In times of minimally invasive treatment methods, the use of piezoelectric equipment is becoming increasingly common among dentists and oral surgeons who perform surgical procedures. Lasers in dentistry are used to perform surgical procedures with minimal discomfort for the patient. However, piezoelectric equipment allows hard tissue to be treated delicately through the use of ultrasonic surgery. So, how to remove tartar using ultrasound and what are the advantages of this method.
What is piezosurgery
The piezoelectric effect is the physical principle that causes quartz crystals to vibrate when an electrical current is applied. Thanks to special mechanisms for transmitting vibration generated by quartz and converted into oscillatory movements of the insert, which allows selective removal of tissue. This procedure has proven effective in various areas of surgery.
The main advantage of piezosurgery is that soft tissues that come into contact with the vibrating material are not damaged. This reduces the risk of injury to vital nerves or blood vessels.
An important property that further confirms the advantages of using piezoelectric equipment is the ability to deflect the vibration of the drug through the instrument. The achieved preparation of less hard and soft tissue allows for smaller approaches and reduces morbidity in patients undergoing apicoectomy.
Stages of professional hygiene of dentures with implants
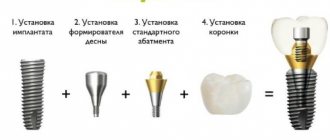
If a single crown or bridge is fixed to the implants with cement mortar, then such prostheses cannot be removed. In this case, comprehensive cleaning is done in exactly the same way as for your own teeth, but with some features. They mainly concern special equipment settings for gentle treatment of the area of implantation and prosthetics.
If you have dentures fixed to implants using screw fastening, then professional hygiene is carried out with the removal of the structure - the denture is additionally cleaned outside the oral cavity.
Ultrasonic tooth extraction
In piezosurgery, tooth extraction using ultrasound is most common. This is one of the most common procedures. So, how are wisdom teeth removed using ultrasound? And how are tooth roots removed using ultrasound? So, they are located deep in the jaw and are not easy to remove with forceps, and besides, sometimes they are hidden under a layer of bone and soft tissue. Therefore, removal using ultrasound is the best option.
In addition, one of the biggest problems that worries patients when having a tooth removed is the fear of pain. In such cases, many are interested in how teeth are removed using ultrasound. After all, with the technology of painless removal using an ultrasonic piezotome, the patient can forget about worries. Piezotomic ultrasound not only helps to safely, painlessly remove teeth, but also reduces the procedure time. In addition, with the help of this drug you can carry out removal with jewelry precision.
Many people are also interested in whether caries can be removed with ultrasound and how caries is treated with a laser. The laser helps minimize bleeding and swelling during soft tissue treatment. Lasers are used to remove decay and prepare enamel for fillings. Lasers are also used to treat or strengthen fillings. For more advanced cases of caries, the laser is used in conjunction with a traditional dental drill.
Mechanical and ultrasonic devices for cleaning teeth in periodontics
Drisko CL, Cochran DL, Blieden T, Bouwsma OJ, Cohen RE, Damoulis P, Fine JB, Greenstein G, Hinrichs J, Somerman MJ, Iacono V, Genco RJ;
Study, Research Committee of the American Academy of Periodontology Ultrasonic and mechanical devices appear to achieve the same results as hand instruments for removing plaque, tartar and endotoxin. Ultrasonic machines used at medium power produce less damage to the root surface than hand or air scalers. Due to the width of the instrument, furcations are more accessible using an ultrasound machine than a hand scaler.
It is not clear after using which scaler the roughness of the root surface is more or less pronounced. But it is also unclear whether root surface roughness influences longer healing. Periodontal cleaning and root planing include thorough removal of plaque, but complete removal of plaque should not be the goal of periodontal treatment. Research has shown that endotoxin is weakly adsorbed to the root surface and can be easily removed by gentle overlapping movements using an ultrasonic scaler. A significant disadvantage of mechanical scalers is the creation of a contaminated aerosol.
J Periodontol. 2000 Nov ;71(11):1792-801
Contraindications to ultrasonic tooth extraction
However, this surgical procedure also has contraindications, due to which it is not recommended to resort to it:
- Condition not suitable for tooth extraction.
