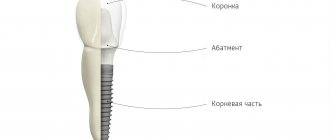
How many baby teeth do children have?
Milk teeth and even some molars begin to form at the stage of intrauterine development. Of course, a child has no visible teeth at birth - they begin to erupt only after 6 months. During this six-month period, they are hidden under the gums, but slowly develop and form, beginning to move outward.
In total, a child grows 20 baby teeth:
- Central and lateral incisors – 8.
- Fangs – 4.
- First and second molars – 8.
Their main function is to form a space where molars will then grow.
Taking care of dental health
By age 2, a child should have 16–20 teeth. But no matter how many there are, parents should be attentive to their health. Regular examinations of the baby’s oral cavity will help identify dental diseases at an early stage of development; if any violations are detected, you should contact the dentist. To prevent dental problems, moms and dads should:
- Properly organize the baby’s nutrition, try to prolong natural feeding: if the mother has breast milk, you need to feed the baby for at least six months . During regular visits to the pediatrician, parents receive recommendations from the doctor on the introduction of complementary foods (vegetable purees, juices, meat soups).
- Wean your child off pacifiers and bottles with nipples in a timely manner, as they damage teeth and can cause bottle caries.
- Give your baby not only soft foods and mashed purees, but also solid foods. At two years old, a child has enough teeth to chew vegetables and fruits. This helps strengthen the developing teeth.
Control the amount of sweets your child consumes.- Brush your baby's teeth with a soft-bristled brush without toothpaste or with a special children's toothpaste with a minimum content of harmful impurities. There are also devices for cleaning teeth that are made of soft silicone - they are put on the finger and clean the baby’s oral cavity.
- Periodically show the child to a pediatric dentist to monitor the condition of the teeth.
- Monitor the quality of water your baby drinks. The content of fluorine and other impurities in water should not exceed the norm.
How many teeth should a child have per year?
During this period, baby teeth begin to cut.
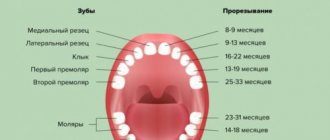
They begin to break out in the following sequence on the upper and lower jaws. On the top:
- 8-12 months. Central incisors.
- 9-13 months. Lateral incisors.
- 16-22 months. Fangs.
- 13-19 months. First molars.
- 25-33 months. Second molars.
In the lower jaw, this process is distributed in time somewhat differently:
- 6-10 months. Central incisors.
- 10-16 months. Lateral incisors.
- 17-23 months. Fangs.
- 14-18 months. First molars.
- 23-31 months. Second molars.
It is worth noting that these time limits are averaged and deviations up or down by 1-3 months are considered normal.
If you want to know how many teeth a child has per year is considered normal, you should refer to the chart described above. You get that at the age of 12 months there should be 6-8 of them.
Adviсe
While the baby is still toothless, parents carefully monitor the growth of the first tooth, often look into the mouth, and monitor the condition of the gums. When a lot of molars grow, they forget about it. We will give some useful tips on how to prevent serious dental problems in young children.
- Examine your baby's mouth frequently at home. Check for stains, chips, and plaque.
- Every mother should have a dental chart for children under 3 years of age.
With its help, it is easy to track the pattern of incisor eruption, the norm by number and age. - Teach your child to brush their teeth 2 times a day. Use games, tasty pasta and other methods of teaching hygiene, set an example.
- Visit your dentist regularly, at least 2-4 times a year. The doctor will notice defects in jaw development in time, tell you how and in what order teeth should be cut, and why they are deteriorating.
Important! The most important condition for maintaining dental health is attention and control from parents.
Changing baby teeth to molars
Around the age of 4, a child’s growth spurt begins, the jaws enlarge and the baby teeth seem to move apart, with gaps appearing between them – trema. If this does not happen and by the age of 5 the teeth are still tight, you need to show the child to the dentist, as there may not be enough space for permanent teeth.
At about 5-6 years of age, baby teeth begin to become loose and gradually fall out, which indicates that the molars are already beginning to grow underneath them. Usually this process of change lasts for 5-8 years and the final formation of the dentition occurs somewhere around 14-15 years.
