From this article you will learn:
- what may cause pain in wisdom teeth,
- what consequences can occur with inflammation in the area of the wisdom tooth,
- What to do if your wisdom tooth hurts very much.
If your wisdom tooth is very painful, the cause of the pain is most often associated with its difficult eruption (due to lack of space for eruption), as well as with inflammation of the gums above the wisdom tooth. In the latter case, patients, in addition to pain and discomfort, additionally complain of swelling and swelling of the gums, bad breath, low temperature, in some cases - painful swallowing and opening the mouth, and even less often - swelling of the cheek.
If there are no symptoms of inflammation (no redness or swelling of the mucous membrane over the wisdom tooth, as well as all of the above symptoms), pain is usually associated with the process of tooth movement. Indeed, if there is not enough space in the dentition, the erupting eighth teeth will put pressure on the 7th molars, which will cause a displacement of all the teeth in front - to the center of the dentition. If pain occurs in an already erupted wisdom tooth, then the cause is usually caries, pulpitis or periodontitis.
Difficulty erupting eighth teeth –
What to do if your wisdom tooth hurts - remove it or treat it? Features of wisdom tooth growth
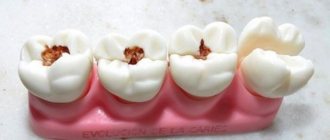
Due to the fact that eights (as wisdom teeth are also called) do not have milk precursors, their appearance and growth are accompanied by painful sensations. The wisdom tooth usually erupts at the age of 20-25, but there are cases of earlier or later “awakening”. This process is almost always accompanied by pain, which often radiates to the ear, causes inflammation of the gums, fever often rises, etc. Patients at the dentist complain that during the eruption of a wisdom tooth, they feel discomfort in the gums. A person must have 4 wisdom teeth: 2 on the lower jaw and 2 on the upper jaw. They are located at the ends of the dentition. Sometimes during teething there is no pain at all, but these are quite rare cases.
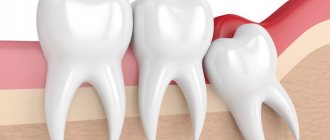
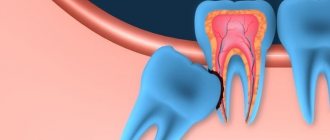
The development and direction of its growth cannot be predicted. It can erupt at an angle at which it simply cannot take its place in the dentition, or there is not anatomically enough space for a wisdom tooth to be there painlessly.
This development of events is called atypical; in this case, it must be removed so as not to provoke inflammatory processes in the gums and not to negatively impact neighboring teeth.
There are 4 subtypes of atypical wisdom teeth: distal, when it grows in the opposite direction to the other teeth, mesial, which climbs onto existing teeth, horizontal, when the tooth is located perpendicular to all other teeth, and vertical, which cannot hatch and sits tightly at the end of the tooth. row.
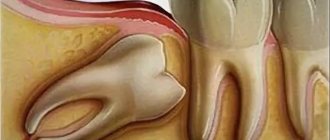
When a wisdom tooth hurts, it happens that the mouth does not open sufficiently due to severe spasm of the jaw muscles or severe pain that blocks its natural movement. If it grows crookedly, then you definitely cannot avoid painful sensations. Sometimes there are cases when a wisdom tooth pecks correctly and grows evenly, but at the same time the gums cover it greatly due to lack of space. This phenomenon is called “wisdom tooth hood.” In this place, there is often an accumulation of pus and the proliferation of various bacteria. Due to the inaccessibility of this place, the measures taken to clean and disinfect it will be only temporary.
Possible complications
If dental pathologies are not treated in a timely manner, a person risks facing unpleasant consequences :
- Teeth will react to sweet, salty, hot and cold foods. The pain syndrome after consuming unwanted products sometimes does not go away for days.
- A person will face the development of tooth decay, the formation of holes, and the destruction of enamel.
- An unpleasant odor will emanate from the mouth, which is difficult to remove with chewing and absorbable drugs.
- An untreated inflammatory process can develop into a cyst or phlegmon.
Attention! In the absence of competent therapy, the patient runs the risk of periostitis, abscess and bone atrophy.
Consequences of failing to see a doctor promptly
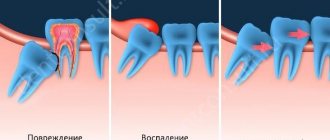
If you turned to a specialist for help late, then most likely you may subsequently encounter pathological phenomena in the oral cavity such as caries of the wisdom tooth itself or adjacent teeth, the development of various periodontal diseases, pericoronitis, displacement or significant damage to neighboring teeth.
