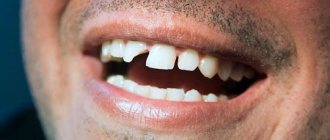
Mechanical damage to a tooth due to injury without violating its integrity is called a bruise. This type of injury is common in children and adults, especially athletes. According to statistics, among all injuries to primary teeth, bruises account for 2.5%; bruises of permanent teeth account for 1.5% of the total number of traumatic injuries in the permanent dentition.
Even if the tooth looks unchanged after a bruise, it is necessary to visit a dentist to prevent the development of complications associated with the injury.
Diagnosis of tooth trauma
In case of tooth injuries, timely assistance is very important to minimize the consequences of damage. It cannot be put off until later (after a day, a week, etc.) - it is important to provide yourself or your child with first aid correctly and contact a dentist as soon as possible. But first you need to figure out what damage is considered a tooth injury.
Mechanical tooth trauma is damage resulting from falls, impacts, accidents and other external influences. They violate the shape of the tooth and the integrity of dental tissues. Mechanical injuries of various types are divided into acute and chronic dental injuries. The first type includes damage to teeth as a result of a single and strong action (falling from a bicycle, swing, scooter, biting too hard food or a toy, a blow to the teeth due to an accident, etc.).
Chronic injuries are associated with bad habits (for example, chewing pencils, pens, seeds) or with a violation of the closure of teeth, due to which the dental tissues are gradually injured.
➢ The peak of injuries to permanent teeth occurs at primary school age - 8-10 years, and for milk teeth - at 2-3 years.
➢ Injury to permanent teeth is less common among professional athletes, since they wear special protection - helmets, mouth guards, and shields.
➢ Most often, injuries occur for everyday reasons: during breaks at school, during active games, at home, on the street, etc.
➢ Trauma to the front teeth, especially the incisors, is the most common occurrence (about 80% of cases).
➢ The risk of damaging teeth is 3 times higher in people with a distal bite, in which the front teeth protrude forward and the lower jaw is in a posterior position.
Main reasons:
- Mechanical damage (for example, if an adult or child hits the crown during a fall, from an impact);
- injury while eating (excessively hard and/or tough food, foreign objects in food);
- bad habits (biting walnuts in the shell, opening bottles with your teeth, etc.);
- consequences of incorrect removal (sometimes the doctor touches a neighboring tooth, injuring it).
Classification of dental injuries
The ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases) classification of dental injuries includes more than ten types of dental injuries. To summarize, all mechanical damage is divided into:
- for injuries to the tooth itself or fractures;
- tooth displacement or dislocation;
- damage to soft tissues and jaws.
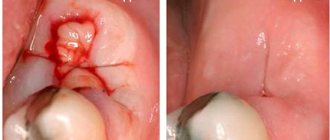
It is also worth noting a bruise - minimal damage to a tooth when it looks intact and visually no damage is visible - no chips, no cracks. But due to the impact, the blood supply to the tooth pulp may be disrupted, and subsequently the tooth may darken. Tooth bruises belong to the first class of injuries according to ICD-10. It hurts to touch, bite and chew food.
First aid for a bruise is to give pain relief if necessary, and consult a dentist as soon as possible.
Symptoms
You can “recognize” a tooth dislocation by the following signs:
- pathological mobility;
- pain that gets worse when touched;
- change in the color of the enamel (it may darken due to a disruption in the supply of nutrients or the ingress of the contents of damaged vessels from the tooth cavity into its hard tissues);
- difficulty eating;
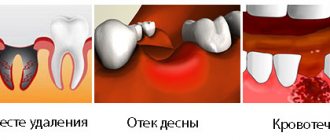
- bleeding gums in the area of injury;
- changes in bite (difficulty or impossible to close the jaws normally).
