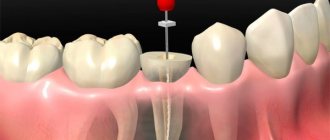
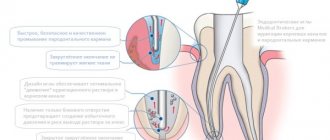
Until quite recently, glass ionomer cements and chemical composites were considered the most effective and reliable materials for filling carious cavities.
And there was a logical explanation for this: high biological compatibility with tooth tissue, speed of filling, budget cost - these are only a small part of the advantages of such materials.
However, despite all the advantages, there are many more negative aspects: low average service life of the filling, low adhesive properties, shrinkage of the material, unaesthetic appearance.
That is why methods and means of filling required a radically new approach and the search for alternative materials.
Light-curing composites began to be used relatively recently, but they have already proven themselves to be the best.
With the use of light composites, it has become possible to carry out restoration work of any complexity, including aesthetic and functional dental operations.
The technology of light curing of the material makes it possible not only to perform fillings, but also to solve a number of highly specialized problems: restoring the surfaces of the front teeth, repairing old fillings, and correctly positioning crooked dental units.
To perform dental filling using light composites, you should definitely contact the specialists of the ManeClinic dental clinic.
We guarantee high quality light-cured materials and a high average service life of fillings made on their basis.
The entire range of work is carried out using modern equipment that emits ultraviolet light, accompanying the polymerization process.
Dental clinic “ManeClinic”: installation of fillings using modern light-curing composite materials at the most affordable price.
The main advantages of modern light-curing composite filling materials
The main advantage of a light filling is the virtual absence of shrinkage during polymerization, which was the main problem with almost any other composite material. The technology for filling a carious cavity based on modern light-curing materials comes down to the layer-by-layer application of small portions of the composite and their illumination. Obviously, this is unattainable with the chemical filling method: it is very problematic for the patient to sit for a long time with his mouth open, waiting for the next volume of material to harden.
Other indisputable advantages of lighting composites include:
- the ability to choose a shade that will best match the natural color of healthy teeth;
- a high level of plasticity of the material over a long period of time, which allows the dentist to give the filling any shape;
- the absence of chemically hazardous substances harmful to health, which guarantees the safety of installation and operation of the seal;
- high average service life;
- absence of addiction and feeling of discomfort after installation;
- the possibility of filling even if more than half of the crown part of the tooth is lost;
- rapid hardening of the material after exposure to a special light lamp.
If you have any questions regarding the features of modern light-curing composite filling materials, please seek professional advice from one of our practitioners. In the area of their direct competence there is a wide range of various aspects: timing of installation of a light seal, category of composite material used, actual cost of providing services, payment methods and systems.
Reviews
Usually, when installing fillings, dentists do not inform the patient of all the technological details of the treatment. But, at the same time, no one is stopping parents from asking what material their baby will wear a filling from.
If you filled your child’s temporary teeth, please share information about what material was used for this, and whether the filling lasted until the temporary tooth was replaced with a permanent one? You can leave a review at the bottom of this page.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Seal tags
Did you like the article? stay tuned
No comments yet
Natural cements
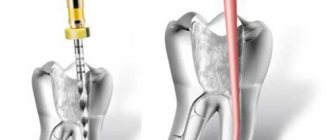
Cements for sealing dental canals are called sealers.
There are a number of natural materials of this type, the main options are discussed below:
Endomethasone N Poudre cement
It is very easily inserted into the dental canal and is subject to slow resorption. It contains additional additives with an antiseptic effect, which is a good prevention of possible inflammation.
Other positive properties include excellent X-ray contrast, which makes it easier to monitor the situation from images. Among the disadvantages are the toxicity of some components, a high risk of pain and the development of an allergic reaction.
Cortisomol
In powder form, it has all the advantages of the previous version; it also contains steroid hormones that relieve pain during rehabilitation after surgery.
The main disadvantage is that it dissolves quite quickly in tissue fluids; moreover, this material stains the enamel, so it cannot be used for the restoration of anterior teeth.
Tubliseal
Fills all microscopic cracks in the shortest possible time, providing perfect sealing, and is also characterized by rapid hardening, which occurs under the influence of heat and moisture.
