Endodontic treatment of tooth roots requires all the knowledge and skill of the dentist. After all, if even the slightest mistake is made, all subsequent work on filling and prosthetics will be done in vain. Our clinic's endodontists have extensive experience in successful root canal treatment and are proud of the good results of their work.
Reasons for performing root canal treatment are:
- deep complicated caries;
- acute and chronic pulpitis;
- periodontitis, etc.
The goal of treatment is to clean the dental ducts and put a filling so that infection does not penetrate into them.
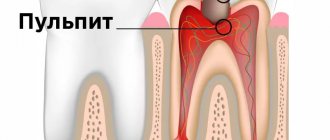
What is pulp and does it need to be removed?
The pulp, or dental nerve, is the connective tissue that fills the tooth cavity. It consists of fibers, nerve endings, lymphatic and blood vessels. The dental nerve supplies bone tissue with nutrients, is responsible for the proper development of the tooth and protects it from infection.
If the pulp is damaged, an inflammatory process begins, and the person experiences severe pain. After removal of the nerve, the tooth becomes “dead,” but with professional manipulation by a doctor, it fully retains its functions.
Stages of dental prosthetics
Dental prosthetics consists of several stages.
- Preparation. Includes consultation with a doctor, diagnosis, and treatment of dental diseases.
- Manufacturing of orthopedic structures in a dental laboratory (Stompraktika has its own laboratory equipped with the latest technology).
- Trying on the finished design and adjusting it (if necessary).
When is dental nerve removal required?
Depulpation is carried out in cases of severe damage to tooth tissue, advanced forms of caries, pulpitis, or benign formations near the root system. In addition, pulp removal is required during prosthetics and in case of medical error during root canal treatment.
Symptoms that you should contact your dentist for:
- constant aching or throbbing pain that does not go away even after taking painkillers;
- increased tooth sensitivity - a reaction to cold or heat, as well as sour, salty, sweet foods;
- pain while chewing food.
Such symptoms indicate the development of some pathology, so if they appear, you should immediately consult a dentist. The initial stages of dental diseases are treated quickly, and sometimes it is even possible to do without depulpation. The main condition is timely diagnosis and adoption of therapeutic measures.
Reference! Many patients are afraid to undergo depulpation, thinking that after it the tooth will begin to quickly decay. In fact, with proper care, it retains its functions for several years, then it is advisable to cover it with a crown. In some cases, pulp removal is the only sure way to preserve the tooth and avoid severe inflammatory processes.
How many visits does it take to treat pulpitis?
People who are faced with painful toothaches are often interested in information about how many visits to the dentist are needed to treat dental pulpitis. It all depends on which particular dental unit the inflammation develops in. Teeth have a different number of root canals, in the front ones there are 1, and in the molars there are 2, 3 or 4, each of which needs to be cleaned of affected tissue, inflammation removed, and then sealed.
How long does pulp removal take?
On average, it takes about 40-50 minutes for pain relief, nerve removal, and root canal treatment. If the doctor administers high-quality anesthesia, it will take effect almost immediately, and the patient will not feel pain throughout the entire process. If the effect of anesthesia weakens during depulpation, an additional injection is given.
Reference! Before administering an injection with anesthesia, the doctor treats the soft tissue with a special freezing agent. That is, the patient will not experience pain either when inserting a needle into the tissue or during the process of removing the dental nerve.
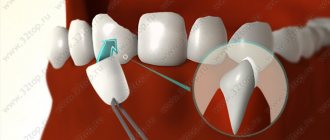
How is the treatment carried out?
The doctor uses special tools to drill a hole in the head of the unit being restored. Through it, it removes diseased pulp and dentin, and also disinfects the outlet space, and then seals it.
There are two main processing methods:
- apical-coronal, i.e. the doctor processes the dental canal from top to bottom, from the head to the mouth of the root;
- coronal-apical, i.e. on the contrary - from bottom to top.
The key to a high-quality procedure is accurate diagnosis of the roots, which is ensured by radiography. The picture is taken before, during and after the procedure. This is necessary in order to assess the length and shape of the dental outlet as accurately as possible. After all, these indicators are individual for each person.
During the procedure, antimicrobial agents are used that have the following effects:
- destroy harmful microflora;
- improve the condition of the preserved tissues of the unit;
- do not cause allergic reactions.
Our clinic actively uses laser technologies, which give excellent results.
They carefully remove dead remains of pulp and dentin without damaging living tissue.
Leave your phone number. The clinic administrator will call you back.
By leaving a request on the site, you consent to the processing of personal data
Make an appointment
Initial consultation
400 rubles
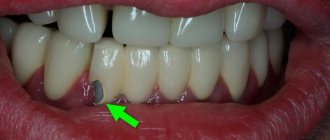
The image shows poorly treated root canals in the lower sixth unit.
BEFORE AFTER
BEFORE AFTER
Stages of depulpation
Modern techniques make it possible to remove the dental nerve in just one visit to the dental office. The process of depulpation begins in the same way as in the treatment of caries.
