26.11.2019
Ultracaine and lidocaine are two of the most discussed drugs for local anesthesia. They are almost always opposed to each other. But opinions about which anesthetic is better are diametrically opposed. Some consider lidocaine to be an effective, reliable and time-tested drug, while others consider it an outdated remedy that has no place in everyday practice. Ultracaine also has not earned an unambiguous positive assessment: rave reviews about the effectiveness of anesthesia are diluted by numerous complaints about side effects.
Research shows that, all other things being equal, the analgesic effect of ultracaine is stronger and toxicity is lower. However, this does not mean that lidocaine should be completely written off. With the right choice of anesthesia technique, it can achieve good analgesia and avoid side effects. On the other hand, errors in determining indications and errors in the technique of medical manipulation can negate all the objective advantages of ultracaine.
For local anesthesia during pregnancy, it is better to use Ultracaine D (without adrenaline), since the safety of lidocaine in this case has not been convincingly proven.
The only case when you should abandon lidocaine in favor of ultracaine is during anesthesia during pregnancy. Both drugs enter the peripheral blood and are able to penetrate the placental barrier. However, ultracaine is metabolized much faster and therefore has much less effect on the fetus.
Compound similarities
For inflammatory diseases, injuries and other situations when it is necessary to relieve pain, anesthetics help solve the problem. Experts advise carefully choosing painkillers, focusing on the purpose of use and the individual characteristics of the body.
In case of exacerbation of diseases, during dental treatment and during simple surgical procedures, it is necessary to use painkillers Ultracaine or Lidocaine.
Ultracaine and Lidocaine are amide anesthetics. They are produced in the form of injection solutions. In the production of both anesthetics, the same excipient is used - water. These drugs have a similar effect on the body, reducing the speed of transmission of nerve impulses, causing tissue numbness.
Both drugs are used for local, regional and infiltration anesthesia.
This is where the similarities end. Despite the fact that the drugs have the same areas of application and solve the same problems, they are quite different. In some cases, it is impossible to replace one remedy with another.
Drug interactions
When used together, Ultracaine and psychotropic drugs (tricyclic series), as well as monoamine oxidase inhibitors, provoke vasoconstriction. In addition, the active components of the drug inhibit insulin production, which reduces the effectiveness of oral hypoglycemic drugs.
Ultracain produces negative reactions when used simultaneously with the following pharmacological agents:
- blockers of receptors for adrenergic substances;
- Heparin, acetylsalicylic acid and other antithrombotic drugs (bleeding occurs);
- Halothane and other narcotic substances prescribed for inhalation (the susceptibility of the muscle tissue of the heart increases).
Differences
Ultracaine and Lidocaine are medications with different active ingredients. Ultracaine is a drug that contains articaine. This substance is quite effective in blocking pain, but has low toxicity. Ultracaine can be used even during pregnancy. Research results have shown that the product does not have a toxic effect on the fetus.
Lidocaine is used in dentistry for tooth extraction, for the treatment of carious cavities, and for pain relief during dental prosthetics. In gynecology, the drug is used for lumbar anesthesia.
Lidocaine contains lidocaine hydrochloride. This substance effectively relieves pain, but even if the dosage is slightly exceeded, it is toxic. There are also differences in the duration of action of the drugs.
General anesthesia
General anesthesia is a last resort when other methods of pain relief are ineffective. When is general anesthesia used for dental treatment:
- serious surgical interventions (for example, in acute or chronic osteomyelitis, multiple tooth extractions);
- if the patient suffers from dental phobia and there is no other way to cure teeth except to go into medicated sleep;
- if the patient (child or adult) suffers from cerebral palsy, autism, Down syndrome, or other serious mental disorders;
- pronounced gag reflex or extremely profuse drooling;
- allergy to local anesthesia, inability to select suitable drugs.
Contraindications:
- serious heart disease, high blood pressure;
- severe respiratory diseases.
You will first need to take a general blood test and an ECG, as well as consult an anesthesiologist and dentist.
Which is better Ultracaine or Lidocaine
Ultracaine is considered a more modern anesthetic. The advantages of its use include:
- high degree of pain relief;
- low toxicity;
- rapid onset of analgesic effect.
Ultracaine is recommended for use for epidural anesthesia, as well as when necessary for pain relief during pregnancy. It is much less toxic, although both drugs tend to penetrate the placental barrier.
