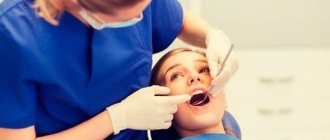
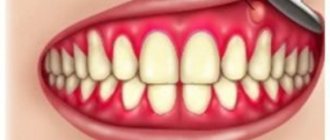
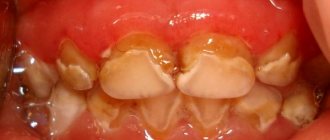
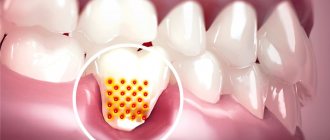
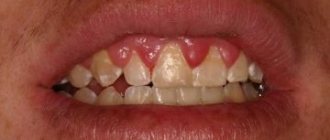
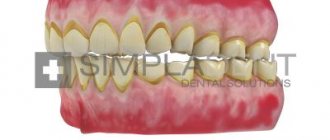
Periodontal diseases belong to the group of pathologies of the oral cavity, when hard and soft tissues surrounding the teeth are affected. The periodontium is a retainer that holds teeth in the jaw bones. Its condition affects the health of the entire oral cavity. The main symptoms manifest themselves in the form of bleeding, swelling, and sore gums. Common diseases of periodontal tissue include periodontal disease, gingivitis, and periodontitis.
To alleviate the patient's painful condition, non-surgical treatment is used. For this use:
- Injections;
- Applications;
- Bandages.
As a rule, dentists have ready-made sets of dressings at their disposal, or doctors make their own applications. They are applied to tissues to relieve pain and achieve an anti-inflammatory effect.
How to apply a bandage
Before proceeding directly to applying a gingival dressing, consider:
- Presence of anesthetic substances;
- Degree of wound protection;
- Anti-inflammatory effect.
The application process consists of the following steps:
- The doctor professionally cleans the tooth surface, removing deposits;
- The gingival margin is treated with antiseptics;
- After this, the bandage, regardless of its type, is applied so that it fits closely to the gingival margin and cervical part. In this way, periodontal pockets are isolated.
The doctor must make sure that the patient is able to articulate normally. If defects remain after the application of medicinal products, they are corrected: parts that interfere with the person’s ability to speak are cut off.
Duration of wearing from several minutes to three days. Soft bandages are most often used. When a longer period is needed to isolate the wound from the environment, for 3-7 days, rigid/elastic products are used. The procedure can be repeated 2-3 times.
Gels containing fluorides (up to 4000-12000 ppm fluoride ions),
used for applications to teeth in order to intensify their secondary mineralization, remineralization and increase the resistance of enamel to acids. Often the gels are acidified, since the incorporation of fluoride into the enamel occurs more actively in a slightly acidic environment. They can be intended for individual use at home or for use in a dental office (Fig. 7). Thus, these topical caries prevention products are classified as both personal dental care products and medical dental prophylaxis products. Fluoride gels available for self-use include neutral sodium gel (5000 ppm), stannous fluoride gel (1000 ppm). ppm). 1.23% sodium fluoride acidified phosphate gel (APF) has become widely used.
Below is the classic composition of such a gel:
- sodium fluoride - 26.50 g,
- sodium phosphate (dibasic) - 10.00 g,
- phosphoric acid 50% (until pH = 3.2 is reached) - 11.00 ml,
- sodium carboxymethylcellulose - 28.00 g,
- sodium saccharin - 500.00 mg,
- flavoring – 10.00 ml,
- distilled water - up to 1 liter.
