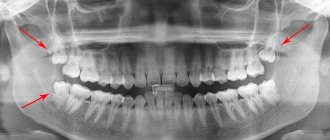
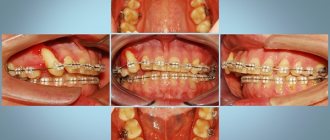
03/14/2020 A Hollywood smile does not always have 32 teeth. There may be only 28 if a person does not have “eights” or they have been removed. Finding out the answer to the question, at what age does the wisdom tooth grow in the upper and lower jaws, is interesting to everyone. They are the last to erupt. Not every person has them inherent in nature or are able to grow to become full-fledged participants in the dentition. 15% of women and men do not even have the rudiments of third molars (“eights”). A panoramic photo of the jaws will give an accurate answer about their presence, but at what age wisdom teeth begin to grow is difficult to predict.
How to know if a wisdom tooth is coming out
A wisdom tooth or “eight” is a third molar that erupts on both sides of both jaws at 16-30 years of age.
Because this age is considered mature, and the third molar is the last one to grow in the jaw, it is called a “wisdom tooth.” Some dentists consider the “eight” to be a vestige, that is, an organ that has lost its significance in the course of evolution. Primitive man needed it to chew rough plant foods - nuts, grains and leaves.
Modern man eats soft food that has undergone culinary processing, so the jaw has become 10-12 cm smaller, and the dental system has been rebuilt. As a result, in 76% of people, the third molar does not erupt, remaining in the bone socket, or grows partially or incorrectly.
From the article on Stom-Firms.ru you will learn how a wisdom tooth grows, why it is difficult for it to erupt and what symptoms arise.
The occurrence of pain
The reasons why a wisdom tooth hurts can be different and the formation of a painful condition is explained by various anatomical and physiological features of the structure of the dentition and possible inflammatory processes that accompany the eruption of a wisdom tooth.
Sometimes it grows, and due to the incorrect angle of its position, it simply puts pressure on neighboring teeth, gradually shifting them towards the center.
It happens that there is simply not enough space for a tooth to fully develop, which gives it the “green light” to deform the intramaxillary space and the ability to grow in any direction.
It also aggravates the pain and the development of pathogenic microorganisms, which only intensify the discomfort. Also, due to its remoteness, inflammatory processes develop faster, and it is more difficult to maintain the necessary hygiene in these places.
When a wisdom tooth hurts badly (if this does not concern the first manifestations of its eruption), then there is a high probability that this is provoked by the formation of some kind of disease that has arisen against this background.
During caries, pain appears after eating sour, hot, spicy or cold food. If these factors are eliminated, the pain should disappear.
In chronic and acute pulpitis, the pain is very different in nature. The acute form is characterized by sharp attacks of pain, which tend to intensify at night. Purulent pulpitis has symptoms of throbbing wave-like pain. In chronic forms of this disease, the pain is aching and periodic, lasting 10-15 minutes.
With periodontitis, wisdom teeth hurt in different ways (the intensity directly depends on the stage of development of the disease). Often pain goes hand in hand with inflammation of the gums, swelling of the cheeks and soft tissues in the mouth, fever and sleep disturbances. In its chronic form, periodontitis rarely bothers a person with pain.
In any case, to accurately diagnose the causes of pain in the wisdom tooth area, you will have to contact an experienced dentist. Doctors recommend that eights be examined every 3-4 months.
How to understand that a wisdom tooth is cutting?
For many, “eights” erupt without causing complaints. But since the sharp edges of the crown irritate the nerve endings of the gums, the following symptoms occur:
- Soreness or dull throbbing pain;
- Swelling of the gums, which can be felt with the tongue;
- Saliva mixed with blood;
- “Gum hood”, that is, raised gum above the crown of the tooth.
The pain intensifies when a person chews, opens his mouth, or lies down. In people with a low pain threshold, it can be severe, even if the tooth grows correctly and does not encounter obstacles.
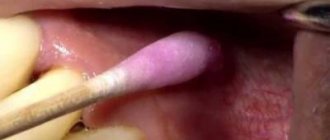
If the third molar cannot “break through” the soft tissue, pericoronitis occurs - inflammation of the gum above the crown. The tooth injures the mucous membrane, tears form in it, in which food particles and bacteria accumulate, causing inflammation. Pus forms under the “gum hood” and can be released into the oral cavity.
If pus spreads to the periodontal tissues and bone, periostitis occurs - a flux that causes the following symptoms:
- The mucous membrane becomes cyanotic;
- The cheek is swollen;
- The pain becomes unbearable and intensifies when you try to open your mouth;
- The patient cannot eat;
- The parotid and submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged;
- Body temperature rises to 38°C.
When the swelling spreads to the cheek, palate and throat, the patient experiences difficulty swallowing. Severe pain is disturbing if the “eight” does not fit in the jaw, grows at an angle, or displaces and compresses the neighboring tooth, the “seven”. Because of this, the bite may change, and caries may appear on the neighboring “seven”.
