- Signs of correct bite
- Types of malocclusion
- Why do you need to correct your bite?
- Until what age can a bite be corrected?
- Ways to correct a bite
- Aligners
- Trainers
- Veneers
- Bracket system
- Types of braces
- Which braces system should you choose?
- How long does it take to correct a bite?
- How to care for braces?
Malocclusion occurs in almost 80% of the Russian population. In a third of cases it requires orthodontic treatment. And it’s not just a matter of aesthetics - if you are often bothered by headaches, earaches and dizziness, then perhaps it’s a malocclusion. An orthodontist deals with the correction and prevention of malocclusions.
The most common misconception about bite is related to age. Many people think that it can only be corrected in childhood, but today, with the advent of new technologies, this can be done at any age.
In this article we will look at the causes and types of malocclusion and why it needs to be corrected. We will also tell you about treatment methods and dispel the most common fears. Orthodontist Olesya Milagina comments on current issues of orthodontic treatment for us.
Correct and incorrect bite of teeth
Of great importance in the development of pathologies of the dental system is the human bite - the relative position of the teeth of the upper and lower jaws when they are tightly and completely closed.
All people are born with mandibular retrograde (the lower jaw in a newborn has a posterior position), but the formation of the bite continues during the first 15 years of life. At the same time, this process is influenced by various factors, as a result of which a person, at the time of reaching adulthood, can develop a correct and incorrect dental bite.
Figure 1. Physiological types of occlusions.
Diagnosis of dental occlusion
Correct diagnosis of a patient’s bite can only be carried out by a qualified specialist, since dentistry describes various types of physiological and abnormal relationships of the jaws. However, you can find out whether a consultation with an orthodontist is required by first checking the relative position of the dentition at home.
How to determine dental malocclusion yourself?
The algorithm of actions is as follows: with a closed mouth, a person swallows saliva and closes his teeth, after which he fixes their position. Then, parting his lips, he examines the relative position of the jaws in the mirror. With a correct (physiological) bite, the following picture is observed:
- absence of gaps in the dentition, incorrect position of individual units in the jawbone;
- the dental units of the upper and lower jaws close tightly and are located on a single line;
- the lower incisors are slightly overlapped by the upper antagonists;
- The midline of the face is located clearly between the first incisors of the upper and lower jaws.
The reason for contacting an orthodontist is the absence of one or more of the described signs. You should also consult a dentist if excessive accumulation of soft plaque is detected on individual teeth, and bleeding gums are observed for a long time.
Types of bite
With undisturbed development of the dental system, the relative position of the upper and lower dentition may be different. There are the following types of correct bite:
- Orthognathia - the upper dental units evenly overlap the lower teeth, forming a single line. In this case, the incisors overlap the lower antagonists up to a third of the height of their coronal part. The cutting edges of the incisors form a cusp contact. This variant of physiological occlusion in dentistry is recognized as a standard and is practically not found among the population.
- Progenia - in this case, the patient’s lower jaw is slightly pushed forward.
- Direct (orthogeny) - the incisors in the upper and lower dentition form contact with the cutting edges.
- Bioprognathia - has the same characteristics as the orthognathic type of bite, however, the incisors of both jaws are tilted towards the vestibule of the mouth.
In all the cases described above, the biomechanics of the patient’s chewing movements are not disturbed and there is no risk of developing pathologies of the dentofacial system.
Figure 2. Abnormal occlusion of teeth.
When should the situation be corrected?
There are often cases when, with a normal physiological occlusion, it is necessary to carry out correction. Direct occlusion leads to tooth wear, and progenic and biprognathic bites can cause aesthetic discomfort, for example, when the upper lip is very short, exposing the front teeth, or when they are large and unsightly.
Abnormal types of closure with obvious defects require mandatory correction, since such pathologies interfere with the normal functioning of the jaws, have a negative effect on the body, and distort the proportions of the face.
There are several pathological levels:
- Violation of the shape, position and number of teeth.
- The size of the dentition is increased or decreased.
- Abnormal positions and sizes of the jaw bones.
The severity of the pathology is influenced by the area and degree of deformation of the constituent elements of the dental system. Therefore, when identifying an abnormal bite, it is important not only to identify the defect, but also to establish the reasons for its development.