- The procedure is prohibited for pregnant women from 1st to 3rd semester.
- After chemotherapy and radiation therapy for 6 months.
- If the patient has an odontogenic infection, stomatitis, or if there is an undiagnosed lesion.
Ultrasound dental treatment is suitable for a wide range of dental indications. Its increased use is due to its ease of handling and selectivity in bone removal, which guarantees maximum safety during bone surgery. In addition, high precision can be achieved, which is a significant advantage, especially in confined spaces.
Cost of services
| Service | Price |
| Preventative cleaning with Air Flow device simple (1 jaw) | RUB 2,670 |
| Preventive cleaning with Air Flow complex (1 jaw) | 3,300 rub. |
| Removal of supragingival deposits from teeth (per tooth) | 200 rub. |
| Sealing fissures with light sealant. curing | 2,400 rub. |
| Treatment with sealant for root dentin Seal and Protect | 180 rub. |
| Fluoridation of teeth | 150 rub. |
| Conducting reminirilizing therapy (per tooth) | 170 rub. |
| Polishing and grinding of teeth | 260 rub. |
| Restoring a damaged tooth crown using fiberglass (with one pin) | 4,700 rub. |
| Restoration inlay made of ceramic composite | 14,500 rub. |
| Impress ceramic restoration inlay | 20,000 rub. |
| Oral hygiene training | 1,200 rub. |
| Depophoresis (1 channel) | 1,100 rub. |
| Endodontic treatment of complicated caries of a baby tooth (including anesthesia) in 2 visits | 3,100 rub. |
| Silvering of a baby tooth (per tooth) | 990 rub. |
| Working with a patient in a chair in case of refusal (30 min) | 1,500 rub. |
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
What to do at home after professional hygiene
To preserve the results of professional cleaning for as long as possible, the patient needs to take into account the peculiarities of home hygiene with implants.
- choose the right toothbrush: a regular (not electric!) brush (soft or medium hard) is recommended, which needs to be changed once every 3-4 months,
- Be sure to use an irrigator: when teeth are completely restored, there is a small gap between the natural and artificial gums - the rinsing space. The irrigator efficiently and effectively removes food particles and soft plaque from there, and also massages soft tissues, stimulates blood circulation and heals the gums around the implants,
- EXCLUDE regular dental floss, brushes and toothpicks: with implants, the sensitivity of the gums is reduced, so the mucous membranes can be injured and infected. For cleaning the rinsing space or the area under the dental bridge, special threads only labeled “superfloss” are recommended.
Maintain overall oral health: take care of cleaning implants and dentures both on your own and in the dentist’s office, and also regularly attend preventive examinations and examination of the condition of the structure. Then the implants will serve you flawlessly for the rest of your life.
Caring for your teeth after ultrasonic cleaning
After the procedure, especially if a lot of plaque has been removed, there is a slightly increased sensitivity of the teeth to temperature and chemical irritants, so for 24 hours after cleaning, patients are advised to refrain from eating excessively hot, cold, sour and salty foods. It is advisable to follow a “white diet” for a couple of days, as after teeth whitening, to exclude strongly coloring foods from the diet (red wine, coffee, black tea, beets, some bright fruits and juices from them) so that the cleaned enamel does not absorb food dyes, and on the contrary, enrich it with solid and fiber-containing products that will prevent the appearance of plaque and stones (fruits, vegetables, nuts, etc.).
If sensitivity is severe, it is recommended to replace your regular toothbrush with a soft-bristled brush for several days and purchase toothpaste that reduces sensitivity.
After each meal, you need to rinse your mouth with clean water - this rule must be observed not only after ultrasonic cleaning, but also constantly.
On the first day or two, it is also recommended to brush your teeth after every meal.
