Pain and pathology in the area of the temporomandibular joint have many clinical manifestations and, accordingly, names (Casten syndrome, myofascial syndrome, arthrosis-arthritis of the jaw joints, chronic subluxation of the lower jaw, dysfunction of the TMJ or temporomandibular joint, etc.). Musculo-articular and pain dysfunction of the TMJ has a code according to ICD-10 and belongs to block K00-K14, subparagraph K07.6. Modern gnathological treatment and clinical protocol for this multifactorial disease may require the involvement of several specialists, gnathologist, osteopath, neurologist, physiotherapist, maxillofacial surgeon, orthodontist, dental orthopedist-prosthetist. Where and how to diagnose and properly treat temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMJ) in Moscow?
- Causes of TMJ dysfunction
- Symptoms and prevention of TMJ dysfunction
- Treatment of TMJ dysfunction
- Center for the treatment of TMJ dysfunction in Moscow
- Cost of treatment for TMJ dysfunction
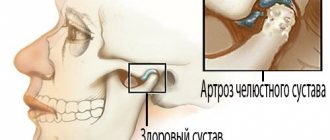
Structure and function of the mandibular joint
In order to better understand what causes pain and muscle dysfunction of the right and left TMJ joint, it is necessary to understand what it is - the temporomandibular joint, its structure and function.
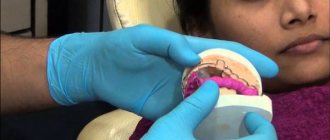
Mandibular joint (TMJ), photo
In the broadest sense, the structure of the mandibular joint has the following elements and features:
- This is a double, in other words, paired (left and right), combined joint (the only one of its kind in humans).
- The jaw joint belongs to the category of complex joints in the human body, with maximum freedom of movement in different directions. It is divided into two floors (divisions): the upper floor is above the jaw disc, the lower floor is under the disc. The joint is covered by an articular capsule.
- Both joints of the lower jaw normally synchronously reproduce movements in 3 planes:
- horizontal: left - right
- vertical: up-down
- sagittal: back - forward (from back to stomach)
- Between the articular head of the lower jaw and the articular cavity of the skull there is a jaw disc, which covers the middle part of the articular head and serves to soften and absorb pressure in the joint.
- The articular mandibular disc is connected to the internal capsular ligaments, which regulate the movement of the disc forward, backward, left and right. The external ligaments of the joint determine the boundaries of the displacement of the lower jaw, together with the group of masticatory muscles.
- All articular surfaces are covered with cartilage, which secretes synovial fluid to lubricate the jaw joint and improve the sliding of the articular head in the joint.
Causes of temporomandibular joint dysfunction
Scientists believe that TMJ dysfunction develops under the influence of many factors. The temporomandibular joint is one of the “target organs” that respond to factors of aggression of various origins. They can be local and systemic. Local factors include acute and chronic joint injury, lack of chewing teeth, bruxism (grinding teeth in sleep). TMJ pain dysfunction syndrome can develop under the influence of stress, anxiety, tension and other emotional factors.
Currently, there are two main theories of temporomandibular joint pain dysfunction syndrome: the theory of occlusal imbalance and the psychophysiological theory. Adherents of the first theory believe that the root cause of functional disorders is a violation of the closure of teeth. It leads to compensatory protective muscle contraction with the development of parafunctional increased activity. In the future, this causes muscle pain syndrome with temporary preservation of the correct position of the head of the lower jaw without disturbing the position of the articular disc.
At the beginning of the disease, residual tension occurs in the muscle, and then a stable local increase in tone develops. It causes short-term painful muscle spasms when you forcefully open your mouth or yawn. In other cases, increased tone leads to stable muscle tension.
If increased tone persists for a long time, vascular, metabolic and inflammatory disorders occur in the muscle. Local hypertonicity becomes a source of pain and turns into trigger points, which can be found in the masticatory muscles, the lateral and medial pterygoids, and the temporal muscle.
