Sometimes there is an unusual condition when the jaw does not open completely or does not open well. A person cannot eat properly, talk, and when trying to open his mouth a little wider, pain appears, sometimes of a sharp nature. Trying to sharply open the mouth, a person feels severe pain in the mandibular joint, and it can also radiate to the temporal region. This condition in which the jaw does not open completely is called muscle contracture. Problems in the periarticular tissues of the temporomandibular joint can also be the cause of such complaints.
Severely limited mouth opening is observed with ankylosis of the temporomandibular joint. With this disease, complete or partial fusion of the articular surfaces occurs. Normal eating becomes impossible, bite and breathing are disrupted. The face takes on a “bird-like” appearance. Treatment of this pathology is surgical. Additionally, massage, exercise therapy, drug therapy and a gentle diet are prescribed.
Description and symptoms of jaw joint dislocation
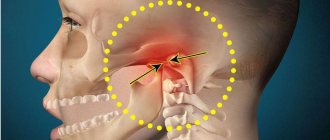
Discomfort in the jaw area most often occurs due to problems with the temporomandibular joint. It is formed by the head of the lower part of the jaw and the tubercle of the temporal bone, which, together with the articular disc, are part of the capsule. The work of this joint is very complex and is associated with a whole set of muscles. If something goes wrong, not only the joint itself suffers, but also the muscles of the neck, head, and cranial nerves, resulting in chronic pain, most often from one – the problematic – part of the head.
Symptoms of TMJ dysfunction are varied - pain in the ears, head, and neck.
Why is it impossible to open your mouth wide or completely?
There are no nerve endings in the joint, so it does not hurt, but discomfort may occur. Toothache also often develops, and there is a feeling of squeezing of the eyes. Another key indicator of TMJ problems is jaw locking. The patient cannot completely close or open his mouth, and in order to make the desired jaw movement, he is forced to look for a position in which the joint functions normally. When moving the jaw left and right, clicking sounds are possible. Secondary manifestations of TMJ pathologies:
- irritability;
- sleep problems;
- general malaise;
- noise in ears;
- Bad mood;
- snore;
- xerostomia;
- muscle pain;
- twitching of the eye muscles;
- drop in visual acuity;
- paresthesia.
According to medical observations, the ANS (temporomandibular joint) plays the role of the center of balance of the whole organism.
Methods and remedies
The choice of treatment method depends not only on the health of the patient’s teeth and gums, but also on his age. Treatment of children is much easier and faster. This is due to the fact that their bone tissue is not yet fully formed. Therefore, it is important to monitor oral health starting from birth and do not forget to show your child to the dentist, even if he has no pain and you do not see any problems. Only a professional doctor will be able to correctly assess the health of the oral cavity and make timely corrections.
- From birth to 7 years of age for a child
To correct the bite, it is enough to do special exercises and massage. The only thing that is important is to wean your baby off bad habits as early as possible, and it is better not to teach him in the first place. If the baby continues to suck his fingers, the treatment will not bring the desired result;
- To correct the bite between the ages of 7 and 12 years
special removable structures are used that guide the teeth in the desired direction. This allows them to be aligned in the correct direction. They need to be worn for several hours a day. They are harmless and do not cause severe inconvenience;
- Plates are used when the first 2 options did not bring the desired result
. Treatment will depend on the specific situation and averages 1.5 years.
In adults, bite correction occurs with the help of braces. With their help, you can eliminate problems even at the age of 40, which is very important, since if the bite is incorrect, it will be impossible to install dentures.
Causes
Dislocation of the lower jaw is a common pathology that occurs due to the ease of injury and the accident factor. It is not necessary to get injured (fight, fall), yawn widely or try to bite off a huge piece of something - sometimes it is enough just to open your mouth unsuccessfully. Other factors that can lead to the development of pathology are loud screams, yawning, inaccurate eating, difficult tooth extraction, malocclusion, bruxism with increased tooth wear.