Indications and contraindications
Ultrasonic tooth extraction can be used in all cases where extraction is necessary. The location and type of tooth does not matter. At the same time, there are a number of indications when a doctor can strongly recommend the use of ultrasound to ensure a predictable result and minimize possible complications:
- the patient has a bleeding disorder;
- abnormal position of teeth;
- complex tooth extraction that is covered with soft tissue growths;
- after an unsuccessful classical removal procedure;
- wisdom tooth removal;
- removal of impacted and dystopic teeth (in particular, eights with pathology);
- tooth extraction and immediate implantation;
- tooth extraction during pregnancy;
- tooth extraction for children, especially those with severe dental phobia.
The procedure also has a number of contraindications, in the presence of which the use of ultrasound is not recommended or strictly prohibited:
- For patients with a pacemaker, ultrasound is completely contraindicated;
- milk and mixed dentition in children (not recommended);
- HIV, hepatitis, tuberculosis;
- bronchial asthma;
- disorders of the central nervous system, mental disorders;
- extensive demineralization of enamel.
Ultrasound in endodontics (part 2)
About the authors
Paolo Generali (Paolo Generali)
Active member of the Italian Society of Endodontics, full member of the Amici di Brugg Association. International lecturer, member of the International Group on Implantology, professor of restorative dentistry at the University of Modena and Reggio Emilia.
Enrico Cassai Enrico Cassai is a professor of endodontics at the University of Ferrara, practicing in a private clinic in Ferrara: he specializes in clinical endodontics, microscopic surgery and aesthetic restorative dentistry.
After studying the history of ultrasound and ultrasonic tips in the article Ultrasound in Endodontics (Part 1), the second part examines the clinical applications of these instruments, which have become fundamental in almost every stage of endodontic treatment.
In practice, they help to perform minimally invasive access to the cavity, and also increase the efficiency of ultrasound, allow the removal of intracanal obstructions and play a key role in retrograde cavity preparation in endodontic surgery.
A list of the most common applications of ultrasound in endodontics, which will be discussed in detail in this article:
Formation of access, search for calcified canals, removal of intrapulpal stones;
Removal of obstacles in root canals (fragments of instruments, intracanal posts, silver pins, broken metal posts);
Activation of irrigants;
Ultrasonic condensation of gutta-percha;
Application of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate (MTA);
Surgical endodontics: treatment and cleaning of the root apex, obturation of the apical region;
Root canal treatment.
Regarding root canal preparation, it is advisable to develop a clinical classification of ultrasonic instruments according to the part of the tooth in which they are to be used. Based on this, the choice of tip characteristics (active/inactive, smooth/notched), intensity of exposure, and the need for water cooling are closely related to the area of the tooth intended for treatment.
Pulp chamber
Creation of access
Modern principles of endodontic treatment are aimed at creating minimally invasive access to the tooth cavity, which, on the one hand, will allow high-quality treatment of root canals, and on the other hand, be gentle on tooth structures.
In this regard, the implementation of the modern concept of access formation, which in the past involved working almost exclusively with diamond burs in high-speed handpieces and pink burs on a micromotor with a blue ring, is now replacing the penetration and gross expansion of the cavity with its identification and expansion in its entirety using ultrasonic handpieces .
The main advantages of ultrasonic technology at this stage are the efficiency of cutting properties, accuracy in relation to dentin and good visibility due to the absence of a micromotor tip. This allows you to achieve good control without damaging the bottom of the pulp chamber, especially in the presence of sclerotic and almost invisible root canal orifices.
The choice of tip used depends on the task being performed. For massive removal of dentin when creating access, an elongated tip is suitable; reinforced tips, resistant to destruction, with an abrasive coating on half of the working part are also recommended for preparation.
For effective preparation, set the tip intensity to medium to high and use periodic irrigation to avoid overheating.
Pulp stones
In cases where a pulp stone blocks the mouth of the root canal, the ultrasonic tip is able to carefully remove the obstruction. For this purpose, it is recommended to use tips with a disk-shaped working part, which wash out pulp stones with a brush-like movement without damaging the bottom of the cavity, and are a good alternative to tips with a smaller working diameter or with a pointed tip.
When using ultrasound at this stage, it is very important to place the tip so as not to disturb the bottom of the pulp chamber, to prevent iatrogenic damage (perforations), and also not to miss important structural features indicating the location of the canal orifices.