Molar growth process
With proper growth, figure eight teeth do not cause any particular trouble to the patient. The physiological process ends with the vertical position of the extreme molar, which eliminates changes in bite, caries and the formation of a hood.
The patient may complain only of slight redness and thickening of the gums, mild pain, which can last from several days to a month.
During the eruption of extreme molars, some pathological phenomena may occur.
Most often, these include tooth deviations from vertical growth:
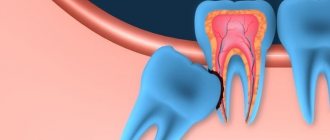
- The process of tilting the molar forward towards the seven is called medial tilt.
The process of tilting the molar forward towards the seven is called medial tilt. It can provoke the onset of caries in a neighboring tooth, the reason for this is constant pressure on the enamel and the accumulation of microorganisms in the gap formed between them.
- With a distal tilt , when the figure eight grows backward, its urgent removal is necessary.
- The eruption of a molar towards the cheek is accompanied by damage to its mucous membrane. The buccal tilt of the tooth can provoke malignant tumors at the site of damage.
- During horizontal and linguistic growth, compression of the roots of sevens , sixes and fives occurs. This causes an inflammatory process that requires immediate removal.
How long does it take for wisdom teeth to erupt?
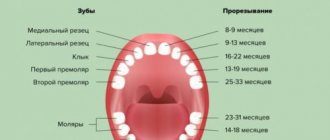
The rudiments of “eights” can be detected as early as 3 years. During adolescence, when the jaw is actively growing, roots form. Normally, teething lasts 3-5 months, while unpleasant sensations may disappear and reappear.
The rate of growth depends on both local and general reasons, which we have collected in a table. The listed reasons, on the one hand, slow down eruption, and on the other hand, they disrupt the ratio of the sizes of the jaw and wisdom teeth.
| General factors | Local factors |
|
|
During puberty and pregnancy, the body releases many substances - cell growth factors. They act on G8 stem cells and stimulate its formation and growth.
When are third molars removed?
There are a number of reasons why removing “eights” is necessary:
- incorrect direction of the tooth during growth;
- lack of space;
- change in the position of the teeth (crowding);
- strong pressure on the seventh molar;
- process of purulent inflammation;
- crown destroyed by caries.
In some cases, your doctor may advise you not to pull out your molars.
For example, if a patient undergoes dental prosthetics, during eruption they will take the correct position, and the canals are clearly visible for further treatment.
How does a figure eight cut through?
With normal growth of a wisdom tooth, the gum above it becomes loose and soft; after a few days, the lateral chewing tubercles of the crown appear above it, and behind them - its central part with grooves. After complete eruption, the crown is located on the same level as the adjacent one.
Growth anomalies of the figure eight include difficult eruption, retention and dystopia. Let's take a closer look at them.
Difficulty erupting wisdom teeth
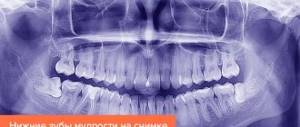
The eruption of the third molar may be delayed for several years if there is some obstacle in its path. For example, the lower eights grow more slowly because the mucous membrane over them is thicker than over the upper teeth. In addition to the gum, the crown needs to grow through the fibers of the buccal muscle and the levator pharynx muscle. If during chewing the mucous membrane is constantly injured, scars and seals form in the gum “hood”, the “eight” will not be able to erupt on its own.
Retention of wisdom teeth
During retention, the third molar is formed, but cannot grow through the bone tissue, so it remains or is retained in the bone socket - the periodontal sac. The cause of retention is growths on the periosteum or cementomas in the alveolar sac. Because of them, the “figure eight” fuses with the socket or with the root of an adjacent tooth.
There are 2 types of retention:
- In complete retention, the crown of the third molar is hidden under the bone plate of the jaw, so it cannot be seen or felt. To detect it, the dentist does a targeted x-ray or orthopantomogram.
- More common is incomplete eruption - semi-retention, when part of the crown grows through the gum, and part remains under it.
“Eight” rarely appears in people over 30 years old, because by this age it becomes denser, fuses with the bone socket and cannot completely come out of it. If nothing bothers the patient, the tooth is not touched.
Wisdom tooth dystopia
With dystopia, the figure eight is located outside the dental arch. Depending on the degree of deviation, the following positions are distinguished:
- Vertical, if the tooth deviates slightly from the longitudinal axis of the “seven”;
- Oblique, when the figure eight crown moves towards the cheek, second molar, tongue or palate;
- Horizontal location, if its axis is perpendicular to the axis of the adjacent tooth.
Both growing wisdom teeth and impacted ones can be dystopic. They are displaced if there is not enough space in the jaw or if the rudiment is located incorrectly, for example, not in the bone socket, but in the ascending ramus of the lower jaw.