- Anesthesia. The doctor treats the soft tissue with a freezing agent, then injects an anesthetic and waits about 15 minutes.
- Preparation for pulp removal. The affected tissue is removed to provide access to the dental nerve.
- Depulpation. To remove the pulp, special instruments are used to quickly and painlessly remove it from the root canal and crown part of the tooth.
- Filling. Safe composites, dental cement and other materials are used for filling. In case of difficult removal, the doctor can place a temporary filling, and at a follow-up appointment, if there are no complications, he will install a permanent one.
Removal can be complete or partial. The second method is used in case of an inflammatory process that has affected only the coronal part of the dental nerve. In this case, after anesthesia and removal of dead tissue, only the affected coronal pulp is cut off, while the root pulp remains completely.
Most often, this technique is used in the treatment of teeth in childhood, when there is a need to preserve the root part, since it is the part that is responsible for the correct formation of the root system.
Duration of dental work
It goes without saying that the time range for performing a particular operation varies significantly depending on the complexity of the initial condition. A small filling measuring 1x1x1 mm is, of course, faster to place than to restore a completely destroyed tooth. Much also depends on the experience and manual skills of the doctor. Some doctors work at cosmic speed (up to 3 times faster than their slower colleagues), but there are only a few such unique specialists in the entire country. The third main link that significantly influences the pace of treatment is the patient’s mood and behavior. Someone obediently opens his mouth and closes it only after the entire event is completed. And some people need rest every 5 minutes, a break with auto-training, they definitely need to ask a lot of questions right during the treatment process, go to the toilet several times, make a phone call, etc. But still, the average time required for a specific operation can be predicted. Here is a table for the most common procedures in dentistry. Below are comments on some columns.
| Type of procedure | Number of visits | Average reception time | Main interval | Recommended appointment time | Total treatment period |
| Dentist consultation | 1-3 | 15 minutes | 5-60 min | 30 min | |
| Consultation with a dentist-therapist | 1-2 | 10 min | 5-15 min | 15 minutes | |
| Consultation with a dental surgeon | 1-2 | 15 minutes | 5-30 min | 15 minutes | |
| Consultation with an orthopedic dentist | 1-3 | 20 minutes | 5-60 min | 30 min | |
| Consultation with an orthopedic dentist with drawing up a treatment plan | 1-3 | 30 min | 10-60 min | 1 hour | |
| Periodontist consultation | 1-2 | 20 minutes | 5-60 min | 30 min | |
| Consultation with a periodontist with filling out a periodontal chart | 1-2 | 1 hour | 30-90 min | 1 hour | |
| Orthodontist consultation | 1-3 | 15 minutes | 5-30 min | 15 minutes | |
| Consultation with a pediatric dentist | 1 | 15 minutes | 10-60 min | 15 minutes | |
| Treatment of caries | 1-2 | 30 min | 10-60 min | 1 hour | 1-7 days |
| Placing a filling | 1 | 15 minutes | 5-30 min | 1 hour | |
| Artistic tooth restoration | 1 | 40 min | 20-60 min | 1 hour | |
| Treatment of pulpitis | 1-4 | 1,5 hour | 0.5-2 hours | 1,5 hour | 1-10 days |
| Treatment of periodontitis | 1-4 | 1,5 hour | 0.5-2 hours | 1,5 hour | 1-3 weeks |
| Unsealing channels | 1-2 | 1,5 hour | 0.5-3 hours | 2 hours | 1-7 days |
| Filling a wedge-shaped defect | 1 | 30 min | 15-60 min | 1 hour | |
| Treatment of caries in children | 1 | 15 minutes | 10-60 min | 1 hour | |
| Treatment of pulpitis in children | 1-3 | 30 min | 20-60 min | 1 hour | 1-10 days |
| Control inspection | 1 | 20 minutes | 5-40 min | 30 min | |
| Professional oral hygiene | 1 | 40 min | 20-90 min | 1 hour | |
| In-office bleaching | 1 | 1 hour | 20-90 min | 1,5 hour | |
| Home whitening | 2(1) | 15 minutes | 10-20 min | 30 min | 2-6 weeks |
| In-canal whitening | 2-4 | 15 minutes | 5-30 min | 30 min | 1-2 weeks |
| Making a crown | 2-3 | 40 min | 30-90 min | 1 hour | 1-3 weeks |
| Making a tab | 2 | 40 min | 30-90 min | 1 hour | 3-10 days |
| Making a veneer | 2-4 | 40 min | 20-90 min | 1 hour | 1-4 weeks |
| Making a bridge | 2-5 | 2 hours | 1-3 hours | 2 hours | 2-4 weeks |
| Making a crown for an implant | 2-3 | 20 minutes | 15-60 min | 1 hour | 1-3 weeks |
| Manufacturing of crowns and CEREC inlays | 1(2) | 2 hours | 2 hours | 1+1 hour | 1 day |
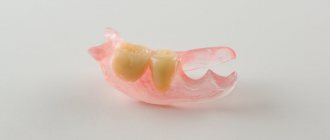
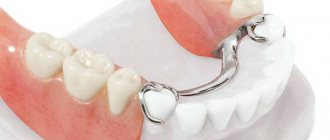
| Manufacturing of a removable partial denture | 2-5 | 20 minutes | 10-30 min | 30 min | 2-3 weeks |
