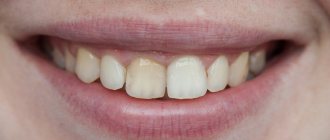
Human teeth are bone formations located in the oral cavity on both jaws, making it possible to grasp, bite and then grind, that is, chew food. Thanks to the teeth, the first stage of mechanical processing of food occurs. High-quality crushed food is well digested in the gastrointestinal tract with the absorption of all microelements necessary for human life. That is why it is so important to have healthy teeth, monitor their condition and consult a dentist on time. Teeth play an important role in the formation and production of correct human speech, so it is important to pay attention to dental health from childhood.
Why do you need to get rid of pathology?
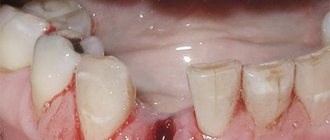
Due to the rotation, the cutting part of the tooth constantly injures the mucous membranes of the cheeks and lips. In this regard, patients often suffer from recurrent stomatitis. They develop trema or diastema and have trouble biting food. Therefore, the teeth must be returned to their natural position, and this should be done as early as possible.
- Tortoanomaly usually occurs in childhood. If a child regularly visits the dentist, the pathology will be detected in a timely manner and quickly eliminated. At the milk stage and at the beginning of the formation of a mixed bite, when the jaw bones are still developing, it will not be difficult to rotate the tooth so that it takes its normal position.
- In an adult with an already formed dental system, turning around will take a lot of time. Moreover, depending on the degree of development of the pathology, even surgical intervention may be required.
Treatment of crooked teeth
All video presentations
Treatment of crooked teeth is a complex orthopedic procedure that includes 4 stages.
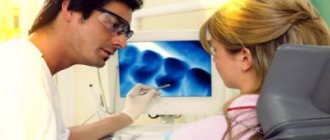
Stage 1 – panoramic shot
At the first stage, diagnostic measures are carried out and the complexity of the upcoming therapy is assessed. Most often, the patient has to undergo a teleroentgenogram or otropantomogram (panoramic image).
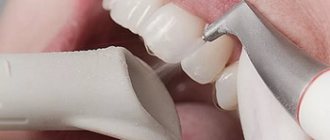
Stage 2 – teeth cleaning
At the second stage, complete sanitation of the patient’s oral cavity is performed. The hygienist thoroughly cleans the teeth, removes tartar, treats carious cavities and remineralizes the teeth.
Stage 3 – braces or children’s plate
At the third stage, the curvature of the dentition is corrected using fixed and removable orthopedic structures. Silicone mouth guards and plastic plates are most often used as removable devices. Most often, such designs are used to treat children. Correction of crooked teeth in adults is carried out using non-removable orthopedic devices - braces. In this case, braces can be either metal or “aesthetic” (sapphire, ceramic or plastic).
Stage 4 – fixation with a retention apparatus
At the fourth stage of treatment, the plate or braces are removed, and a so-called retention device is installed instead. This device is used to consolidate the effect of the therapy.
Features of diagnosing dental anomalies
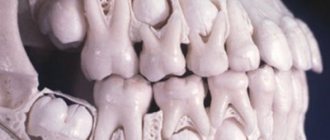
The diagnosis is made even if the tooth is rotated only a few degrees around its axis. Cases of turning at an angle of up to 45° are classified as minor, and all others are classified as significant. The maximum rotation angle of the dental crown is 180°.
To diagnose and develop a pathology correction program, the patient may be prescribed:
- X-ray of the problem area;
- orthopantomogram, which allows assessing the quality of tissue;
- anthropometric analysis, during which, using specially prepared models of the patient’s jaws, the parameters of the components of his dental system are determined and their relationship is analyzed.
Diagnostics makes it possible to identify the cause of tortocclusion and develop a treatment program that corresponds to the degree of its severity and the condition of the dental tissues. When the teeth are rotated by 10–20°, they resort to straightening the teeth with braces, a trainer or a plate. When the angle is 20–40°, special orthodontic devices based on a spring arch and elastic rings are used. In even more complex cases, orthodontic treatment is combined with surgical treatment.
