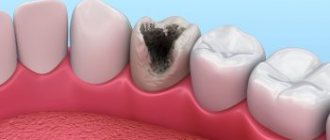
Dental orthopedics combines many techniques for restoring units. Thanks to modern methods, it is possible to restore a tooth’s appearance, correct its shape and change the color of the enamel. Dental orthopedics is not only about restoring aesthetic parameters. This is essential for overall oral health. The fact is that the absence of even one unit can lead to unpleasant consequences: atrophy of the jaw tissue, displacement of teeth, the formation of gaps between units, disruption of chewing function, and so on. We will look at the benefits and what they are in more detail below.
Benefits of dental orthopedics
This direction in dentistry has several significant advantages:
- In a short period of time, aesthetic values can be restored.
- It has a reasonable price, especially when it comes to dental products that can be removed independently.
- Easy to carry out hygienic manipulations.
- You can choose different designs and select suitable fastenings.
- Any number of units can be restored, even with complete edentia.
- Dental orthopedics reduces the risk of developing bone tissue deficiency if the product involves a full load on the jaw.
- Minimum contraindications.
- Long service life. In most cases, artificial products will last more than 5 years.
- Chewing function is restored.
- The serious psychological consequences that arise from missing units can easily be avoided.
A dentist will help you decide on the type of product. The specialist will assess the condition of the oral cavity and advise (taking into account financial and physical characteristics) which design is right for you.
Removable
Indications for installing removable structures are:
- molars and premolars are lost;
- smile zone defect;
- fangs and incisors are lost;
- the need for a temporary prosthesis.
Removable dental prosthetics are carried out by installing the following types of structures:
- Dentures on implants that are implanted into bone tissue. The prosthesis is attached to this implant. The fastening can be spherical or beam. The second type is more physiological, since it distributes the chewing load better. This type of prosthetics is indicated if teeth have been lost for a long time.
- Completely removable dentures are suitable for completely edentulous patients. This type of construction is called “false jaws”. The specialist first makes an impression. Then the jaw itself is made with imitation gums and teeth. To prevent injury to the gums and displacement of the denture when chewing, the doctor may recommend a fixing gel to the patient. Usually the “false jaws” are removed at night. The material for the jaw can be acrylic, nylon, or acry-free. There are also clasp dentures. These are partial dentures that provide even load on the gums.
Based on the method of fixation, a distinction is made between dentures with suction cups and those held in place by a special fixing gel.
The most modern are “skyless” prostheses, the so-called “sandwiches”. They are fixed on the gums and held due to their own shape. Such designs do not require the use of fixing gels or adhesives. One of the advantages is the absence of distortion of the taste of food and the urge to vomit, which occurs in wearers of conventional false jaws.
What types of dental orthopedics are there?
First of all, dental orthopedics is divided into two main areas:
- Fixed. These elements are installed in the dental office. You won't be able to remove them at home. They are fixed in various ways for a long time. Such products are removed only when absolutely necessary, also in the dental office. Experts recommend this technique in the absence of one or more units. When using these elements, you don't have to worry about artificial units falling out at the wrong time. Fixed orthopedics, as a rule, creates a more natural aesthetics than removable structures.
- Removable. From the name you can easily understand the essence of these products. In this case, we are talking about false jaws, that is, at any time a person can remove this prosthesis from the oral cavity and easily return it to its place. Most often used by older people with complete edentia.
If you want to install permanent products, then the dental clinic will offer you the following options:
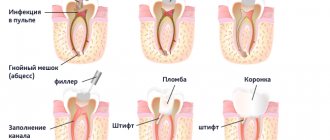
- Ceramic filling or inlay. It is made from an impression in the laboratory. Used for chipped or significant tooth damage due to caries activity. This design is much better than a conventional filling and will last at least 3 years.
- Dental Crowns. They are made of ceramics, cermets or plastics. Used to restore one or more teeth.
- Dental bridge. It consists of several crowns combined into a single element. Replaces from 2 to several units, looks like a bridge supported by natural teeth.
Removable dental orthopedics, based on the material and fastening method used to create a fully removable or partially removable dental structure, is divided into the following types:
- Acrylic. Dental orthopedics using acrylic dentures is very popular. First of all, this is the cheapest option for restoring teeth. The dental element consists of a curved arch, which has a simulated part of the gum and artificial units. A significant disadvantage is the frequent occurrence of an allergic reaction to the material used.
- Nylon. This material is several points superior to acrylic, so the price is also slightly higher. More comfortable to wear, nylon is less likely to cause an allergic reaction, and is comfortable for daily wear.