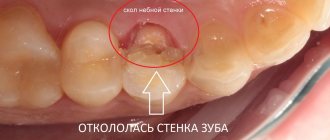
Dental injuries in the form of fractures
Chips of enamel, fractures of the coronal part with damage to the pulp, fractures of the roots - all these injuries fall into the category of “tooth fracture”. There are 3 options for fractures of primary teeth:
- if the baby tooth is slightly injured, then the doctor usually monitors its condition;
- In case of significant damage, the baby tooth is removed in order to preserve the permanent tooth germ, since the injured baby tooth becomes a source of infection. This often happens with longitudinal fractures - when the tooth cracks in half lengthwise, and it is no longer possible to save it;
- in other cases, the tooth can be saved through restoration and canal treatment. In young children, treatment is often carried out during sleep.
First aid for a tooth fracture: It is very important to collect all the tooth fragments and put them in water or milk. If you collect all the parts of the tooth and quickly, within half an hour, get to the dentist, the tooth can be restored and it will be successfully fixed in the socket. If it was not possible to collect the tooth particles, then treatment of the tooth injury is carried out:
- In case of minor damage to the enamel (chips, cracks), tooth polishing is not performed - the dentist restores the tooth by installing a filling.
- If there is severe damage to the crown of the tooth, endodontic treatment may be required to preserve the pulp and then the installation of an inlay and/or crown.
- If the root is fractured, the tooth is rigidly splinted for 3-4 months, and the dentist monitors the condition of the pulp. Sometimes it is necessary to treat the canal of a coronal fragment, but there is no need to connect the fragments with pins. The tooth can almost always be saved, since this is a sterile injury, and the treatment prognosis is favorable, and therefore it is not necessary to remove teeth with a broken root.
The peculiarities of dental prosthetics in children are the impossibility of using implants, so a lost tooth is replaced with a removable plate, an artificial tooth is fixed with fiberglass to adjacent teeth, or orthodontic mini-screws are used to fix the prosthesis with a temporary screw. Tooth replantation is also used - transplantation of a lateral tooth in place of a missing one.
Treatment
- For mild bruises, treatment consists of resting the tooth for 3-4 weeks by reducing the load during chewing: the menu includes soft and semi-liquid foods, and a blender is used to grind hard foods.
- To ensure rest for baby teeth, temporary bite separation with the help of mouth guards is used; if a permanent tooth is bruised, splinting is performed. The splint allows you to immobilize an injured tooth and redistribute the load during chewing onto healthy teeth.
- If the pulp dies due to an impact, the tooth cavity is opened and the pulp is removed, after which the root canals are filled and a permanent filling is installed. If the crown of a tooth darkens, it can be whitened.
- When a baby tooth is bruised, grinding of the cutting edge of the crown of the antagonist tooth is used to prevent tooth contact and reduce pain. This method is not used for permanent teeth.
- To relieve pain, it is recommended to take an anesthetic tablet (ibuprofen, ketorolac, nimesulide) and apply an anesthetic gel (Dentol, Kamistad) to the gums around the tooth.
- When swelling of the soft tissues of the face accompanies a bruise, cold compresses are applied: a plastic bottle with cold water (not lower than +4°C) is wrapped in a cloth and held on the area of swelling for 15-20 minutes.
- A course of magnetic laser therapy is carried out - a combined effect on injured tissue of a magnetic field and low-intensity laser radiation. The method helps improve healing processes, relieves swelling and inflammation. The course consists of 10 daily procedures lasting 5 minutes.
- UHF therapy is indicated to accelerate tissue regeneration.
Dislocation
When a tooth is dislocated, sometimes it is impossible to completely close the mouth, or the tooth becomes loose and changes its position relative to other teeth. How to distinguish a tooth dislocation from a fracture? If the appearance of the teeth has changed - they have become shorter, tilted, etc., and the gums are bleeding, then you are dealing with a dislocation.
First aid for dislocation is the most correct tactic: do not let the child close the teeth, do not touch them and do not try to set them back on their own, because such displacements can be accompanied by injuries to the bone and gums. It is best to immediately contact a dentist, who will take a three-dimensional photograph, return the teeth to the correct position, and apply dental plaster for several weeks. The sooner you do this, the better.
Experts distinguish between many types of dislocations, including partial, complete and impacted.
