From this article you will learn:
- timing of removal of temporary teeth,
- how this procedure is performed at the dentist,
- How to pull out a child's baby tooth at home.
Removal of a baby tooth is a surgical procedure that is performed in pediatric dentistry, for example, to remove “retained” primary teeth (i.e., those that have lingered in the oral cavity longer than they should). The second group of reasons that may require the removal of baby teeth in children is 1) some types of traumatic injuries, 2) with complicated caries, i.e. with the development of inflammation at the apex of the root of a baby tooth.
The physiological change of baby teeth to permanent ones normally begins in a child at 6-7 years of age (and in girls, the loss of baby teeth reliably begins earlier and proceeds faster than in boys). The last thing children lose is their temporary second molars, which should happen around 12-13 years of age. The appearance of mobility of baby teeth is associated with the growth of the rudiments of permanent teeth in the jaw. An increase in their size leads to pressure on the roots of baby teeth, which leads to resorption of the latter (i.e., their resorption).
Removing a baby tooth in a child: photo
Increasing root resorption over time leads to the fact that the baby tooth ceases to be fixed in the bone tissue of the jaw, and will be held only by the soft tissue of the gums. Parents are very often interested in how to pull out a baby tooth (for example, in a situation where a child’s baby tooth is very loose). This can be done quite simply only with strong tooth mobility, which will indicate that the roots of the baby tooth have been almost completely resorbed.
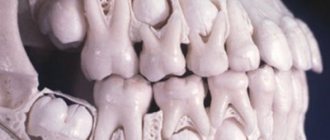
Pay attention to the timing of baby teeth loss in Table No. 1. Both teething and tooth loss (regardless of whether they are milk or permanent) occur in compliance with the timing, pairing rules, and sequence. Parents often ask: what to do in a situation where a molar is already growing, but the baby tooth has not fallen out. The fact is that sometimes the growth and eruption of the permanent tooth germ may occur in the wrong direction, and in this case the roots of the baby tooth will not undergo significant resorption (accordingly, there will not be much mobility).
Removal of baby teeth in children in such a situation can only be performed by a dentist (under local anesthesia or sedation). Believe me, you should not try to pull out a child’s baby tooth yourself if the tooth has only slight mobility or is immobile. The latter will mean that the roots of the baby tooth are not sufficiently resorbed and are still deeply embedded in the bone tissue.
Important: if the deadline for replacing a baby tooth has already arrived (see table), but the baby tooth has no mobility, and there are no signs of eruption of a permanent tooth, this may indicate the absence of a permanent tooth germ or its injury, or its death as a result development of inflammation at the roots of a baby tooth. In this case, the temporary baby tooth can remain for quite a long time, and this situation does not require its removal.
Features of tooth extraction in children
Pediatric dentistry is focused on the treatment and prevention of oral diseases. In this case, psychological support for the baby is important. Specialists must act delicately, instilling trust and relieving the child of fears. This is especially important in case of forced tooth extraction. Therefore, there are several unspoken rules of the pediatric dentist.
- Do not use the word “pain” or the particle “not.” Children do not accept denial and react sharply to unpleasant phrases.
- Do not discuss the details of the procedure in the office. Medical terms and unfamiliar words frighten the baby.
- Try to hide dental instruments from the eyes of the small patient. Forceps, packages of syringes and drill attachments can drive even the most courageous tomboy into hysterics.
This procedure requires high professionalism and great care from the doctor. With one careless movement, he can damage the germ of a new tooth and the tissue of the socket, which will cause a delay in eruption and various dentofacial deviations.
Features of anesthesia in children in dentistry
In pediatric practice, pain relief plays a primary role. If an adult patient is able to endure mild discomfort and spend several hours in a row in a chair, then the child’s psyche is not yet ready for this. A painful procedure can instill a lifelong fear of dentists and interfere with quality treatment. Moreover, anesthesia gives the desired psychological effect and helps the child trust the doctor.
Features of pain relief in children
- Most drugs can only be used from the age of four, which imposes severe restrictions on the treatment of very young patients.
- The anesthesiologist must be highly qualified and be able to correctly calculate the dosage.
- The child may be afraid of treatment and dental instruments, especially needles.
- Children are often allergic to anesthetics.
