Cement for dental crowns
Causes of crown loss
What to do if a dental crown falls out
Cement for dental crowns
Features of various cements for crowns
Prevention of crown loss
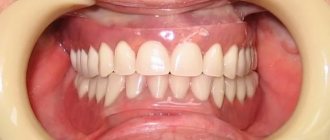
To restore a badly damaged tooth, a crown is needed. This is an orthopedic structure in the form of a cap, which is attached to the tooth using special cement. It protects the tooth from damage and maintains its functionality. However, due to improper hygiene or unprofessionalism of the doctor, the crown may fall off. What to do if a dental crown falls out? Can I attach it myself? Or is it better to seek help from a doctor?
Recommendations from experts
Before installing a crown on a damaged tooth, it is ground down and then dental cement specially designed for this purpose is applied. Thanks to this material, the crown is attached very firmly and does not move when chewing. After hardening, this material becomes very durable. A prosthesis fixed with this mass can last for more than 10 years, while a person does not experience any unpleasant taste or smell emanating from it.
Even if you buy the strongest glue, there is no guarantee that it will be able to withstand heavy loads. It often happens that the crown falls off and you have to go to the dentist. If you cannot visit a doctor, you can try to solve the problem yourself at home.
Causes of crown loss
Several factors can provoke an unpleasant situation associated with dental crowns. They depend both on the actions of the doctor and on the actions of the patient.
- Low quality materials and cement.
- Violation of the manufacturing technique of an orthopedic structure.
- Mistakes at the stage of preparation for prosthetics.
- Development of the inflammatory process under the crown.
- End of service life of the structure.
- Mechanical injury.
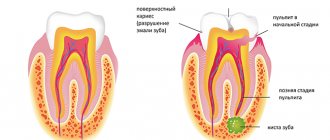
The permanent crown is fixed with dental cement and lasts for several years. If the doctor did everything correctly at the preparation stage, then the structure retains its tightness and strength for a long time, and it should not fall out. This can happen due to the development of caries, which appears due to irregular or improper oral hygiene. Therefore, it is so important not to skip brushing your teeth and use additional hygiene products. And also undergo professional oral hygiene at a dental clinic once every six months.
Functions of tooth root cement –
1) Protective function – the content of inorganic components in cement reaches 70%, which makes it resistant to mechanical loads. Consequently, one of its functions will be to protect root dentin from damaging effects.
2) Participation in the formation of periodontium - the formation of periodontal fibers occurs simultaneously both from the cementum of the tooth root and from the bone plate of the alveoli. According to a number of authors, these collagen fibers are subsequently intertwined with each other through immature collagen (procollagen), turning them into a single whole. The depth of immersion of periodontal fibers into the cement of the tooth root is from 3 to 5 μ.t.
3) Fixing (retaining) - cement of the tooth root together with the compact plate of the alveolus and periodontal fibers - ensures fixation of the tooth in the alveolus.
4) Compensatory function - when the length of the tooth decreases as a result of physiological abrasion of the enamel, increased production of cement occurs in the area of the apex of the tooth root. As a result, the tooth is pushed out of the alveoli into the oral cavity, and thus the size of the clinical crown of the tooth increases. This becomes especially noticeable in elderly patients.
5) Participation in reparative processes - for example, when the cause of root resorption is eliminated, its partial restoration may occur. Or, if there is a crack in the tooth root, cement may form between the fragments, which can lead to the elimination of the defect.
What to do if a tooth crown falls out
- First of all, you need to save the fallen structure and try to make an appointment with the dentist as soon as possible. For example, contact our specialists by phone: 220-86-30.
- Remember that the tooth that was under the crown was left without protection, so it must be treated as carefully as possible. It is necessary to chew food on the opposite side, trying to minimize the load on the tooth to avoid fracture.
- If pain occurs, take a pain reliever.
- If it is not possible to see a doctor in the near future, then try to carefully put the structure in place; before doing this, it must be thoroughly rinsed and dried. This will help preserve the prepared tooth until your visit to the dentist.
The next method is temporary!
an orthopedic dentist within three days
- Buy dental cement (sold at the pharmacy).
- Clean the crown thoroughly with toothpaste. Dry it with a sterile piece of cloth.
- Clean the tooth from food debris using a soft-bristled toothbrush.
- Apply cement to the crown, place the crown on the tooth and hold it in place for one minute. Then close both jaws and remain in this position for about two minutes.
- Remove any remaining cement using gauze.
Never try to glue a crown with superglue. The glue is very toxic, and contact with saliva can lead to dire consequences!
Fixing crowns using a screw method: are there any disadvantages?
The peculiarity of this method is that the abutment is not used as part of the structure, and the crown is screwed to the implant directly, using a screw. In this case, the prosthetist pre-fabricates a special crown with a hole for the screw. It would seem fast and reliable, why not? However, this fairly advanced technology is not without its drawbacks, in particular:
- aesthetic. It will not be possible to preserve the integrity of the crown covering the tooth: the shaft through which the fastening element passes will have to be closed with a composite filling. On the front teeth it will most likely be visible, so the patient will have to give up the dream of a perfect smile;
- functional. Due to the nuances of installation, the hole may occur in an area that is constantly under load, for example, on the cutting edge or masticatory tubercle. In this case, chips, cracks and gradual “eating” of the filling composite material are possible.
In addition, the manufacturing process of bridges for implant-supported prosthetics often involves minimal inaccuracies. When using dental cement in this case, correction can be carried out using a solution.
