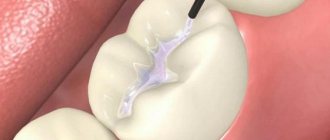
When nerve removal is indispensable
In modern dental practice, both complete and partial resection are used. Indications for the procedure:
- deep carious tissue damage;
- chronic pulpitis (including asymptomatic);
- bactericidal infection spread by the apex of the tooth root;
- the presence of an extensive pulp area, the threat of developing periodontitis or transition to periodontitis;
- trauma leading to nerve exposure and tooth destruction;
- the need to correct a medical error;
- the need for prosthetics with low crowns.
Unbearable pain can also be an indication for depulpation.
The dentist will never prescribe such a serious intervention as long as it is possible to save the tooth.
Important
: problematic “eights” when affected by caries, as a rule, are removed. This is due to the location of the “wisdom” teeth at the end of the dentition, which makes cleaning them from plaque and stone and filling the canals very problematic. Indications for removal are also the wrong direction of eruption, displacement of the dentition, malocclusion, and the development of pulpitis.
What is the dental nerve called?
In dentistry, the dental nerve, or pulp, is a complex structure - an interweaving of nerves and vessels located inside the root and crown of the tooth and responding to external stimuli.
Depulpation allows you to save the damaged tooth, but has negative consequences:
- Since the pulp acts as a barrier to infections, removing the nerve deprives the tooth of the necessary level of blood supply and mineralization, which shortens its “life.”
- A tooth deprived of a nerve loses sensitivity, the enamel becomes more fragile and faded, and the strength of the tooth decreases.
Stages of the depulpation process
- X-ray – necessary to assess the condition of the pulp, the number, length and branching of the canals to be filled.
- Anesthesia - local or complete anesthesia completely covers the issue of pain when removing a nerve (it doesn’t hurt!). At the same time, general anesthesia is used relatively rarely - when treating children, with true dental phobia, etc.
- Installation of a rubber dam - a latex film for insulating a tooth. A modern solution to improve the dentist’s working conditions and protect against the possible spread of microorganisms through saliva.
- The actual removal of the nerve is the excision of tissues affected by caries, opening the pulp chamber and extracting the nerve with a special instrument (pulpoextractor). In modern practice, this is a careful cutting of the pulp without affecting sensitive areas.
- Installation of a temporary filling (for a period of 1-2 weeks).
- Control x-ray.
If the x-ray and the condition of the tooth are satisfactory, after the control period a permanent filling is installed.
Is caries treatment painful?
Many people are convinced that caries is painful to treat, and therefore are afraid to go to the dentist. The problem goes back to the recent past, when anesthetics were not used in dentistry. Just a few decades ago, no one could even imagine that it was possible to treat teeth with anesthesia, and all manipulations were performed “live.”
In this article
- Is caries treatment painful?
- Is it painful to treat dental caries with anesthesia?
- Is anesthesia always necessary?
- How to treat caries with an injection step by step?
- Is it painful to treat caries on the front teeth?
- What anesthesia is used in the treatment of caries?
- Who is contraindicated for anesthesia?
- Conclusion
Of course, with this approach it was very painful to treat deep caries and other stages of this disease that affected the sensitive parts of the tooth. Fortunately, dental treatment methods have changed, modern safe anesthetics have appeared, and it has become easier to treat with an injection.
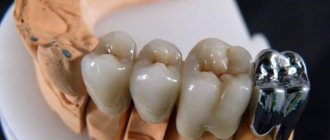
Depulpation before prosthetic crowns
Depulpation is unconditional if there is serious tooth decay. It is preferable to remove the dental nerve during prosthetics in the following cases:
- The size of the teeth determines the low position of the crown (too small or short teeth);
- The inclination of the prosthetic tooth is from 15°;
- Increased sensitivity of teeth;
- According to aesthetic requirements.
The need to remove the dental nerve during prosthetics is dictated by deep removal of the top layer of dental tissue: if the doctor is not sufficiently qualified, heating or touching the nerve can cause an attack of unbearable pain. However, cases of nerve-sparing crown installation also occur in modern dental practice.
If over time the nerve under the crown becomes bothersome, it is possible to remove the pulp through the top of the crown and fill the hole after removal.
