Causes
The main reason for a malocclusion is often the lack of attentiveness of parents to their child.
The jaw on the lower side of a newborn is almost always smaller than the upper, which is the norm. Spontaneous correction occurs in the first year of the baby’s life, which is facilitated by natural feeding. Artificial nutrition involves the use of a bottle. A large hole in the nipple can negatively affect the development of the bite. In this case, the mixture easily penetrates into the baby’s cavity, this eliminates the participation of the lower part of the baby’s jaw in the extraction of food, which inhibits its development.
Other reasons include:
- lack of roughage in the diet;
- the habit of maintaining the same position for a long time during rest (hands under the cheek, throwing back the head, pressing the head to the mother’s chest);
- lack of minerals and vitamins in the child’s body.
Children who have acquired bad habits, which manifest themselves in the form of thumb sucking or other objects, or lip biting, are at risk. Breathing, carried out most of the time through the mouth, can also provoke a distorted formation of the bite.
This effect is mainly observed in cases of problems with the nose (congenital septal defect, frequent sinusitis, sinusitis, etc.). If you observe such symptoms, you should seek help from a doctor to avoid even greater complications.
Myths about malocclusions in children:
Causes
There are different causes of malocclusion in children. However, in most cases it is difficult for doctors to determine one predisposing factor that led to the violation. Pathology manifests itself against the background of a complex of problems with the child’s body, including:
- Diabetes.
- Long-term chronic lesions of the ENT organs.
- Colds.
- Inflammation.
- Neuralgia.
Malocclusion also manifests itself with an unbalanced diet or unhealthy lifestyle.
Each factor has a different effect on jaw structure and requires detailed study.
Often the pathology develops due to a genetic predisposition. If close relatives have a history of such problems, the likelihood of a bad bite in the child will be as high as possible.
Timely treatment and radical preventive measures can correct the position of the teeth and prevent the progression of abnormal phenomena in the future. More complex disorders require surgical intervention.
Sometimes problems with a child’s bite are explained by the unhealthy lifestyle of a pregnant woman who abused bad habits or did not receive the proper amount of vitamins and nutrients. To prevent this, you need to eat right and take care of your body during pregnancy.
Incorrect jaw structure due to bad habits is an acquired pathology that develops at an early age. Children often chew on dirty or hard objects, causing their teeth to lose their strength, become crooked and unhealthy. Another deviation occurs due to prolonged sucking of pacifiers. Therefore, doctors advise weaning the child off this accessory to avoid improper swallowing or unnatural placement of the tongue in the mouth.
Other predisposing factors include allergic reactions, viral and colds, as well as problems with adenoids or posture. If you have elevated blood sugar levels or nervous disorders, it is important to immediately contact the clinic and begin complex therapy.
Limited intake of fortified foods is a common cause of unhealthy bites. It is necessary to give your child more solid fruits and vegetables so that his jaws develop normally and receive optimal load.
A dangerous problem awaits young patients during the replacement of baby teeth with permanent ones. In most cases, this applies to those dentitions that are covered with caries, pulpitis or periodontitis. The development of pathology is also facilitated by the long-term preservation of baby teeth or the growth of one tooth over another.
Symptoms
Parents can independently notice the incorrect formation of a child’s bite from the age of 3.
The following signs indicate a problem:
- slow tooth growth;
- uneven rows;
- unfolding, tilting and other deformations of the jaw;
- the presence of gaps in the dentition;
- pushing forward of the lower jaw (beyond the boundaries of the upper arch) or, conversely, its weak development;
- expansion of the upper arch of the jaw;
- when closing the jaw, the upper arch overlaps the crowns of the lower by more than 1/3;
- when children smile, the gums on the upper jaw are clearly visible;
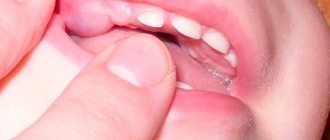
- lack of joining of chewing teeth, the presence of a large gap between them.
Another symptom often indicates an incorrectly formed bite - the mouth is open almost all the time. The child’s tongue cannot take the desired position; when biting food, discomfort is also felt due to the lack of contact between the front teeth.