But in the process of screw fixation, with visually imperceptible inaccuracies, there is a risk of “attracting” the crowns by excessively screwing in the screw. What does this mean? At best, it will result in unpleasant sensations of tension in the patient’s oral cavity; at worst, it will result in a broken fastener, which will then have to be removed from the implant, which is a rather complicated procedure.
Cement for dental crowns
Now let's talk about what dental cement is, with which the doctor fixes the crown on the tooth. Few people know, but it comes in different types. The dentist always decides which option is right for you, based on clinical indications.
There are five types of dental cement:
- composites;
- zinc phosphates;
- glass ionomers;
- polycarboxylates;
- polymer modified glass ionomers.
They all have their advantages and disadvantages, so it would be incorrect to say which one is the best.
When choosing a particular type of cement for fixing a crown, the doctor looks at the following indicators.
- Strength is the ability of cement, after hardening, to compress and unclench when teeth are closed during chewing.
- Adhesiveness is the ability of a substance to adhere to tooth tissue.
- Irritability – the likelihood of an allergic reaction.
- How difficult it will be to remove it.
- Aesthetics.
Structure, types of cement
Cementum is represented by cells and intercellular substance. The cells are cementocytes, cementoclasts and cementoblasts.
Histologically, there are 2 types of cement: acellular and cellular.
Acellular cement, or primary cement as it is called, does not contain cells - only calcified intercellular substance. Its thickness is 23-40 microns. Covers the neck of the tooth.
Secondary cement (or cellular) covers the root with a small layer, located below the neck of the tooth. Cementocytes, process cells, are found in large numbers in the interroot sections and in the area of the apical part of the root. Cemetoblasts are also isolated, which are located on the surface of the cement. Cementocytes are localized in the thickness of the cementum of the tooth. Secondary cement is localized on acellular or dentin.
Compared to the primary, the secondary is formed much faster. Cementocytes are characterized by many branching processes and the presence of a large nucleus. When they die, they leave gaps in deeper layers. Closer to the periphery, cementoblasts are similar to cementoblasts and are more “active”. The latter contribute to the deposition of cement.
The intercellular substance is represented by collagen fibers, which, depending on their location, are divided into several types:
- growing into dentin;
- extending into the periodontium;
- localized within the cement, internal;
- growing into the periosteum of the alveoli.
The intercellular substance is also represented by mineralized glycosaminoglycans and matrix. Intercellular fibers are formed by their own cells (that is, cementum cells) and run parallel to the root. The fibers of the periodontal ligament, which are also part of the alveolar bone, pass at right angles to the tooth.
Features of various cements for crowns
Table 1. Features of various cements for crowns
| Type of cement | Example | Characteristics | Application |
| Composite cement | High strength and adhesiveness, aesthetics. | Suitable for fixing not only ceramic crowns, but also veneers and lumineers. | |
| Zinc phosphate cement | One of the very first cements used. Easy to use. Has average strength and adhesiveness. May temporarily increase tooth sensitivity (up to 3 weeks). | Suitable for single crowns and small bridges. | |
| Glass ionomer cement | This aluminosilicate glass with a high fluorine content is an excellent caries prevention. High adhesion, but low strength. | It is used for increased risk of caries and high tooth sensitivity. | |
| Polycarboxylate cement | High biocompatibility, serves as additional prevention of caries. However, it has low adhesiveness and strength. | Used for fixing single crowns with high tooth sensitivity. | |
| Modified glass ionomer cement | Innovative material. Combines the advantages of composites and glass ionomers: high strength and adhesiveness. | It is used for installing both single crowns and bridges. Suitable for people with an increased tendency to caries. |
What is hypercementosis
Sometimes during treatment of periodontitis in children or adults, dentists diagnose excessive cement deposition. It often forms over the entire root surface and is caused by chronic infection of the periapical area. Against the background of hypercementosis, the root sometimes fuses with the alveolar wall. This disease develops more often in the lower jaw - mainly in molars and premolars.
The cement in baby teeth is thinner than in molars. As a rule, this is acellular cement, while secondary cement occurs occasionally in the apical part of the root. This trend is also noticeable if we compare the structure of enamel and dentin of adult and children’s teeth: in childhood they are thinner, therefore more sensitive to external factors that cause caries.
Prevention of crown loss
Once you have a crown installed, we recommend making sure it lasts a long time. To do this, you need to remember and follow simple rules.
- Forget about sticky candies, chewing gum, the habit of biting your nails, the tip of a pencil or pen.
- Brush your teeth regularly. If you haven't used brushes or an irrigator yet, now is the time. Also, don't forget about mouthwash.
- Monitor the condition of the crown. If even small defects are detected, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
- Once every six months, come for a check-up with an orthopedic dentist and do professional oral hygiene.
The loss of a crown causes great inconvenience. If this happens, you should immediately contact your dentist.
The role of cement in periodontal regeneration
Not only the substances of the bone socket tissue are responsible for regeneration in the periodontium, but also the presence of certain chemical compounds contained in the intercellular substance of the cement layer of the tooth:
- CGF factor (cement growth factor);
- CAP protein (responsible for the adhesion of periodontal fibroblasts - cells that synthesize proteins that maintain the state of the structure and functioning of the cells of the dental bone environment).
Equally important is the presence of growth factors in it, which appear in huge volumes in the damaged area, favoring tissue regeneration:
- IGF-1;
- IGF-P;
- TFR-31;
- TRFR.