| Making a complete removable denture | 3-6 | 20 minutes | 5-30 min | 30 min | 2-4 weeks |
| Removable denture repair | 2 | 10 min | 0-15 min | 15 minutes | 1-3 days |
| Repair of crowns, bridges | 0-1 | 15 minutes | 0-60 min | 15 minutes | |
| Cementing a fallen crown | 0-1 | 10 min | 0-20 min | 30 min | |
| Removal of a mobile, baby tooth | 1 | 5 minutes | 1-15 min | 15 minutes | |
| Removal of a tooth | 1 | 15 minutes | 5-40 min | 1 hour | |
| Wisdom tooth removal | 1 | 20 minutes | 1-60 min | 1 hour | |
| Removal of an unerupted (impacted) tooth | 1 | 30 min | 15-90 min | 1,5 hour | |
| Closed curettage | 1 | 10 min | 5-15 min | 15 minutes | |
| Open curettage | 1 | 20 minutes | 10-30 min | 30 min | |
| Closing gum recession | 1 | 40 min | 20-60 min | 1 hour | |
| Guided tissue regeneration | 1 | 40 min | 20-60 min | 1 hour | |
| Implant installation | 1 | 30 min | 20-60 min | 1 hour | |
| Single-stage implantation | 1 | 40 min | 30-90 min | 1,5 hour | |
| Augmentation (building up) of bone tissue | 1 | 40 min | 20-90 min | 1,5 hour | |
| Closed sinus lift | 1 | 15 minutes | 5-20 min | 1 hour | |
| Open sinus lift | 1 | 40 min | 15-60 min | 1,5 hour | |
| Orthodontic treatment with braces | 5-50 | 1.5 years | 0.5-3 years | 15 minutes | 1.5-2 years |
| Orthodontic treatment with lingual braces | 5-50 | 2 years | 0.5-3.5 years | 15 minutes | 1.5-2.5 years |
| Orthodontic treatment with aligners (Invisalign, etc.) | 5-15 | 9 months | 0.5-1.5 years | 15 minutes | 0.5-1 year |
Comments:
1. This refers to the time frame for one procedure: treatment of one tooth, placement of one filling, removal of one tooth, and so on. Performing two or more similar operations in one visit (especially with adjacent teeth) usually reduces the time required for each of them. So, if a doctor places a filling on one tooth in 50 minutes, he can install two fillings of the same size not in 100 minutes, but in 80. Three in 100 minutes, and so on...
2. Something can be completed entirely in one visit. In other cases, 2 or more visits are required. Zero in this column means that in a significant number of cases such manipulation cannot be performed and you need to be mentally prepared for another (more complex) one.
3. If there are several techniques and they differ significantly in time, this will be indicated in separate comments. In the absence of a comment, it should be assumed that each of the visits continues approximately the same.
4. The most common range, which includes 90% of such manipulations.
5. This is the recommended time for the initial appointment, when neither you nor the doctor yet know exactly the degree of complexity, but you can roughly guess what the first appointment will be filled with. Usually it is slightly longer than the average time, since it includes possible delays, preparatory procedures (anesthesia, etc.), recommendations and discussion.
6. This is the period from the first to the last visit for work performed in several visits. An empty column is left where there is no need to come again.
7. When it is difficult to immediately determine the required specialization of a dentist, it is better to contact a general dentist (general dentist) for the first time. Even if he is forced to send you to a more specialized specialist, he can be questioned on many other (very often also existing) dental issues.
8. Quite often, one consultation is not enough, since data from additional studies (x-rays, orthopantomograms, CT, MRI, etc.) is required.
9. The first consultation can be either shorter than subsequent ones (if it is useless to assume anything without additional research - it will be like fortune telling) or longer (when the main issues are clarified immediately, and at the second consultation only a verdict is made from 2-3 previously selected probable diagnoses).
10. The consultation may take an hour or more, but the first appointment should not take that long. It is better to conduct a complex, detailed discussion the second or third time, when the doctor at home has thoroughly “digested” the difficult case. Well, half an hour is enough to clarify basic questions.
11. Dental therapists are sometimes divided into endodontists (who treat canals) and restorers (who specialize in highly aesthetic dental restorations with filling material). The duration of their consultations is approximately the same.
12. Usually one consultation with a dental therapist is enough. But subject to the availability of the necessary radiographs or computed tomography. If they are not available, but can be done in the same clinic, then basically everything is determined on the first visit. If the required equipment is not available, then there is a need for a second consultation after the patient brings the necessary research results.