To effectively carry out such manipulations, the tips should also be adjusted in the range of intensity from medium to maximum, and periodic irrigation should be used to avoid overheating.
Calcified canals
In all cases where it is necessary to examine the grooves and isthmuses of the cavity floor in order to find hidden and calcified canals, such as the second mesiobuccal canal in upper molars or sclerotic canals in traumatized teeth, the use of special ultrasonic tips is highly recommended. In practice, long-term failure of endodontic treatment is most often associated with such untreated accessory canals.
In these clinical situations, large, coarse, partially diamond-coated tips should be used during the initial removal of calcifications, obstructions, filling material, and secondary dentin as they provide maximum cutting power and improve control when working in the pulp chamber.
The next stage, when locating the canal mouths, should be carried out with thinner and longer tips, which significantly facilitate work in deeper areas, while maintaining visibility and preventing iatrogenic damage, such as perforation of the upper third of the canal.
Upper third of the channel
Ultrasonic instruments are effective in removing foreign objects from the upper and middle third of the root canal, such as posts, hardened cement, silver posts, and instrument fragments. To remove dentin mass, a diamond or abrasive-coated tip is used to achieve straight-line access combined with enhanced coaxial illumination. In deeper areas of the canal, smooth and less aggressive tips are used. Use ultrasonic nozzles to apply a light touch and repeat the movements during operation, starting with minimum power, increasing it if necessary. Overheating of the instrument and tooth structures is prevented by periodically activating the tip and abundantly supplying a lubricating and cooling emulsion, since water, in addition to cooling and washing away debris, impairs the clarity of visibility of the working field. Some handpieces have a water inlet port, while others are designed to work in dry conditions.
Deleting posts
The effectiveness of post removal depends on several factors, such as the depth of fixation in the root, the type, design and material of the post, the structure of the tooth, and the type of fixation cement. Special ultrasonic tips have been developed to remove posts. They are usually shorter and larger than regular ones. When working, they are placed directly on the post and made circular movements for 5-10 minutes without water, and then the base of the post is freed from restoration or cement material using traditional diamond burs. Ultrasound can weaken the bond between cement and post. If the post cannot be removed by this method, take a smaller and longer tip and make a groove around the post. There are recommendations to reduce the extra-root part of the post to the diameter of the intra-root part in order to reduce the stress required to remove it. An alternative, so-called indirect method, is to use a large tip that transmits vibration through a small conductor.
Ultrasound destroys the structure of hardened cement, making it easier to remove the post.
The tip should not be excessively thin, as small-diameter ultrasonic devices are weaker and prone to breakage, especially when used for long periods of time on resistant materials. On the other hand, the tip should not be too large, as it should be in close contact with the post when moving around it in a counterclockwise direction. Typically, the ultrasonic device is set to maximum power.
Fiber posts
Fiber posts can also be removed using an ultrasonic tip. This topic is covered extensively in an article by Riccardo Tonini.
Silver pins and tool fragments
Not long ago, silver pins were used as a filling material. Their removal can be easy if the area of the pin can be reached with special pliers called Stieglitz forceps, but it can be difficult when the pin is fixed deep in the canal. A fine ultrasonic tip can be effective in removing such obstructions, but keep in mind that silver points are very thin, so the tip should be used at very low power with light pressure and work primarily on the dentin rather than the silver itself. Removal of instrument fragments is performed using a similar technique. First of all, the broken file is subjected to a circular action of a thin ultrasonic tip, which transmits vibration to it. To remove broken instruments, tips made of a new titanium-niobium alloy have recently appeared on the market.
Apical third of the canal
Special tips are used in the apical third of the canal. In addition to the titanium-niobium tips described above, titanium alloys are often used for this work; the tips are suitable for smooth, uncoated ones. Curved tools are also used, then the power should be low and the pressure very light. Excessive force and power may damage the device. Such tips are used for any of the tasks listed above, and also apply MTA cement at minimum power. There is also an indirect method for inserting MTA using a large ultrasonic tip that transmits vibrations to the endodontic plugger.