All about malocclusion:
Correction
With a distal bite, the development of the apical points of the alveolar and basal arches of the upper jaw is restrained, and the growth of the child’s lower jaw is activated. For this purpose, during the period of loss of baby teeth, the following devices can be used:
- Andresen activator
- Engle's arc apparatus
- Ainsworth arc apparatus
- Herbst arc apparatus
- functional Frenkel apparatus of the first or second type
Removable plates are placed on the teeth, and a vestibular retraction arch helps reduce tremors. Also, the goal of treatment is to give the desired direction to the growth of the maxillofacial bones. To do this, a facebow is installed outside, which the child wears at home; there is no need to wear it to school.
Types of anomalies
The choice of correction method depends on the nature of the bite distortion. In dentistry, anomalies are classified into different types, which differ in symptoms.
| Name | Description, severe symptoms |
| Open | With this type of anomaly, there is a weak closure of the upper and lower dentition (the defect is pronounced on the front teeth), which leads to poor chewing of food, incorrect speech pronunciation and problems with swallowing. |
| Mesial | A feature of the mesial type of bite is the significant protrusion of the lower dental arch. This reduces the interaction of the cutters and their functionality when grinding products. As a result, problems with the digestive system appear. |
| Distal | The anomaly is characterized by a significant protrusion of the upper row in relation to the lower one, as a result of which the chin takes on a slanted shape, the lower lip sinks, and the upper lip becomes shorter. In addition to the aesthetic problem, there are disturbances associated with chewing food, swallowing, breathing, and speaking. |
| Cross | The anomaly can be recognized by the overlap of the upper and lower arches when the jaw closes. In this case, the center points of the top and bottom rows are shifted. Due to this defect, the risk of developing caries and problems with the gastrointestinal tract increases. Pathological changes appear from the anterior dental rows and on the sides. |
| Deep | A characteristic feature of this anomaly is a pronounced protrusion of the upper row above the lower one. In this case, the incisors do not fit together well when the jaw is closed, which makes chewing food difficult. Pain in the jaw joints is often noted. When you smile, the upper gum is clearly visible. |
| Diastema | A special feature of the anomaly is the gap located between the central incisors. This reduces the functionality of the incisors, causing speech to produce a whistling effect. |
Types of anomalies are clearly shown:
Types of dental malocclusion in children
A change in bite is not always a pathological process that prevents the free closing of the jaws or disruption of the masticatory apparatus. Doctors highlight the following table of types of pathology:
| Prognathia-distal occlusion. | It is a common problem due to which parents turn to pediatric orthodontists. It manifests itself at an early age, when the muscle joints on the lower jaws are not sufficiently developed, and the upper row of teeth appears protruding. To stop the progression of abnormalities, it is enough to add solid foods, including vegetables and fruits, to the child’s daily diet. With this approach, it will be possible to avoid violations without the help of doctors. |
| Progenia-mesial occlusion. | In most cases, the pathology develops against the background of a genetic predisposition or improper fixation of the nipple during breastfeeding. The faster the problem can be diagnosed and the right measures taken, the fewer problems the child will have in the future. |
| Deep bite | Often inexperienced parents classify this form as a distal bite. However, it is accompanied by the overlap of the lower teeth with the upper ones without pressing the lower jaw back. Key manifestations include speech problems and soft tissue lesions. |
| Crossbite | Occurs when baby teeth are replaced by permanent teeth. As the pathology progresses, one part of the upper dentition will overlap one part of the lower one, and the other will move slightly back. |
| Open bite | Manifests itself in the form of non-closing of teeth of both rows. In most cases, the problem affects the incisors, but it is diagnosed on molars or premolars. |
To timely identify anomalies, it is necessary to visit the orthodontist’s office at least once every 6 months. Regular diagnostics will allow you to quickly find the problem and take measures to eliminate it.