With a long-term change in occlusal relationships, the load on the joint increases due to the type of compression. He begins to adapt to new intra-articular relationships. When compensatory capabilities are depleted, the shock-absorbing properties of the soft tissue components of the joint are lost. Compensation for the increased load on the tissues of the joint is manifested by degenerative changes and adaptive changes in the elements of the joint, which leads to pain.
Temporomandibular joint pain dysfunction syndrome also develops in patients suffering from depressive disorders. Many people in a state of emotional stress experience spontaneous contraction of the masticatory muscles. They experience spasm, loss of coordination, occlusal disorders, and injury to the soft tissues of the joint. Violation of occlusion against the background of chronic stressful situations turns out to be a direct cause of joint dysfunction.
Causes of TMJ dysfunction
Conventionally, we can distinguish 3 main reasons for the development and etiology of the clinic of TMJ jaw joint dysfunction:
- Imbalance and disruption of the nervous coordination of the jaw muscles that raise and lower the lower jaw. Most often, the tone and tension of the muscle fibers in the right and left masticatory muscles are first disturbed, and then their imbalance occurs, irritation of the bilaminar zone and pain when chewing and swallowing.
- Chronic stress, over a long period of time (from a year or more), caused by a disorder of the central nervous system and higher nervous activity.
- Malocclusion and occlusion (closing) of teeth, coupled with non-standard sizes and position of the jaws relative to each other and the base of the skull.
As a rule, all of the above factors, to a greater or lesser extent, occur if a diagnosis of TMJ dysfunction syndrome is made. Reviews from patients and a forum on the Internet confirm this.
A hereditary predisposition to dysfunction of the jaw joints has been proven, with genetic anomalies associated with malocclusion, especially with micrognathia and macrognathia of the lower or upper jaw.
Temporomandibular joint diseases
Go to:
- Maxillofacial Surgery
Facial pain is one of the most common complaints of patients turning to us for help. At the same time, we observe true facial pain in a third of patients, while secondary facial pain caused by pathology of the ENT organs, ophthalmological problems and dental disorders make up the vast majority of cases. One of the main nosological forms is temporomandibular joint dysfunction syndrome (TMJ) - one of the most difficult and controversial diagnoses in modern medicine. Up to 40% of people experience symptoms of temporomandibular joint disease, but not everyone seeks medical help.
What is temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMJ)?
The head of the lower jaw, the articular surface of the temporal bone, the articular disc located between them, the articular capsule, as well as the ligamentous apparatus and masticatory muscles take part in the formation of our joint. The joints are located anterior to the ear canal and work synergistically.
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction means that one of the components of our joint is not functioning properly. This joint is one of the most complex in the human body, it is responsible for the movement of the lower jaw forward, backward and from side to side. Any pathological condition that does not allow this complex system of muscles, ligaments, discs and bones to work properly leads to its dysfunction.
How does the TMJ function?
The temporomandibular joint is a combination joint, representing the functional combination of two anatomically separate joints (left and right). The articulating surfaces of the head of the mandible and the articular surface of the temporal bone are supplemented by a fibrous intra-articular disc located between them, which is attached with its edges to the articular capsule and divides the articular cavity into two sections. Both temporomandibular joints function simultaneously, representing a single combined joint; thanks to the intra-articular disc, movements in three directions are possible in it.
- vertical axis: lowering and raising the lower jaw (opening and closing the mouth) - occurs in the lower part of the joint, between the cartilaginous disc and the head of the lower jaw;
- sagittal axis: displacement of the lower jaw forward and backward - occurs in the upper part of the joint, between the cartilaginous disc and the articular surface of the temporal bone;
- frontal axis: lateral movements (rotation of the lower jaw) during chewing - on one side, the head of the lower jaw together with the cartilaginous disc emerges from the articular fossa onto the tubercle, and on the opposite side, the head of the lower jaw rotates relative to the articular cavity around a vertical axis.
What are the symptoms of temporomandibular joint disorders?
