Papilloma in this place is formed from cells of the mucous membrane, most often it is observed in women. It is not difficult to detect growths; it is much more difficult to get rid of them.
Description of pointed papilloma on the tongue
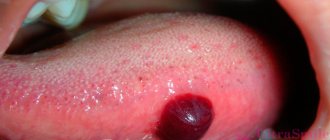
Papillomas on the tongue are a common form of human papillomavirus, which is presented in the form of a bumpy tumor or red papilla that is formed from epithelial cells of the oral cavity. They are small in size (up to two centimeters). Typically, formations appear in those parts of the epithelium that are most susceptible to injury: under the tongue and on the tongue, on its tip or side, back, at the root.
Papilloma on the tongue
Note! Particular attention should be paid to the occurrence of papillomas on the leaf papillae of the tongue, as they can develop into an oncological neoplasm, which often causes death.
Papilloma on the tongue
The growth begins to grow, as the connective tissue is penetrated by a large number of capillaries, nerves and lymphatic vessels. Over time, the papilloma (condyloma) turns into an ulcer, which bleeds and causes pain.
Typically, a growth on the root of the tongue is diagnosed accidentally; a person may not even be aware of its presence. But most often, the pathology clearly manifests symptoms, bringing not only physical, but also aesthetic discomfort to its owner. If processes appear under the tongue, they will cause discomfort to the person, as they will often be injured when eating.
Symptoms
A benign tumor in humans often does not manifest itself at all, so in most cases it is not detected on time. Subsequently, there is a feeling that there is a foreign body on the tongue.
Some formations are painful, especially if they are pressed or disturbed. Due to the large size of the tumor, there are difficulties while talking and eating. Sometimes redness and swelling occur, which cannot be removed without special therapy.
If over time the growth changes its structure, shade or growth rate, this may be a sign of degeneration into a malignant tumor.
Types of papillomas on the tongue
In medicine, the following types of neoplasms are distinguished:
- Reactive papillomatosis, which experiences constant viral, mechanical or thermal effects;
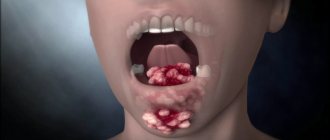
- Neoplatic papillomatosis is rare. It represents the presence on the tongue of a large number of formations in the form of nodes or papules, which can be single or multiple.
It is also customary to distinguish the following types of papillomas depending on their external structure:
- Flat formations are characterized by an elevation above the epithelium of more than two millimeters, they have a wide structure (up to one and a half centimeters), light color and are formed one at a time. Usually the growths are localized on the side of the tongue or on its back. In a child, this pathology is presented in the form of epithelial hyperplasia, in which the tissues of the mucous membrane of the tongue begin to grow greatly;
Flat papillomas on the tongue - Pointed growths have the appearance of papillae with a sharp, light-colored end. They are usually localized under the tongue, so they are often injured. Papillomas tend to form groups, gradually growing and increasing in size, they create inconvenience in eating while making a conversation;
Pointed growths
- Thread-like processes protrude above the surface of the epithelium up to four millimeters, they are not wide, have a darker color and are formed in groups of several papillomas.
Filiform papillomas
Kinds
There are 2 types of growths :
- Reactive - appear due to constant mechanical damage to the tongue, burns.
- Neoplastic – a consequence of disorders in the body. Most often, many such neoplasms appear in various parts of the oral cavity.
By shape
Growths on the tongue can have different shapes :
- Most often, neoplasms have clear boundaries and are colored white, pink, or red.
- The pointed formations are pink, have a stalk, cause significant discomfort, are often injured, grow quickly and occupy large areas of the mucosa.
- Flat growths have a rounded shape and resemble plaques in appearance. They grow slowly, are damaged less often, and practically do not bother.
- With stomatitis, reactions to medications, microtraumas, the growths look like pimples and blisters.
By location on the tongue
Growths can appear on any part of the tongue mucosa. The main places of localization are the tip, lateral surfaces, and root. Most often they occur on the side; less often, tumors form on the hard palate and lower surface.