Ultracaine penetrates deeper into tissues. It is less susceptible to destruction under the influence of an acidic environment.
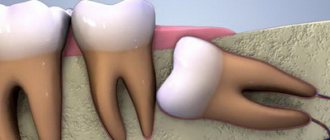
Differences in the action of Lidocaine and Ultracaine appear when infiltration anesthesia is carried out in full. In this case, the drug is injected directly into the area that needs to be numbed. Ultracaine penetrates deeper into tissues. It is less susceptible to destruction under the influence of an acidic environment. This matters when there is inflammation. In dentistry, if there is inflammation on the gums, Lidocaine may be weak, so it is better to opt for a more modern anesthetic.
Which is stronger
The analgesic effect of Ultracaine is approximately 2 times higher compared to the relatively outdated Lidocaine. When using it, the time spent visiting the doctor is reduced, since it begins to act within 3-5 minutes after the injection. With conduction anesthesia, when the drug is injected directly into the nerve, the drugs differ slightly in their strength.
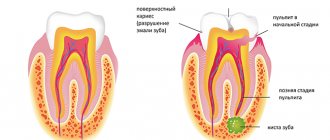
Mechanism of action of amide series local anesthetics
The spread of a pain impulse in a nerve fiber occurs due to a change in the polarity of the cell membrane. The change in potential is ensured by the work of special membrane protein complexes, sodium and potassium channels. The former are responsible for the excitation and spread of the sensitive impulse, the latter – for restoring the original balance.
The local anesthetic molecule consists of fat-soluble and water-soluble fragments, which are linked by an amide bond. The lipophilic aromatic ring allows the anesthetic to penetrate deep into the cell membrane of the nerve fiber, and the hydrophilic group acts from the inside, blocking the activity of sodium channels. Sodium transport does not occur across the cell membrane, so the pain impulse is blocked.
Contraindications for the use of Ultracaine and Lidocaine
Despite the reduced toxicity, Ultracaine has contraindications. Absolute restrictions include:
- hypoxia;
- glaucoma;
- intolerance to anesthetic components;
- cardiac tachycardia;
- anemia (lack of vitamin B12).
Relative contraindications include heart problems, bronchial asthma, and diabetes. In these cases, the use of Ultracaine is possible, but it must be justified, and the anesthetic should be used only under the supervision of a specialist. This type of pain relief is permitted during breastfeeding and pregnancy.
Lidocaine is not prohibited for children, but it can only be used from 12 years of age.
Lidocaine also has contraindications for use:
- severe cardiovascular diseases;
- tachycardia;
- state of shock;
- bradycardia;
- increased sensitivity to amide anesthetics;
- severe liver dysfunction.
Lidocaine is not prohibited for children, but it can only be used from 12 years of age. Lidocaine can be prescribed to pregnant women only if there are vital indications for anesthesia and it is impossible to replace it with a safer drug.
Lidocaine is not recommended for use for arrhythmia, but this contraindication is relative. Elderly people should use this anesthetic with caution.
Overdose
If the doctor administers too much of the drug, an overdose may occur. It is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Motor excitation.
- Impaired consciousness.
- Dizziness.
If the patient has the above signs of overdose, the following must be done:
- Immediately stop introducing the drug into the body.
- It is necessary to provide access to fresh air to the patient.
- If respiratory function is impaired, it is necessary to connect the person to an oxygen mask. If breathing has stopped completely, it is necessary to perform artificial respiration, intubate the trachea and connect to an artificial respiration apparatus.
- Some patients experience involuntary muscle twitching during an overdose; in this case, small and ultra-small doses of barbiturates must be introduced into the body.
- In case of anaphylactic shock, drugs based on plasma substitutes, albumin and glucocorticosteroids must be introduced into the body; it is also necessary to monitor the respiratory and cardiac systems.
- For arterial hypertension, vasodilators must be introduced into the body.
- For tachycardia, beta-adrenergic blockers should be administered.
Side effects of Ultracaine and Lidocaine
When using Ultracaine, the following side effects may occur:
- increased blood pressure;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- darkening and “double vision” in the eyes;
- convulsions;
- swelling;
- redness of the mucous membranes.
Allergies to anesthetics are common. If the drug is being administered for the first time, you must first conduct a test.
The doctor injects the patient with a small amount of anesthetic and only after assessing the result can the dosage be increased.