During the active stage of growth, the gums may bleed, it becomes painful to swallow, and when you press on the gums, purulent discharge is possible.
There are also frequent cases when the cheek, tongue, gums are swollen as a result of pathogenic processes, or even the lymph node is inflamed.
The eruption of a wisdom tooth often provokes fever and severe headache, which can only be relieved with painkillers. This process cannot be started, as this will lead to the early loss of 7 teeth in a row that are in contact with the wisdom tooth. There is also compaction of the soft tissues of the gums or cheeks, cysts, neuritis, crowding of teeth, leading to their modification and degeneration, developing into benign or malignant neoplasms, inflammation in the bony part of the jaw is also common.
In general, when a wisdom tooth hurts, this is a direct signal that you need to act quickly! Only a dentist can help you solve this problem quickly and as efficiently as possible.
Treatment of wisdom teeth during pregnancy
When a wisdom tooth hurts in pregnant women, this makes additional adjustments to the treatment process, since due to the mother’s need for a large amount of calcium, its lack can accelerate the development of caries and periodontal disease.
Failure to promptly address these problems can cause the growth and spread of pathogenic microorganisms, which can adversely affect the development of the child. Such processes during pregnancy are extremely undesirable.
In order not to provoke the occurrence of the above-mentioned negative phenomena, most often, if it grows incorrectly, putting the neighboring teeth and cheek at risk, squeezing the nerve endings and disrupting the bite, doctors decide to remove the wisdom tooth in the pregnant woman.
Before this operation, the doctor will direct you to take an x-ray in order to find out the location of its roots in the dentition. After this, an incision is made in the gum and the wisdom tooth is removed from the socket in the jaw.
This surgical intervention occurs under local anesthesia. The operation can be performed from the 13th to the 32nd week of pregnancy, the first 2 months and the last such treatment procedure is prohibited. To avoid an additional stressful situation for the mother and fetus, painkillers have been developed that do not have negative consequences, but still, this problem is best avoided by carrying out preventive examinations before conception. After the operation, a rehabilitation period begins, which should promote the fastest healing of the wound. Rinsing the mouth with medicinal decoctions, disinfection using medications prescribed by the dentist, and avoiding burning drinks and food during this period will be mandatory attributes. Brushing the teeth closest to it is also prohibited for a couple of days.
It is no secret that during pregnancy, interference with the natural processes that occur in the body is extremely unacceptable. This postulate applies to various types of operations, even minor ones (such as tooth extraction).
Loss of blood, severe pain, and general ailments cause additional stimulation of the defense mechanisms in our body, which provokes depletion of vitamin and mineral reserves, which in turn can negatively affect its recovery. All this can negatively affect the development of the fetus.
The occurrence of pain
The reasons why a wisdom tooth hurts can be different and the formation of a painful condition is explained by various anatomical and physiological features of the structure of the dentition and possible inflammatory processes that accompany the eruption of a wisdom tooth.
Sometimes it grows, and due to the incorrect angle of its position, it simply puts pressure on neighboring teeth, gradually shifting them towards the center.
It happens that there is simply not enough space for a tooth to fully develop, which gives it the “green light” to deform the intramaxillary space and the ability to grow in any direction.
It also aggravates the pain and the development of pathogenic microorganisms, which only intensify the discomfort. Also, due to its remoteness, inflammatory processes develop faster, and it is more difficult to maintain the necessary hygiene in these places.
When a wisdom tooth hurts badly (if this does not concern the first manifestations of its eruption), then there is a high probability that this is provoked by the formation of some kind of disease that has arisen against this background.
During caries, pain appears after eating sour, hot, spicy or cold food. If these factors are eliminated, the pain should disappear.
In chronic and acute pulpitis, the pain is very different in nature. The acute form is characterized by sharp attacks of pain, which tend to intensify at night. Purulent pulpitis has symptoms of throbbing wave-like pain. In chronic forms of this disease, the pain is aching and periodic, lasting 10-15 minutes.
With periodontitis, wisdom teeth hurt in different ways (the intensity directly depends on the stage of development of the disease). Often pain goes hand in hand with inflammation of the gums, swelling of the cheeks and soft tissues in the mouth, fever and sleep disturbances. In its chronic form, periodontitis rarely bothers a person with pain.
In any case, to accurately diagnose the causes of pain in the wisdom tooth area, you will have to contact an experienced dentist. Doctors recommend that eights be examined every 3-4 months.
Diagnostics
A comprehensive examination of the condition of teeth and soft tissues is considered the main step before starting competent dental treatment.