Causes of malocclusion
In orthodontics, the reason that leads to disruption of the process of bite formation in people has not yet been established. There are numerous provoking factors that contribute to the development of abnormal interposition of antagonist teeth. However, their absolute pathogenetic significance has not been established, since the presence of the same factor in different people does not always lead to the formation of malocclusion.
The development of an abnormal relationship between the upper and lower dentition in a patient can be provoked by artificial feeding, prolonged use of pacifiers in childhood (more than 1 year), incorrect introduction of complementary foods (prolonged feeding of a child with soft food), impaired nasal breathing in a child, curvature of the spinal column, etc.
Removable
The entire period of loss of baby teeth and growth of permanent teeth - from 5-6 years to 11-13 years - the child has a mixed bite. Permanent teeth erupt at certain times and in a certain sequence. If these deadlines are greatly violated in one direction or the other, this can lead to various consequences.
photo: mixed bite in a child
Irregular eruption of permanent teeth
Too early eruption can serve as a symptom of endocrine disorders and even indicate the growth of tumor formations in the jaw.
If, on the contrary, growth is seriously delayed, then such teeth are called impacted - formed, but not grown . This phenomenon can cause not only frequent neurological pain, affect the development and position of neighboring teeth, but also provoke the development of tumors.
How to check your teeth bite yourself, criteria for determining correct and incorrect bite
Correct bite is the location of the teeth in which they fit tightly together. It is the key to health and a beautiful smile, and ensures full chewing function. Unfortunately, not all people can boast of such a bite.
Deviations from the norm are accompanied by an aesthetic defect and the appearance of a number of health problems. Let's take a closer look at how to check your dental bite yourself, and when treatment is recommended.
How to check your bite yourself?
Many people are interested in how to understand that the bite is incorrect. Severe violations are visually clearly visible (for example, a chin that is set very forward or, on the contrary, a chin that is set too far back). A dentist will help you reliably determine the presence and type of problem, but at home you can carry out light manipulations and independently identify a violation of occlusion.
How to check your bite? To assess the closure line, it is necessary to perform a swallowing movement, fixing the incisors and molars in this position. Next, the lips are opened and the position in which the upper and lower teeth are relative to each other is assessed.
If they touch, there are no deviations from the norm. The incisors and canines of the lower jaw should overlap the upper units by 1/3 of the height of the crowns.
In addition, the line passing between the teeth on the upper jaw must coincide with the line passing between the teeth located on the lower jaw. During the process of chewing food, molars and premolars must be in close contact with each other.
The palatal cusps of the upper molars should fit comfortably on the chewing grooves of the lower molars.
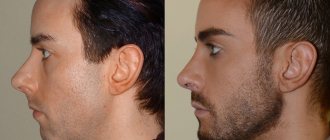
A person with a correct bite has proportional and pleasant facial features
Symptoms and signs of correct bite
Visually correct occlusion can be determined by the following signs:
- the lower and upper teeth are in close contact (located on the same line);
- there are no gaps between the teeth;
- the central incisors are located in the middle;
- the lower part of the face is symmetrical;
- the upper teeth slightly overlap the lower teeth;
- no crooked teeth.
Knowing how to determine the correct bite, you can avoid a number of problems.
If the upper and lower dentitions are in close contact, we can talk about the correct bite
About the importance of proper bite
The bite is a system consisting of dentition, muscles and joints. Its violation negatively affects self-esteem; a person becomes withdrawn and unsociable. A correct bite is also important for your overall health.
Deviation from the norm is accompanied by the appearance of problems with the temporomandibular joints, chewing muscles, posture, digestive and respiratory systems. Incorrect occlusion can complicate implantation and prosthetics.
Is treatment necessary?
All people need to know how to check their bite, even if they have no health problems. Timely detection of deviations from the norm will allow you to quickly cope with the disease and avoid negative consequences. Correcting malocclusion is a necessary procedure that is used at any age.
The method of treatment is determined depending on the type of occlusion and the individual characteristics of the jaw structure. Most often they resort to installing braces - non-removable orthodontic structures. Each tooth is fixed in the correct position.
Due to the fastening bracket, the direction of its development is corrected, which contributes to the formation of correct occlusion.
Need for correction
The need to correct anomalies is due to the serious consequences they have for health.