General indications for tooth extraction in children
The child’s dentition is formed according to certain patterns: the incisors erupt first, followed by the molars. Then the baby teeth are gradually replaced by permanent teeth. If this process occurs correctly, without deviations from the norm, there is no need to specifically remove baby teeth. However, there are situations when this is necessary:
- advanced caries;
- the last stage of development of a cyst on the gum;
- severe tooth injury;
- a tooth that fails to develop and erupt.
Removing a child’s front tooth is a particularly unpleasant procedure, as the aesthetics of the smile suffers. Usually, surgery is resorted to in the following circumstances:
- exposure of the pulp due to a fracture of the coronal part;
- severe tooth decay with the impossibility of prosthetics;
- inflammatory diseases that cannot be treated.
Most often, children have to part with their teeth in the chewing area. Molars are more susceptible to destruction than premolars and incisors. Removing a child's molars, which are the last in the dentition, is complicated by their inaccessibility and strength: they fit quite tightly to the gums, have wide roots and massive walls.
Sometimes children develop an anomaly such as an extra tooth, which can move the “neighbors” and lead to curvature of the entire row. If it does not interfere with the normal formation of the remaining teeth, you can leave it and try to integrate it into the bite, but most often they resort to removing the supernumerary tooth in the child.
The factors described above are the general and most common indications. Let us consider separately the reasons for the removal of baby and permanent teeth.
Indications for the procedure
Indications for removal may be as follows:
- deep caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, periostitis: the doctor will conduct therapeutic treatment, do everything possible for recovery, but if this is not possible, he may decide to remove it. Here it would be advisable to remind parents that baby teeth succumb to the destructive effects of bacteria much faster than adults. In this case, the baby may not show any concern, the process will proceed painlessly until the appearance of pulpitis and periostitis. To avoid the problem and not think about further prosthetics, you need to show your child to the dentist 3-4 times a year,
- cyst, root granuloma, fistula on the gum: the problem is that the inflammatory process on the root can most directly threaten the health and formation of the rudiments of the permanent element,
- loosening: if a baby tooth does not fall out on its own, but is very loose and interferes with proper nutrition, speaking and, in general, just living, then the procedure for its removal is unlikely to be avoided,
- keeping a baby tooth longer than expected: in this case, it may interfere with the eruption of the permanent unit and therefore must be extracted,
- serious injury: deep crack, root fracture as a result of a fall, mechanical impact,
- the presence of a supernumerary or additional tooth,
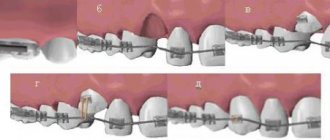
- the need to correct malocclusions using plates and other removable structures,
- eruption disorders: a milk element that has not fully erupted or is growing in the wrong direction will have to be removed if it threatens the health of the “neighbors”, the formation of the bite, causes pain and discomfort, or injures the mucous membrane.
Removal of baby teeth in children
Milk teeth maintain the gum contour and ensure proper development of the jaw and chewing muscles. Therefore, it is important to wait until they fall out on their own. Unfortunately, this does not always happen, and the dentist is forced to prescribe surgery if there are the following indications for the removal of baby teeth in children:
- the tooth is loose, but has not fallen out for a long time;
- the temporary tooth caused inflammation of the oral tissues;
- The permanent tooth has begun to emerge;
- a fistula has formed on the gum;
- a cyst appeared on the root;
- The tooth has decayed due to caries.
Removal of a child's front milk tooth may be associated with fractures, chips and other injuries, as well as inflammatory processes.
Is it necessary to treat minor caries in baby teeth?
So, we found out that the consequence of premature tooth extraction can be a disruption in the physical and emotional development of the child. But it is important to understand that even if you notice small caries on your baby’s teeth, you should consult a dentist. An untreated baby tooth can cause problems such as:
- Defective rudiment of molars. A diseased milk tooth can infect with caries the germ of the permanent tooth being formed underneath it. If the rudiment is damaged, there is a high risk of developing a defective tooth or its absence.
- Gastrointestinal diseases. It is teeth affected by caries that cause many somatic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Gastritis, duodenitis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, pancreatitis, dyspepsia, pancreatitis and other unpleasant diseases often develop against the background of damaged teeth.
- Development of diseases of the ears, nose and throat. Few parents know that caries provokes chronic runny nose, tonsillitis, sinusitis, inflammation of the tonsils and other respiratory diseases.
