- Published by: Laima Jansons
Tumors of the ear and cheek can be different in structure and nature of origin. Some of them only visually spoil the appearance, without causing discomfort to the patient, while other pathological formations cause pain and deterioration of well-being.
It is impossible to cope with the problem on your own. A proper diagnosis will require a visit to the doctor's office.
Photo 1. A tumor in the ear area is a serious symptom that requires immediate medical attention. Source: Flickr (wellan)
Common Causes
A pea-sized lump that feels like a ball under your fingers causes a lot of anxiety for people who are attentive to their health. To determine the cause of the lump behind the ear, you first need to conduct a small examination. Soreness, mobility or immobility, whether body temperature is elevated - all this is important and is assessed.
The formation of lumps behind the ears in adults can be influenced by:
- excessive production of sebaceous fat;
- acute respiratory viral infection;
- decreased general immunity;
- neglect of personal hygiene rules;
- scratches, wounds on the skin and their further infection.
Sometimes, under a hard ball behind the skin, there is an inflammatory process of the hair follicle, in other words, an ordinary pimple from which pus can come out. The site of inflammation may itch, and when touched, a burning sensation or pain may be felt. Acne often goes away on its own, especially if you wipe it with cleansing lotions.
A pimple behind the ear should not be squeezed or scratched, as this often leads to infection and abscess.
Another common reason for the formation of lumps behind the left and right ears is enlarged lymph nodes against the background of reduced immunity.
Most often this happens during colds. In this case, there is inflammation of the lymph nodes on the back of the head, on the neck, under the jaw or between the ear and jaw. These formations usually go away on their own as you recover.
If you experience severe pain or notice a significant increase in temperature, you should seek medical help.
Effective medical assistance
Seeking help from a doctor if you have a lump on your head near your ear is the best decision. First of all, he finds the starting point and finds out whether the patient has any diseases, since the formation of a lump can be affected by:
- infection getting under the skin. Most often this happens due to an unprofessional puncture of the earlobe or ear cartilage from behind;
- development of a chronic disease, such as diabetes, etc.;
- increased production of sebaceous glands;
- weakened immune system;
- increased sweating.
When to sound the alarm
If you discover that a lump has appeared behind your ear and that it hurts when pressed or even lightly stroked, you should not immediately panic. But it should be borne in mind that the reasons for the formation of a growth are not limited to acne and colds. Only an experienced doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
You should not delay visiting a professional if:
- The lump increases in size;
- The lymph nodes are significantly enlarged and painful;
- The appearance of a lump is accompanied by an increase in body temperature;
- The formation did not appear during the period of a cold.
The listed signs may be symptoms of a significant disruption of the body's functioning, including cancer. Only a doctor will conduct a correct diagnosis, prescribe additional examinations, make a final diagnosis and recommend a course of treatment.
If a disturbing lump appears behind the ear in a child, it is recommended to consult a doctor immediately.
It must be said that children have more delicate skin and a higher risk of damage and then infection. This is especially true given children's negligence regarding hygiene.
You should not let the course of the disease in children take its course and self-medicate. Yesterday's pea behind a child's ear can at any moment grow into a cyst the size of a Christmas ball.
The main serious reasons for the formation of lumps behind the ears can be presented in the summary table:
| Diagnosis | Description | Symptoms | Danger | Diagnostic methods |
| Lymphadenitis | Inflammation of regional lymph nodes. Caused by infection or viral diseases | Soreness, redness of the skin. Motionless under your fingers. Signs of body intoxication | Development of a purulent process, in severe cases - sepsis | CBC (complete blood count), ultrasound, sometimes biopsy |
| Lipoma | Benign fatty tumor | Softness, mobility, feels like a rolling ball. Painless | It is necessary to differentiate from malignant formation | Inspection. Sometimes consultation with an oncologist to confirm benignity |
| Atheroma | Sebaceous cyst | Round shape, firm, mobile, painless | Tends to enlarge and become inflamed | Histological examination |
| Fibroma | Benign tumor of connective and fibrous tissue | Soft, may be pedunculated, usually painless | Risk of infection if damaged | Histology to confirm benignity |
| Mumps | Viral infectious disease accompanied by enlargement of the parotid salivary glands | More often the inflammation is bilateral and painful. Signs of general intoxication of the body, pain when swallowing | Possible development of meningitis as a complication | Examination by a general practitioner or pediatrician, serological tests |
As the table shows, some formations are not easily distinguished from each other. Lipoma, atheroma and fibroma have many similarities, but at the same time there are differences that are noticeable only to the eye of an experienced doctor.
And again, it all comes down to the fact that you cannot do without medical advice.
Diagnosis of a malignant ear tumor
The easiest way to diagnose a malignant tumor is located on the auricle. The otolaryngologist can make an initial determination based on the appearance of the mass, as well as whether it bleeds and how closely it is adhered to the surrounding tissue. But the final diagnosis will be made only as a result of histological examination.