13. An implantologist is also a dental surgeon. Consultation on implantation usually lasts a little longer than on tooth extraction.
14. When planning implantation and other bone operations, computed tomography plays a key role. If you have it, it is better to send it to the doctor in advance by email. This will shorten the visit time or even one entire visit. Of course, you need to give the surgeon the opportunity to familiarize yourself with it, i.e. Make an appointment for at least the next day.
15. 15 minutes is usually not enough to study a CT scan, so send it in advance. Or at least verbally warn about the need to allocate more time to you.
16. An orthopedic dentist is a specialist whose consultation is necessary first of all in the presence of problems from different areas of dentistry. If you need to treat, remove, straighten, and replace teeth at the same time (or some 2-3 options from the above), you need to go to an orthopedist. He refers it to a therapist, surgeon, or orthodontist if necessary. It is not recommended to go to him, for example, after all your teeth have been treated by a therapist. Because some manipulations may be unnecessary. And others, on the contrary, are missing - which will require a return to the therapist.
17. If prosthetics are needed not for 1-2 teeth, but for a significant number, be prepared for the fact that at the first appointment only diagnostic impressions will be taken. And the main discussion will come next time, when the doctor (and dental technician) use the cast diagnostic models to plan the optimal treatment plan.
18. If you need a detailed treatment plan with cost calculations, then you also need to warn about this. It will take a few extra minutes to complete.
19. A dental therapist and a dental surgeon can also serve as a periodontist.
20. Filling out a periodontal chart with measurements of each tooth at at least 6 points takes significant time. Often it is not carried out on the first visit.
21. The first consultation with the orthodontist is introductory. It can be used to photograph and take diagnostic impressions. After calculating the diagnostic models, that is, at the next visit, a substantive discussion of the treatment plan will take place.
22. The examination itself, diagnosis and discussion of treatment with parents in most cases takes 15 minutes. But the time it takes to establish contact with a child (find an approach to everyone, don’t scare them, get permission to open your mouth) can vary greatly depending on the age, temperament and mood of the little patient. Each pediatric dentist determines it himself. Some people believe that if an agreement cannot be reached in 15 minutes, then further attempts are futile. Other doctors are ready to patiently adjust the child and take twice or three times longer.
23. Treatment of caries most often ends with the installation of a filling. But if the tooth is more than 50% damaged, an inlay or onlay is recommended.
24. In one visit, caries is treated if a filling is installed. If an inlay or onlay is being made, 2 visits are required. Also, sometimes in case of deep caries and suspicion of pulpitis, a permanent filling is not placed immediately, but the patient is allowed to find and observe the tooth for a week.
25. Treatment of 2-3 adjacent teeth significantly shortens the average time for each of them. Since one anesthesia and one application of a rubber dam is enough, carious tissue on contact surfaces is removed more easily and quickly.
26. In general, placing a filling is only part of the procedure for treating caries, wedge-shaped defects, traumatic chipping of a tooth, etc. Before installing a filling, the tooth must be prepared in one way or another. But sometimes there are cases when this preparation is minimal (takes less than a minute).
27. Although (as can be seen from the other columns of this line) the time for filling a tooth in most cases does not exceed 30 minutes, often additional manipulations take almost the same amount. Therefore, when making an appointment for a filling, it is better to reserve 1 hour.
28. Artistic restoration is a filling with special additional characteristics.
29. An artist can paint his picture for decades. Also, a dental artist, in principle, is not limited by time for sculpting a masterpiece. But still, usually some reasonable limits are respected.
30. Treatment for pulpitis varies greatly in duration. And by the number of visits, and by the time of each of them. Firstly, there are 2 methods of treating pulpitis: vital (when the pulp is removed during the first visit under anesthesia) and outdated, but rarely used devital (when “arsenic” is first applied, and depulpation is resorted to directly on the second visit). Secondly, the pace of treatment strongly depends on the number of canals: there can be from 1 to 5 of them in a tooth. Thirdly, some doctors permanently fill the canals on the first visit (most), others put a temporary drug in the canals, and the final filling channels will be carried out next time. Fourthly, the smartest dentists try to sculpt a filling for a newly treated tooth already on the first visit. Others postpone this stage to another day, or even recommend restoring a pulpless tooth not with a filling, but with a more serious structure - a crown, inlay, onlay (which is correct).
31. Thus, everything fits into one visit when the removal of the pulp (under anesthesia), filling the canal with permanent material, and restoring the tooth with filling material are carried out immediately. There will be 4 visits if: first, arsenic is applied, then the pulp is removed and a temporary preparation is left in the canals, then the canals are completely filled, and finally, the tooth is restored with a permanent filling (but this scenario is rare). If agreement is reached to restore the tooth not with a filling, but with an orthopedic construction, then more visits may be required. But they will relate to the treatment of pulpitis only indirectly. Therefore, we do not take them into account here; they need to be added additionally, looking at the corresponding rows of the table.