- Bad breath. Many parents wonder why their child has bad breath. The cause of the smell, as a rule, is precisely caries, invisible to the inexperienced eye. The baby begins to develop complexes and problems with communication appear.
- Pulpitis. Untreated caries will eventually transform into pulpitis, which means the child will suffer from pain and insomnia and will have to undergo painful treatment from a doctor.
Removal of permanent teeth
Removal of a permanent tooth in a child is carried out only in the following situations:
- Caries.
If the doctor sees that a decayed tooth cannot be treated, most likely he will suggest removing it. - Fracture.
A tooth fragment can injure the mucous membrane; it can either be restored or removed. - Crowding.
When installing braces or plates, it is sometimes necessary to remove one tooth to allow others to develop freely. - Complications after treatment.
Sometimes, after poor-quality dental procedures, problems arise that can only be solved by getting rid of the tooth.
Wisdom tooth removal
Typically, wisdom teeth appear at the age of 20 or older, but in some cases it is recommended to remove their buds. There are the following reasons for the removal of wisdom teeth in children:
- displacement of the follicle of the third molar;
- prerequisites for malocclusion;
- lack of space for wisdom teeth.
A specialist can recommend removal of a child’s wisdom teeth only after a thorough examination and consultation with other specialized doctors. You must first determine what position the molar is in and what place it will later occupy in the jaw.
Consequences of early removal of primary occlusion elements
Early removal of baby teeth is associated with certain risks: the presence of free space in the row will lead to displacement of the “neighbors”, which as a result can cause problems with the permanent occlusion.
Important! Early tooth extraction can be considered to be removal of a tooth more than a year before a permanent one appears in its place.
The absence of a chewing tooth can affect the characteristics of digestion, which is associated with insufficiently good chewing of food, the front one can cause speech defects and psychological discomfort in the child, difficulties in communication and low self-esteem. And do not forget that even at a young age, if one tooth is lost, the best option to solve the problem is temporary prosthetics.
Anesthesia for tooth extraction
In modern clinics, various types of anesthesia are used to remove teeth for children without pain. The specialist selects the appropriate drug in accordance with the severity of the clinical picture. During the operation, one of the following methods of pain relief is used:
- Sedation is putting you into a sleepy state to reduce anxiety.
- Application anesthesia - treatment of the gums with an anesthetic solution to remove a loose tooth or before injection.
- Local anesthesia is the administration of an anesthetic through an injection.
- Anesthesia is used in difficult cases and when removing teeth for a child under 2 years old.
Features of the use of anesthesia
I would like to dwell in more detail on the issue of pain relief during the removal of baby teeth. Anesthesia is not needed in all cases. So, when extracting a very loose temporary tooth, you don’t have to resort to it, since its root is already in a very mobile state, and the procedure will not cause pain. Sometimes, in order to carry out manipulations, the doctor uses superficial anesthesia - he pre-treats the area of influence with a special gel, which is most preferable for children psychologically.
For more complex procedures, three main methods of anesthesia are used:
- local or infiltration: involves anesthesia by administering an anesthetic with a syringe. The advantages of the method include high efficiency, the disadvantages are the allergenicity of many drugs, as well as the possible pain of the injection itself. In order for the procedure to go well, the doctor selects an anesthetic individually, based on the collection of anamnesis from the child’s parents. This method is often used in conjunction with the application anesthesia described above - the doctor applies a special agent to the gum so that the injection does not hurt,
- sedation or light sleep: the method allows you to achieve relaxation of the nervous system and psychological comfort. At the same time, the little patient is not in deep sleep, as during anesthesia, but in superficial sleep and quickly comes to his senses after the procedure. Sedation has few contraindications and complications. The procedure involves the administration of special drugs in the form of injection and inhalation. For young children, sedatives are sometimes added to drinks, for example, orange juice,
- general anesthesia: removal under anesthesia is carried out less frequently, such a measure strictly requires the presence of certain indications - the complexity of the procedure, the need for subsequent sanitation (for example, opening an abscess, surgical treatment of a large root cyst), the hyperexcitability of the child and other features of the nervous system that will not allow him to stay conscious in a chair, calm and relaxed, removal of several units at once, impossibility of local anesthesia.