Reasons for the development of lingual papillomas
The reasons for the appearance of growths on the tongue can be different. The main factors in the development of pathology are human papillomavirus and reduced immunity, which activates it in the body. The appearance of formations in the mouth is caused by human infection with such strains of the virus as 1,2,3, as well as 16 and 18.
Human infection occurs in several ways:
- Contact with a carrier of infection;
- Use of contaminated household items;
- Transmission of HPV from mother to child during labor.
Once in the body of a healthy person, the virus is in a passive state; if the immune system is impaired or there is a lack of vitamins, minerals and other nutrients, it is activated and begins to actively multiply, causing the appearance of growths on the person’s tongue.
Flat papillomas on a child’s tongue
Note! In childhood, papillomas in the mouth often appear due to poor oral hygiene. They are often located on the tongue, near the frenulum.
The following factors contribute to a decrease in immunity and activation of the virus:
Sores in the mouth
Prolonged stress;- Failure to comply with oral hygiene rules;
- Abuse of alcohol and nicotine;
- Presence of chronic diseases;
- Old age or childhood;
- Presence of wounds, scratches in the mouth.
If you have good, stable immunity, neoplasms on the tongue do not arise or go away on their own.
Mechanism of occurrence
Growths on the tongue are formed from epithelium, fat cells, muscle fibers, nerves, blood and lymphatic vessels.
The tumor can arise against the background of embryogenesis disorders - the rudiments of foreign tissue structures get onto the tongue. Under favorable conditions, HPV begins to actively multiply and penetrates the basal cells of the epithelium. The DNA of the virus invades the DNA of cells, changes their functions, causes them to actively and chaotically divide and multiply.
Doctor about condylomas in the mouth:
Red bumps
Red bumps on the tip, sides or back of the tongue may have specific causes or factors that also cause this redness. For example, ulcers and Kawasaki disease are responsible for red bumps on the surface of the tongue.
Other causes of redness include inflammatory infections such as colds and flu. Taste bud irritation and repetitive trauma to the tongue are other possible triggers.
Have you previously been diagnosed with allergies or herpes? If you constantly get painful red pimples or large bumps at the root of the tongue, contact an ENT specialist or dentist as soon as possible.
Diagnostic methods
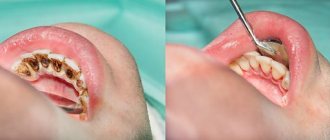
Knowing which doctor to contact, the patient is recommended to undergo diagnostics in order to avoid complications of the pathology. Polyp growths on the front of the tongue are immediately visible; they interfere with eating and speaking, bleed, and are easy to injure. If there are growths on the lower part of the tongue, the doctor detects it during a visual examination when he asks the person to show his tongue.
A doctor, having noticed a neoplasm, which can also be localized on the root, studies its structure, that is, establishes the type of pathology. The structure of papilloma on the tongue is fine-grained and rough.
In children, the formations occupy large areas; they can be covered with a white coating, so identifying the disease in childhood is much easier. Having seen such manifestations, the doctor usually determines immediately that it may be papilloma.
Elderly people often experience an oncological tumor that may resemble papilloma. The only difference between a cancerous tumor is its strong compaction.
PCR
Then the doctor can send for PCR to determine the type of pathogen, perform a biopsy, after which the biopsy is sent for histological examination.
The doctor also differentiates papilloma on the tongue from diseases such as cancer, cyst, ulcer (callus) formed due to stomatitis. After passing the examination, the patient is prescribed appropriate treatment.
Can growths be malignant?
At any moment, the growth can degenerate into a malignant tumor. Causes: constant damage to the tumor when talking or chewing food. Tongue cancer is classified as squamous cell; other forms, such as basal cell carcinoma or carcinoma, are rarely diagnosed.
Types of malignant tumors:
- An ulcer is a dense neoplasm that turns into an ulcer; it often hurts and bleeds. Located on the lower surface of the tongue.
- Infiltrative - a seal on the tip or back surface of the tongue, covered with a white coating. Constantly and severely painful.
- Papillary - a solid tumor on a stalk, formed on the lateral surfaces. Characterized by slow growth.
The prevalence of tongue cancer is 5 cases per 100 thousand population . The disease is easy to diagnose. But people often do not notice or ignore the symptoms of the pathology and go to the doctor with already advanced forms of the disease.