The relationship between teeth and internal organs
- By any, even the most insignificant tooth decay, you can determine which organ is not in order. By the upper and lower incisors (1-2), for example, the condition is judged:
- kidney
- Bladder
- ears.
Fangs (3) are “responsible” for the liver and gall bladder, molars (4-7) for:
- stomach
- spleen
- lungs
and the so-called wisdom teeth can tell about the condition of the heart and small intestine.
— Is it possible to determine by the nature of tooth damage which organ is sick and what exactly is sick?
- Yes. Let's take, for example, pulpitis. This is the most unpleasant dental disease. It is this that makes people want to “climb the wall” - this pain is so unbearable.
Pulpitis, in essence, is inflammation of the dental nerve. If you look at which tooth is affected by pulpitis, and then determine the corresponding organ using the diagram, you can make a preliminary diagnosis - gastritis, colitis, cholecystitis.
caries has become a very “popular” disease recently . If you have discovered this disease in yourself, you can easily find out which organ needs treatment: the diagram indicates the liver - you most likely have hepatitis, the stomach - gastritis or an ulcer, and if the decayed tooth correlates with the ears, then it may develop otitis media.
In general, toothache is a kind of signaling about problems in the human body. Love your teeth.
Why does thorotoanomaly occur?
Most often, the tooth is forced to take a pathological position due to lack of space in the jawbone due to macrodentia (large teeth in relation to the bone) or an excessively narrow jaw. In this case, it tends to turn around so as to take up as little space as possible, and the minimum will be achieved when turning at an angle of 45°. But pathology arises not only due to the primary lack of free space.
- The crown can rotate in the socket due to constant pressure exerted on it from the side or below, either by a supernumerary tooth, or by complete “neighbors” that erupt not entirely physiologically - for example, with a delay.
- Quite often, erupting permanent teeth unfold due to the persistence of the milk teeth that precede them. If during the period when baby teeth fall out, the “old” one is in no hurry to fall out, then the “new” molar will have to bypass the obstacle, deviating to the side or turning around the vertical. Pathology can be avoided by timely removal of worn-out milk teeth.
- Sometimes the cause of non-physiological tooth eruption is a dental follicle that is incorrectly formed during pregnancy or in early infancy.
- Often a permanent tooth rotates as a result of a mechanical injury received by a child at the stage of changing the primary bite to a permanent one.
Negative consequences of crooked teeth
Inflammatory processes of teeth
It is important to understand that in places where teeth are crowded, the most favorable areas are created for the concentration and proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. Even an experienced dental hygienist is often unable to clean hard-to-reach areas. That is why the presence of crooked teeth often becomes one of the factors contributing to the development of inflammatory processes.
Periodontal disease and premature tooth loss
It is also worth noting that crooked teeth prevent the uniform and correct distribution of the natural load on the dentition. As a result, some groups of teeth take on increased load from the masticatory muscles, while others receive less of it. Incorrect distribution of the load entails atrophy of certain areas of the periodontium, the development of periodontal disease, loosening and premature loss of teeth.
Pathology in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract
Incorrect load distribution also leads to a decrease in the functional efficiency of the dentofacial apparatus. As a result, insufficiently chewed food constantly ends up in the human stomach. The digestive system begins to work intensively, which ultimately leads to the appearance of various malfunctions and pathologies in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
How to remove gaps between teeth?
Modern dentistry offers the following options:
- Veneers. They are dental onlays attached to the front surface of the patient's teeth. Their main purpose is to correct the aesthetics of the dentition without the need for orthodontic treatment. Veneers are made in Moscow strictly individually in a dental laboratory. At the first stage, the patient’s tooth is ground down (a thin layer of enamel is removed), and an impression is made of it, which serves as a sample for creating a veneer. Making a veneer takes from 7 to 14 days, during which time the patient wears temporary veneer structures. After the permanent veneers are made, fitting is carried out, their compliance with aesthetic standards and the wishes of the patient is checked, if everything is good, the specialist fixes the veneer. The advantages of this option include the ability to correct even wide gaps between teeth in the shortest possible time.