Disadvantages include rapid leaching from the canals and the presence of corticosteroids in the composition, which impair the protective qualities of some tissues.
Canason
It has excellent properties: it is not washed out or dissolved by tissue liquids, it seals channels well, has an antiseptic effect, relieves inflammation, provides protection against bacteria, and is perfectly displayed in photographs.
The only drawback is the complexity and duration of the procedure.
Filling baby teeth
In pediatric dental practice, both phosphate cements and compomers - composites combined with glass ionomers - are used as permanent filling materials.
Both have the ability to enrich tooth tissue with fluoride, but the latter are more resistant to destruction and have high aesthetic characteristics. Some dentists use chemical-curing compounds with colored components to make fillings for children.
What to do in case of destruction of tartar and caries
If the destruction is minor and there is no pain, the doctor drills into the damaged darkened areas, cleans them of plaque, disinfects them and closes the resulting hole with a special compound. If a tooth hurts badly, it means that caries has affected the pulp - the loose, fibrous connective tissue that fills the tooth cavity. In this case, you will have to come for treatment more than once.
First, the doctor will clean the walls of the resulting cavity, then fill it with an antiseptic, fix it with a temporary filling and isolate the damaged surface from external influences.
If the pain does not go away after a certain time, it is necessary to remove the nerve, since the destruction has reached it. The doctor will cement the root canals and restore the tooth crown, selecting the necessary filling materials.
Materials for dental restoration
At the moment, there is no impeccable material in dentistry that is similar to natural teeth in all respects. But you can select impressions that match the natural shade of tartar as closely as possible.
For this purpose, the composition is pre-selected. Sealants are used to prevent caries. When cracks, grooves or other small flaws form on the enamel, they are sealed with special substances that form a film to stop further tooth decay. Fluoride ions inside the sealant protect against erosion.
Adhesives (substances that connect materials by surface adhesion) are needed to improve the adhesion of the filling to the walls of the tooth.
Some mixtures have anti-inflammatory and restorative properties. They are used as therapeutic pads under fillings.
There are compounds that are compatible with soft tissues and fill root canals well, but are not strong enough.
Temporary restorative pastes either quickly wear out or break down. Therefore, they are suitable only for short-term sealing of hollows during treatment and diagnosis.
To install long-term fillings, compositions that most closely match the characteristics of your own dental tissues are suitable. It is with their help that the exact shape of the cast is reproduced.
Research on restorative compounds
The search for a universal dental composition for dental reconstruction does not stop and every year filling materials continue to be improved. But before new products are widely used, they must undergo a series of studies to ensure compliance with existing standards. To do this, newly created samples are carefully studied in accredited laboratories in 3 areas:
The physical and mechanical direction makes it possible to find out:
• Consistency of the material; • change in temperature of the mass during hardening; • volume of the substance during the solidification process; • color stability; • the optimal amount of time required for curing the mass; • water absorption of the substance; • solubility coefficient in water and other media; • hardness level; • transparency of the substrate; • percentage of abrasion; • adhesion ability; • presence of radiopacity; • thermal conductivity value.
Tracking biological properties allows us to understand:
• how toxic the substances are if swallowed; • degree of cumulative toxicity of the material; • local irritant effect; • ability to cause allergic reactions.
Research into the biological compatibility of restoration materials provides a guarantee of additional safety.
Clinical trials
At this stage, the compositions are mastered in dental clinics at research institutes. Based on the experience gained, recommendations on the use of the compositions are given.
A final understanding of the qualities and properties of improved materials for reconstruction is provided only by long-term observations of their practical application.
Basic requirements for temporary filling materials:
1. They interact well with body tissues, do not irritate and do not enter into putrefactive or oxidative reactions in the oral cavity; 2. They have a strong and tight adhesion to hard tissues; 3.Do not differ in appearance from a natural tooth; 4. Correspond to the quality and properties of natural dental tissues; 5. Dentin is regenerated (a type of bone tissue covered with enamel in the crown and cement in the root).
Formulations for temporary use
Cement paste was first used for filling teeth in 1832.