Painful TMJ dysfunction or TMJ pain dysfunction syndrome has many synonyms: Costen's syndrome, myofascial pain syndrome of TMJ dysfunction, TMJ dysfunction, craniomandibular dysfunction syndrome, mandibular dysfunction, musculo-articular dysfunction of the TMJ, etc.
This symptom complex was first described by otolaryngologist J. Costen, who observed it in patients with missing teeth and in people with low occlusion. Painful joint dysfunction is characterized by the following manifestations:
- headache (fronto-temporo-parietal localization), ear pain, as well as pain and pressing sensations behind the eyes;
- “crunching” or “clicking” when opening or closing the mouth;
- pain when yawning and wide open mouth;
- spasm of the chewing muscles;
- displacement of the center line of the jaw;
- malocclusion.
The variety of clinical manifestations of temporomandibular joint dysfunction is determined by the polyetiology (multiple causes) of the pathological processes developing in it, which complicates diagnosis and treatment.
What Causes TMJ Disorders?
In general, TMJ disorders are a multifactorial process. These factors can be divided into two types: problems associated with the masticatory muscles and problems with the joint itself. Muscle problems are the most common type, especially for young people.
Muscle problems can be caused by:
- Muscle hyperactivity. This can happen if you clench your jaw frequently, especially while sleeping, which is quite common.
- Scar changes in the masticatory muscles
- Increased sensitivity to pain. This may be due to stress, or some other process that affects pain sensitivity
- Joint problems can be caused by
- Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the joint
- Inflammation in the joint (arthritis)
- TMJ injury
How are TMJ disorders diagnosed?
The diagnosis is made based on symptoms and additional examination methods.
Possible examinations:
- Blood tests that may be useful to look for signs of inflammation;
- MRI - this method is used to give a detailed morphological picture of the joint;
- Arthroscopy (using a fiber optic device) to look "inside" the joint);
- Electromyography (EMG) is an objective method for studying the neuromuscular system by recording the electrical potentials of the masticatory muscles, which allows one to assess the functional state of the dental system;
- Densitometry is a method for measuring bone mineral density, that is, the content of calcium, which is its main structural element. The information obtained is subjected to computer processing, the thickness and size of the bones, and their volumetric density are calculated. Such indicators make it possible to judge the resistance of bone tissue to mechanical stress.
What is the treatment for temporomandibular disorders?
Most problems in the mandibular joint can be eliminated using simple procedures, such as painkillers and muscle relaxants, a course of physiotherapy and exercise therapy, and advice on how to relieve the joint, procedures aimed at relaxation and anti-stress therapy. These are the so-called orthopedic methods using mouthguards and bite pads.
In case of more severe disorders in the joint or the ineffectiveness of conservative methods, they resort to injections of botulinum toxin into the masticatory muscles if they are hyperactive and intra-articular administration of steroids.
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical treatment using endoscopic equipment. A very small percentage of patients may be eligible for open joint surgery. As a rule, these are gross deformations of the joint in the form of ankylosis.
What are the prospects for the treatment of temporomandibular disorders?
Most TMJ disorders improve over time.
Symptoms and prevention of TMJ dysfunction
At the PartnerMed dental clinic, diagnosis of TMJ dysfunction is carried out by a gnathologist. He also draws up a treatment plan. When making a diagnosis, the following symptoms are taken into account:
- Pain in the jaw joints
- As a rule, with TMJ dysfunction, chronic pain occurs in the temporal, trapezius, chewing and a number of other muscles. Dull or aching dental, eye, headache and facial pain appears, and trigeminal neuralgia syndrome may develop, which forces differential diagnosis with arthritis and osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, as well as otitis media.
- Difficulty opening the mouth
- There is a kind of blocking of movements or jamming in the TMJ. In order to open your mouth, you must first move your jaw slightly to the left, right, forward or backward.
- Clicking in the jaw
- At the moment of opening the mouth, chewing and yawning, clicks and crunching occur in the TMJ joint. Other noises are also possible in the form of grinding, popping, sometimes loud enough to be heard by strangers.