32. Approximately 1.5 hours are needed to treat a single-canal tooth entirely or a 3-4-canal tooth without final restoration (a permanent filling is placed at the next visit).
33. If the doctor does not meet the deadline in an hour and a half, he always has the opportunity to stop at some stage: put the medicine in the tooth and put a temporary filling. And complete the labor-intensive processing of the canals on your next visit.
34. As with pulpitis, treatment of periodontitis can take varying amounts of time and number of visits. In addition to the variety in the number of canals and the possibility of transferring the final restoration of the tooth to a separate visit for periodontitis, in most cases the canals are not completely filled at the first appointment. It is not so much the tooth itself that needs to be cured, but the inflammatory tissue around it (cyst). This usually takes 2-3 weeks. But some doctors consider it advisable to add a fresh portion of the drug (calcium hydroxide) several times. Two or three times or even several months - until they are completely sure that the bone tissue around the tooth has healed. On the other hand, among dentists there are also supporters of treating periodontitis in one visit (in some situations they achieve no less success than those who adhere to multi-visit tactics).
35. One visit - if the canals are immediately processed, filled with permanent material, the tooth is restored with a permanent filling. 2 visits - this is if, according to the classical treatment regimen, the treatment is carried out with temporary injection of Ca(OH)2 into the channels. In 3 or more appointments - when the antiseptic is changed several times, or tooth restoration takes a separate stage.
36. Unsealing the canals is necessary for periodontitis, when the tooth has previously been treated endodontically, but the treatment did not give a successful result. This type of work in most cases is much more complicated than primary intervention for periodontitis. Because instead of empty canals, the dentist must treat those previously filled by the previous doctor. This is often very difficult and unpredictable. You can go through the canal to the top in one minute, or you can not even advance a quarter of the length in a whole hour. It all depends on the material and the efforts of the previous doctor: it is very difficult (and sometimes even impossible) to remove cement or resorcinol-formalin paste from the canals. An attempt at forced unfilling can only lead to the formation of perforation (false channel), which will completely minimize the chances of saving the tooth. Therefore, to reduce risks, such manipulation must be carried out carefully, without fanatical use of force. Theoretically, the time and number of techniques are unlimited, but in practice, extra effort can only be spent up to a certain limit. This limit is individual for each doctor and patient. But for most, average numbers can be derived in this situation.
37. Usually, on the first visit, either the canals can be unsealed, or a decision is made that further attempts are inappropriate. But if there are some intermediate results, the chances of achieving success a second time are relatively high - you can continue the work you started in the second round.
38. Unsealing canals is a monotonous procedure. For many patients, sitting with their mouth open in the dentist’s chair for more than 2 hours is difficult. By reducing the dose to one hour, there will be little chance of achieving a good result.
39. Before you begin to remove the filling material itself from the canal, you need to drill out the old filling, and sometimes remove the pin.
40. Since fillings for wedge-shaped defects last less, and many doctors warn patients about this without providing a guarantee, there is a tendency among dentists to place them less responsibly. And, accordingly, faster than it should. In fact, the approach to treating a tooth and isolating it with a cofferdam should be no less thorough than when treating caries. Even, perhaps, more careful - after all, it is more difficult for a filling to hold onto a wedge-shaped defect, and therefore the installation technique will not forgive even small errors.
41. Here we are talking, of course, not about silvering, but about the full treatment of caries by filling a tooth.
42. One hour is needed to form a trusting relationship with a child. The younger the patient, the more time it takes to persuade.
43. Pulpitis of baby teeth is treated according to a simplified scheme. The canals are not treated as thoroughly as permanent teeth. With pulpitis of a permanent tooth, the treatment time for the canals is also shorter than in adults, since they are wider.
44. Technologies of vital (in one visit) and non-vital (in two visits) treatment are found in both permanent and baby teeth. Tooth restoration with a filling can be carried out at the second or third appointment.
45. The patient should come for a follow-up examination to the dentist every six months (unless more often was recommended). Depending on your specialization, the examination should be carried out either by the specialist you primarily visited (general practitioner, orthopedist, periodontist, orthodontist) or by a general dentist (generalist).
46. This refers to the time spent brushing all your teeth at once. The procedure includes air-abrasive treatment (Air-Flow), ultrasonic cleaning and polishing of teeth with paste.
47. In rare cases, if patients are hypersensitive, it must be performed under local anesthesia - then it is more advisable (in order not to do many injections at once) to split the procedure into 2 visits. The first one cleans the upper jaw, the second one cleans the lower jaw. Or vice versa.
48. The amount of tartar and plaque varies from patient to patient. It depends on the quality of personal hygiene and the duration of the last professional cleaning. If you haven’t brushed your teeth at the dentist for many years and plaque is clearly visible even on the front surface, then be mentally prepared for a longer appointment.