- Bracket systems. The safest, high-quality method, loyal to dental tissues, but also the longest. To correct the bite, braces are used. If the patient is a child whose baby teeth have only recently been replaced by permanent teeth, braces are the best option. Modern braces are almost invisible, so they do not cause discomfort in everyday life. In addition, you can always order lingual braces, which are attached to the inside of the dentition, which means they are absolutely invisible. The time for wearing braces is determined by the dentist individually in each case - the timing depends on the structure of the teeth, the age of the patient, the size of the gap and other factors. Usually we are talking about a time range from six months to two years.
- Artistic composite restoration. This is the most preferred method when it comes to eliminating gaps between fangs, incisors, and slight curvature. Composites are photopolymer elastic materials that are applied layer by layer and harden under a photopolymerizer (special lamp). The advantages of artistic dental restoration include the speed of achieving results (restoration takes up to half an hour to two hours), the absence of painful sensations for the patient, and the absence of the need to grind down tooth enamel.
The above are not all the ways to get rid of gaps between teeth. Perhaps your dentist, having assessed the condition of your oral cavity, will offer you a more effective and/or profitable alternative - this could be a plastic transparent mouthguard (easily removed, allowing you to combine the adjustment of the position of your teeth with their whitening), corrective fillings or crowns.
Anomalies in the shape and size of teeth - symptoms and treatment
Anomalies in the shape and size of teeth are variations in the development of teeth and the dental system that deviate from the norm.
Malformations of the dental system are divided into major (congenital) and minor. Congenital anomalies include facial clefts, such as cleft lip, cleft palate, etc.; to small ones - anomalies in the eruption, number, shape, size and structure of teeth. Unlike congenital malformations, minor anomalies are not accompanied by significant impairments and do not threaten the patient’s life, but they significantly affect the aesthetics of the tooth and treatment tactics, and can also lead to caries, malocclusion and other complications [1].
This article describes frequently occurring minor anomalies in the shape and size of teeth: macro- and microdentia, fusion of teeth, etc. Absolute and relative indicators of their frequency and prevalence are shown in the table below [11].
| Types of anomalies | Anomaly subtypes | Frequency of anomalies in the population (%) | Prevalence of anomalies (%) |
| Size anomalies | Macrodentia | 0,42 | 0,16 |
| Microdentia | 7,87 | 3,08 | |
| Shape anomalies | Fusion and fusion of teeth | 0,21 | 0,08 |
| Taurodontism | 11,27 | 4,41 |
Subtypes of anomalies and reasons for their development
All anomalies in the shape and development of teeth can be formed under the influence of negative factors that disrupt the development of fetal tissues and organs during pregnancy. These include:
- medications;
- nutritional supplements;
- viruses;
- industrial poisons;
- alcohol;
- tobacco smoke, etc.
Macrodentia is characterized by an increase in the size of the teeth - a large crown and a tapering root. It can affect both all and individual teeth [5]. The prevalence of macrodentia in permanent teeth is 0.03-1.9%. This pathology occurs more often in men. The large size of the crown causes problems with teething and leads to deformation of the dentition [9][10].
Microdentia is characterized by the reduction of one or all teeth [6]. According to epidemiological studies, the prevalence of the anomaly ranges from 1.5% to 2%, and is more common in women than in men [19]. Teeth with this pathology usually have a cone shape.
Macro- and microdentia can be hereditary. Since the formation of follicles (buds) of permanent teeth occurs at different times, starting from the 5th month of intrauterine development and up to 3 years, the number of abnormal teeth will depend on the impact of negative factors during this period.
Taurodontism (bull tooth) refers to abnormalities in tooth shape. It manifests itself in the form of an enlarged pulp chamber - the “core” of the tooth, consisting of connective tissue, nerves, blood and lymph vessels. The base of the pulp moves closer to the apex of the tooth, and there is no narrowing at the level of the cemento-enamel junction [12].