In addition, depending on the dominance of various causes during the development of the disease, there may be difficulties in swallowing food, pain in the tongue, ringing and noise in the ears, dry mouth, changes in the sensitivity of the lips, palate and other pathological manifestations.
In order to make a complete and final diagnosis of TMJ dysfunction, the following clinical examinations are carried out as prescribed by a gnathologist:
- CT and MRI of joints (it is most advisable to do a dynamic MRI of the TMJ)
- Blood tests, including rheumatoid factor, allergy status, extended immunogram
- Consultation with a gnathologist and an osteopathic dentist (or an osteopath working together with a dentist)
- Functional diagnostics of dentition (taking into account lateral and frontal separation of teeth)
- Diagnostics of tooth models in an articulator
- MPI analysis (finding the correct position of the lower jaw)
- Electromyography
- Electronic axiography and condylography
Request a call back or dial our number!
+7
This phone call does not obligate you to anything. Just give us a chance and we will help you!
Proper prevention of TMJ jaw joint dysfunction requires timely getting rid of bad habits, chewing gum, and frequent consumption of very hard foods, such as chewing dried squid and fish with beer. When engaging in professional sports such as boxing, wrestling, and mixfight, be sure to use protective equipment, helmets, and protective mouthguards. It is necessary to regularly consult a gnathologist for the treatment of bruxism, jaw clicking and other gnathological diseases.
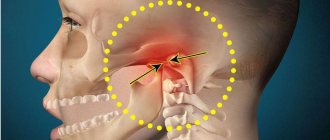
TMJ dysfunction, photo
Signs of TMJ pain dysfunction syndrome
In the clinical picture of the disease, 2 periods are distinguished: dysfunction and painful spasm of the masticatory muscles. At the initial stage of the disease, patients complain of joint noise, crunching and clicking in the joint. They are bothered by pain when palpating the masticatory muscles.
The following symptoms are noted:
- deviation of the lower jaw to the side when opening the mouth;
- S-shaped movements of the lower jaw;
- feeling of stuffiness in the ear;
- ringing and noise in the ears;
- hearing loss.
There are no radiological changes in the joint. During the period of painful spasm, a sharp restriction in mouth opening and severe muscle pain of a neuralgic nature suddenly appear in the face and head. In some patients, in the early stages of the disease, periodic exacerbations occur, followed by spontaneous cessation of pain and dysfunction. An exacerbation of the disease often occurs with a sharp overload of the masticatory muscles (opening the mouth wide, chewing solid food) or during an emotional crisis. Over time, the number of muscle trigger zones in spasmed muscles increases. They become sharply painful, the pain begins to radiate to various areas of the head.
Treatment of TMJ dysfunction
Effective and modern methods of treating TMJ dysfunction involve an interdisciplinary approach. This means that medications, speech limitation, physiotherapy, osteopathy, exercise therapy, myogymnastics, splints and distraction mouthguards for the lower jaw, orthopedic and orthodontic structures are selected by a single team consisting of doctors of different specialties, gnathologists, osteopaths, neurologists, psychologists, orthodontists and others specialists. Methods and methods for treating TMJ dysfunction in Moscow, St. Petersburg and other large Russian cities are not fundamentally different from each other and have a common algorithm.
Depending on the predominance of one or another etiological factor, emphasis may be placed to a greater or lesser extent on different methods of treating jaw joint dysfunction. However, the same algorithm and clinical protocols exist for the treatment of chronic TMJ dysfunction.
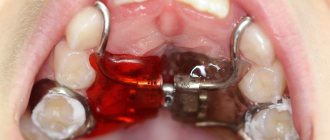
Standard treatment regimen for TMJ
- Relief of pain in the TMJ using a distraction cap and analgesics;
- Carrying out physiotherapy and drug complex therapy to relieve intra-articular inflammation;
- Normalization of masticatory muscle tone using splint therapy (and possibly Botox);
- Determination of the correct constructive occlusion of the oral cavity;
- Temporary prosthetics of the oral cavity using a silicone key for constructive occlusion;
- Final prosthetics with fixed dentures.