To conduct an express allergy test, the drug can be applied to the skin or mucous membranes and the reaction can be checked after 5 minutes.
When using Lidocaine, side effects may occur such as:
- breathing problems;
- nausea and vomiting;
- convulsions;
- allergic skin reactions;
- numbness of the tongue (when used in dentistry);
- loss of consciousness.
- involuntary urination.
Severe side effects often occur when the recommended dosage is exceeded. When using Lidocaine, the dose of the drug must be calculated more accurately. After using this anesthetic, a slight loss of visual acuity may occur. After a few hours everything returns to normal.
Immediately after treatment with Lidocaine, it is not recommended to drive a vehicle or perform work that requires increased attention.
If severe side effects occur, the anesthetic should be discontinued. It is necessary to provide additional air flow into the room and monitor the patient’s pulse and blood pressure.
Indications
Ultracaine D-S with a standard concentration of epinephrine hydrochloride is used for:
- Removal of teeth (one or more).
- Crown installation.
- Carrying out a variety of medical procedures.
- Dental filling.
- Carrying out some other standard dental operations (including patients with serious concomitant pathologies).
Ultracaine D-S with an increased concentration of epinephrine hydrochloride is used for:
- Surgery on the mucous membrane and/or bone.
- Dental pulp surgery.
- Removal of broken teeth.
- Removal of teeth affected by periodontitis.
- Resection of the upper part of the tooth root.
- As a pain reliever for inflammation of the jaws or face.
How to use
Lidocaine is produced in the form of solutions of different concentrations, poured into ampoules, and spray. For dental procedures that do not require long-term anesthesia, as well as diagnostic procedures, when cutting the perineum during childbirth, removing sutures, treating wounds, the spray is applied to the area that needs to be numbed.
The product should be sprayed from a short distance, avoiding particles getting into the respiratory tract and eyes. If the surface to be treated is large enough, you can spray lidocaine onto a cotton swab and wipe the skin with it.
Lidocaine solution 2% is intended for subcutaneous or intramuscular administration. The dosage is selected individually in each case. In dentistry, 1-2 ml of solution is administered once. If long-term anesthesia is required, the dose of the drug may be increased.
Lidocaine solution 2% is also used in ophthalmology. The drug is instilled into the conjunctival sac. This procedure must be carried out under the supervision of a physician. Lidocaine 10% is used in the form of applications or intramuscularly (to relieve arrhythmic attacks).
Ultracaine is produced in the form of a solution, packaged in ampoules of 1.7 and 2.0 ml. The drug must be administered subcutaneously to ensure high-quality anesthesia. The dosage in each case is calculated individually. For local anesthesia, you can soak a cotton swab in the solution and wipe the skin or mucous membranes with it.
Instructions for use in dentistry
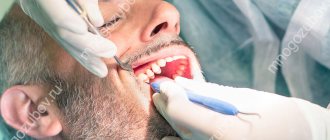
Do not inject yourself!
The injection of Ultracaine is carried out by a doctor. Only a professional can inject correctly without damaging the vessel with the needle tip.
To avoid intra-articular puncture, it is recommended to perform a test before injection using special syringes (for example, Uniject K, Uniject® K).
Testing (aspiration) involves releasing a small amount of solution from a single dose to determine the correct direction for the injection and identify possible allergies. When releasing the solution, tissue sensitivity must be taken into account.
Ultracaine is injected into the oral cavity (into the mucous membrane, into the gum tissue located around the circumference of the causative tooth).
Important! It is impossible to make a puncture with a syringe in inflamed areas, as well as to administer the drug Ultracain intravenously.
Rules for administering the solution for conduction/infiltration anesthesia and the norms of single doses:
- removal of a unit, regardless of the row, when there is no inflammatory process - 1.7 ml per tooth (the puncture is made in the transitional fold);
- tooth preparation – from 0.5 to 1.7 ml for each unit;
- trimming the palate , the need to apply surgical sutures - 0.1 ml;
- removal of premolars on the lower row in the absence of inflammation - 1.7 ml;
- for additional pain relief , when the first dose did not give the desired effect - 1.0 - 1.7 ml into the submucosa in the zone of the transitional fold (frontal side);
- simple tooth filling – 1 ml;
- a complex process with filling and removal of a unit - up to 1.7 ml.