In some European countries, topical gels are used as part of mandatory dental brushing programs (6–12 times a year) or are recommended for weekly home use in persons over 8 years of age. The concentration of fluoride in products used independently is lower than their concentration in products intended for use by specialists. Applications are usually carried out not daily, but at certain intervals. To carry out the application, the gel is applied to the teeth using a toothbrush or applicator for several minutes, after which the mouth is thoroughly rinsed. Application with gel applied to an impression tray or a special two-jaw plastic tray is more effective and safe. Many companies produce application spoons of various sizes for this purpose. It is more convenient to use individually made spoons. About 2.5 ml (5-10 drops) of gel (about 40% of the spoon's capacity) is usually applied to an adult's spoon. Gels for home use, as well as toothpastes, can be involuntarily swallowed (according to various sources, from 15 to 100% , on average 30%), therefore the fluorine content in them corresponds to that in traditional fluoride-containing pastes. Gels with a high fluoride content can only be used in a clinical setting under the supervision of a physician and using a saliva ejector. The duration of application should not exceed 4 minutes. If there are porcelain dentures in the mouth, which can be destroyed by acidic solutions and gels, they should be isolated (lubricated with Vaseline) before application. Before applying the gel, you must brush your teeth, 30 seconds after application, rinse your mouth with water or a saturated solution of sodium bicarbonate and do not drink or eat for 30 minutes. Fluoride gels for individual and medical use are indicated for high caries intensity, the presence of general and local cariogenic factors (in particular, according to WHO recommendations, orthodontic patients and in patients with xerostomia who are undergoing radiation therapy), the presence of foci of enamel demineralization on the teeth, and dental hyperesthesia.
Is it necessary to carry out extensions?
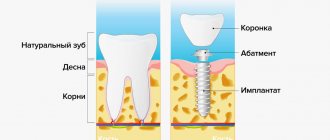
The condition of the bone and soft tissue determines how the future crown will look and function. Gum augmentation during implantation, the price of which is determined by the method used, is a mandatory procedure if there are indications for it. It is impossible to ensure the immobility of the implant if the patient has a clear lack of bone tissue. In order for the crown to be visually attractive and fully perform its functions, it must be surrounded by keratinized gum of the required density, height and width. If everything is normal, then the risk of injury to the cervical area of the crown is completely eliminated, because it is reliably protected by the gum, therefore, the implant does not become exposed. But if the implant is exposed, then this is fraught not only with the appearance of a cosmetic defect, but also with inflammatory processes, which are harbingers of serious dental diseases. When a patient experiences bone tissue atrophy, this does not mean that installation of implants is impossible. You just need to contact a medical and dental clinic, where he will be offered several options for solving the problem. Gum regeneration at the Shifa clinic is an effective treatment at an attractive price.
Applications give excellent results
- Aloe grows in almost every home. Take a mature leaf, cut off the spines, cut it in the middle and “put it on” the sore tooth. Despite the tolerable bitterness, keep the application for half an hour. To strengthen the gums when bleeding, at least 10 procedures should be done.
- Mix 30 drops of almond oil and 5 drops of clove oil, prepare cotton strands, which should be dipped in the oil mixture, and apply them to the gums for a quarter of an hour.
Attention!
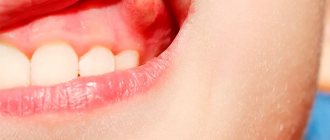
If loose teeth are not the result of injury or malocclusion, you should consult a doctor to rule out periodontal disease, a cyst, or a neoplasm. Only an integrated approach will help solve the problem of bleeding gums and stop loose teeth.
This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details!
Gels intended for application to the mucous membrane of the gums,
represent an extremely small group. These, in particular, include drugs with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory additives used before and after periodontal surgery. This group also includes Oralbalance Gel, containing lactoperoxidase, glucose oxidase and xylitol. Like Biotene toothpaste, the gel replenishes the normal protective properties of saliva, reducing bacterial contamination. Due to the content of polyglyceryl methacrylate, the gel moisturizes tissue and is recommended for use in cases of xerostomia. The gel is applied to the tongue and gums. It is not recommended to combine with detergents. Parodium gel (Pierre Fabre, France) contains chlorhexidine digluconate (0.02 g), Tangut rhubarb extract, which has an anti-inflammatory effect (0.20 g), formaldehyde (0.10 g) and is applied with a finger or special applicator on the gums 3 times a day for the prevention and treatment of periodontal diseases. Dentim-gel (Mirra, Russia) contains biologically active substances isolated by cold extraction and biotechnological potentiation from a special collection of medicinal plants, lavender essential oil, alcoholic extract of sweet clover. The gel has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and deodorizing effects and is recommended for application and gentle rubbing into the gums for preventive purposes in the presence of inflammatory processes in the periodontium.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and hold LEFT Ctrl and press Enter.
