Author: Brodsky Sergey Evgenievich Deputy Chief Physician, Candidate of Medical Sciences in the specialties: dentistry and medical microbiology Any person is inclined to believe that if the nerve is removed from the tooth, then it will no longer hurt. However, this opinion is not entirely true. A dead tooth can hurt, as well as react to cold and hot, and this phenomenon is called hypersthesia, increased sensitivity of the dental unit. These unpleasant sensations require a visit to the dentist, as they may indicate inflammation that has begun in a dead tooth or other dental problems.
Deputy Chief physician Sergey Evgenievich Brodsky
Sign up for a free consultation
+7
In what cases is the nerve removed from a tooth?
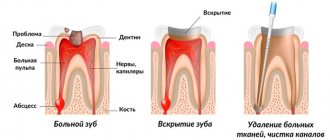
First, let's look at why pulp removal (dental nerve) or depulpation is performed. The need for depulpation arises for several reasons. Practicing dentists identify the following indications for this operation:
- the occurrence of pulpitis: damage to the neurovascular bundle due to the spread of caries,
- extensive deep carious cavity: if the defect is more than 50% of the total volume of the crown, then a filling cannot be placed (it will not hold well and will quickly fall out), and other restoration options - pins, inlays, crowns - involve depulpation,
- the presence of several carious cavities: grinding down the enamel and removing infected dentin can significantly increase the size of the defect, i.e. again, the crown will have to be restored in such a way that pulp removal will have to be carried out,
- mechanical trauma: when a horizontal root crack is detected, for example, periodontitis: inflammation of the tissues of the ligamentous apparatus-1 surrounding the roots.
Causes
The causes of dental hyperesthesia can be very diverse, ranging from mechanical damage to the surface of tooth enamel and ending with general disturbances in the functioning of the human body. The most common causes of enamel hyperesthesia are:
- damage to tooth enamel by short-term exposure to organic or mineral acids;
- exposure of dentinal canals as a result of carious and non-carious lesions of teeth;
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system as a result of pregnancy or menopause;
- disturbances of phosphorus-calcium metabolism in the human body;
- previously suffered general or neuropsychological diseases of the human body;
- exposure to ionizing radiation on the human body;
- habit of eating a lot of sour berries, fruits, juices, fruit drinks.
Sensitive tooth enamel occurs when the dentinal tubules become exposed for one or more reasons and a variety of irritants affect the sensitivity of the pulp. In this case, even simple inhalation of cold air or brushing your teeth can cause painful sensations. Teeth in the cervical area are especially sensitive, because the enamel is thinnest there, and if the gum moves away from the tooth, it almost immediately begins to react sharply to various irritants.
Separately, we should dwell on the mechanism of hyperesthesia. As you know, dentin is penetrated by many tiny tubes - the so-called dentinal canals, in which there are processes of nerve cells that are connected to the pulp. Dentinal tubules are filled with fluid that is in constant motion. Any change in the speed of fluid movement causes a pain reaction.
If the enamel is thinned, this leads to exposure of the dentinal tubules, and under the influence of various irritants, the speed of fluid movement in the dentinal tubules constantly changes, causing acute short-term pain, as a result of which the patient complains of very sensitive teeth.
Features of nerve removal
Experienced doctors perform depulpation only as a last resort. But sometimes it is impossible to do without it. What is the procedure? First, an x-ray is taken, from which the dentist draws conclusions about the condition of the pulp (nerve tissue), areas around the root and gets an idea of how deep the inflammation has spread. The specialist assesses the length of the nerve and the features of its location, then gets to work and acts in several stages:
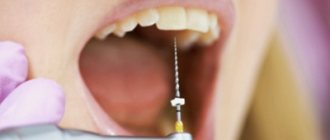
- anesthesia: local anesthesia to relieve the patient of inevitable discomfort. Modern drugs make it possible to carry out all manipulations absolutely painlessly,
- caries removal: the dentist drills out the affected areas of enamel and dentin using a drill,
- nerve removal: using a special tool called a pulp extractor, which is screwed into the canal, the dentist removes the neurovascular bundle in several stages,
- expansion and cleaning of the canals: carried out so that the doctor can efficiently clean the canals from remnants of nervous tissue and prepare them for filling. The channels are expanded with thin burs, which help to level and smooth the inner surface of the walls,
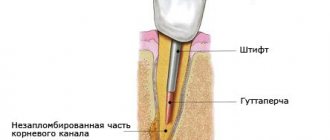
- filling: a material specially designed for filling (for example, gutta-percha) is injected to the entire depth of the root. The consistency of this substance allows you to fill the cavity entirely so that there are no empty areas left there. The upper part is covered with composite material. In some cases, a large inlay is placed or a crown is installed over the filling.
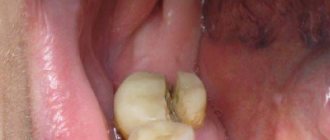
A tooth left without a nerve is called “dead.” It becomes insensitive to irritants, and enamel mineralization stops. It loses its whiteness and acquires a dark shade. To restore an aesthetic appearance, the dentist may suggest performing intra-canal whitening, installing a veneer or an aesthetic ceramic (or metal-ceramic) crown.
Prevention
Prevention of hyperesthesia is as follows:
- complete oral hygiene, which includes systematic brushing of teeth using appropriate pastes that do not contain abrasive particles and do not destroy tooth enamel;
- professional hygiene in the clinic at least once every six months;
- correct brushing technique, which involves using a medium-hard brush that does not injure the teeth and gums;
- minimal use of whitening paste, as it contains abrasive particles and chemical elements that can cause damage to the enamel and leaching of calcium from it;
- consumption of foods containing phosphorus and calcium;
- limiting the consumption of sour fruits, berries and juices;
- systematic visits to the dentist at least twice a year.