49. This is whitening in the dentist's chair.
50. Usually pure procedure time: 3-4 times x 15 min = 45-60 min. But with increased tooth sensitivity, not everyone can withstand the allotted time completely and stop the process earlier. Anesthesia for whitening is not recommended.
51. You do home whitening at home yourself, but you need a dentist to make individual trays into which the whitening preparation will be applied.
52. Whitening trays are made approximately 1.5-2 hours after taking impressions. You can wait or have an in-office whitening session at this time. Or you can come separately and just pick up the finished mouth guards.
53. This is the period for home whitening itself. Some people's teeth respond to lightening faster, others slower. The initial coloration and sensitivity of the teeth also affect the duration of the procedure.
54. Endodontic whitening is performed only for pulpless teeth. The whitening agent is placed inside the tooth, covered with a temporary filling, and the patient wears it for several days.
55. If the effectiveness of whitening the first time turns out to be insufficient, you can repeat the procedure one more time or two.
56. We are talking about a permanent crown made of metal-ceramic or all-ceramic. The production of a temporary crown is included in the specified average time (this is mandatory).
57. Ideally, the crown is made in 2 visits. In the first step, the tooth is prepared, impressions are taken, and a temporary crown is made. In the second, a permanent crown made in a dental laboratory is tried on and fixed with permanent cement. But this is only if all the parameters are performed perfectly the first time. In reality, you often have to adjust, fix, or improve something. This is especially true for prosthetics of front teeth. It is possible to satisfy all the aesthetic needs of the patient on the first try either if you have an outstanding dental technician, or if these requests are completely unpretentious. Therefore, not two, but three visits should be considered quite normal - the crown adjusted by the technician should be much closer to high quality standards.
58. The first appointment lasts longer than the second or third. But if the crown is fixed with composite cement, then the final visit may take about an hour.
59. The most common time for making a crown in a dental laboratory is 2 weeks. Of course, if the laboratory has little work to do, you can make a crown faster. But a good laboratory rarely experiences a lack of orders. Therefore, as a rule, she asks for increased payment for accelerated execution.
60. There are 2 types of inlays: stump and coronal. Both take approximately the same time to produce. This also applies to overlays.
61. The core inlay is usually produced more quickly. But, as in the case of crowns, the workload of the laboratory also plays an important role.
62. A veneer is a laboratory ceramic restoration on the front surface of a tooth. In this case, the inner surface is not ground down or is only partially ground down (this is its difference from a crown - it requires preparation of the tooth from all sides). Lumineers are a subtype of veneers. Initially it was just a commercial name for the product. Now other companies offer their products under this brand.
63. Veneers, by definition, require a particularly scrupulous attitude to aesthetics. Therefore, additional color and shape corrections with this type of work are the rule rather than the exception. 2 visits are a big success, 3-4 are quite normal.
64. Since veneers are often ordered more than one at a time, the more of them there are, the less time is spent on average on one tooth.
65. A bridge prosthesis consisting of three units (two crowns on the supporting teeth and an artificial tooth located between them) is the easiest to make. In this case, two visits may be enough. But the longer the prosthesis, the more complex the production process. Therefore, more visits may be required before the aesthetics, comfort, and fit of the prosthesis are achieved.
66. The first appointment, at which impressions are taken, lasts less than when installing a crown on a tooth - because there is no need to grind anything down. The second or third visits take about the same time.
67. This technology makes it possible to perform an orthopedic design without the participation of a dental laboratory. The doctor takes an optical impression, models the future crown or inlay on a computer, and a milling machine cuts out a part of the desired shape from the blank. Then the dentist paints the restoration, giving it individual features and fixes it in the oral cavity.
68. Since the main advantage of such production is speed, often all the work is done within one day. After taking impressions, the patient awaits the results right in the clinic (or walks nearby). But you can, of course, come for final cementing the next day.
69. Partially removable dentures are used when at least one (or several) teeth are present on the jaw. Plastic plate, clasp, locking, nylon (flexible) dentures - their production time does not depend on the material.
70. Taking impressions, determining the bite, fitting the frame (for clasp and locking dentures), trying on the teeth and, finally, handing over the finished prosthesis - these are the main stages of making removable dentures, each of which requires a separate visit. True, if there are a few missing teeth, some of them are reduced.
71. A complete removable denture is made when there is not a single tooth left on the jaw.
72. These figures do not take into account the visits required to adjust a prosthesis that has already been delivered. Immediately after starting use, the prosthesis almost always chafes here and there. Therefore, you need to come back one to three times to eliminate areas that injure the mucous membrane.
73. It is not always possible to repair a removable denture. If the doctor considers it possible, he takes an impression of the prosthesis and sends it to the laboratory. Sometimes you don’t even need to take an impression (for example, if only a crack has appeared on the prosthesis).
74. Repair of a fixed structure (crown, bridge) is rarely feasible. The only thing that can be done is to cover a small chip in the ceramic with a composite filling material. And even then: the service life of such a “patch” is short-lived.