Diagnostics
If characteristic signs indicating abnormal bite formation are identified, you must make an appointment with an orthodontist . He sees young patients in pediatric dentistry. Based on the results of the consultation, the child may be recommended to be seen by other specialists: otolaryngologist, dentist, periodontist, speech therapist .
After a thorough examination, the orthodontist will send you for an X-ray to take a panoramic image (orthopantomogram) and a side view of the skull. Based on the data obtained, a diagnostic plaster model of the dentition is made.
During diagnosis, myography and tomography may also be needed. The collected information, photographs and impressions allow for computer modeling of the correction results.
Crossbite correction
The purpose of treatment: to establish the most correct arrangement of teeth in the row and the position of the child’s lower jaw. If a child with baby teeth has a crossbite, it is necessary to separate the dentition. To do this, crowns or trays are installed on the molars, as well as on the lateral teeth - plate devices with bite plates.
In cases of cross occlusion and severe lateral displacement of the lower jaw, a chin sling is sometimes used. Plate devices, adjustable with screws and springs, are suitable for expanding the dental, alveolar and basal arches of the child’s jaws.
Correction Methods
After examination and diagnosis, the orthodontist identifies the pathology of the disease and selects the appropriate method of treating the bite .
Myotherapy is special exercises that involve the muscles of facial expression and mastication, as well as the muscles of the floor of the mouth. This method will help correct temporary disorders, and when diagnosing a mixed malocclusion, it is used in combination with wearing orthodontic products (pacifier, trainer, plate).
Pacifiers
Trainers
Plates
The hardware technique is used to correct most malocclusions. The designs used are divided into removable and non-removable, which determines the mode of their wearing. According to the principle of influence, the devices are:
- mechanical - the dentition is fixed thanks to the elements of the orthodontic structure: arches, ligatures, screws, elastic traction (bracket system, Derichsweiler, Ainsworth apparatus);
- functional guides - the pressing force comes through the occlusal pad, inclined plane, bite pad (Schwartz, Bynin mouth guard, orthodontic plate);
- functional - the devices are equipped with a shutter element for the lips, tongue, cheeks, which relieves excessive muscle pressure on the bone tissue of the jaw (Schonherr plates, Klammt apparatus, Frenkel regulator).
Bracket system
Derichsweiler apparatus
Ainsworth apparatus
Schochner plate
Klammt apparatus
Frenkel regulator
The surgical method is rarely used when other types of treatment have failed to achieve the desired results. Surgical intervention is performed only on a formed bite.
The orthopedic method restores the shape of damaged or lost teeth through the installation of special inlays and small bridges.
Video on the topic:
Correction of deep bite
It takes a lot of effort to correct this effect when a child has baby teeth. In practice, it turns out that improper closure occurs again in a child after the appearance of permanent teeth. Treatment of deep bite involves preschool children performing special exercises, the purpose of which is to develop the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles, which push the lower jaw forward. To coordinate pressure on the teeth of the lower row, the following devices are used:
- Andresen's plate apparatus
- bite blocks
- Klammt activator
- fixed orthodontic devices of various designs
Price
Pricing for bite correction includes not only the cost of orthodontic products, but also their fixation, removal, and elimination of other dental problems identified after an examination of the oral cavity.
In addition, the method of correcting the bite differs in the principle of influence, duration, and price. Eg:
- plate activation – from 1100 RUR;
- plate - from 14,000 rubles;
- retainer - from 5500 rub.;
- capa - 5800 rubles or more;
- fixation of the bracket system – from 15,000 rubles;
- removal of braces – from 10,000 rubles.
When to start correcting your bite
Like any disease, it is better to start correcting your bite earlier, from about 3-5 years of age .
At an early stage of improper tooth formation, it is often sufficient to use removable plates or trainers. They are made of elastic silicone, so jaw growth does not deform orthodontic products, unlike braces. Modern vestibular plates and myofunctional trainers prevent malocclusion. The principle of their operation is based not so much on fixing the teeth, but on the effect on the chewing muscles and tongue, which have a direct impact on the formation of the dentition.
Important! There is no point in delaying the treatment process; the developing soft and bone tissues are easier to correct, which reduces the period of exposure to orthodontic products on the jaws.