The maximum permissible daily amount of Ultracaine for local anesthesia:
- adult patients – 7 ml;
- children's group – 5 ml.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
Lidocaine and Ultracaine are available from pharmacies with a doctor's prescription. Lidocaine spray is available without a prescription.
Price
Lidocaine is cheaper than Ultracaine, and the price difference is quite large. A pack of 10 Ultracain ampoules can be purchased at a pharmacy for 1100-1300 rubles. A similar package with Lidocaine ampoules costs 40-50 rubles. The average price of Lidocaine in the form of a spray is 200-250 rubles.
Several types of Ultracaine can be purchased in pharmacies. Varieties that are designed specifically for allergy sufferers are higher than classic Ultracaine.
After using the drug, you should not drive
If you are treating or removing teeth with Ultracaine, then after that, stop driving vehicles for at least half a day, as well as perform dangerous activities that require high concentration, for example, working with production machines and various mechanisms. The drug may cause weakness and drowsiness, and your attention will be temporarily distracted.
After using the drug, you should not drive
If the work involves a risk to your health or the well-being of other people (certain sports, driving heavy special equipment, stunt performers, responsible production), then it is better to ask in advance for the day when you plan to undergo treatment with pain relief, or choose non-working days to visit the dentist.
Precautionary measures
The treating dentist must remember to take certain precautions:
- Ultracaine solution is administered exclusively intramuscularly; intravenous administration is strictly prohibited.
- Use is not recommended if the patient has cholinesterase deficiency. Otherwise, the effect of the injection may last longer than the specified period.
- Ultracaine is not injected into inflamed areas of the oral cavity.
- The drug is collected using new instruments. Reusing syringes is unacceptable.
- Cartridges must be carefully checked for integrity and serviceability.
- Before the injection, the doctor warns the patient about possible difficulties in driving under the influence of the drug.
Let's figure out whether it is possible to take a dental x-ray during pregnancy, and how dangerous it is for the expectant mother and fetus. In this article we will try to explain why teeth hurt more at night.
Here https://dentist-pro.ru/lechenie/zuby/v-chem-prichiny-razrusheniya-i-podlezhat-li-oni-vosstanovleniyu.html common causes of rapid tooth decay are listed.
Reviews about the drug
“I’m allergic and don’t tolerate many medications well, including anesthesia, so any trip to the dentist used to be a real torment for me. Once I even developed terrible urticaria due to lidocaine in combination with some other substance, the name of which I no longer remember. But that was until it appeared - Ultracaine in a green package! Now I ask you to install only this one for me, because... no allergies occur. I’m also glad that the price for pain relief is low; last time I paid 200 rubles for an injection.”
Rima2205, review from otzovik.com
“We have used this more than once, it has a very fast action, I know, because... sometimes they inject a sore tooth in several approaches: the first time there is always an unpleasant sensation from the injection, and when the procedure is repeated literally 10 minutes later, there is no sensitivity at all!”
Anna Kalinina, Samara, review from yell.ru
“Ultracaine always helped without fail, but once it misfired: we were treating pulpitis, before that in the morning I took the painkiller “Ketanov” and an hour before the dentist’s appointment I swallowed a pill, because... it hurt a lot. And what do you think, the doctor gave me one injection, but it didn’t work. After 20 minutes, the second one again has no effect, as soon as it starts drilling, the pain is hellish. Only with the third dose did it work, because the tooth had to be treated somehow, and I couldn’t bear another night and day with such pain. True, after 3 doses, my anesthesia only wore off in the morning of the next day, but in a normal situation it wears off within 2-3 hours. My doctor said that this all happened because of Ketanov, and there was no need to drink it before treatment.”
DanilovN, review from 32top.ru
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
anesthesia
- M.V. Storozheva. Features of the choice of drugs for local anesthesia in patients with a burdened allergic history. Ukrainian Dental Almanac, 2014.
Expert "Ultracain" is a high-quality, safe and inexpensive drug. The manufacturer made sure that doctors and patients had a choice by creating three varieties: without epinephrine, and also with different concentrations. The choice is made based on the clinical situation and health status of the patient. For pregnant women, allergy sufferers, people with bronchial asthma and serious heart pathologies, it is better to use a form without epinephrine, namely labeled D.” Dentist-therapist Elena Vladimirovna Orlova
Consulting specialist
Dzhutova Aida Vladimirovna
Doctor rating: 8.8 out of 10 (5) Specialization: Implant surgeon, periodontist Experience: 9 years