- Bugelny. Metal-ceramic crowns are firmly held on a metal arch, which distinguishes it with very strong fixation. Bone tissue atrophy is excluded, since the clasp prosthesis evenly distributes the load. The best choice when restoring several missing teeth at once.
There is also a technique for restoring dentition, which is popular with most patients. Adhesive dental orthopedics is a relatively new technology in dental practice. Its peculiarity is the absence of turning of support units.
Video about types of orthopedic structures
Main types of dentures
There are completely different types of dentures and bridges to choose the one that suits any patient.
Classification of prostheses by type of design, its mission and area of application:
Removable
They are used if some significant part of the row is lost or if all the teeth are lost. They are fixed to the gums with special anatomically shaped suction plates. There are nylon and acrylic plates.
Modern types of partial removable dentures: telescopic, plate, yoke and nylon.
Advantages
They can replace real teeth at low cost, even if the distance between the remaining teeth is large. They are considered the most common and easy to get used to.
Patients can also insert and remove the structure themselves. They are secured using metal clasps and attachments. It is the attachments that have special locks, thanks to which they are firmly installed and invisible.
Flaws
Metal clasps can be noticed when a person smiles. Removable dentures require special and regular care to prevent the spread of bacteria.
If you wear them for a long period, bone tissue atrophy occurs over time. They are short-lived and need to be replaced. It is not advisable to eat very hard and sticky food.
Fixed
Used if some teeth are lost and to give new shapes and colors to teeth.
Advantages
Correction of chewing functions and correct bite. Beautiful aesthetic appearance. There are no negative consequences of missing teeth. Long-term use of prostheses.
Renewal of a lost tooth without trimming adjacent healthy teeth. Design of additional support for installation of the prosthesis. Most similar to natural teeth.
Flaws
The biggest drawback is the high price. Long preparation for installation of the prosthesis.
*Also read: Stomatitis in the elderly - causes and treatment
You need a base to attach to; it is impossible to attach to the gum. Grinding is required, which is not entirely pleasant.
Implantation
A complex medical procedure involving the implantation of an implant or pin into the bone tissue.
When the structure fuses with the tissues, complete fixation occurs.
Also watch and read about the all-on-4 technology for restoring teeth
Advantages
Restoration of aesthetic, harmonious appearance and functional action. There is no need to attach or hook onto adjacent teeth. The person has no discomfort and can serve for a lifetime.
Dental implant
The chewing load is evenly distributed and there is no change in the row of teeth. It can be installed in the presence of almost all teeth and in complete absence.
Flaws
Long time of engraftment of the structure. There are many contraindications to surgery and complications after surgery are possible.
Not a cheap method. You may experience discomfort during and after surgery.
What problems can be solved with dental orthopedics?
With the help of dental orthopedics, the following problems can be solved:
- Replace missing units with a prosthesis.
- Restore a severely damaged tooth
- Restore chewing function in complete absence of teeth.
- Prevent jaw tissue atrophy.
Dental orthopedics is designed to restore lost or damaged units. If only 1-3 teeth are missing, experts recommend installing non-removable dental products. If more than 3 teeth are missing, a clasp denture can be installed. Acrylic or nylon products are most often installed in the absence of a large number of teeth; they will cost much less, but in terms of comfort and aesthetic indicators they will be inferior to more expensive analogues.
With complete edentia, there are two scenarios for the development of events.
- The most common option is to make a completely removable structure from acrylic or nylon. It's fast and inexpensive, but sometimes it causes discomfort, which, however, can be fixed.
- But, if you have a budget, then it is better to install ceramic crowns supported by implants. This option will look much more aesthetically pleasing, and most importantly, it is more reliable and does not cause inconvenience.
If there is a badly damaged tooth, it can be restored by installing a ceramic filling or inlay, which will last much longer than a composite filling.
If dental orthopedics turns you off due to the need to sharpen adjacent units, there is a way out! In this case, give preference to the adhesive method of orthopedics. This technique is more gentle and eliminates the negative impact on supporting teeth.
How does the process of dental orthopedics work?
Regardless of the type of product, any dental element must be manufactured individually, taking into account anatomical features. Dentures are made in a laboratory.
- The patient must come for the first consultation, during which the doctor will help determine the choice of type of prosthetics, and may also prescribe additional tests.
- On the same day, an x-ray is taken to assess the condition of the oral cavity and bone tissue.
- Next, the preparatory process usually begins, which includes the necessary procedures to eliminate diseases of the teeth and gums.
