Content:
- Why is it necessary to replace baby teeth with permanent ones?
- When do the first baby teeth fall out?
- Which baby teeth fall out first?
- Drop order
- At what age do radical units appear?
- Possible abnormalities in the child
- Why do empty spaces remain unoccupied for a long time?
As the child grows, the baby teeth are replaced by permanent ones. This is a natural process, without which the full functioning of the dentofacial apparatus is impossible. But parents should treat it with the utmost responsibility, since very often violations in the sequence of loss of temporary units cause serious malocclusions that have to be treated in the future.
Change process
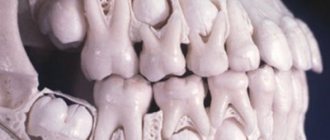
The jaw of a child under 5 years of age is distinguished by a small jaw arch , which is not capable of accommodating the entire set of full-fledged molars. Therefore, it is first filled with temporary crowns, which are characterized by their small size and thin, shortened root.
They prepare the gums for secondary eruption and determine the location in the jaw arch for permanent teeth. During the process of replacement, the root of temporary teeth gradually dissolves and the crown part is only slightly retained by the gum tissue.
The permanent tooth, developing in place of the milk root, eventually pushes out the temporary crown .
The shift period begins at 5–6 years of age and ends at approximately 14 years of age.
The change occurs in the same order in which the eruption took place. Depending on the individual developmental characteristics of the child’s body, the timing of the loss of each crown may vary. The divergence period ranges from several months to 2 years .
Why is it necessary to replace baby teeth with permanent ones?
The chewing apparatus is improving and developing. In infancy, it is adapted exclusively for the intake of liquid food - breast milk. But closer to six months, you can already see baby teeth in children’s mouths. They allow the baby to get acquainted with the variety of solid adult foods.
There are few temporary teeth - ten pieces in each jaw. This is quite enough for the baby to eat well and talk normally. Closer to primary school age, the jaw grows. She is ready to cope with more serious chewing loads. Then children's incisors, canines and molars begin to wobble. They are replaced by a constant shift.
Clinical picture
Despite the fact that a temporary tooth, due to its anatomical structure, is considered prepared at the time of loss, this process is still accompanied by the formation of a wound and slight blood loss.
In place of the fallen crown, a shallow hole , covered with isolated areas of injured soft tissue. Basically, the separation of the crown from the gum occurs gradually, unnoticed by the child, and by the time it falls out, only small areas of the gum hold it in place.
Thanks to this, the change is almost painless . Minor tissue injury may be accompanied by minor and short-term bleeding .
As a rule, blood can be observed within 5 to 15 minutes after prolapse and in most cases stops on its own, without the use of special manipulations.
In addition to a slight bleeding, after the loss, there may be a slight swelling of the gums around the hole, which goes away within a day.
If the listed phenomena do not go away during the first day after the prolapse and increase the intensity of their manifestation, then this may be a signal of the onset of inflammation in the socket. In this case, you need to immediately contact a specialist for help.
What causes teeth grinding in their sleep in children and how to get rid of it.
This article describes how to treat oral stomatitis in children.
Does a child have a fever when teething at 2 years old? Find out here how to knock it down.
Which baby teeth fall out first?
According to the standard pattern for replacing baby teeth, the lower incisors are the first to fall out. They are located in the center of the jaw. They can loosen one by one or almost simultaneously.
Following them, the opposite upper units begin to move. This is why you can often see children five or six years old with a funny toothless smile.
Nutritional features during this period
When permanent teeth erupt, their enamel is not yet fully formed. This maturation process continues for several more years. During this period, high-quality and nutritious nutrition plays an extremely important role for children:
- Every day, your baby’s diet should include foods rich in calcium: cottage cheese, hard cheeses, milk.
- Twice a week you need to eat dishes made from fish, a source of phosphorus. For children, it is better to use low-fat varieties: hake, pike perch, pollock.
- Eating fresh vegetables and fruits, some of which should be in solid form. This is necessary to stimulate the resorption of the roots of baby teeth and the eruption of permanent teeth.
- Refusal of white pastries, chocolate and sweets. Sweet carbonated waters pose a particular danger to fragile enamel.
- Sometimes, when a child refuses dairy products, it becomes necessary to take multivitamin complexes containing calcium.
During the period of teeth change, too hard or sticky foods should be prohibited: nuts, candies, toffees. They can cause premature loss or injury of a baby tooth, which will lead to impaired growth of the molar. It is also undesirable for children to include in their diet foods containing active dyes, which can ruin the color of the enamel for the rest of their lives.
Drop order
The dropout pattern looks like this:
- 5-7 years - central incisors;
- 7-8 - lateral incisors;
- 9-11 - first molars of the upper jaw and second molars of the lower jaw;
- 9-12 - fangs;
- 10-13 - second molars of the upper dentition and first lower ones.