Regular consumption of very hard foods and a love of opening different packages with your teeth increases the chances of TMJ subluxation.
According to another medical theory, the causes of TMJ dysfunction are myogenic - that is, they lie in problems with the facial muscles. We are talking about their overload during chewing, tonic spasms, and increased speech activity. Problems with the central nervous system also have an impact - constant stress and exhaustion negatively affect facial muscles and joint mobility.
Some people have a congenital predisposition to TMJ dysfunction - for example, if the sizes of the articular fossa and heads do not initially match, jaw asymmetry occurs. And according to statistics, women often turn to doctors with jaw dislocations - the fact is that the male ligamentous apparatus is more developed and stronger, and therefore can withstand significant loads. In men, problems in the TMJ often develop against the background of rheumatism, polyarthritis, and gout.
Associated symptoms
An early signal of joint dysfunction is the characteristic clicking sound that is heard when opening the mouth. Other signs are as follows:
- malaise and weakness;
- insomnia;
- apathy or increased irritability;
- dry mouth;
- ringing and noise in the ears;
- muscle pain;
- night snoring;
- muscle twitching in the eye;
- decreased vision.
Classic signs of a dislocation are: difficulty chewing, difficulty speaking, dysphagia, severe salivation, pain in the area of the joints or one joint. The lower jaw looks visually slanted, shifted to the side, and the face becomes asymmetrical in appearance. The habit of chewing on any hard objects, as well as opening bottles with your teeth, can sooner or later result in a dislocated joint.
Treatment
Treatment of jaw dislocation should be carried out only by a doctor; he chooses the method taking into account the diagnostic results. The fact is that, despite similar symptoms, each type of injury has its own characteristics and methods of elimination. The main method of therapy is reduction of the jaw joint, which can be carried out using the Hippocratic, Blechman-Gershuny, or Popescu Method. The jaw is pressed with your hands (gently) and set in the required position. If everything is done correctly, it will need to be secured with a bandage, which will help avoid recurrence of loss.
Never try to straighten your jaw yourself. Only a specialist can carry out this procedure correctly.
Old dislocations can often only be removed surgically; after surgery you need to wear special devices. Dentures can also be used for habitual dislocation of the lower jaw. They can be removable or permanent and are used to limit the degree of mobility of the joints of the lower jaw. The duration of wearing is determined by the doctor - it depends on the recovery time of the sprained ligaments.
You cannot adjust the jaw at home yourself, as this can only worsen the patient’s condition.
What can you do at home if your jaw is stuck?
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs reduce pain and stop the inflammatory process. They are always prescribed for jaw dislocation, internally and externally; the standard treatment period is 2 weeks; if necessary, it can be extended. To speed up recovery after reduction or surgery, techniques such as ultrasound, electrophoresis, and laser therapy can be used. After completion of treatment, discomfort in the injured area rarely remains; it is eliminated using special ointments.
Take first aid measures to alleviate a person’s condition when their jaw is jammed:
- limit jaw mobility by securing it with a bandage in the least painful position;
- give me a painkiller.
The prognosis for treatment for dislocations is positive, but no one is immune from relapses. To minimize the risks of their development, wear special dentures to limit mouth opening, correct teeth, especially if a tooth is dislocated, which could cause displacement of the joint, promptly treat and prosthetize chewing teeth, and do myogymnastics (it strengthens the chewing muscles). In the future, to avoid dislocations and injuries to the jaw, monitor the amplitude of mouth opening.
What to do
To eliminate the problem of difficulty opening your mouth, you should visit a dentist.
The specialist will conduct an examination, prescribe appropriate diagnostic measures, and discover the cause of the inflammatory process. Therapy will directly depend on the condition of the joint, the degree of contracture, and the cause that provoked the pathology. What to do can only be decided by a qualified specialist. Also, in order to prescribe competent therapy, the time during which the pathological condition lasts is important. There are two main approaches to the treatment of contracture – conservative and radical. To begin with, conservative treatment is prescribed, which includes the use of the following measures and medications:
- Anti-inflammatory medications.