- Then an impression of the teeth is taken, from which the technician makes a plaster mold, on the basis of which the entire structure is cast.
- Once the prosthesis is ready, it needs to be tried on, the dentist will look at how well the structure fits, and the patient will point out the shortcomings that need to be eliminated in the laboratory.
- The final stage will be the final installation of the orthopedic structure in its place. If this is a removable denture, then the dentist will help with installation the first time, but in the future the patient will no longer need additional help and will independently cope with its installation or removal.
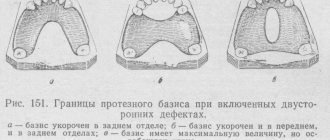
Classification of prostheses
Orthopedic treatment of various diseases has constantly improved, and along with it, the designs of dentures used have improved. The variety of prosthetic structures has prompted researchers to begin classifying them. However, serious difficulties were encountered here. This is explained by the following reasons. Firstly, prostheses are used to restore defects of the masticatory apparatus and the face of various etiologies. Secondly, the clinical picture is diverse and even with the same localization of the dentition defect in different patients, it can have fundamental differences. This places corresponding demands on the prostheses in terms of design. If we add to this that the materials from which prosthetics are made are different, the wide variety of their types becomes clear. Until now, it has not been possible to create a classification that would take into account all the features of dentures, both from a medical and technical point of view. Most often, the classification was based on one of the characteristics of a prosthesis (removable or non-removable, preventive or therapeutic), which, naturally, gave rise to an abundance of very different taxonomies of prostheses.
The oldest classification divides dentures into removable and fixed, and according to the nature of the design - into plate, bridge, arch (clasp), pin, single crowns, inlays, etc. This classification has been repeatedly criticized, since it is based mainly on the design features of dentures and ways to fix them. Other classifications have been proposed. Thus, K. Rumpel divides all prostheses into preventive and functional. The first group includes prostheses that are used to prevent any disease. Functional dentures are needed to restore chewing function. This division is arbitrary, since preventive dentures can also, to some extent, take part in restoring chewing function, although this is not their most important purpose. On the other hand, functional prostheses can also solve preventive problems.
K. Rumpel divides functional prostheses, in turn, into physiological, semi-physiological and non-physiological. He classifies the first as fixed dentures, which transfer chewing pressure to the teeth, and the second - dentures, in which chewing pressure is transferred to both the teeth and the mucous membrane. These types of prostheses include arch ones. K. Rumpel considers the third group (non-physiological dentures) to be removable laminar dentures, in which chewing pressure is transmitted only to the mucous membrane.
However, this classification in its last part also suffers from a serious drawback, since not a single prosthesis can be either “physiological” or “semi-physiological”.
I. A. Betelman suggests replacing the term “physiological” with the term “dental”, “non-physiological” with the term “gingival”, and “semi-physiological” with the term “dental-gingival”.
I. M. Oksman, in accordance with the location of defects in the dental system, distinguishes:
- 1) prostheses that replace defects in hard dental tissues;
- 2) prostheses that replace dental defects;
- 3) dentures for toothless jaws;
- 4) dentofacial prostheses.
Despite the existence of various classifications in general medical practice, as we have already mentioned, the most common classification is based on the principles of fixation and technical features of prostheses. Design features refer to the properties of prostheses, on which their therapeutic qualities largely depend. Therefore, no classification can exclude them if it claims to be widespread.
Contraindications and disadvantages
Like any other medical service, dental orthopedics in general has some contraindications. However, most of them are temporary. For example, any disease of the body in the acute stage. Of course, after recovery a person can begin prosthetics.
Fixed dentures have many advantages, but there are also disadvantages:
- They have a high cost compared to the removable option.
- It is necessary to grind the supporting units. Their appearance after the procedure leaves much to be desired.
- Not suitable for all patients. There are some contraindications.
Removable:
- Visible in the oral cavity.
- They get in the way when worn and sometimes rub the gums.
- There is a risk of jaw tissue atrophy.
- Moral discomfort, the patient constantly worries that the false jaw may fall out.
- Insufficiently stable fixation.
The following indirect factors also include contraindications:
- Pregnancy and lactation period.
- Prohibition of any type of anesthesia.
- Oncological diseases.
- Nervous system disorders.
- Minor age.
- Various blood diseases.
- Human immunodeficiency virus or complex diabetes mellitus.
Please note that indirect contraindications are relevant only for fixed structures. False teeth, which can be easily removed from the oral cavity, have no indirect contraindications for manufacture and installation.