The danger of such a procedure is associated with the risk of complications in the future due to surgery on the exposed dental nerve.
Materials
In modern dentistry, a wide variety of materials are used for filling teeth. Since the purpose of filling is not only to close the hole in the tooth, but also to restore its physiological and anatomical functions, the material must be selected according to the load on the tooth and its location.
For example, in case of serious damage to the structure of the chewing tooth, polymers that can withstand heavy loads are used as a filling substance, and for the front teeth it is customary to use light-curing composites, since their properties help to match the color of the filling to the natural color. At the same time, silicophosphate or silicate cements are most often used for incisors.
The basic requirements for materials used to fill canals are as follows:
- complete sealing of root canals;
- absence of a chemical reaction that changes the color of the tooth;
- no shrinkage of the filling;
- easy removal from the dental cavity if repeated treatment is necessary;
- insolubility in the soft tissues of the tooth.
Gutta-percha meets most of the requirements from this list, but has one significant drawback, namely the complete inability of the material to block the vital activity of microorganisms in the sealed cavity. Glass ionomer cements, on the contrary, prevent this process. Not only are they particularly durable, but they are also fully compatible with dental tissues, release fluorides that help strengthen dentin, and do not shrink. When using this material, filling teeth has minimal consequences, however, it also has its drawback - increased acidity. In connection with this fact, a special calcium-based medical pad should be installed under such a filling.
There are other types of filling materials such as pastes, plastics and amalgam. Modern dentistry is trying to avoid the use of amalgam fillings, since they contain mercury, which is very harmful to the body; moreover, this material is not wear-resistant and very unreliable.
About dental anesthesia
Standard dental practice is an injection of anesthetic; Taking tablet analgesics before going to the dentist is not recommended, as it leads to a decrease in the effectiveness of anesthesia (usually the effect of an anesthetic injection is 45 minutes). For patients suffering from a fear of injections, it is possible to use paste anesthesia, which has a similar effect.
The choice of anesthesia is up to the dentist; Taking into account the individual pain sensitivity threshold of each patient, the standard dose is sometimes doubled or even tripled. With proper selection of an anesthetic, discomfort during the procedure for the patient is excluded.
Why can a tooth hurt after pulp removal?
This often happens: the nerve has already been removed, but the pain remains. Such manifestations are acceptable in the first 3-4 days as a natural reaction of the body (for example, to clenching the jaws or to temperature stimuli).
Other causes of toothache after pulp removal:
- Careless cleaning of the canals, preservation and intensification of the inflammatory process due to incomplete removal of tissue damaged by caries.
- Using during the procedure a pulp extractor that is not suitable for the size of the canal or improper handling of the instrument.
- Broken dental instrument, retention of its remains in the upper part of the root (such a medical error leads to the need to remove the tooth).
- The occurrence of a secondary inflammatory process in the treated canals (residual pulpitis) occurs against the background of an incompletely removed nerve.
- Allergic reaction of the patient to the filling material.
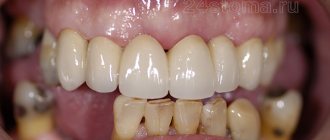
Change in enamel color after nerve removal
If the dental clinic follows international depulpation protocols, such phenomena are excluded. However, in budgetary institutions there are frequent cases of using outdated practices.
The color of the enamel after nerve removal can be affected by:
- Improper preparation of the tooth for installation of a filling;
- Poor quality instrumental processing of channels;
- Low quality filling materials.
Thus, when using resorcinol-formalin paste (the use of the material is practiced in the treatment of baby teeth), the enamel acquires a pinkish tint; When using endomethasone, the tooth may turn yellow after a few years.
How to treat caries with an injection step by step?
At other stages of caries, teeth are treated approximately according to the same scheme, which includes several stages:
- Cleaning teeth.
The doctor removes tartar and plaque from the surface of the tooth being treated.
- Selecting the shade of the filling.
The dentist selects the material for filling, focusing on the natural color of the enamel of the damaged tooth. To do this, he uses the so-called Vita scale - a plastic strip with samples of different shades.
- Anesthesia.