Formation of tongue cancer
Stages and symptoms of tongue cancer:
- Initial . Whitish spots appear on the tongue, most often on the lateral surfaces. These are papillary growths that look very similar to plaque. During examination, doctors often mistake formations for manifestations of glossitis and stomatitis. There is no pain or discomfort.
- Stage of clinical manifestations . The spots gradually become denser and transform into a tumor. Pain appears, which often radiates to the neck, ears, and temporal region; the tongue, neck, and face swell. When the formation becomes infected and suppurates, unpleasant odor from the mouth is disturbing. Problems arise with swallowing, articulation, and some areas of the tongue become numb. Metastases often spread to the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes.
- Launched . Necrosis and tissue decay begins, the tumor penetrates deep into the tongue.
- Terminal . Metastases extend beyond the oral cavity - lungs, liver, bones. Treatment at this stage is ineffective, and the prognosis is disappointing.
Specific diagnosis involves examining a smear of the fingerprint to identify cancer cells. A biopsy of the tumor is required. Additional research methods - ultrasound of the tongue, lower jaw and neck, x-ray or CT scan of the skull are prescribed to identify metastases.
Video about tongue cancer:
Treatment methods:
- Surgical . To radically remove a malignant tumor, partial resection or complete removal of the tongue is performed. When the tumor grows into the surrounding tissue, complete resection is performed, down to the bones of the lower jaw.
- Radiation therapy . The tumor is irradiated with X-rays. Radiotherapy is carried out before and after surgery.
- Polychemotherapy . A method of treating advanced forms of the disease, used in the presence of distant metastases. Drugs – Cisplatin, Methotrexate.
Surgery
Radio rays
Polychemotherapy
Attention! One of the main differences between malignant and benign neoplasms is that cancerous tumors are very dense. They rise somewhat above the mucous membrane and have an uneven surface.
Drug therapy
Interferon
Treatment of papillomas should be comprehensive, which includes drug and surgical therapy. Before prescribing medications, the doctor cleans the oral cavity, eliminating white plaque and pockets through which infection can enter the body.
For this purpose, the oral cavity is sanitized, and then treated with ointment, which has an antiviral effect. This could be, for example, “Bonaftone”, “Adimal” or “Megosin” ointment. It is necessary to treat the oral cavity from below and from above.
Then the doctor prescribes antiviral and immunostimulating drugs, for example, Interferon or Panavir, and vitamin complexes. Their action is aimed at increasing the body's defenses. The doctor selects medications based on the individual characteristics of the body, taking into account contraindications and side effects.
Preventive measures
The main methods of prevention are strengthening the immune system and maintaining good hygiene.
How to prevent growths from appearing:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- exercise regularly, spend more time outdoors;
- avoid stressful situations, learn to relax, master meditative techniques;
- wash your hands frequently and thoroughly, especially after going outside or visiting the toilet;
- Always use only your own towels and personal items;
- adjust your diet - give up unhealthy and heavy foods, eat more vegetables and fruits, fermented milk products, cereals, lean meat and fish;
- observe the drinking regime - you need to drink 1.5-2 liters of clean still water per day;
- promptly identify and treat dental diseases and pathologies of internal organs.
An effective method for preventing the formation of papillomas on the tongue is HPV vaccination. The Cervarix and Gardasil vaccines have contraindications and side effects, so they are not suitable for everyone. Vaccination does not completely protect against infection, but it does promote the production of antibodies that help the body fight infection more quickly.
It is advisable to vaccinate up to 26 years of age. The protective effect is designed for 8 years. Contraindications: pregnancy and breastfeeding, any gum problems.
Surgery
Surgical removal of papillomas is often performed.
To eliminate the pathology, the following surgical treatment methods can be used:
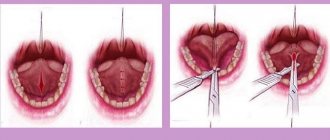
- Surgery. In this case, the surgeon can use one of the methods of excision of papillomas, such as a scalpel, cyberknife, special scissors, loops or conchotome;
- Laser therapy is used very often, as it does not cause pain or discomfort in the patient;
- Electrocoagulation, in which the growths are cauterized;
- Removing bubbles using radio waves.