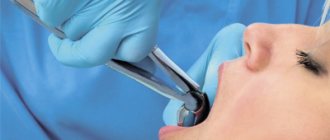
Delete or leave unchanged
This is a topic of active debate among dentists and researchers. Regardless of how old people are when wisdom teeth appear, doctors recommend removing them. There are a number of contraindications for removal:
- missing 1 or 2 molars (6 and 7 in a row);
- the tooth position is vertical;
- history of viral infections in the active stage;
- There is a possibility of treatment for caries.
Age 17, 20 or 35 – it is not so important at what age a wisdom tooth comes out in the jaw. If you feel good, there are no acute inflammatory processes in the gums, and there is no crowding of other teeth, removal can be postponed. This is normal dental practice. If there is aching pain, intoxication with high fever, signs of gumboil, removal is indicated in 99% of cases. Knowing the information at what age wisdom teeth come out in men and women, you can mentally prepare for this process. Everything else and the peculiarities of the development of events depend on genetics and nature. Monitor your condition, undergo preventive examinations on time and, if urgently necessary, seek dental care.
How to relieve pain when wisdom teeth erupt
To reduce pain and swelling, you can massage the gum with your finger or apply a piece of ice to it. Hands must be thoroughly washed and disinfected. The gums need to be massaged gently, in a circular motion; you should not rub too hard, otherwise you can damage it and cause bleeding. Massage is not done if pus is secreted from under the “gum hood”, otherwise the infection can spread to the bone and periodontium.
Ice can be applied up to 5 times a day for a few minutes. The cold causes the tissues to become numb, and the pain decreases for a short time. Peppermint candies also help.
If the gums have become loose and the figure eight has partially erupted, you should:
- Chew on the healthy side so that food does not accidentally fall under the “hood”;
- Avoid hot and spicy foods, which irritate the mucous membranes and increase pain;
- Carefully monitor oral hygiene to prevent pericoronitis;
- Rinse your mouth with antiseptics or infusions of sage and chamomile.
You cannot remove food particles with your fingernail, injure the mucous membrane with a toothbrush, or try to “speed up” tooth eruption with hot compresses.
For severe pain, you can take a painkiller orally or use gels. If the swelling and pain intensify, the body temperature rises, and the third molar does not erupt, contact your dentist. He will examine the oral cavity, take an x-ray and prescribe painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. In case of pericoronitis, it is enough to cut off the gingival hood so that the “eight” takes its correct position in the dentition. In difficult cases, the dentist will recommend removing the wisdom tooth.
Possible complications
Inflamed gums cause pain when chewing or swallowing, poor health and fever.
Pericoronitis is one of the serious complications that can occur during the eruption of third molars.
The disease is characterized by an inflammatory process that affects the tissue around the tooth.
Inflamed gums cause pain when chewing or swallowing, poor health and fever.
A characteristic feature of pericoronitis is the abundant proliferation of bacteria under the hood.
Around the third day, the disease becomes purulent. The patient complains of severe toothaches and pain radiating to the ear and temples, painful opening of the mouth.
The presence of pus under the formed hood causes intoxication of the body, which is manifested by high temperature. The patient has severe facial asymmetry on the side of the diseased tooth, pale face and inflammation of the lymph nodes.
Due to the proximity of the figure eight to the second molar, a small gap is formed in which food debris accumulates. The proliferation of bacteria in most cases leads to the appearance of caries.
A tooth that has already come out is considered the most convenient place for bacteria to multiply: its inconvenient location makes them difficult to clean. After some time, the gums become inflamed and swollen. Flux occurs with fever, severe pain and a swollen cheek.
When the upper tooth erupts, the trigeminal nerve may become inflamed, which is manifested by involuntary contraction of the facial muscles and sharp pain. With late therapy, facial paralysis may occur.
An abscess is a purulent disease that causes an unpleasant odor from the mouth, severe throbbing pain, a constant bitter taste and swelling.
What is the diagnosis
Doctors often use 2 terms when describing problems with wisdom teeth.
Retention – when a tooth fails to erupt. It grew, but remained inside the jaw completely or partially. This can create a focus of inflammation, which either subsides or worsens again. But the most unpleasant consequence can be a cyst around the tooth if it has not erupted at all.
Dystopia is an abnormally positioned tooth, for example, horizontally. At first, such a tooth germ may not bother you at all. But when it starts to grow, it can lead to a lot of problems. You also need to remember that the tooth simultaneously grows in 2 directions towards the crown and towards the roots. If such a rudiment is tilted, then the tooth may appear from the side of the cheek or, conversely, grow inside the mouth and scratch the tongue.
One of the options for dystopia is a horizontal arrangement.
During the process of growth, a slightly inclined tooth in a narrow jaw can “catch” on the neighboring one, which will lead to an accident. The growing tooth will turn around and lie horizontally. Further, the growing tooth can gradually displace the remaining teeth and lead to crowding of the front teeth. This will create a new problem, not only an aesthetic one, but daily hygiene becomes more difficult and the risk of caries increases.
Often dystopia is combined with retention, which provides more reasons to remove problematic eights.