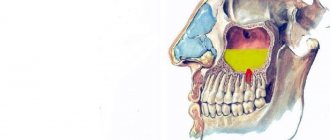
A tumor located in the ear canal is usually diagnosed using otoscopy. It is otoscopy that can reveal the presence or absence of a widespread ulcer, which is usually colored dark red. By probing the very bottom of such an ulcer, you can determine the degree of looseness of the cartilage tissue or bone surface.
Using microtoscopy, you can determine how far the tumor process has spread into the outer ear. In the case of a malignant tumor of the middle ear, otoscopy will help to identify all possible changes that have occurred on the side of the eardrum, determining how much it is bulging or torn by the tumor.
Diagnosing a tumor in the tympanic cavity is very difficult and is only possible when the formation begins to spread to surrounding structures. Suspicion of a malignant tumor is usually detected by X-ray of bone destruction, which is clearly different from the nature of ordinary chronic otitis media.
The extent of the ear tumor can be determined based on the results of a CT scan of the skull or MRI of the brain.
Treatment of neoplasm
Self-medication of a lump behind the ear can worsen the situation and lead to harmful consequences. If you are confident in the viral nature of the swollen area, attention should be paid to treating the underlying disease, most often a cold.
If the follicle is inflamed, it is recommended to use salicylic acid or alcohol to cleanse the affected area.
The sore spot should not be heated or rubbed, especially with warming ointments.
In other cases, treatment should begin with a visit to the therapist.
Depending on the preliminary diagnosis, the therapist (general practitioner) will be able to determine whether the intervention of more specialized specialists is required. Perhaps he will refer the patient for additional diagnostics to an otolaryngologist, surgeon, neurologist, dentist, and so on. It is possible that you will need to carry out hardware diagnostics - CT, MRI, X-ray or ultrasound. In doubtful cases, a tissue biopsy will be required to rule out malignancy of the tumor.
Mumps
Mumps can also cause a tumor. It is the salivary glands located next to the ears that have become inflamed, which means they have noticeably increased in size. At the same time, the patient, and these are mainly children, experience an inflammatory process of the throat mucosa, an increase in temperature and a general weak condition. This disease, which has a popular name - “mumps”, is accompanied by painful manifestations in the affected areas. The danger of mumps is that it is transmitted by airborne droplets, and the infection easily spreads to a healthy person. Therefore, complete isolation of the patient is required.
What to do if a lump appears?
Many patients are made nervous by such a small thing as a lump behind the ear - a raised lump near the bone that hurts when pressed. In most cases, this pathology does not cause pain and does not require medical intervention, but the condition may worsen, and a visit to the doctor cannot be avoided. In order to save time and effort, adults often turn to traditional medicine or simply self-medicate, which is strictly prohibited, as it can lead to serious consequences.
There is no need to panic.
Education in 60% of cases is painless. The patient does not notice that a small bump has appeared behind his earlobe, and calmly walks like this until it disappears on its own. You should consult a specialist if the pathology is accompanied by symptoms such as:
- It's a dull pain;
- change in color of the damaged area;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- the formation of a lump is not infectious in nature.
It is strictly contraindicated to warm the lump in any way (with ointments, sunlight, rubbing, when working with fire) or to squeeze out the contents of the growth. This can cause an inflammatory process, make the area swell even more, and worsen the course of the disease. It is also prohibited to treat the cone with iodine or use other traditional methods. The only thing worth doing is to ensure that the affected area is clean to prevent infection.
Prognosis for ear tumor
If we talk about a benign ear tumor, in most cases it has a favorable prognosis for both life and recovery after treatment has been carried out. The only exceptions are those vascular tumors that grow through important anatomical structures and, if not removed in a timely manner, can transform into malignant formations.
Another thing is a malignant tumor, which always has a serious and often disappointing prognosis. Since the diagnosis of malignant tumors at the initial stage is very difficult, it can be extremely difficult to identify and cure the disease immediately. A spreading malignant tumor usually leads to the death of the patient. This happens from cancer cachexia, meningitis, complications from the central nervous system or arrosive bleeding.
Folk remedies
If a lump appears behind the ear behind the ear, folk remedies can be used to help resolve it and relieve associated symptoms:
- echinacea tincture;
- compresses with onions;
- ointment with garlic;
- aloe juice
Echinacea tincture is taken orally for lymphadenitis, diluting 10 drops of the product with ¼ glass of water. Drink the product 4 times during the day. Additionally, it is recommended to take vitamin C (750-1500 mg daily).
To prepare a composition for local treatment of wen, you need to grind the pulp of the baked onion, add 1 tbsp to it. l. grated laundry soap. The finished product is applied to the bump in the form of a compress. The process is repeated twice a day.
After chopping a few cloves of garlic, combine the resulting mass with 1 tbsp. l. vegetable oil. After thoroughly mixing the ointment, every day they carefully treat the lump that has popped up behind the ear. Fresh aloe juice helps treat behind-the-ear formations that are prone to inflammation. Wipe the problem area with the product daily until the condition improves.
A lump that appears near the ear as a result of oncological pathology requires careful diagnosis and surgical treatment.