This happens in the following order:
- 5-6 years – lower and upper incisors.
- 7-8 years – lower and upper lateral incisors.
- 8-10 years – upper and lower molars.
- 9-11 years – upper and lower canines.
- 11-13 years – upper and lower molars.
Milk teeth are replaced by permanent molars. Their number at the age of 14-16 years is 28. At the same time, the third molars (wisdom teeth) are already formed, but they begin to grow only after 18 years. True, not all people grow them. It all depends on individual characteristics.
Possible dental problems
Parents of mature toddlers, in addition to the number of teeth at three years old, are also concerned about other dental problems. They are identified independently at home, at the next appointment with the dentist. List common deviations from standards.
The child has dark tooth enamel, yellowish molars
The cause of discoloration is poor cleaning, ignoring the rules of oral hygiene, taking iron-containing medications, and diseases of the internal organs.
Carious spots on teeth
Most adults are greatly mistaken if they believe that baby teeth do not need to be treated for caries. Pathogenic bacteria infect dental tissue, settle in the oral cavity for a long time, and subsequently destroy molars. The tooth begins to turn black from the central part, sometimes large black spots of different sizes appear on the enamel.
To avoid caries on baby teeth, you need to accustom your baby to daily hygiene and consume sufficient amounts of vitamins and minerals in food.
Periodontitis
When the tissue around the tooth becomes inflamed or the integrity of the cortical plate is compromised, the child’s gums become swollen, the cheeks increase in size, and the baby experiences constant aching pain. The cause of the disease is advanced caries and fungal infections.
At the age of 8-10 years, dentists are forced to remove a molar tooth for children with periodontitis, since the tissue changes are already irreversible.
It is important to pay attention to this problem during the period when it is possible to treat inflamed elements of the jaw.
Pulpitis
The nutrition of the hard tissues of the incisors is disrupted. The pulp is located inside the dental canal and consists of a nerve, a vessel, and connective cells. Destruction of the structure of this part of the molar leads to tissue starvation, death, and the incisors will crumble. Pulpitis affects not only the erupted tooth, but its rudiments.
Hypoplasia of tooth enamel
Molars become thinner, easily ground down and worn out. The pathology is genetic in nature and develops in utero.
Malocclusion
The teeth of the opposite rows do not close together due to prolonged sucking of a pacifier, heredity, bad habits: holding a finger in the mouth, gnawing on toys, etc.
How many teeth should a child have?
It all depends on age. The maximum number of teeth in the period from birth to 5-6 years is 20 - these are milk teeth. Then, until the age of 15-16, the molars begin to erupt, pushing out the milk teeth. Ultimately, their number grows to 28.
The latest are the third molars. They grow only after 18 years of age, but not everyone has them.
It is worth noting that the period of formation and eruption of baby teeth is very individual. In some children, all 20 teeth grow by the age of 2, while in others - by 2.5 or later. Such delays within a year are considered normal and are not a developmental anomaly.
If teeth do not start cutting in the first year of the baby’s life, you should consult a doctor to find out the reasons.
To the list of posts
Causes of abnormal deviation from the norm
It’s great if the teeth erupt on time and do not change in color, shape, or size. In this case, the baby definitely develops in a normal rhythm, he has no deviations in physical and general somatic health.
The culprits of dental defects, including lack of teeth at the age of three, may be:
- Heredity.
- Congenital malformations.
- Undeveloped gum muscles.
- Bad ecology.
- Adenoids, chronic rhinitis, otitis.
- Non-compliance with the diet by the mother during pregnancy.
- Deficiency of vitamins, minerals (after birth, inside the womb).
- Trisomies (chromosomal abnormalities).
The true cause of jaw development abnormalities in children can be identified using laboratory tests, an external examination of a small patient, and a survey of parents. Early diagnosis of diseases and malfunctions of internal organs and systems will help prevent the disease from developing and prescribe timely treatment.
Why is tooth decay dangerous for children?
At 2 years old, teeth should not only be in the required quantity, but also in normal condition. Despite the fact that information about the need to take care of the oral cavity is available to almost all modern parents, many of them do not take this problem seriously enough.