Lack of diagnosis leads to incorrect selection of drugs and the development of adverse reactions. Research methods are prescribed on an individual basis, depending on the patient’s health condition.
The universal rules of examination include:
- Taking an anamnesis , talking with the patient about the symptoms that bother him, visual inspection of the problem area, palpation of painful areas.
- Inspection and verification of installed fillings and prostheses.
- Checking occlusion , identifying jaw defects, detecting injuries to gums or teeth.
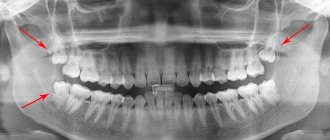
- X-ray diagnostics . The procedure helps to assess the condition of soft tissues, identify irregularities, inflammation and various pathologies. X-rays are used to detect hidden cavities. The procedure helps to evaluate the shape of the canals and find out their number.
- Targeted radiology . The procedure is carried out using a radiovisiograph, which helps to assess the internal condition of the teeth. The resulting image is of good quality and allows you to carefully examine the problem area.
- Panoramic shot . During the process, the patient is given a detailed photograph, allowing the condition of two jaws to be assessed at once. Using a panoramic image, the doctor has the opportunity to carefully examine the tissues surrounding the diseased tooth. This diagnostic method helps to detect the first signs of caries, inflammation, damage to the root system, and the development of cystic neoplasms.
- CT . Computed tomography is used to obtain more detailed information about the condition of the patient's teeth. Most often, this study is prescribed for serious jaw injuries, swelling, and purulent inflammation. Also, a CT scan will be required before implant therapy.
- Electroodontometry . The procedure helps determine the condition of the pulp located in the pulp chamber of the tooth.
Reference! In some cases, the fluorescent method, temperature tests, and special colored markers are used to assess the condition of teeth.
Remove or treat?
In addition to difficulties in maintaining hygiene, in the remote corners of the dentition where wisdom teeth are located, there is also a problem in their treatment, all for the same reason (their location).
Manipulating medical instruments can also be difficult.
In cases where normal treatment is difficult, the dentist considers the need to remove the figure eight.
To make the right decision, there are a number of indications and contraindications for wisdom tooth removal. X-rays give a clear picture of whether there are positive prospects for treatment, or whether it is easier to remove the wisdom tooth.
There is a myth that the purpose of wisdom teeth is that they are the last to fall out in old age and can prolong the process of fully chewing food.
The modern scientific approach allows us to look at the wisdom tooth rather as a rudimentary part of the oral cavity, which over time has lost its true purpose and value (like the appendix).
In fairly rare cases, eights (wisdom teeth) grow straight or, if slightly displaced, can be treated. In most cases, an adequate therapeutic effect on them seems extremely irrational. Their appearance will be especially unpleasant for those who have spent a lot of time and money straightening their teeth. The appearance of neoplasms in the oral cavity can disrupt previously taken measures to restore the aesthetic “order” of your teeth.
So in the vast majority of cases, when a wisdom tooth hurts, and even entails the formation of concomitant diseases, the dentist decides to remove the eight.
A wisdom tooth is certainly needed if it has an antagonist tooth and is involved in chewing, occupying the correct position in the dentition.
The correct position is especially important - it happens that the tooth has not fully erupted, is bent in one direction or another, or is generally tilted towards the cheek.
If we talk about the lower right wisdom tooth, then its antagonist will be the upper right wisdom tooth, with which it intersects. Removing one of the pair leads to the other moving out of the jaw down or up, and the subsequent loss of this tooth as well. Therefore, if a wisdom tooth occupies its normal place in the jaw, is involved in the act of chewing and has an antagonist tooth, then it is not advisable to remove it. But this state of affairs is extremely rare in medical practice.
Causes of cheek pain
During the growth of the last teeth, pain in the cheek may occur, the causes of which are:
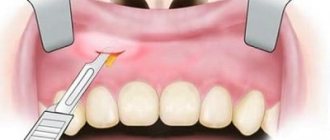
- The outer teeth may be partially covered by gum skin, under which food particles accumulate and bacteria multiply. This place becomes inflamed and festers over time. Festering quickly spreads through soft tissues. In some situations, it is better to remove the tooth. To save a tooth, the skin over it is opened and the sore spot is treated.
- When the growing last tooth does not have enough space on the gum line, it can change the direction of its growth and deviate towards the cheek . The mucous membrane of the cheek is constantly injured, a wound and pain appear. Harmful microorganisms multiply in the wound, inflammation occurs, followed by swelling of the cheek. In this episode, the tooth is removed.