You can send no more than 5 messages in 30 minutes!
Liked? Tell your friends!
Why does bone tissue atrophy?
There are several reasons why bone tissue changes:
- presence of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity
- injuries of the jaw apparatus
- age-related changes
- tumors
- acquired and congenital anomalies
- individual characteristics of the body
- complex tooth extraction
All this affects the condition of the gums, into which, if desired, an implant can be installed, but it is not necessary, because during wearing and operation the risk of its displacement and loosening is very high. In addition, degenerative processes intensify, during which the gums recede even more, which leads to exposure of the artificial root.
According to existing rules, when installing an implant, which is the basis for prosthetics of a chewing tooth, the width of the bone tissue cannot be less than 7 mm, and the minimum height is 10 mm. If during an examination by a doctor at the Shifa clinic it is determined that the size of the bone tissue does not correspond to the required size, then gum augmentation surgery is especially indicated for such a patient. Before surgery, oral diseases must be eliminated and dental plaque removed to avoid infection.
In what ways can you grow gums?
Block plate landing
The meaning of the procedure is as follows: in order to restore a small area of the jaw, bone tissue is transplanted. A stranger or the patient himself can act as a donor; moreover, the necessary material can be obtained artificially. Sometimes animals, such as bulls, act as donors, but this happens extremely rarely, and the most common options are the patient’s own tissue and synthetic material. The operation takes place in two stages: the surgical intervention is preceded by the preparation of the material and the patient, who will certainly require anesthesia. The block plate (that’s what autogenous material is called) is fixed to the jaw using special screws, and on top it is covered with a layer of bone chips and a membrane. Afterwards, the gums are sutured. This operation has its advantages: firstly, rejection of the block plate is a fairly rare phenomenon, and secondly, this procedure is characterized by high speed. It is worth noting that implantation can begin only when the block plate has completely taken root. During the first week after surgery, swelling and pain may appear, so while the body is recovering, the patient should protect himself from stress, excessive physical activity and visiting the sauna and bathhouse. In addition, there is a whole list of contraindications, which can be found during a preliminary consultation with a specialist at the Shifa clinic.
Sinus lift
If the thickness of the bone tissue is insufficient, this is a serious obstacle to implantation. This defect is especially typical for elderly patients, as well as for people with such anatomical features. Sinus lifting is performed on the upper jaw, and before performing this operation, the dentist has to carry out a whole range of preparatory measures. Surgery can be performed in two ways: Open method. During the procedure, a small diameter hole is made in the gum and jaw, through which, using appropriate instruments, the clinic specialist performs a jewel-like delicate manipulation - shifts the bottom of the nasal and maxillary sinuses. As a result, free space is created for artificial bone tissue. Private method. This operation is appropriate to perform only when it is necessary to add a small amount of bone. A hole for the implant is immediately drilled in the jaw, taking into account that the distance to the maxillary sinus should not exceed 3 mm. Its bottom moves in a similar way, and bone chips are introduced into the resulting cavity. The good thing about this method is that you can immediately install the implant. Sinus lifting, regardless of the technique used, also has a number of contraindications; moreover, the tissues after this surgical intervention take quite a long time to recover. All this time, the patient should not visit baths, saunas and swimming pools, and he will have to sneeze with great caution. The price of gum augmentation at the SHiFA clinic depends on what method was used, and the type of material used also affects the final cost.
Guided regeneration
This method of gum extension is characterized by low trauma and its unusual nature. Thanks to the method of directed regeneration, the volume of bone tissue increases due to the natural growth of biomaterial - membranes. A cavity is created under the biological tissue itself, which is filled with bone chips, as a result of which young bone-forming cells gradually grow. The membrane is played by self-absorbable or non-absorbable materials that require subsequent removal. Their presence is mandatory, since it is the membranes that isolate the implant from the soft tissues and prevent bone chips from being washed out of the wound.