Some mothers and fathers are in no hurry to take their 2-year-old child to the dentist even after detecting signs of tooth decay. There is a common misconception that once baby teeth fall out, their condition does not matter, because in the future the child will have a permanent set of teeth. But in fact, caries and other dental damage should always be treated, regardless of age. There are several reasons for this:
- With any unevenness in the enamel, and even more so in the presence of a carious cavity, it becomes more difficult to brush your teeth. As a result, part of the plaque is not removed, and the place where it remains becomes a focus for the development of infection. Stomatitis and ENT diseases may become more frequent. Microbes that accumulate on teeth can even infect a child’s internal organs.
- Progressive damage to the tooth can affect its internal part, the pulp. Pulpitis causes severe pain, which causes a 2-year-old child a lot of suffering.
Half-destroyed milk teeth with foci of purulent inflammation can adversely affect the formation of permanent dentition, and the development of the rudiments of new teeth may be disrupted.
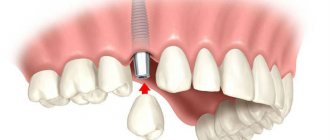
If your child has dental diseases, he or she may need a filling or surgical treatment - tooth extraction, which should be carried out only if it cannot be saved.
Caring for your baby’s teeth should begin not when the first teeth appear, but during pregnancy. At two years old, your baby should be taught hygiene habits so that he can properly care for his oral cavity throughout his life.
Normally, a child should have 20 teeth by the age of two. If their number noticeably lags behind the norm, or other suspicious symptoms are noticed - damage to the enamel or malocclusion - you need to consult a doctor. Periodic dental examinations will help diagnose dental problems in a timely manner and maintain the health of your permanent dentition.
Parents helping their child when his molars are being cut
The process of erupting molars is long and painful. During these periods, parents should try to be very attentive and tolerant towards their baby. To reduce pain and anxiety, pediatric dentists recommend using special gels that are cooled in teethers.
If your temperature rises or alarming symptoms such as runny nose or cough appear, you should definitely consult a pediatrician. The doctor will determine the exact cause and may prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs.
Teething is a period when increased attention to oral hygiene is required. For this age, you need to choose the right toothpaste for your child. For example, children's toothpaste from the ASEPTA baby series for children aged 0 to 3 years significantly reduces the number of harmful microbes in the child's mouth, so that the difficult period of teething passes without unnecessary hassle.
What signs are used to determine the appearance of molars?
There are several symptoms that, to a certain extent, may indicate that the child will soon have a permanent one in place of a baby tooth:
- The tooth is loose - this indicates that the root has begun to dissolve, as a result of which the fixation of the baby tooth has weakened.
- The tooth fell out - the reason for this is that the permanent tooth has already formed and pushed it out.
- A swelling appeared on the gum at the site of eruption.
- Body temperature has increased.
Take into account! The growth of permanent teeth leads to a weakening of children's immunity. Therefore, you need to give your child vitamins and take him to the dentist for preventative visits.
Growth pattern
At the time of birth, a child already has formed rudiments of both milk and molar teeth. The process of development of the latter, if they have no analogues among dairy products, begins when the child is about a year old.
Almost all baby teeth erupt by age 3. At the age of 6, they gradually begin to be replaced by permanent (indigenous) ones. This process usually ends by age 13. If the total number of milk teeth is 20, then the molars are 32. Permanent teeth erupt in the following sequence:
- 6-7 years. The appearance of central incisors from below.
- 7-8 years old. Change of central incisors from above and lateral incisors from below.
- 8-9 years old. The appearance of the lateral incisors of the upper jaw.
- 9-12 years old. Change of canines and premolars.
- 12 years and older. Change of molars and the appearance of teeth that had no analogues among milk teeth.
The period of eruption generally depends on both external and internal factors. In particular, it is influenced by complications during childbirth, the nature of the child’s nutrition, climatic conditions, genetic predisposition and much more.
Typically, by the age of 14, a child has an almost complete set of teeth. Wisdom teeth normally appear in older teenagers, but most often they appear in adults. Sometimes they don't show up at all.