Wisdom tooth removal
When a wisdom tooth hurts, a person is ready to take extreme measures to get rid of this unpleasant sensation. This is how mistakes occur that can lead to unpleasant consequences, so self-medication is strictly prohibited. The doctor will most likely recommend removing it, so be prepared for this.
Due to their inconvenient location, figure eights often begin to form various pathogenic microorganisms faster than the dentist can sometimes notice. Such auxiliary factors for the development of unpleasant complications as sudden climate change, decreased immunity, colds, etc. I can trigger chronic disease mechanisms that will be periodic and disturb a person from time to time for many years.
The main prerequisites for the removal of a wisdom tooth are: its incorrect position in the dentition, lack of space for it to break through, the figure of eight negatively affects the tooth located nearby and inflammation of the “hood” under which it is located.
If a person has a strong nervous system, then before removal he is given local anesthesia, which will make the surgical intervention painless. General anesthesia is administered extremely rarely (for phobic fear or possible fainting). The tooth and its “surroundings” are treated with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory agents only in the presence of suppuration. In normal cases, the operation lasts about 10 minutes.
After a wisdom tooth is removed, the hole that remains is sutured. If the removal of the wisdom tooth was completed without complications, then the patient is prescribed antibiotic therapy, baths with antiseptic agents, and a return visit to remove the sutures and undergo an examination. In case of complications, to remove it, it is possible to cut the gums, drill out the bone tissue with further suturing of the soft tissues, etc.
Pulsations in the tooth not associated with dental problems
Pulsating sensations in the area of the teeth and gums do not always signal dental problems. Negative symptoms appear in the following diseases :
- stomach diseases . When the gastrointestinal tract is not functioning properly, erupting wisdom teeth most often pulsate. In addition, the patient’s general condition worsens;
- liver failure . With liver diseases, patients often experience throbbing pain in the area of the upper canines;
- sinusitis . With sinusitis, the teeth in the upper row pulsate. In addition, the patient has pain in the jaw and temporal area.
Pain syndrome may also indicate a lack of oxygen due to heavy physical activity and disease of the central nervous system.
Restorative procedures after removal of the figure eight
It must be remembered that after the removal of the figure eight, the wisdom tooth (more precisely, the place where it grew) hurts for some time. Even phantom pain is possible, but in rare cases. A person who has had this tooth removed must refuse to eat for the first 3 hours; they can drink drinks at room temperature. The doctor prescribes antiseptic drugs and medicinal herbs, which should be used to rinse the area in the first 24 hours after surgery.
Ice, which can be applied to the site of wisdom tooth extraction in the first hours after removal, will have a mild antibacterial and analgesic effect. Also, baths with various medicinal compositions will bring the desired effect (take the solution into your mouth and hold for about 1 minute).
Antibiotics and painkillers should be used strictly as prescribed by the attending physician. After the time recommended by the dentist has passed, you will need to come back to have the sutures removed.
Expert opinion
Emir Romanovich Omerelli
Maxillofacial surgeon, implantologist
Experience: more than 13 years
Whatever pain relief option you choose, it is important to remember that the absence of pain does not mean the absence of problems. The best option for a person with acute pain is to urgently come to the dental clinic. Moreover, acute pain is a reason for appointment out of turn and without an appointment. Timely correction of the situation - treatment or tooth extraction - will minimize the harm caused to the diseased organ of the oral cavity and the entire body as a whole.
Relieving pain
And yet, if you have wisdom tooth pain, and you do not have the opportunity to urgently go to the dentist, you need to know the basic important measures, by taking which you can, in a short period of time, partially or completely stop it. You can use herbal decoctions for rinsing the mouth based on oak bark, tincture of sage, chamomile, calendula, turnip, chicory root, propolis, etc.
It cleanses the inflamed area very well and washes it when a wisdom tooth hurts, using a solution of soda and applying a cold compress. A drug such as Maraslavin is often used in dentistry; it can be purchased at almost any pharmacy. To relieve pain, you need to moisten a cotton swab and apply it to the area that is bothering you. This procedure can be repeated 4-8 times a day. This will definitely bring temporary relief.
Chlorhexidine and Eludril are excellent at fighting bacterial growth.
Anti-inflammatory drugs such as Paracetamol, Ibuprofen and Nimesulide will help if you also have a fever along with wisdom tooth pain. These medicines, together with the use of herbal products, will reduce the fever and produce an antibacterial effect. Analgin can be used with local anesthetics to relieve pain.
All of the above measures will only bring a temporary effect until you seek help from a professional dentist to eliminate the causes and consequences of painful sensations associated with the breakthrough or activation of acute or chronic diseases of a given tooth.