- Analgesics.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Therapeutic exercises.
All of the above measures are intended to reduce the severity of the inflammatory process and gradually force the mouth to open.
If the cause of contracture of the muscular system is the introduction of anesthesia or overstretching of the muscle during prolonged opening of the jaw, such conditions usually go away on their own within a few days and do not require special treatment. If the reasons lie elsewhere, a visit to a specialist is mandatory.
In the event that this pathology is caused by adhesions, scars, tissue fusion, it is advisable to use radical treatment, which involves surgical intervention. Surgical treatment consists of excision of modified tissues and replacement of lost areas of tissue. Typically, these procedures are performed by oral and maxillofacial surgeons.
Possible complications
In the absence of proper treatment, the primary dislocation of the jaw turns into an old one, and if you correct it yourself incorrectly (we strongly advise you not to do this), over time, with a high degree of probability, the need for surgical intervention will arise. This material will tell you what to do if toothache radiates to your temple.
The main complications of TMJ dislocation:
- bruxism;
Bruxism or teeth grinding leads to excessive tooth wear or complete loss.
- erasing enamel;
- pain when chewing;
- clicks;
- arthrosis
A medical consultation is required, since a jammed jaw may indicate not only a dislocation of the joint, but also a fracture, osteomyelitis of the jaw, arteritis of the facial artery, and dysfunctional changes in the jaw apparatus. And the sooner they are detected, the more positive the treatment prognosis will be. Find out why you grind your teeth in your sleep here.
If your jaw is jammed, your doctor will first try conservative methods, and if they don’t help, he will recommend other options.
What problems arise from malocclusion?
- Speech problems;
- Unpleasant sensations when chewing and swallowing food;
- Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract;
- The occurrence of headaches;
- Problems with the spine;
- Incorrect placement of teeth in a row;
- Problems with teeth and their loss at an early age;
- The occurrence of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
Diagnostics
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, you may need to see several specialists.
Additional symptoms can tell you which doctor will help:
- To establish the reasons, a detailed examination by a specialized specialist is required.
If your teeth and oral cavity are sore, you should consult a dentist;
- If you suspect a facial injury, contact a traumatologist;
- If you have a sore throat or ear, see a therapist or ENT specialist;
- If there is a boil on the face - see a surgeon;
- If additional symptoms do not help determine the pathology, see a therapist or neurologist;
- Consultation with an oncologist may be required.
To establish the causes, you need a detailed examination by a specialized specialist; if there is discharge, its analysis, as well as x-rays of the jaws, general and biochemical blood tests.
These examinations will tell you what additional measures need to be taken to determine the cause of the disease.
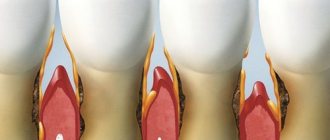
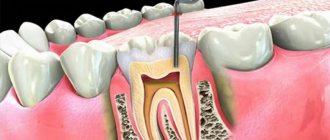
Inflammation
The inflammatory process (furuncle, osteomyelitis, abscess, phlegmon, etc.) on the skin of the lower jaw, oral mucosa, soft tissues of the cheek can involve the joint and masticatory muscles. Such conditions require urgent intervention.
Causes of pain
Impaired mouth opening is associated with the involvement of the joint, muscles or nerves that allow the mouth to open. Another reason is that when moving in the joint, the position of the inflamed tissues changes.
The nature of the sensations and accompanying symptoms
The pain is constant, sharp, twitching. Associated symptoms include fever, swelling of the face on the affected side, enlarged lymph nodes under the jaw and on the neck, and decreased jaw mobility.
If there is inflammation under the skin, the skin becomes hot and thins. A boil on the face (more common in men) is clearly visible.
Treatment methods
Purulent inflammatory processes are treated surgically. The doctor opens the affected area, washes it with antibiotics, and leaves a drainage to drain the pus. The patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics, regular dressings, and washing of the postoperative wound with antiseptic solutions.