Gels for self-application on teeth and gums
Gels intended for home applications comprise at least two different groups.
Gels containing fluoride
(up to 4000-12000 ppm fluoride ions), used
for applications to teeth
in order to intensify their secondary mineralization, remineralization and increase the resistance of enamel to acids. Often the gels are acidified, since the incorporation of fluoride into the enamel occurs more actively in a slightly acidic environment. They can be intended for individual use at home or for use in a dental office (Fig. 7). Thus, these means of local caries prevention relate to both personal dental care and medical dental prophylaxis.
Fluoride gels available for self-use
include neutral sodium gel (5000 ppm), stannous fluoride gel (1000 ppm). 1.23% sodium fluoride acidified phosphate gel (APF) has become widely used. Below is the classic composition of such a gel:
- sodium fluoride - 26.50 g
- sodium phosphate (dibasic) - 10.00 g
- phosphoric acid 50% (until pH = 3.2 is reached)
- 11.00 ml
- sodium carboxymethylcellulose - 28.00 g
- sodium saccharin - 500.00 mg
- flavoring – 10.00 ml
- distilled water - up to 1 l
In some European countries, topical gels are used as part of mandatory dental brushing programs (6–12 times a year) or are recommended for weekly home use in persons over 8 years of age. The concentration of fluoride in self-administered products is lower than that in products intended for professional use.
Applications are usually carried out not daily, but at certain intervals.
To carry out the application, the gel is applied to the teeth using a toothbrush or applicator for several minutes, after which the mouth is thoroughly rinsed. Application with gel applied to an impression tray or a special two-jaw plastic tray is more effective and safe. Many companies produce application spoons of various sizes for this purpose. It is more convenient to use individually made spoons. About 2.5 ml (5-10 drops) of gel is usually applied to an adult’s spoon (about 40% of the spoon’s capacity).
Gels for home use, just like toothpastes, can be involuntarily swallowed (according to various sources, from 15 to 100%, on average 30%), therefore the fluoride content in them corresponds to that in traditional fluoride-containing toothpastes. Gels with a high fluoride content can only be used in a clinical setting under the supervision of a physician and using a saliva ejector.
The duration of the application should not exceed 4 minutes. If you have porcelain dentures in your mouth,
which can be destroyed by acidic solutions and gels, they should be isolated (lubricated with Vaseline) before application. Before applying the gel, you must brush your teeth, 30 seconds after application, rinse your mouth with water or a saturated sodium bicarbonate solution, and do not drink or eat for 30 minutes.
Fluoride gels for individual and medical use are indicated in case of high intensity of caries, the presence of general and local cariogenic factors (in particular, according to WHO recommendations, orthodontic patients and in patients with xerostomia who are undergoing radiation therapy), the presence of foci of enamel demineralization on the teeth, and dental hyperesthesia.
Gels intended for application to the mucous membrane of the gums,
represent an extremely small group. These, in particular, include drugs with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory additives used before and after periodontal surgery.
This group also includes Oralbalance Gel, containing lactoperoxidase, glucose oxidase and xylitol. Like Biotene toothpaste, the gel replenishes the normal protective properties of saliva, reducing bacterial contamination. Due to the content of polyglyceryl methacrylate, the gel moisturizes tissue and is recommended for use in cases of xerostomia. The gel is applied to the tongue and gums. It is not recommended to combine with detergents.
Parodium gel (Pierre Fabre, France) contains chlorhexidine digluconate (0.02 g), Tangut rhubarb extract, which has an anti-inflammatory effect (0.20 g), formaldehyde (0.10 g) and is applied with a finger or a special applicator to the gums 3 times a day. day for the prevention and treatment of periodontal diseases.
Dentim-gel (Mirra, Russia) contains biologically active substances isolated by cold extraction and biotechnological potentiation from a special collection of medicinal plants, lavender essential oil, and alcoholic extract of sweet clover. The gel has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and deodorizing effects and is recommended for application and gentle rubbing into the gums for preventive purposes in the presence of inflammatory processes in the periodontium.