Ultrasound devices have revolutionized surgical endodontics. Special retrograde tips provide access to 3 mm or more in the apical third of the canal, including the apical constriction, and allow filling material to be placed deep in the canal, thereby increasing the predictability of the procedure. Powerful endodontic devices such as Piezosurgery® are used for osseous access and retrograde preparation.
Conclusion
Currently, ultrasound technology has become an essential assistant in everyday practice in endodontics. Its use in combination with enhanced coaxial illumination makes cases that until recently were difficult easier and more predictable.
Diagnosis plays a decisive role in selecting the appropriate ultrasound tip type, level and method of use, especially when the operator has the tools, techniques and knowledge to resolve clinical cases.
Moreover, a simple case can become incredibly difficult if the diagnosis is inaccurate or the selection of instruments is inappropriate. Ultrasonic tips for endodontic use vary in size, shape and material, and there is no one universal tip to solve all existing problems; all varieties are in demand. Handpiece and drive compatibility can be an issue, so follow the manufacturer's instructions to avoid the risk of device failure and other malfunctions. It is advisable to start with lower power settings and then increase it as needed. The pressure should always be light. The air flow is sufficient to prevent overheating at low power. Some handpieces are water-cooled. Water is more effective for cooling, but reduces visibility of the work area. There is evidence that vented tips are less durable than tips designed for dry conditions.
In fact, visibility of the surgical field is the main advantage of ultrasonic devices compared to rotating devices. In the first case, the source of ultrasonic vibrations does not impair visibility, and in the second, the head of the rotating tip, being on the long axis of the working tool, can cover the visualization line. This great advantage also means that ultrasonic handpieces should always be used with a good view of the working area and should not be attempted to be used blindly, as this can be dangerous.
Source: https://forum.stomatologija.su/
Pros and cons of ultrasonic tartar removal
Today in dentistry, teeth are most often cleaned using ultrasound, because this is one of the few methods that guarantees the removal of hard deposits. Among other advantages of ultrasonic cleaning, experts highlight the following characteristics:
- effective cleaning of all types of deposits,
- additional antimicrobial treatment,
- removing dirt from hard-to-reach places, including under the gums,
- safety for enamel due to the absence of direct contact of the device tip with its surface,
- absence of pain during the procedure - discomfort is usually experienced only by patients with increased sensitivity of the mucous membrane,
- affordable price.
On the other hand, ultrasound also has some disadvantages. So, for example, there is a risk of going to a dental clinic, where they use outdated models of scalers - in the process of work, they can slightly injure the enamel layer. Possible complications that may develop after cleaning are mainly associated with medical errors. Examining a stone in hard-to-reach places is not an easy task; it requires attention and concentration from a specialist, as well as relevant work experience. The presence of extensive fillings, veneers, crowns and other fixed structures in the mouth is associated with the risk of damage to them while using the scaler.
Is it possible to whiten dentures on implants?
Let us answer briefly: no, you cannot use any bleaching products (neither professional nor homemade). Including whitening toothpastes. All these products contain abrasive substances and acids that can change the structure of the prosthesis. But in reality they are not needed.
Even at the manufacturing stage, the patient and the orthopedic dentist together select the shade and the desired degree of whiteness of the crowns. Adaptive prostheses are made from metal-plastic – it is a lightweight and fairly porous material. It absorbs moisture and dyes. However, with careful care, the prosthesis will retain its original color throughout its entire service life - up to 3, and sometimes even 5 years.
At the second stage, that is, with permanent prosthetics, better materials are used for the manufacture of prostheses. These are ceramic composite, ceramics and zirconium dioxide - restoration materials with high and maximum aesthetics. They are resistant to pigmentation even when exposed to food dyes, and if adequate hygiene is maintained, they will not darken.
However, it is important to remember that any dentures, even the highest quality ones, can change color due to dental plaque. In this case, professional removal of plaque and stone, followed by polishing the surface of the prosthesis, will help restore the original shade. If the prosthesis can be removed and cleaned in a special device, it will look new regardless of the period of wear.
That is, comprehensive hygiene at the dentist is the best option for maintaining aesthetics.