If necessary, the tumor is excised along with the tissues that surround it to avoid recurrence. A lump behind the ear, which appears as a result of inflammation of the lymph node, is treated with drugs that fight the main cause of the inflammatory process - an infection or virus. In this case, the treatment regimen is prescribed by the doctor after diagnosis.
Types of malignant ear tumor
Any malignant tumor has a primary and secondary nature. Researchers distinguish three types of malignant tumors: infiltrative, solitary vegetative and ulcerative. According to its histological structure, a malignant ear tumor looks like a spinocellular epithelioma and, in rare cases, a basal cell carcinoma. However, the rarest case is the manifestation of a malignant ear tumor in the form of a sarcoma. Let us now consider each type in more detail:
- Spinocellular epithelioma. This type of malignant tumor is characterized by its rapid growth. If such a tumor is localized on the auricle, then it takes on a warty appearance, having a wide base that will bleed with the slightest injury. If such a tumor is located in the ear canal, it will be presented in the form of a kidney-shaped outgrowth (or erosion) or a diffuse process that covers the entire ear canal;
- Basalioma of the ear. This type of malignant tumor is characterized by slow growth and a later process of metastasis. If such a tumor is located on the auricle, then its appearance will be similar to an ulcer or a flat scar. If the localization of basalioma is at the site of attachment of the auricle to the skull, then this may cause its partial (or complete) amputation.
- Sarcoma of the auricle. This type of malignant tumor is characterized by a slow course and later manifestation. As for sarcoma of the auditory canal, on the contrary, it will grow quite intensively, quickly spreading into the cavity of the middle ear.
Lump behind a child's ear
Many diseases are accompanied by similar symptoms; a lump behind the ear may well indicate a serious internal illness, or a minor cosmetic problem that will take 15 minutes to eliminate. A lump that suddenly appears below, inside or near a child’s ear worries parents, but before starting treatment on their own, you need to visit an ENT doctor. If there is a seal behind the ear, you should not:
- rub;
- heat;
- Apply iodine mesh to the pine cone.
If your child has suffered an infectious disease or just had a cold, you can watch the lump for a while. Gradually it should decrease in size. A sedentary, “stony” lump should alert you immediately and do not put off going to the doctor. A mobile, shifting formation under the skin, most likely a lipoma, atheroma.
A common cause of the appearance of a round ball behind the ear is considered to be inflammation of the lymph node. Lymph nodes act as a filter that destroys pathogens. An inflamed lymph node indicates a focus of chronic, acute infection in the body. A lump that suddenly appears behind the ear may be an inflamed parotid lymph node. There may be several reasons for its formation:
The final conclusion is always made by the doctor.
There is no need to be alarmed if your baby has been prescribed a biopsy; this test is the best way to rule out a dangerous disease and begin treatment on time. An increase in size of the lump, pain, and a rise in temperature indicate lymphadenitis - inflammation of the lymph node itself. The inflamed lymph node suppurates, and shooting pains appear behind the ear. Purulent lymphadenitis can cause general blood poisoning.
Rarely, fortunately, a lump behind the ear is a symptom of malignant degeneration of the lymph node itself or cancer. A malignant tumor of a lymph node is lymphoma, dense, “stony”; pain is rarely noted on palpation. The disease is accompanied by loss of appetite, weakness, and night sweats.
Symptoms of a malignant ear tumor
Symptoms of an ear tumor, and especially its malignant form, are primarily expressed by pain. The pain, as a rule, has a baking and burning tint, reminiscent of the pain of a burn. At first, such pain occurs only once, then repeats with enviable regularity and, in the end, becomes constant. It is pain that is the main sign of the continuous intensive growth of a malignant ear tumor. Almost always, the patient feels pain radiating to the temporal lobe. A patient suffering from a malignant tumor in the ear is faced with constant discharge from the ear, which is purulent and bloody in nature. If an ear tumor closes the ear canal, this leads to the development of hearing loss in the patient.
If the malignant tumor is located in the tympanic cavity, then the clinical picture will be almost the same as that of chronic purulent otitis media: tinnitus, increasing hearing loss, which leads to final deafness, pain. It is precisely the discovery of a sharp decrease in hearing and constant incessant pain that may lead the patient to think about the presence of a malignant tumor. It should be said about the special nature of pain with a malignant tumor of the ear. This pain is deep-seated and constant, worsening at night. Even when there is heavy discharge from the ear cavity, the unbearable pain does not stop for a minute, but, on the contrary, only increases.
Another symptom of a malignant tumor is vestibular dysfunction. The latter occurs because the malignant tumor, spreading to the area of the windows, begins to put pressure on them.
A common symptom of a malignant tumor is facial nerve paresis, and all because as the tumor grows, it destroys the facial canal, which leads to facial nerve paresis. Enlarged regional lymph nodes, as well as thickening of the parotid glands, are other characteristic symptoms of the presence of this disease in humans.
Often a malignant tumor can grow into the ethmoid bone, nasopharynx or cranial cavity. If the tumor grows into the cranial cavity, the first thing that will be affected is the trunks of the cerebellopontine angle, the symptoms of which will be trigeminal neuralgia, as well as possible neuritis of the cochlear nerve or paralysis of the facial nerve.