Important! Anesthesia is a last resort for children of any age. It involves a serious impact on the body and requires the mandatory presence of an anesthesiologist, resuscitator, and a thorough preliminary examination. The child will need more time to return to normal after the procedure. Nevertheless, anesthesia is simply irreplaceable in some cases.
Care after tooth extraction
What frightens the parents more than the removal procedure is the condition of the baby after the operation, since they have already left the specialist’s office and are left with the problem alone. In this situation, all mothers and fathers have almost the same questions.
What to do after a child’s tooth extraction?
The doctor will give the little patient a cotton pad or gauze pad that needs to be placed in the empty hole to stop the bleeding. Removing a baby tooth does not cause excessive blood flow, so after half an hour you can safely remove the cotton wool, but removing a permanent tooth is accompanied by severe bleeding.
The appearance of a blood clot means that the healing process is going well, as it protects the bone from air and prevents inflammation.
What medications should I take?
If the dentist prescribes an antibiotic after a child’s tooth extraction, follow the recommendations and do not give the child other medications so as not to provoke complications.
How to rinse your child's mouth after tooth extraction?
For three days after surgery, rinsing your mouth is strictly prohibited, so as not to dislodge the blood clot and cause an infection. Three days after tooth extraction, the child can rinse the mouth using any means - strengthening tinctures of tree bark, soothing herbal decoctions or medicinal solutions.
How much can you eat after a child’s tooth extraction?
For the first few days, you should refrain from hot dishes and fermented milk products, eating only soft and liquid foods. It is best to chew on the side opposite the extracted tooth.
Contraindications for removal
There is a list of relative contraindications that will require postponing the removal procedure until better times. Experts include diseases of the central nervous system, exacerbation of chronic diseases, fever, acute inflammatory phenomena in the oral cavity, infectious diseases (whooping cough, ARVI, influenza, mononucleosis, etc.), location of the root near a tumor or plexus of blood vessels. However, in emergency cases, removal can be carried out immediately - this is especially true for cases accompanied by a high risk of tissue infection and blood poisoning.
Complications after surgery
Do not give in to panic and call the ambulance service at the slightest ailment of the baby. Some consequences of tooth extraction do not harm children's health in any way. The following symptoms are considered normal:
- The child’s gums ache after tooth extraction - apply ice, this will reduce the discomfort.
- After tooth extraction, the child has swelling - after the third day it will begin to subside; ice also helps eliminate the discomfort.
- A swollen cheek after tooth extraction in a child indicates a slight inflammatory process, which will go away on its own after some time.
- Light bleeding in a child after tooth extraction should also not cause concern; even the next day the saliva may be slightly reddish.
- A low temperature after tooth extraction in a child is the result of the child’s worries and nervous overstrain; when he calms down, the temperature will drop.
A child is afraid to have a tooth removed, what to do?
A child is afraid to have a tooth removed, what to do?
Our children are a mirror of our emotions, a reflection of our hopes, fears, and experiences. In them we put the feelings that we experience at different moments in life. The fear of going to the doctor, which you developed in childhood, will pass on to your child if you don’t calm yourself down at the right moment and tell yourself: “everything will be fine, we can handle it, it’s not scary.” If you instill in your child from childhood a feeling of safety in the hands of a doctor, every trip will be a joy for both you and him. Dental treatment will be a fun game, and daily oral care will be a fun and favorite activity.
Now let's talk about the removal of baby teeth, fears and questions associated with this operation.
Unfortunately, sometimes baby teeth need to be removed, and there are several absolute indications for their removal, these are:
1) Eruption of permanent teeth, without loss of milk teeth;
2) Traumatic lesions in which there is a fracture or damage to the tooth apparatus that is impossible for therapeutic restoration;
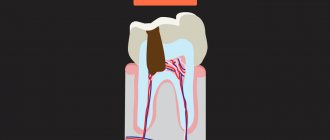
3) Periodontitis of the baby tooth, that is, the penetration of inflammation from the tooth tissue into the bone tissue. Most often, this condition is characterized by the presence of pain or fistulous tract in the gum area of the tooth. It is also possible that the infectious process will immediately develop into swelling of the buccal area; this condition requires immediate intervention;
4) Mobility of the baby tooth due to the resorption of its roots during physiological change.