Anesthesia injections help make the procedure painless and reduce discomfort during the treatment of caries. The type of drug and dose are selected taking into account the age and individual characteristics of the patient. The anesthesia usually lasts from 40 minutes to several hours. Sometimes the gums hurt a little after the injection, but this does not compare with the pain when treating deep caries without anesthesia.
- Isolation of the tooth before treatment.
It is performed by placing a small plate - a rubber dam - on a row of teeth. As a result, one or more necessary teeth are completely isolated from the others. This allows the dentist to do a better job and prevent blood and saliva from getting on the cleaned surface, which guarantees its reliable connection to the filling in the future.
- Preparation of a carious cavity.
Cleansing the tooth of all tissues that have been damaged by caries and parts of the tooth enamel above the carious cavity. If you leave the caries at least partially and install a filling, after a couple of months the problem may recur. And in the future complications may develop - pulpitis and periodontitis.
- Formation of a carious cavity.
The doctor creates the best conditions for installing the filling by forming special support points. It makes indentations, notches, irregularities in the cavity, and smoothes the edges of the enamel. This is required for the filling to fit tightly to the walls of the tooth.
- Washing the cavity.
After the above procedures, the carious cavity is washed and sprayed with a stream of air to remove dentin sawdust.
- Medical treatment of carious cavity.
It is produced using antiseptic solutions to prevent the new development of caries. Then the doctor dries the cavity well so that drops of moisture do not interfere with the close contact of the filling with the tooth tissues.
- Acid etching.
It is performed so that the adhesive, which is applied after etching for a stronger fixation of the filling material, can penetrate deeper into the dental tissue. To do this, use a special gel with phosphoric acid. After etching, the gel is washed off well and the tooth is dried.
- Application of adhesive.
It is applied to the tooth to firmly fix the light-curing filling material; after absorption, it is illuminated using a special lamp.
- Application of a therapeutic and insulating pad.
This step can be performed either before or after acid etching. Spacers are an intermediate layer between the dentin or pulp and the filling material. Therapeutic pads protect the tooth from external adverse influences and help stop inflammation; they are most often used to treat deep caries. Isolating gaskets protect the pulp, the soft connective tissue of the tooth, from the negative effects of filling materials.
- Placing a filling.
The doctor takes turns, layer by layer, applying filling materials and drying each of them with a dental lamp.
- Grinding, polishing.
The restored tooth with filling is ground and polished to perfect smoothness and evenness. This gives it a natural shine and eliminates the smallest imperfections and gaps that cause inconvenience. At this stage, caries treatment ends. Thus, anesthesia with an injection is given at the very beginning of dental treatment, and all other stages are absolutely painless for the patient.
Possible complications
A medical error associated with poor-quality disinfection of the canal when removing a nerve can trigger the process of suppuration with subsequent transition to a periodontal abscess (in the absence of adequate treatment). This complication leads to the need for tooth extraction.
Other possible complications:
- Pain for several days after nerve removal. The duration of discomfort is individual for each patient; if pain persists for a long time, it is necessary to consult a doctor to re-open the canals and carry out disinfection.
- Increased bleeding of the canal occurs when the pulp extractor is removed after the pulp has been torn off. To avoid this phenomenon, many specialists carry out the procedure in stages with copious rinsing of the tissues with an antiseptic. Bleeding control is carried out directly at the appointment.
- The appearance of granuloma, fistula, cyst, gumboil.
Specific problems can arise if the material is applied incorrectly: if the filling extends beyond the boundaries of the root apex, the jaw nerve may be pinched.
If you experience pain in the lips and chin, you should urgently consult a dentist: a possible complication is facial paralysis.
Septanest (France)
They are produced in two forms with an adrenaline content of 1:100,000 and 1:200,000. Unlike Ultracaine and Ubistezin, the anesthetic contains preservatives that have a strong allergenic effect.
The drug Scandonest is produced based on mepivacaine. The anesthetic does not contain preservatives or vasoconstrictors. Recommended for anesthesia for pregnant and lactating women suffering from cardiovascular diseases, bronchial asthma and thyroid diseases.
Important. When visiting a dentist, be sure to tell the doctor if you have allergies or chronic diseases. This will help the doctor choose the right anesthetic for you.