To prevent the disease, your dentist will help you choose an effective remedy for tooth sensitivity that will reliably protect your enamel from damage. If the patient has sensitivity to frost, cold, or hot, the doctor will also select a remedy for tooth sensitivity that seals the dentinal tubules, preventing changes in the speed of fluid movement inside them and preventing the occurrence of painful sensations.
Features of dental nerve removal
On a note! Upon completion of the manipulations, the doctor must evaluate the result. For control, an x-ray is taken again, from which the dentist makes a conclusion about the quality of treatment. After a properly performed operation, the pulpless tooth will serve the owner for many years and can even become a support for a prosthesis.
Why does pain occur after removal?
Experts identify several factors that cause pain in a sealed tooth without a nerve - this can be either a normal condition or a pathological one. To be able to distinguish them, you should know some nuances.
It is normal to feel painful discomfort in the first few days after visiting the dental office. Under the influence of the drill, healthy dental tissues heat up, hence the unpleasant sensations. Pain occurs with pressure or during eating - for one to three days or a week.
Important! Pain may be the result of a complication, injury, inflammation, or an error made by the doctor at some stage of treatment. If the pain does not go away even after two to three weeks or suddenly arises a few days after the procedure, especially at night, this is a reason to contact the clinic.
The dentist must determine the cause and prescribe treatment if necessary. The filling will likely need to be removed and the root canals re-treated. In any case, it is better not to delay going to a specialist.
Pain after dental treatment
The main causes of pain in the root of a tooth without a nerve are presented below.
1. Damage to periodontal tissue
When processing canals with special instruments, their edges may go beyond the border of the root and touch sensitive tissues. Also, unpleasant sensations can be caused by a small amount of antiseptic getting outside the root canal, which the dentist uses to disinfect the treated cavities. Such procedures involve the use of potent drugs, and their effects may well cause irritation. If the dentist did everything correctly, in both cases considered, the pain usually goes away after a few days.
2. Unsatisfactory canal filling
As a result, internal inflammation often develops, which is visible only on an x-ray. There are two possible reasons. First: the canals were not completely sealed. If during filling there are voids in the canal, areas that are not completely filled, over time harmful bacteria will begin to multiply in them, which will cause inflammation. The spread of infection can lead to the accumulation of pus at the root and the occurrence of periodontitis. The second reason suggests that the filling material has reached beyond the root apex, which also contributes to severe discomfort.
3. A piece of dental instrument remains in the root canal
During expansion, cleaning or filling, a piece of one of the devices could break off and get stuck in the canal. In most cases, this happens due to the fault of the doctor - if he violates the technique of working with the instrument. The exception is when the dentist deals with curved canals. Sometimes it is possible to get the piece out, but if it gets too deep, it will be impossible to remove it. The presence of a foreign object, even a tiny one, will prevent the specialist from performing the filling properly. This means that voids form in the canal, which will become a springboard for the proliferation of microbes and the occurrence of inflammation. Over time, it will spread to the periodontium, and if left untreated, to the jaw bone and soft tissues.
What to do with prolonged pain?
If you have a pain in a filled tooth without a nerve, and the pain does not go away within a few days, you should seek medical help. Most often, the problem can be solved, otherwise the dentist will suggest removing the affected unit of the dentition and installing an implant or dental bridge.
How does dental retreatment occur?
Depending on the cause of the ailment, there are several ways to relieve the patient of pain under a filling in a healed tooth without a nerve:
if the canals are not completely sealed, you will have to treat again - removing the old filling material and installing a new one. This must be done as quickly as possible, otherwise inflammation on the roots will lead to the loss of an incisor or molar. In addition, the specialist may decide to perform a surgical resection of the upper part of the root. Then there will be no need to carry out all the manipulations again if the filling material gets outside the canals: everything will depend on the amount of the substance. If there is only a small amount of it, the pain usually subsides naturally, and the tooth does not need to be re-treated. It is acceptable if mild discomfort continues for up to one to two months. Whether it is necessary to wait until the pain goes away on its own and treat immediately - this is decided by the doctor, focusing on the dynamics of the patient’s sensations. If the pain gradually disappears, it is likely that you will not have to repeat the manipulations.
If a lot of material gets outside the root, the doctor often performs an operation to cut off the tip of the root. To remove particles of filling material, the dentist makes a hole in the jawbone and removes excess material through it. It sounds scary, but in practice it is not the most difficult procedure. It lasts no more than an hour if a piece of the instrument remains in the canal: professional dentists try to remove the foreign body immediately after detection in order to prevent complications. The fragment is removed using ultrasound, the waves of which knock the particle out of the canal.
Another method involves creating a new channel close to the stuck debris. It is expanded, disinfected and the instrument is removed through it. It is also possible to use the method of resection of the root apex already described above and remove it along with the stuck piece if perforation has occurred: this is the most difficult case, requiring filling with a special expensive material. If the occurrence of perforations was caused by a dentist, the medical organization must correct the situation at its own expense.
Filling can be carried out both in the standard way - from inside the dental cavity, and from the outside, creating access to the perforated area through surgery, if an allergy to the filling material is detected: the patient can be relieved of pain only after repeating the treatment procedures with replacing the filling substance. Reaction to hot food: is this possible? There are known cases when hot food or drinks cause pain in a pulpless tooth. Normally, this should not happen, because the doctor removed the pulp, which made the unit of the dentition insensitive to thermal influences.
However, if particles of nerve tissue remain inside, sensitivity may persist and cause discomfort. Another scenario: inflammation from the pulp has spread further, and exposure to hot foods or liquids causes pain in these tissues. To accurately determine the cause, you should contact a professional. X-rays and examination using a special microscope will help identify the source of residual sensitivity.