Accordingly, there are various options for carrying out the operation of removing baby teeth, depending on the picture with which you came. In turn, for the youngest children who need to give a tooth to the tooth fairy, it is sometimes difficult to form an idea of the necessity and painlessness of the intervention; in this case, if there are indications and no contraindications, we are talking about sanitation of the oral cavity either under sedation or in a state of medication sleep. If there are no indications for these interventions, then removal is carried out in the usual way. You can read more about each type of treatment in the articles on our website dedicated directly to these manipulations.
What does the doctor look for when planning the nature of the intervention?
First of all, we take into account the health status, age and character of our patient. We carefully collect anamnesis, find out the presence or absence of allergic reactions in the child, after which, after conducting a direct examination of the baby’s oral cavity, we begin to explain our treatment plan to parents and relatives.
What are the possible options for tooth extraction surgery?
Let's start with more acute and unusual situations, which most often cause questions from parents.
All our actions must be minimally traumatic and painless for the child, therefore the presence of neurological disorders, allergic reactions to local anesthetics and the duration of the necessary treatment, we define as indications for treatment in a state of medicinal sleep. It is also very important to understand that there are not only general but also local indications for surgery under anesthesia:
1) The presence of a fistula tract, as a sign of the transition of the inflammatory process from the hard tissues of the tooth to the bone tissue. Usually parents bring their children when they notice a fistulous tract on the gum, next to the causative tooth. At the same time, you may notice that your child complains of pain when biting, when brushing teeth, or food getting stuck.
2) The appearance of swelling of the buccal, infraorbital area, pain when touching this area in the baby. We must remember that a rise in temperature, deterioration of condition, lethargy, poor appetite is an alarming sign: urgent surgical intervention is necessary. The rate of inflammation in children is much faster than in adults, and the health of the baby is in your hands.
Why do these conditions require removal not only under local, but also general anesthesia?
In the maxillofacial area, as in any other system of your body, there is an acid-base environment maintained by microelements, hormones, and other substances that create a state of homeostasis. Gradually, in the area of inflammation, due to the displacement and disruption of normal acid-base reactions, a predominance appears in the direction of the acidic environment. At the same time, local anesthetics used in dentistry are characterized by an alkaline environment. As you already understood, when an anesthetic is introduced into the inflamed area, it is neutralized and suppressed by an acidic environment. Accordingly, to avoid pain during surgery, to achieve adequate and complete analgesia, it is necessary to combine general and local analgesia methods.
Most often, this is how the chewing molars of milk teeth are lost, caries spreads lower and lower in the tissues of the tooth, ending with inflammation in the form of periodontitis of milk teeth. Since the roots of these teeth are intact, that is, they have not yet undergone resorption due to age-related changes to permanent ones, their removal may require a little more time from the doctor. Technically, it is staged, it resembles removal in an adult; all stages of this procedure will be discussed further.
Early loss will require further production of a prophylactic replacement structure on the adjacent teeth, to preserve the chewing function and avoid displacement of the adjacent teeth to the place of the removed one.
It’s another matter when we need to treat or remove teeth without inflammatory causes in children. There are two possible scenarios here:
1 – option. The child sits well in the dentist’s chair, is not afraid, and allows all the manipulations to be carried out. In this case, we work under local anesthesia and calmly go to the store for ice cream in half an hour.
Option 2. These are children who are tense or unfamiliar with the dentist’s chair. In such cases, it is recommended to carry out removal under nitrous oxide, which helps relieve anxiety and fear, helps the child relax and not be distracted by the doctor’s manipulations. In turn, the visit will not leave fear and anxiety in the heart of our little patient and will help create a positive picture of the perception of dental treatment. And yes, of course, we definitely take the baby for ice cream in this case too.
Now let’s talk a little more about what actions we perform to give our baby tooth to the tooth fairy.
The procedure for removing a baby tooth itself is a sequence of basic steps familiar to everyone. First of all, after getting to know each other and determining the scope of our activities, we begin pain relief; it is performed taking into account the condition of your child and his health.
The worst thing at this stage, most often, ends! After the period necessary for the anesthetic to take effect, we separate the gum tissue from the tooth itself and begin luxation movements, in other words, rock it, after which we take out the baby tooth and check its integrity. Inspection of the hole is mandatory; we visually check the formed hole and let the baby bite on a sterile gauze ball. For 10 minutes, the child lies calmly, rests, we give him the tooth, show him and tell him about the milk fairy and her wonderful gifts.