The diagram shows that the timing of changing units is quite arbitrary and quite long. This is why some children already have a permanent bite at the age of ten, while others still walk around at the age of 12 with actively loose baby teeth.
At what age do radical units appear?
We can talk about adult occlusion only a few years after the start of the change in time units. Typically, a stronger replacement will erupt several weeks or months (or, if pulled out prematurely, years) after the baby teeth fall out.
Central incisors grow from 6 to 8 years of age, lateral incisors from 7 to 9, premolars and canines from 9 to 12. Molars begin to grow at approximately six years of age. They immediately grow permanently, replacing the empty space.
What to do?
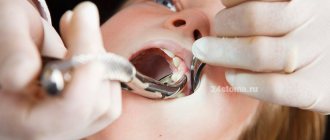
If a breast crown falls out, there is no need to immediately run to the dentist. In order to reduce the risk of infection in the wound and eliminate negative consequences, the following steps must be taken:
- Immediately after the prolapse, it is necessary to form a tampon from cotton wool or medical gauze and place it on top of the hole. The child should lightly press it with his teeth and fix it in this position for 15 minutes .
During this period, a blood clot is formed in the socket cavity, which performs protective functions. As the hole becomes overgrown, it will disintegrate on its own.
- During the day, you can irrigate the wound with antiseptic drugs .
- In order to relieve swelling, it is recommended to take baths with a solution prepared from ½ teaspoon of salt .
- Before eating, to minimize pain, it is recommended to treat the edges of the wound with lidocaine-based dental gel . For children, a special drug called calgel .
- You should not give your child food within 2 hours after a tooth falls out.
- On the first day, you should avoid eating foods at borderline temperatures, as well as foods high in acids.
Possible abnormalities in the child
Parents should know when to expect changes in their child's bite . Late change of baby teeth, like premature change, is undesirable. They speak of lateness when an eight-year-old child has not yet lost any of his incisors; they speak of early eruption if a five-year-old child has already lost many of his incisors and fallen out. It is important to find out the cause of the changes occurring and, if possible, eliminate it.
Factors due to which the bite changes earlier than standard periods:
- severe jaw injuries;
- congenital diseases leading to anomalies in the eruption of temporary and permanent units;
- advanced caries, due to which crowns and roots are destroyed faster than necessary.
As for a late shift, it is possible due to:
- rickets, calcium and vitamin D deficiency in the child’s body;
- hereditary characteristics of the dentofacial apparatus;
- some infectious pathologies.
Changing mechanism
It is necessary to say a few words about what the mechanism of tooth change in children is. The jaw of babies is small, so it cannot immediately accommodate the number of teeth a person needs
.
Baby teeth are a kind of guides for permanent molars. They are slightly smaller and slightly different in structure. After all, in order to grow completely, the crown part must first cut through the gum.
This is a rather problematic process - children are capricious, sometimes they can even develop a fever. Therefore, a mechanism is needed to prepare the gums for such an “operation.”
So, baby teeth prepare the gums for the appearance of permanent ones and “knock out” a certain place on the jaw for them. The rudiments of radicals are already present in a small organism from the very beginning. They are simply biding their time. This brings us to an understanding of the change mechanism.
Despite the opinion of many that only molars have roots, milk teeth also have them, only they are thinner and do not stick too tightly into the socket. The process of loosening begins after the primordia begin to grow. They destroy existing roots, thereby promoting hair loss.
From the above, we can conclude that after the loss of milk teeth, problems with growth and the appearance of molars in children may arise if their rudiments were somehow damaged
. This, of course, is not the only reason, but it is the most common.
Why do empty spaces remain unoccupied for a long time?
It often happens that a child walks around with a toothless smile for a long time, but the situation still does not change. When examining his oral cavity, the parents do not see even a hint of an imminent full bite. This happens when:
- Retentions. Dental pathology in which a segment of gum tissue is shown very little or not at all. The violation may be complete or partial. In any case, if it occurs, you should consult your dentist. Sometimes the situation can only be corrected through surgery.
- Edentia. The banal absence of a permanent germ. So, for example, a temporary fang falls out, and there is nothing to replace it with. The anomaly can be confirmed using x-ray diagnostics - the images show that the rudiment is missing. Fortunately, congenital adentia is rarely diagnosed in young patients. If it is, only prosthetics will save you.
- Impacts. Difficulties with eruption with this diagnosis are explained by the fact that the crowns of the “neighbors” are too close to each other and do not leave room for the crown, which should be between them. Deviations can also be detected using x-rays.
If there are any problems with the bite, parents should show the baby to the doctor. Moreover, children should have annual checkups at the dentist's office. This simple measure serves as an excellent prevention of serious complications and reduces the likelihood of an unattractive smile in adulthood.