75. Crowns never fall out without a reason. Patients almost always resort to low-quality cement in the hope that a new “stronger” one will be able to hold a seemingly good restoration for a long time. In fact, in 99% of cases, it is not cement that causes the loss, but poor-quality manufacturing of the crown itself. Therefore, in the vast majority of situations, it cannot be cemented again - you need to make a new one.
76. Sometimes patients confuse a mobile tooth (whose root is mobile) and a broken wall. The swinging wall of a fracture can be easily removed in a minute, but the root itself will most likely be far from easy to remove. There is also confusion with baby teeth - it is easy to remove such a tooth during the period of physiological change, when its roots have practically resolved. But if a baby tooth has to be removed several years earlier, then the removal may be similar in complexity to tooth extraction in adults.
77. The removal time is influenced by many factors, so it can vary quite a lot. Speed is not the main thing - it is much more important to carry out the operation as less traumatic as possible, so that healing takes place without complications. And subsequent implantation can be carried out without additional augmentations.
78. Removal of the upper wisdom teeth usually takes place faster than the removal of the lower ones. But in any case, it is recommended to take an x-ray before the operation in order to understand the degree of complexity in advance.
79. Before removing such a tooth, you still need to get to it. An incision is made in the gum, the bone tissue above the tooth is excised, and the tooth itself can be sawn into several parts. After the tooth is extracted, the gums are sutured. The further the wisdom tooth is from the surface, the more difficult and longer it will take to remove it. A preliminary x-ray is required (or even better - a computed tomography).
80. After 7-14 days, you still need to come back once to remove the stitches, but here it is indicated how many visits the operation itself will take.
81. Closed curettage is the main method of treating mild forms of periodontitis. Periodontal pockets are cleaned using Gracie curettes or ultrasound.
82. Open curettage is indicated for moderate periodontitis. In this case, an incision is made in the gum, a flap is peeled off, the root surface is processed under direct visual control, and sutures are applied at the end.
83. The “gold standard” for closing gum recession is the transplantation of one’s own connective tissue (gingival) graft into the area of the exposed root neck. There are also alternative methods when a second surgical field is not used - they are performed somewhat faster.
84. Here we mean an operation with a deep periodontal pocket, when, after curettage of its contents, bone tissue (or its substitute) is introduced and a membrane is installed.
85. Of course, we are talking about root-shaped screw implants here. Basal, lamellar and other marginal types of implantation are not considered.
86. With single-stage implantation, after tooth extraction, the implant is immediately installed in the socket.
87. If there is a lack of bone tissue, its volume must be increased before installing the implant. This is achieved by a separate operation, which can be carried out in several ways.
88. Sinus lift is moving the bottom of the maxillary sinus upward. It is performed when there is a lack of bone tissue in height in the area of 4-7 teeth of the upper jaw. A closed sinus lift is indicated for minor bone deficiency. This is a simple procedure and is performed immediately before the implant is installed.
89. Open sinus lift is a separate operation. Used for significant atrophy of bone tissue. Typically, implants are installed after a few months, once the success is confirmed.
90. Here we will indicate the time costs not for a single visit (they are quite simple: 15 minutes, with the exception of the visit when braces are installed), but for the entire treatment. This period is of much more interest to patients.
91. Ligature braces require visits to the orthodontist every 2-3 weeks. Self-ligating (ligature-free) braces - once every 1-3 months.
92. At the first appointment, the orthodontist never fixes braces. And when that day comes, the doctor himself will select the required interval. Installing braces can take up to 2 hours.
93. The duration of treatment with lingual braces is approximately six months longer than with vestibular braces.
94. Aligners are clear, removable aligners. Effective for minor bite pathologies.
95. The patient receives a set of mouth guards, which he changes at home every 1-2 weeks. You need to visit the orthodontist for follow-up examinations once every 1-2 months.
How long does it take to install braces on one jaw?
The procedure always starts with the upper jaw, and there are several reasons for this. It takes time to get used to a foreign object on the teeth. If suddenly a person cannot, for physiological reasons, wear braces for a long time, it is always easier to remove them from one jaw than from both. In addition, the entire attachment process takes approximately an hour and a half for the jaw. This is a very painstaking and tedious process for the doctor and the patient, so it is better to divide it into two stages. After about a month, braces are placed on the lower jaw. After one and a half to two months, a follow-up visit to the doctor will be required to assess the condition of the dental arch.
Recommendations after removal
In order to avoid inflammation and diseases of the oral cavity, it is necessary to follow a number of recommendations. First of all, you should avoid eating and drinking for three hours after the tooth has been pulled out. Dentists also advise:
- Take pain reliever before the anesthesia wears off. This will help you better endure this period, since severe pain may occur when the effect of the drug stops. It is recommended to use NSAID-based products, for example, Ibuprofen, which will not only help relieve pain, but also have an anti-inflammatory effect. It is necessary to take the drug on the first day, then as needed.