In each specific case, the doctor prescribes one or another method of surgical treatment. After removal of papillomas, medications are also prescribed to increase immunity and strengthen the body.
Note! If there are a large number of papillomas in the oral cavity, relapses of the disease often occur, so the physician must provide for further possible treatment of the person.
Children usually do not undergo surgical removal of growths, but if absolutely necessary, the doctor should use anesthesia.
Kipferon
If growths are detected in a pregnant woman, she may be prescribed drugs such as Viferon or Kipferon. The question of their removal is considered only by an experienced doctor, since there is a risk of complications. Typically, treatment is prescribed that is aimed at combating HPV.
Video: laser removal of papillomas on the tongue
How to get rid of growths?
Neoplasms on the tongue appear rarely. It does not matter the diet, the temperature of the food consumed or bad habits.
Let's look at methods for removing growths:
- Antibacterial agents help relieve inflammation and are used when rinsing and treating growths. Antiseptics and immunocorrectors are also used.
- The use of antibiotics to suppress and destroy the virus.
- Comprehensive measures involve the use of medications to overcome the effect of the virus after surgical removal. At the last stage, a vitamin complex is prescribed to restore the body’s protective functions.
The operation to remove tumors is simple. Surgeons excise the wart and cauterize the wound. Removal of tumors using radio waves is becoming increasingly popular due to its low incidence of injury, absence of pain, and harmlessness to children.
ethnoscience
Treatment with folk remedies is possible only after consultation with your doctor. Typically, such treatment acts as an additional method, but it is not recommended to use it as an independent method of therapy, since complications such as oncology may develop.
Together with medications, the patient can use herbal infusions and decoctions to increase the body's defenses. Infusions can be prepared from rose hips, lemon balm, chamomile, plantain and other herbs.
You can drink 100 milliliters of red potato juice every day.
Celandine has a good effect. Its juice is applied to the affected areas if the growths are small. The procedure is repeated three times a day, the full course of treatment is about one month.
Removal
The method by which the papilloma will be removed must be chosen by the treating specialist. It depends on the location and characteristics of the body. There are the following ways to eliminate tumors:
- Surgical excision using a surgical scalpel. After the procedure, “cauterization” is performed. A similar technique is used in the presence of single growths or when they are inaccessible and it is impossible to use other methods.
- Laser elimination. The most effective, painless method with no adverse effects. The disadvantage is the high cost of the procedure.
- Electrocoagulation. The method involves cauterizing the growth with an electric current. The disadvantages include painful manipulation and a long rehabilitation period.
- Radio wave surgery. The technique is similar to the previous one, only instead of current, high-frequency radio waves act on the papilloma. The pain is insignificant, the number of adverse effects is minimal and the rehabilitation period is short.
- Cryodestruction. The most unpopular surgical method for eliminating papilloma on the tongue. The tumor is removed by influencing it with cold. The wart is frozen to liquid nitrogen temperature. The growth will be frozen and die within a week.
If the technique involves excision of the wart, then the biomaterial is sent for histological diagnosis in order to analyze the structure of the growth.
Prognosis and prevention
Usually, the prognosis of the disease is good, provided that you contact a medical facility in a timely manner and carry out effective treatment in compliance with all doctor’s instructions.
During therapy, patients are advised to eat properly and lead a healthy lifestyle. In advanced cases, a cancerous tumor may develop, so do not delay your visit to the doctor.
For the purpose of prevention, doctors recommend monitoring oral hygiene, strengthening the immune system, leading a healthy lifestyle, avoiding promiscuity, and promptly treating concomitant pathologies and STDs.
Diagnosis of benign tumors of the tongue
Most often, benign tumors of the tongue are diagnosed already at a stage of significant size, since before this the course of the disease is asymptomatic. Small tumors are diagnosed by a doctor during a routine examination of the oral cavity, as well as after injuries or injuries. The tumor is determined through a visual examination by a specialist and palpation of the formation, but a final diagnosis is possible only after a histological examination of the tissue - this allows us to determine the type of tumor. Histology is carried out not only with the help of a biopsy - taking a part of the tissue, but also after complete removal of the tumor without fail.