Partial dislocation
With such damage, the tooth partially falls out of the socket. Often the alveolar wall is damaged, there is a tear in the periodontal fibers, and therefore the tooth becomes loose, bleeding occurs, and severe pain occurs when pressing and chewing. However, the anatomical structure is not disturbed, so the main task is to fix the tooth in the correct position in the socket until healing. In case of partial dislocation, this is achieved using special caps or splinting. The key point is to get the victim to the dentist as quickly as possible.
Complete dislocation
The tooth completely falls out of the socket, which is accompanied by heavy bleeding. When a baby tooth falls out, it is not reinserted, since placing the baby tooth in the socket can damage the germ of the permanent one. But if a permanent tooth falls out, then the necessary first aid is to find the tooth, wash it with water, but do not rub it or treat it with alcohol, since there are still living cells on it. Then the tooth needs to be inserted into the socket or, if this is not possible, put the tooth in milk and call the clinic to get instructions on how to do this.
If the tooth is placed back into the socket within 5 minutes, the prognosis is favorable - the tooth will successfully take root. Over a period of 5 to 10 minutes, the chances decrease as the number of living cells decreases. If the tooth has been exposed to air for a long time and has dried out, it will not take root for long, just a few years.
In any case, you need to get to the clinic as soon as possible - preferably within half an hour. If this is not possible, then contacting a dentist is still necessary. It is necessary to carry out root canal treatment, since when a tooth is severely displaced or falls out completely, the blood supply to it stops.
Impacted dislocation
Milk teeth are very often driven deep into the socket, since when they fall, the impact force is directed from bottom to top. This is very dangerous for the buds of permanent teeth, which are located behind the roots of baby teeth. Due to such trauma, various disturbances in the formation of the enamel of permanent teeth can occur, which manifest themselves in the form of yellow and white spots or defects in the shape of the tooth. It is necessary to take a targeted picture on a visiograph to assess the risks for permanent teeth. If a baby tooth is impacted too deeply, it is removed to reduce the risk of developing defects in permanent teeth. Sometimes tooth reduction is performed, in which the dentist very carefully returns the impacted tooth to its correct position and then splints it.
Tooth injuries are often accompanied by damage to soft tissues - cheeks, gums, lips. In this case, the dentist prescribes mild antiseptics - most often chlorhexidine preparations, as well as a gentle diet without harsh foods.
Make an appointment
right now!
Tishkina Olga Sergeevna
Therapist
Where to go with a dental injury
But if you have already provided first aid to a child or adult for a tooth injury, then why also contact a dentist? The fact is that there are damages that cannot be seen with the naked eye - for example, a fracture of the tooth root inside the bone, fractures of the jaw bones and the walls of the tooth socket. Even after successfully placing the tooth back into the socket, splinting is necessary - this is the temporary stabilization of the tooth using a wire that is attached to adjacent teeth. In some cases, it is necessary to suture the edges of the wound or prescribe antibiotics.
If you ignore the problem and do not consult a doctor on time (or do not visit the clinic at all), complications will arise. The tooth may darken, become mobile, and the most common complication after a tooth injury is pulp necrosis, in which the neurovascular bundle inside the tooth dies. The dentist uses special tests to determine the vitality and condition of the pulp. Leaving dead tissue inside a tooth can lead to tooth root resorption as the body begins to perceive it as a foreign body due to infection. This leads to tooth loss in a fairly short time. This is why it is very important to have your teeth examined by specialists after an injury.
The Iceberg Dental Traumatology Center has a free hotline where doctors and patients can obtain information on the treatment of dental injuries.
Prevention
To prevent dental injuries, you must:
- Observe safety precautions at work, arrange the workplace and carry out potentially hazardous work in accordance with established rules.
- Properly equip playrooms for children and supervise children while playing.
- Follow traffic rules and use seat belts when traveling, as even minor emergency braking of the car carries a high risk of injury.
- Avoid conflict situations that lead to fights.
- Ensure the safety of sports games using special equipment (helmets, masks, dental guards).
- Carefully select sports grounds: they must comply with safety requirements.