Correction of malocclusion occurs most easily and quickly in childhood and adolescence, during the formation of the jaw apparatus. But this does not mean that it is impossible in adults.
Modern dentistry has in its arsenal many means and methods for correcting anomalies - myogymnastics, orthodontic devices developed in a huge number, and surgical methods.
In particularly difficult cases, combinations of these remedies can be used that can cope with almost any anomaly at any age.
In the vast majority of cases, correction is possible and necessary. The only exceptions may be minor anomalies or situations where a not too pronounced disorder occurs in elderly patients, making treatment inappropriate.
Problems due to malocclusion
Improper occlusion is accompanied by a number of problems. These include:
- diseases of the gums and soft tissues (periodontitis);
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- loss of incisors and molars (due to uneven chewing load);
- dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint;
- narrowing of the airway lumen;
- disturbance of blood supply.
It is important to monitor the formation of the correct bite from childhood, when any pathologies can be corrected with minimal effort
Diagnostic measures
Diagnostic methods and means for determining the type of bite are extremely diverse. Just listing them can take a lot of time. Therefore, we will focus only on the main ones. These include:
- interview and history taking;
- extraoral examination;
- intraoral diagnostics;
- additional methods and tools.
An important point during the interview is to clarify the nature of the pregnancy and the presence of anomalies in relatives.
During an extraoral examination, attention is paid to the symmetry of the face, the ratio of its lower third to the upper third, the ability to open the mouth freely (the distance between the teeth is normally 4.5-5 cm) and other facial features.
The most important is the intraoral examination, which clarifies the main parameters of the jaw apparatus:
- position and shape of rows;
- the nature of their closure;
- condition of teeth (position, shape, color, presence/absence, gaps/crowding, etc.);
- condition of the mucous membranes, the presence of injuries on them;
- and many other features.
Additional tools include various functional tests, examination of diagnostic plaster models of the jaws, transversal, sagittal and vertical measurements, radiography, and tomography.
Fluoroscopy is very informative, especially teleradiography, which provides frontal and lateral photographs of the face, allowing one to evaluate the relative position of the jaws.
Useful general information is provided by orthopantomography, which can also be used to determine the volume of the nasal sinuses.
After collecting and studying all the information, a treatment method is selected and a plan is drawn up.
What is dental anchorage and how is it used in orthodontics.
In this post, read how to correct a tooth midline shift.
Here https://www.vash-dentist.ru/ortodontiya/prikus/etiologiya-retrognatii.html find out why retrognathia of the upper jaw is dangerous.
Prevention methods
It is important to monitor the formation of correct occlusion from early childhood. Proper breastfeeding, correct positioning of the head during sleep, timely introduction of rough food into complementary foods, absence of bad habits (for example, thumb sucking), timely contact with a dentist - all these are components of preventing the formation of improper occlusion.
At the same time, it is important to treat pathologies of the throat, ear and nose in a timely manner so that the child does not predominantly breathe through the mouth.
What is a bite?
Dental occlusion is the relationship between the teeth of the upper and lower jaw, including in movement. In orthodontics (the branch of dentistry responsible for the study and treatment of anomalies in the development of teeth and the jaw system) there is the concept of correct and incorrect bite. And if in the first case the teeth are even, straight, and the jaws function without pain or any problems, then in the second case any troubles can arise - from clicking joints, disruption of the aesthetics of the smile, and to problems with closing the jaws. And all these ailments must be eliminated.
Correction of bite with internal braces Win – 180,000 rub.
All inclusive! Preparation and treatment of the oral cavity, consultation with an orthodontic specialist, installation and adjustment of orthodontic structures. The price is for one jaw.
Free consultation with an orthodontist +7 (495) 789-39-31 or write to us
The cost of braces: a brief overview
Of course, it is impossible to give exact prices at the moment: the cost of all braces, as well as dental services, is gradually increasing. In addition, the final amount depends on the condition of the teeth and the final design of the braces. But general information can be provided.
The most affordable braces systems are classic ones, which are classified as ligature, are installed on the outside of the teeth and are made of medical steel. Their cost ranges from several thousand rubles. Plastic systems of the same type cost approximately the same.
Ceramic ones will be more expensive - the bill will already be several tens of thousands of rubles. Sapphire ones will be slightly more expensive. Titanium and gold cost even more due to high prices for materials.