Taurodontism can occur at any age; it is most often found in patients 13-19 years old [11]. As a rule, the anomaly does not appear before this age, since the roots of permanent chewing teeth form before the age of 13.
Dental evagination (protrusion) affects the crown of the tooth. The anomaly occurs during the period of formation and formation of tooth buds. It appears in the form of an additional tubercle that protrudes from the crown of the tooth. This tubercle consists of enamel and dentin. Its size, structure and location vary widely. It can be horny, conical or pyramidal in shape. Otherwise, such an anomaly is called a tuberculate protrusion, a claw-shaped tubercle, a Leong premolar, and an occlusal enamel pearl.
The reasons for the development of evagination are not fully understood. The influence of X-linked and autosomal dominant inheritance is assumed [2]. With X-linked inheritance, the anomaly appears only in men, and women are only carriers of the mutant gene. With autosomal dominant inheritance, boys and girls with dental evagination are born equally often, and at least one of the child’s parents also has this anomaly.
Dental invagination causes the enamel to retreat into the dental crown. Otherwise, such an anomaly is called a “tooth in a tooth.” Intussusception occurs before calcification of dental tissues during fetal development [13]. It can affect any tooth, but most often occurs on the upper lateral incisors (front teeth).
Is it painful to have a wisdom tooth removed?
Is wisdom tooth extraction accompanied by pain? This is one of the most common questions.
The fact is that very rarely “eights” grow healthy; usually their eruption causes pathological processes that are dangerous to the patient’s health, so their removal is required. Surgical removal of the “eight” is always accompanied by pain, the process is especially difficult due to curvature and other disorders of the third molar. The procedure must be carried out with the use of painkillers. Most often, dentists use drugs based on articaine - “Ultracaine”, “Ubistezin”. The use of local anesthetics allows you to completely eliminate pain during surgery. However, the process of administering the drug itself may be accompanied by pain. In addition, when the anesthesia wears off (after about 6 hours), intense pain occurs.
Severe pain during the removal of the third molar is inevitable in cases where the patient has not consulted a specialist for a long time, the inflammatory process has started, resulting in purulent formations. Sometimes tooth extraction is performed under general anesthesia. In other situations, surgery is painless.
The upper “eights” are much easier to remove than the lower ones. This feature is due to the fact that wisdom teeth in the lower dentition have more powerful and sinuous roots. To properly carry out the procedure for removing the third molar, the dentist sends the patient for an x-ray before the operation.
Prevention of crooked teeth
The main measures aimed at preventing tooth curvature are:
- giving up the habit of touching growing teeth (including with the tongue);
- inclusion of solid foods (crackers, carrots, radishes) in the diet;
- giving up the habit of cracking nuts and seeds with your teeth, gnawing writing utensils and other hard objects;
- nasal breathing.
In addition, you can prevent the development of pathology by regularly undergoing preventive examinations at the dental clinic. The problem of crooked teeth is much easier to eliminate in the very first stages of its development.
Possible consequences
Dental defects must be corrected in a timely manner. On chipped teeth, the enamel becomes thinner, so they quickly turn yellow and soon acquire a brown tint. In addition, the cracks are filled with plaque, which mineralizes and becomes a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria. Because of this, the risk of developing caries, pulpitis, gingivitis and periodontitis increases.
Congenital dental anomalies also lead to various problems. Let's list the main ones:
- speech dysfunction,
- formation of mouth breathing,
- uneven distribution of chewing load,
- development of gastrointestinal tract diseases.
To avoid serious health problems and maintain the integrity of the dentition, it is necessary to correct uneven incisors.
Is it necessary to correct the diastema and what will happen if nothing is done?
The occurrence of this problem will require a mandatory consultation with a dentist. The doctor will examine the oral cavity and order an x-ray, and then select treatment to eliminate the diastema.
If the patient does not listen to the dentist’s recommendation and ignores the existing problem, he risks facing serious consequences:
- diseases of the dentofacial apparatus;
- problems with speech (lisp, whistling);
- periodontal diseases;
- tooth loss.