Treatment of TMJ, photo.
Center for the treatment of TMJ dysfunction in Moscow
Today, clinics and treatment centers for TMJ dysfunction in Moscow, various forums and patient reviews make it possible to determine the gold standard of effective treatment methods and related equipment that most effectively treats this disease.
The list of necessary diagnostic and treatment equipment used by leading specialized institutions, including the Partner Med clinic, includes:
- Articulators and facebows "Girbach"
- Axiograph "Gamma"
- "Mist Tens" device
- Computer electromyograph "Synapsis"
- Fox osteopathic apparatus
- Computer occlusion analyzers “T-scan”
and some other devices.
The course for the treatment of TMJ dysfunction at the Partner Med dental clinic lasts from 3 to 12 months, depending on the complexity and number of necessary diagnostic and treatment procedures in each specific clinical case.
Advantages of the TMJ Treatment Center Partner-Med
Experience at least 5 years
Only doctors with 8-30 years of experience practice at the Partner-Med clinic
15 year labor guarantee
Only a qualified dentist gives an extended guarantee of up to 15 years on his work.
Study abroad
Our doctors annually improve their qualifications in specialized clinics in Europe.
Chief Physician, Dmitry Nikolaevich Salatsky
Sign up for a gnathological consultation
+7
Cost of treatment for TMJ dysfunction
Answering questions frequently asked by patients: “How much does treatment for TMJ dysfunction cost, with a discount, at a promotion? Where and how much cheaper are the prices for such turnkey treatment, in Moscow, St. Petersburg or other cities of Russia?”, it should be noted that the price of treatment for pathology and dysfunction of the TMJ jaw joints and the cost of its individual stages depends on the following points:
The cost of diagnosing TMJ dysfunction starts from 10,000 rubles and can reach 80,000 rubles or more. The price of treatment starts from 15,000 rubles and can reach 300,000 rubles or more.
- From the complexity of diagnosis and the number of medical procedures
- From the qualifications of gnathologists, orthodontists and other specialists
- From the pricing policy of each specific dental center
Just pick up the phone and call us!
8
We will definitely make you an offer that you cannot refuse!
Examination of patients with TMJ pain dysfunction syndrome
When examining patients with temporomandibular joint pain dysfunction syndrome, the doctor clarifies the patient’s complaints and finds out whether he has had acute and chronic psychogenic injuries. He finds out the presence of local provoking factors. After this, he conducts an external examination, palpation and auscultation of the temporomandibular joint, palpates the masticatory muscles, muscles of the shoulder girdle and neck, and identifies trigger points in them.
The dentist evaluates the degree of mouth opening and the pattern of movement of the lower jaw, bite and alignment of teeth. In order to find out the cause of pain dysfunction syndrome, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use the following diagnostic methods:
- functional research methods (axiography, electromyography of masticatory muscles);
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- panoramic survey radiography;
- orthopantomography.
Patients are consulted by a dental surgeon or maxillofacial surgeon, orthodontist, orthopedist, psychotherapist, neurologist, gastroenterologist, and otorhinolaryngologist. Doctors carry out differential diagnosis of TMJ pain dysfunction syndrome with the following diseases:
- pathology of the temporomandibular joint - infectious, traumatic, rheumatoid, psoriatic arthritis, deforming arthrosis;
- muscle diseases - bacterial and viral myalgia;
- facial pain due to neuralgia of the branches of the trigeminal nerve, glossopharyngeal and tympanic nerve, pterygopalatine ganglion;
- migraine, temporal arteritis.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital take an individual approach to treating patients with temporomandibular joint pain dysfunction syndrome. Complex cases of the disease are discussed at a meeting of the Expert Council with the participation of candidates and doctors of medical sciences. If necessary, patients are advised by leading specialists from specialized partner clinics.