However, the cost is affected not only by the material from which the braces are made. In particular, you will have to spend at least 40 thousand rubles on non-ligature systems, even if they are created from ordinary medical steel. The reason is a more complex design and high requirements for the product. The same applies to lingual systems: they must be much smaller, but must provide the same fixation and pressure as conventional vestibular braces. Their cost can exceed 100 thousand rubles.
More accurate information on prices can be found by going to the price list section, or by contacting our manager by phone.
How to identify malocclusion
This is interesting! The ancient Cro-Magnon hunters almost did not suffer from problems associated with malocclusions. Today, every fifth inhabitant of the planet has pathologies of the jaw system. According to scientists, people's teeth have undergone negative anatomical changes due to the transition from raw and rough food to boiled and soft food, from gathering to the benefits of civilization. Our chewing apparatus simply stopped receiving the required load 1 .
All other positions of the teeth relative to each other and in the row as a whole are considered deviations or anomalies. Depending on the degree of malocclusion, we can talk about the consequences - in some cases they are limited to the displacement of teeth and psychological discomfort due to an ugly smile, and in some cases they lead to serious inflammatory processes in the jaw joints, the inability to close the jaws and even problems with nutrition.
In order to determine whether you have bite pathologies, stand in front of a mirror, close your jaws and look at the overlap of the front teeth, as well as the degree of closure of the lateral chewing teeth.
A bite is considered incorrect if the following anomalies are present:
- if one of the jaws is underdeveloped relative to the other, it is noticeably smaller in size,
- if the lower jaw is displaced to the side,
- if the lower jaw is strongly pushed forward, with the lower teeth overlapping the upper ones,
- if the lower jaw, on the contrary, is strongly “pushed” back and the upper jaw protrudes forward,
- if the teeth of the two jaws do not meet (side or front),
- if some of the teeth intersect with each other in a chaotic manner,
- if the teeth are rotated relative to their axis or tilted (this can even affect only one tooth), there is crowding in the row,
- there are spaces between the teeth.
Improper jaw closure and spinal problems
When the jaw is in an unnatural position caused by improper closure of the teeth, the muscles of the jaw first contract asymmetrically and the nerves in the neck are irritated. Over time, this leads to an automatic change in the posture of the head, and then the body, trying to compensate for the neglected process, changes muscle tension at the level of the shoulder girdle, then the back and lower back.
Each person adapts to such changes differently, but sooner or later painful sensations begin to arise in the body, caused by constant contraction of muscles or pinching of blood vessels. Migraines or dizziness, tinnitus and pain in various parts of the spine can become constant companions.
Consequences of malocclusion
The main consequences of malocclusion are psychological discomfort due to the incorrect position of the teeth, as well as difficulties in eating and speaking.
In more severe forms of malocclusion, the symmetry of the face changes, serious problems with chewing appear (up to complete impossibility), the mucous membranes of the oral cavity are injured (gums, tongue, inner sides of the cheeks), the child may not learn to speak at all, breathing worsens, pain and inflammation appear. processes in the temporomandibular joint, which is responsible for the physiologically correct and comfortable movement of the jaws.
Damon Q metal braces – only RUR 72,000!
Consultation with a doctor is free! Call now: +7 (495) 789-39-31
There is no need to be afraid of malocclusion; it is important to identify the presence of abnormalities at an early age and begin correcting the position of teeth and jaws as quickly as possible. After all, a small child’s jaw is developing and the teeth will be easy to adjust. Fortunately, dentists today have a whole arsenal of tools for this, from metal plates and arches to effective braces.
{SOURCE}
conclusions
Pathological occlusion is dangerous due to serious consequences not only for the dental apparatus, but also for the general health of a person. The degree of its danger depends on the type and severity of the anomaly.
In many cases, the development of anomalies can be avoided by performing simple preventive measures aimed at eliminating risk factors in infancy and childhood.
If a malocclusion has nevertheless developed, it needs to be corrected as quickly as possible.
The most favorable period for this is childhood and adolescence. However, anomalies can be corrected at any age. The only question is how much time and money this will require.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags diagnostics bite correction
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
Properties and features of compomer filling materials
Next article
What is torque in braces and what is its significance in orthodontic treatment?