All! Your baby is the biggest hero, and not because he endured pain and let you hold him, but because he sat quietly and was a real smart girl.
Now that you and I, dear parents, have understood all the intricacies of the process, calmed ourselves and our grandparents, we can talk about the psychological preparation of the child for the trip to the doctor itself. Your main task is:
1) You can and should set your child up for positive emotions at home, tell a fairy tale about how the tooth fairy loves baby teeth, that she, like Santa Claus, has helpers everywhere and they make sure that for every lost tooth the child receives a gift;
2) Prepare the child for the situation in the doctor’s office, tell him that he has a magic chair that he can ride on, special sticks that, like an elephant, collect water. We, in turn, will always offer your child his favorite cartoons during the treatment process and create the most favorable atmosphere;
At the end of treatment, your baby always deserves a reward. Everyone enjoys receiving gifts, knowing that for your merits you will receive a pleasant prize, be it a promotion at work, or a gift under the pillow from the tooth fairy for a child. Therefore, of course, the final stage of your preparation will be a reward for your hero.
For clarification and clarity of all that has been said, we invite you to consider several clinical cases from our practice.
Flux, fever and diarrhea after tooth extraction
More serious negative consequences when removing a baby tooth in children can only arise as a result of poor quality work by the doctor or due to infection. If the following signs are detected, parents must immediately contact a specialist.
- Flux after tooth extraction in a child, preventing swallowing, breathing and muscle movement.
- Prolonged bleeding.
- Severe and prolonged pain in the gums that does not go away even after taking painkillers.
- After tooth extraction, the child’s temperature rose above 38 degrees.
- Abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhea after tooth extraction in a child.
A few words about caries prevention
The appearance of caries in babies can be prevented if you pay close attention to the child’s oral care and nutrition.
- It is necessary to develop the correct diet for the baby: up to 3-4 years of age, it is recommended to limit the consumption of sweets as much as possible; it is carbohydrates that provoke the development of caries in children. You should include as much dairy products, herbs, fruits, vegetables, and fish in your daily meals.
- At an early age, it is worth teaching your child to strictly adhere to a diet. You shouldn’t “follow” your beloved baby’s desire to snack on cookies in the middle of the night or drink sweet juice after brushing your teeth in the evening.
- Your baby should be taught to brush his teeth from the moment his first tooth appears. From the age of 1.5 years you can use a brush, and at an early age you can wipe the oral cavity of the crumbs with gauze swabs and special napkins. Also, on the recommendation of the dentist, you can treat the oral cavity with special anti-caries gels. For these purposes, “ASEPTA baby” wet wipes are perfect for cleaning the baby’s mouth, which will give the baby freshness, prevent the spread of bacteria and reduce discomfort during teething.
- It is also important for parents to follow the rules of hygiene - you should not lick your child’s spoon or pacifier, or eat from the same plate with him, because cariogenic bacteria from adults can spread to them.
Now you understand how important it is to cure caries of baby teeth at the first stage of development. Keep an eye on your baby’s health, and the problem of the consequences of removing baby teeth will be unfamiliar to you.
How much does tooth extraction cost?
Many people believe that the cost of the procedure for adults is much higher than for children, and the price for removing a baby tooth in children is lower than for extracting a permanent tooth. This is not entirely true. The amount of payment for the pediatric dentist depends on the complexity of the case, and the cost of removing temporary and permanent teeth is determined by the indications and concomitant diseases. In the table below, we have listed the main problems with which people turn to a pediatric dentist and the prices for tooth extraction for children.
| Service | Price |
Consultation | from 500 rubles |
Removing a baby tooth | from 1,100 rubles |
Removal of a permanent single-root tooth | from 1,200 rubles |
Removal of a permanent multi-rooted tooth | from 3,000 rubles |
Complex tooth extraction | from 4,000 rubles |
Wisdom tooth removal | from 3,000 rubles |
Removal of a supernumerary tooth | from 1,200 rubles |
Application anesthesia | from 250 rubles |
Local anesthesia | from 500 rubles |
Sedation | from 1,500 rubles |
General anesthesia for 30 minutes | from 4,000 rubles |
General anesthesia for 60 minutes | from 10,000 rubles |
General anesthesia for more than an hour | from 12,000 rubles |
Local anesthesia in children in dentistry
Local anesthesia for dental treatment is used everywhere, since it provides the necessary analgesic effect, but at the same time maintains a certain sensitivity and has the fewest contraindications. Children, as a rule, tolerate it well.