In addition, eliminating a small defect is always easier than struggling for years with complex forms of malocclusion, when changes are noticeable even on the child’s face.
Ignoring a solution to the problem will affect not only the lack of a beautiful smile. In addition to the aesthetic side, a distorted bite provokes other complications :
- gum disease;
- abrasion of teeth;
- breathing problems;
- improper formation of the face in the jaw area.
In the presence of malocclusion, any infectious and inflammatory diseases have a negative impact on the process of bone tissue formation.
Exercises to correct your bite:
Correction of mesial bite
The goal of treating such a malocclusion is to correct the protrusion of the lower jaw or promote the development of the upper jaw. For this purpose the following devices are used:
- Frenkel activator type III
- removable Andresen-Goipl apparatus
- Klammt activator
- Wunderer or Delaire apparatus
- orthodontic cap with chin sling bandage
- Adams, Nord or Schwartz records
- single-jaw stationary Angle arch
In order to inhibit the growth of the bone structures of the lower jaw, children 13-14 years old can undergo dental surgery. During this procedure, the buds of the lower eighth teeth, the so-called wisdom teeth, which begin to grow when the child is between the ages of 6 and 14, are removed.
What to do with malocclusion at 1 year, 2 years, 3 years or more
The bite in children is considered fully formed when they reach 14-15 years of age.
However, you should not wait until the teeth straighten spontaneously by this time. Starting from 1 year, it is worth taking preventive measures to prevent the development of the defect. This process includes:
- reasonable use of a pacifier/pacifier (pay attention to the time of use and hole parameters);
- changing the baby’s posture during rest (if the hands are always under the cheek or the face rests against some object).
From the age of 2, the baby is weaned off the pacifier; this must be done correctly so that the finger does not become a substitute for it. If you have difficulty weaning your child from a pacifier, you should purchase an orthopedic one.
From 3-5 years of age, obvious signs indicating a malocclusion are eliminated with the help of removable orthodontic structures. They are selected by a specialist, so a trip to the clinic is inevitable.
In the age range from 6 to 9 years, the following products are used :
- mouthguards;
- vestibular plates;
- retainers.
Reference! If previously undertaken methods did not produce a positive result, then from the age of 12 a decision is made to install a brace system.
Orthodontist about bite correction at different ages:
Treatment
Treatment of malocclusion is called orthodontic treatment, and it takes a long time. The treatment method depends on the type of malocclusion in the child. The younger the child is, the easier it will be to correct bite defects. In most cases, removable pre-orthodontic trainers, plates, mouth guards or elasto-aligners are used. Soft and hard trainers should be worn during the daytime and at night for 1-1.5 hours. They help wean children two to five years old from bad habits (sucking the tongue and sticking it between the teeth or biting the lower lip). Trainers help teeth erupt correctly and straighten the front incisors when they grow crookedly.
Custom-made removable dental guards made from polycarbonate are called dental trays or aligners (elasto-aligners). They are used mainly to correct the bite in children from 6 to 12 years old, if the forearms are twisted, excessively tilted forward or into the oral cavity. Mouthguards are worn 2-3 hours a day or more.
Braces are non-removable structures that are attached to a child’s permanent teeth. They must straighten the teeth and dentition due to constant pressure on the alveolar arches of the jaw from special arches that are fixed in the grooves of the braces. Braces are worn from 12 to 26 months (depending on how crooked the child’s teeth are). When braces are removed, retention plates are installed to help keep the teeth where they are when straightened. The period of wearing these plates can be up to 3 years. For alveolar prognathia, braces are used for treatment, but they are not relevant if the child has other types of occlusion disorders.
Preventive measures
The formation of malocclusion in a child is easier to prevent than to treat, so parents should pay more attention to the child’s behavior in order to promptly correct emerging bad habits.
From the moment teething begins, you should regularly visit the dentist to monitor the process.