- Take antiallergic medications. Often, the doctor recommends taking Suprastin. The drug helps relieve swelling of the gums, which occurs in cases of difficult removal.
- Use antibiotics if necessary . Prescribed only by the attending physician. You cannot take these medications on your own, as they have a number of side effects. One of the most popular antibiotics is Amoxiclav.
Important! After pulling out a wisdom tooth, it is strictly forbidden to take Aspirin and its analogues, since the drug reduces blood clotting, which can cause bleeding or the formation of a hematoma.
If you experience pain that does not go away or gets worse within 1-2 days, you should consult a doctor.
In certain cases, the dentist may recommend rinsing and taking other medications, depending on the method of removal and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Oral preparation
The very first step before installing braces is a professional consultation with an orthodontist. The specialist examines the oral cavity, evaluates the teeth and gums. After this, he directs the patient to a panoramic photograph of the jaw. Having it in hand, the doctor receives a complete clinical picture and draws conclusions regarding the installation of orthodontic structures - whether it is advisable to prescribe the procedure in a particular case.
Braces are installed only on absolutely healthy teeth. Therefore, if the doctor identifies dental problems in the patient, they must first be eliminated. Treatment of caries may be necessary, including filling, and some other manipulations. Professional hygienic cleaning of the oral cavity is also required to remove plaque and tartar. Teeth must be clean and healthy before installing braces. Only after successful completion of the therapeutic process can the doctor prescribe the procedure.
How dental implants are placed: clinical methods
Implantation can be done using 2 methods. A one-step procedure means the simultaneous installation of an implant and abutment. This technology does not require repeated surgical intervention and has the following features:
- The patient wears a temporary crown while a permanent prosthesis is made.
- After 2-3 weeks, healing occurs, and the doctor replaces the crown with a permanent one.
- This method is possible thanks to modern implants of various sizes for any part of the bone - without the need to build it up.
A two-stage installation consists of fully implanting the screw into the bone, and sutures are placed on the gum incision. After several months, a second incision is made in the gum, a former is installed, and after a couple of weeks the crown is fixed.
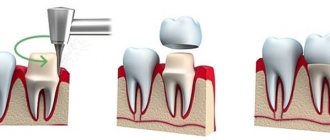
What are metal-ceramic dental crowns and bridges made of?
The crown consists of 2 parts – the frame and the covering.
If the crown is metal-ceramic, then the frame is made of metal . In the Health Clinic Istok is a special alloy made in Germany - GIALLOY . The frame is covered with ceramic mass , which is baked in an oven at 400C. The color of the ceramic mass is selected by the doctor in accordance with the color of your teeth or at the request of the patient. The Istok Health Clinic uses ceramics from well-known manufacturers Noritake, Ivoclar, Duceram Plus, e-max Ceram
Direct installation of braces
Although the common expression is “getting your braces on,” they are technically bonded using a special solution. There are two fixation methods:
- Direct bonding involves attaching braces to each tooth separately. First, it is thoroughly dried, treated with a composition to give a slight roughness and dried again, and only then braces are placed. This is a painstaking procedure that requires high professionalism from the orthodontist.
- Indirect bonding involves bonding braces at the same time. The doctor attaches them to a cast of the jaw in advance, and then simply “transfers” them to the teeth, using special trays for this. Of course, this method takes much less time. The indirect bonding method is used in orthodontics more often than direct bonding.
The procedure itself is completely painless, but requires great perseverance from the patient. He will have to sit motionless throughout the entire process with his mouth open while the doctor performs the necessary manipulations.
Is it painful to remove a nerve from a tooth?
Modern dentistry has the widest possibilities and powerful universal anesthesia. Thanks to this, removal of the flock nerve is a painless procedure that is carried out during the visit. The only discomfort that the patient may feel concerns the injection into the gum. This can also be easily avoided by applying anesthesia, after which inserting a needle will not cause any discomfort.
Pain may occur in rare cases for one of the following reasons:
- Individual characteristics of the path of nerves, which is why standard techniques provide insufficient pain relief.
- Taking painkillers the day before by the patient, in particular from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may reduce the effectiveness of anesthesia.
- The patient took alcohol before visiting the doctor.
- The patient belongs to the 2% of all people with immunity to anesthetics.
The solution to the problem in each case is the same - repeated anesthesia.
The structure of implants, how they are made
In appearance, the implant is practically no different from real teeth. It has a reliable design that allows it to be fixed in the bone and soft tissues of the jaw and gums. Implants are made on a titanium base, have a root part, which is installed first, and an abutment. It represents the apex, which serves as a support, connecting the root and the crown.
There are different types of dental implants, which differ in shape, type of installation, and material of manufacture. They generally have a screw length of up to 19 mm and a width of up to 5 mm.
Is it painful to install a metal-ceramic crown?
Installing a metal-ceramic crown is a completely painless process.
The only unpleasant moment may be taking impressions with impression material, especially if you have an increased gag reflex. In this case, it is better to resort to 3D prosthetics CEREC.