The material consisted of a solution of phosphoric acid combined with calcium oxide powder. Later, to increase the strength of the substance, glass powder was added to the composition. Until the mid-20th century, cements, along with metals, were the main filling agents. In modern dentistry, various modifications of cements are used to solve many problems.
To close the hollow for a short time, use the following materials.
Zinc sulphate cements
A powder from a mixture of zinc oxide with the addition of kaolin or dextrin and zinc sulfate is mixed on a glass plate. Distilled water is used for preparation. The resulting paste is placed into the treated hole with a trowel or spatula. Seal with a cotton swab.
Zinc oxide provides good adhesion to hard tissues, and zinc sulfate with kaolin is responsible for the strength and ductility of the resulting substance. The mixture hardens within 2-3 minutes. This composition is inexpensive and easy to work with.
Minus: it wears out quickly, which is why it can last no longer than 2-3 days.
Zinc-eugenol cements
Dentine paste is available in ready-made form. There is also a mixture of zinc oxide and peach or clove oils, containing up to 70% eugenol, which form a paste that hardens in 2-3 hours.
Eugenol is an essential oil of natural origin. Has an anti-inflammatory and calming effect on the pulp.
It is used as therapeutic pads and for crown restoration. When interacting with composites, eugenol distorts the course of polymerization, which reduces the use of such compositions for treatment. The advantages of cements of this group include ease of use, high biological compatibility and healing properties that regenerate the pulp.
Zinc phosphate (zinc oxide and phosphoric acid)
To improve the properties, oxides of metals such as bismuth, silver, magnesium, and silicon are added in small quantities to zinc oxide. Then the powder is combined with orthophosphoric acid, diluted in water with small admixtures of zinc and aluminum phosphates. The addition of silver and bismuth gives the composition a bactericidal effect.
Excellent compatibility with soft tissues predetermines its primary use as insulating pads for permanent restoration. Root canals are also filled. If sealing is required for a period longer than 2-3 weeks, then it is used on a temporary basis.
Cements of this group are very plastic and adhere well to the walls of the tooth. The composition is characterized by low thermal conductivity and radiopacity. It is worth considering that the materials are not strong enough, decrease in volume when cured, are porous, and do not match the color of tooth enamel. They interact chemically with saliva and can irritate the pulp due to the acid reaction of the cement paste.
Polycarboxylate cements
Polyacrylic acid dissolved in water is combined with zinc oxide and magnesium oxide. The result is a plastic mass with excellent adhesion. It does not irritate the pulp and has low thermal conductivity.
Unlike phosphate cements, it is less susceptible to chemical interaction with saliva, but is prone to destruction from mechanical stress.
Disadvantage: too long time for complete hardening - 10-12 hours. Used for fastening orthodontic products, as insulating pads and as temporary fillings.
Polymer cements
Polymer cements are actively used in dental practice, since, unlike natural analogues, they are much less washed out by woven liquids, do not stain tooth enamel, and have some other advantages.
Below are the types of such materials:
AH Plus
It is a cement paste that provides good bonding with dentin, slight shrinkage of the filling and excellent sealing of the canal, which is due to the ease of penetration into even the smallest cracks.
The disadvantage is the frequent occurrence of allergies and the risk of other side effects upon contact with mucous membranes.
Adseal
It is a polymer that provides maximum sealing without dissolution in woven liquids, and is also ideally compatible with materials.
The only drawback is the risk of irritation if there is contact with certain tissues.
Diaket
It is a plastic polymer and when used, there is no shrinkage of the filling. This cement has an antiseptic effect and does not cause irritation upon contact with soft tissues or mucous membranes.
Among the disadvantages are incompatibility with gutta-percha pins, as well as increased pain of the operation, which persists for another 2-3 days.
Which material to choose?
The choice of material is the responsibility of the attending physician; if it is possible to use several options, he will explain them, explaining the features of each of them.
When making such a choice, the dentist takes into account the following factors:
- The type of tooth that is planned to be treated, as well as the current condition of its roots.
- Features of the shape of the canal, as well as its patency.
- Condition of the crown.
- Plans for further treatment.
- The patient's available budget, since the cost of materials can vary greatly.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=2&v=XD0Dmqk0BAY