control over the oral cavity is necessary to avoid re-inflammation. In acute periodontitis, all of the listed symptoms are characteristic, only 2-3 of them may appear, and this is already a signal to visit the dentist. Purulent periodontitis is especially pronounced. In this case, the pain is acute, body temperature rises, and gumboil formation is possible.
Forms of periodontitis:
- Fibrous. In this case, periodontal tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue. It is often asymptomatic and can be detected by external signs: changes in enamel color, bad breath, pulp death.
- Granulating. It leaks quickly and destroys bone tissue. It is characterized by painful sensations when pressing on the gums or chewing food. A pulling or bursting pain may be observed without mechanical impact on the tooth.
- Granulomatous. This is a dangerous type of disease because it is asymptomatic, while destructive processes take place inside the periodontium, which are accompanied by the appearance of cysts and granulomas. If left untreated, the tooth may simply fall out. An infection locked in a granuloma or cyst can “explode” under the influence of the slightest irritant: provoke inflammation (for example, sepsis).
- Apical. The simplest form, easy to treat. It occurs as a result of untreated pulpitis and is localized in one place near the root.
Characteristic symptoms
- discomfort in the area of the causative tooth, a feeling that it has become longer,
- pain when pressing, when eating,
- enlarged lymph nodes,
- general weakness, headache, fever,
- swelling of the tissues surrounding the diseased tooth,
- redness of the gums in the causative area,
- discharge of purulent exudate,
- tooth mobility.
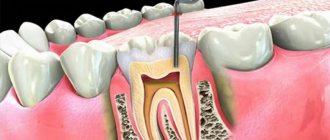
The photo shows periodontitis