For prevention purposes, the following recommendations should be followed:
- periodically give the child a lip massage to increase the elasticity of the tissues, treat the frenulum of the tongue and the alveolar processes of erupted teeth with massage movements;
- myotherapy (exercises that develop and correct the muscles of the face and oral cavity);
- in case of manifestations of ENT diseases, consult a doctor in time to prescribe treatment;
- instill in your child the habit of regular cleaning of teeth and other surfaces of the oral cavity;
- limit your consumption of sweets.
Prevention video:
Open bite correction
If a child has an open bite, in most cases the upper jaw is narrowed. For this reason, removable expansion plates of various modifications are used, equipped with a spring or screw for children whose permanent teeth have just begun to emerge. They are used for treatment and construction to increase the anterior parts of the upper alveolar arch, to reduce the lateral parts of the alveolar zones, which is selected individually in each case.
If the discrepancy between the incisors and canines is large, for children over 12 years of age, intermaxillary traction techniques using Angle orthodontic devices with additional traction can be used. The second way of correction is the use of plastic mouth guards, which are placed on both jaws (front teeth).
Popular questions
What is a physiological bite? How is it different from pathological?
Physiological is a bite that is formed within normal limits. The following signs indicate this :
- good contact between the teeth of the upper and lower rows;
- absence of interdental gaps;
- the incisors located on top extend beyond the lower ones by about 1/3 of the length.
Pathological occlusion is characterized by various disorders of jaw closure, the presence of tooth deformations and increased intervals between them. This effect occurs due to genetic factors, as well as previous dental diseases (periodontitis, acromegaly, periodontal disease, etc.).
Can a pacifier cause malocclusion?
The sucking reflex is natural, but prolonged use of a pacifier can negatively affect the formation of the bite.
Until the age of two, parents only need to regulate the time, after which they can seriously begin to fight the bad habit. After the child reaches 2 years of age, it is recommended to replace the regular pacifier with an orthodontic one. It is more voluminous, which allows the tongue to take the desired position. You shouldn’t suddenly take the pacifier away, because the baby will easily switch to thumb sucking, and this will only worsen the problem. In early infancy (up to a year and a half), there is no need to worry about the pacifier.
What to do if your jaw is misaligned?
Poor alignment of the jaw is often explained by the influence of bad habits (staying in one position for a long time, putting your hands under your cheek).
With this anomaly, in addition to malocclusion, facial asymmetry appears. To correct the defect, an integrated approach is used, including special gymnastics for the face and wearing polymer plates that fix the jaw in the correct position. Often, for treatment purposes, trainers are installed - silicone products that look like boxing mouth guards.
What to do if your teeth touch the roof of your mouth?
This sign indicates the initial stage of development of a deep malocclusion.
To achieve correction of the defect, the goal is set: to create conditions under which the growth of the lateral zones of the alveolar process in the vertical direction would be activated. The main factor in this process is the redistribution of the load during chewing work. In this case, it is recommended to install a bite block.
How to identify malocclusion in a child
It is not difficult to determine the development of an unhealthy bite. However, making an accurate diagnosis is only possible after consultation with a specialist at a dental clinic. It is better to visit the orthodontist's office regularly and have examinations from an early age. If baby teeth are closely spaced, complications may arise during the eruption of permanent teeth. It is difficult to visually diagnose a problem in a child under 3 years of age. Therefore, parents take into account a number of related factors.
Incorrect breathing. The child constantly opens his mouth and cannot breathe normally through his nose. At the same time, there are no colds of any kind.
Snore. Often, with a bad bite, children begin to snore in their sleep. If the problem is permanent, it is better to contact the clinic immediately.
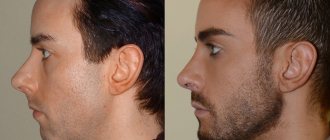
Formation of the jaw. You should pay attention to the formation of the jaws. In the absence of violations, the disproportion between the upper and lower rows of teeth will be minimal. In addition, the incorrect position of the jaws is accompanied by frequent protrusion of the lower one.
Posture disorders. If problems arise with posture or the spine, it is important to examine the oral cavity and jaws for pathologies.