Types of local anesthesia
The choice of one type or another depends on the procedure to be performed by the doctor, the age and psychological state of the child.
Application anesthesia
Local anesthesia in children in dentistry is not complete without the use of special anesthetic solutions or gels (most often based on lidocaine), which are used to treat the gums before starting treatment. The active substance easily passes through a thin layer of the mucous membrane and dulls sensitivity. As a rule, topical anesthesia is used to numb the site of the future injection - this is a typical feature of anesthesia in children in dentistry. But even one “freezing” with a gel or spray is enough for some procedures - for example, to remove mobile baby teeth, the roots of which have almost completely dissolved.
Topical anesthesia products in children's clinics have a pleasant taste and aroma to make it easier for the child to tolerate treatment.
Injection anesthesia
In pediatric practice, articaine-based anesthetics are most often used, which are administered using a syringe. This drug is approximately five times more powerful than novocaine, but is less toxic and less likely to cause allergies. It can be prescribed from the age of four.
Injection anesthesia has its own varieties. Pediatric dentists use infiltration or conduction anesthesia depending on the indications. In the first case, an injection is made into the mucous membrane at the border of the alveolar process and the transitional fold so that the anesthetic reaches the endings of the dental nerves. In the second case, the solution has an effect on the branches of the trigeminal nerve. Conductive anesthesia in children in dentistry is permissible from the age of six and is indicated for tooth extraction - mainly in the lower jaw.
Instruments for injection anesthesia
In children's clinics, they are gradually moving away from the use of classic syringes and ampoule solutions. They are replaced by more thoughtful and, importantly, psychologically comfortable solutions for the child.
- Needleless injector.
The anesthetic in such a device is supplied through a minimal (up to 0.1 millimeter) hole under very high pressure. The jet penetrates the surface of the mucous membrane or skin and enters the tissue. The analgesic effect with this principle of administration occurs faster, and a smaller volume of the drug is required. The absence of a needle in the injector is the key to a child’s good mood. - A carpule syringe
is a cartridge containing an anesthetic and, usually, a vasoconstrictor that helps prolong the pain-relieving effect of the solution. Unlike traditional ampoules, the carpule provides ideal sterility and more accurate dosage of all components. A special needle is placed on the cartridge: it is much thinner than the needle of a regular syringe and minimizes discomfort. - A computer syringe
is completely different from a regular syringe, so pain relief will be more comfortable for the child. The supply of solution in such a device is controlled electronically, and for the desired effect a smaller dosage of the drug is required. When the anesthetic is administered using a computer syringe, the child's face will not be as numb, so he will feel better during treatment.
How to prepare a child for tooth extraction
If tooth extraction is unavoidable, try your best to minimize the child’s stress. For example, tell him a fairy tale about how one tooth began to behave badly and interfere with the others, so it needs to be “pulled out.” Before going to the clinic, you can also discuss some pleasant event with your child, be it going to the movies, the circus, or buying a toy, which you will do immediately after removing a capricious tooth. The main thing is not to panic, and then the confident and calm attitude of the parents will certainly give the child the strength to courageously endure this frightening but necessary procedure.
You can avoid tooth extraction surgery in children if you carefully monitor the condition of the oral cavity throughout the entire period of dentition formation, monitor the quality of hygienic procedures and regularly take children to preventive appointments with the dentist.
Can I solve the problem myself?
If the tooth is sick, then, of course, you need to see a doctor. There can be no talk of any independent treatment. But if a tooth becomes loose, many parents do not rush to the dentist, trying to remove it themselves. But it is undesirable to do this, because unlike a doctor, adults will not be able to accurately foresee situations and vouch for the safety of the child’s health.
However, if the period for the loss of the deciduous unit of the dentition has come, it is wobbly and literally “hanging by a thread,” you can try to remove it yourself. The main thing is the child’s positive attitude and the absence of concomitant oral diseases. To do this, you can give the baby, for example, an apple or a carrot - perhaps, during the process of mechanical action, the baby tooth will fall out on its own, unable to withstand the load. Care after a home removal is similar to what your doctor recommends after an in-office procedure.
Category: Tooth extraction Published by Mister stomatolog