In this article we decided to tell you about the problem of tooth extraction. We will discuss what complex and simple removal is, how long the operation can take, and also how important the doctor’s deep knowledge and golden hands are if parting with a tooth is inevitable. And of course, we’ll touch on the burning questions: “what am I paying for?” and “why is it so expensive?”
Fortunately, today the list of diagnoses for which a diseased tooth has to be removed is not so long. Modern dentists in most cases try to preserve teeth as much as possible. It’s sad that miracles don’t always happen (you can read about it here) and sometimes you still have to part with damaged teeth. About some of the intricacies of tooth extraction - in the material of the head of the therapeutic department of the Rudenta clinic, Ruzanna Samvelovna Babajanyan.
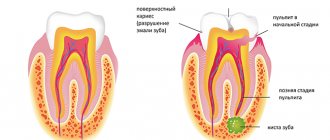
Anatomy of the alveolar process
The alveolar, or dental, process (from Latin - processus alveolaris) is the part of the upper and lower jaws that extends from their bodies and contains teeth. The development and normal functioning of this structure is ensured by the roots of the teeth located in it. The alveolar process appears only after teeth erupt and almost completely disappears with their loss. After a tooth is removed, the corresponding area undergoes resorption (resorption). Dental alveoli, or sockets, are individual cells of the alveolar process in which teeth are located. They are separated from each other by bony interdental (interalveolar) partitions. Inside the alveoli of multi-rooted teeth there are also internal (intra-alveolar) interradicular septa, which extend from the bottom of the alveoli and divide the alveoli into chambers (according to the number of roots). The alveolar socket of the tooth has clear, defined boundaries, and it has all the conditions for bone regeneration; you just need to help it maintain its contour.
Delete, cannot be pardoned
This is exactly how you have to “punctuate” this sentence in only a few cases, but it’s useful to know about them. Perhaps this will still help someone save their tooth.
So, one of the most common indications for tooth extraction is... neglected teeth. If the patient, due to some circumstances, does not contact the dentist in time, the tooth roots affected by infection and inflammation will eventually resolve. It is absolutely pointless to restore such teeth and cover them with a crown, since they will not serve.
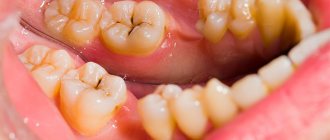
You won’t believe it, but caries can affect not only teeth, but it can even reach their roots. And root caries, that is, tooth destruction below the gum level, is a direct indication for removal. It is impossible to save such a tooth.
Another “popular” case is pulpless teeth not covered with a crown (that is, teeth whose nerves have been removed, most often due to pulpitis). They have rather thin walls, and often such teeth cannot withstand the chewing load and break. If a vertical fracture occurs 7 millimeters below the gum level, then such a tooth cannot be saved and must be removed.
Also, an indication for tooth extraction is destruction of the interradicular septum (this is a bone partition separating the roots of a multi-rooted tooth), which in most cases leads to the formation of a cyst. In general, doctors do not risk treating teeth if there is a large cyst. After all, it is impossible to say for sure whether the process will improve or worsen. Therefore, in order not to take risks, it is better to remove such a tooth (especially if it turns out that the tooth affected by the cyst is located next to the implant: in this case, the cyst can harm it too).
Also, an indication for removal is perforation (that is, a perforation occurs, and in very simple words, this is the formation of an opening, hole) of the tooth, which often arises as a complication during treatment - the passage of the tooth canal. This is, in fact, a medical error (and unfortunately, no one is immune from errors of this kind). However, whether the tooth needs to be removed or can be saved depends on where the perforation is located. If the tooth is not very lucky and the doctor damages its wall in the area where the roots begin to bifurcate (hence, by the way, its name - the area of bifurcation, or bifurcation), and at the same time the interradicular septum gets damaged (and it is located in this area between the roots , which, by the way, follows from its name), then in this case “parting” with the tooth is inevitable. But if a perforation occurs below this area and only the tooth root itself is damaged, then it makes sense to fight for such a tooth: in most cases, the perforation is closed as an additional canal of the tooth, thus saving it.
Removal is often caused by the so-called Popov-Godon phenomenon, when the tooth has shifted, that is, moved down or up, due to the absence of an antagonist. Just imagine: a patient had to have a tooth removed - for example, the seventh - in the upper jaw. After some time, the seventh tooth on the lower jaw (the same antagonist) will begin to rise upward, filling the “vacated” space. No wonder doctors often say: “Nature does not like emptiness.” In this case, the interradicular septum is exposed, and infection constantly penetrates there, forming a cyst, or the bone tissue gradually disappears. Unfortunately, even prosthetics of these teeth will be unfavorable, so they have to be removed.
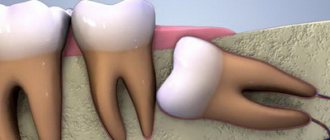
And of course, we have to part with the most capricious and complicated wisdom teeth, which cause a lot of trouble for both their owners and doctors. Impacted (not erupted) or dystopic (abnormally growing or incorrectly located) “eights” are also a direct indication for removal. And in the case of ordinary caries, the eighth teeth are removed and not treated.
That is, doctors actually remove teeth only in cases where it is not possible to save them. In all other cases, teeth can be saved, and today the phrase “cannot be treated, must be removed” is not heard so often.
By the way!
In our clinic, the patient’s desire to remove teeth and install implants or a removable denture (“for the future, so that the teeth don’t hurt”) is not a medical indication for tooth extraction. For the purpose of “prevention” we do not remove teeth!
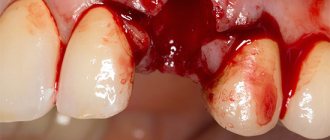
Hole preservation procedure
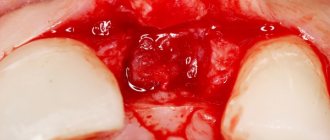
Preservation of the socket of an extracted tooth is a fairly simple and effective operation for preserving bone volume and maximizing the preservation of the natural contours of the alveolar socket. This surgical procedure is performed under local anesthesia and does not pose any risk.
Usually the operation is carried out in several stages:
- treatment of the hole after tooth extraction with special antiseptic compounds;
- installation of a membrane to protect the vestibular wall;
- filling the socket cavity with granular bone-forming substance;
- fixation of the operating surface by tensioning the free edges of the connective tissue;
- applying a bandage or a thin, neat suture.
Complete healing of the postoperative area occurs by the fourth week, and after 3–4 months, in some cases 6 months, if the condition is satisfactory, this area can be used to install an implant.
Symptoms of a tooth fracture
Injuries often go unnoticed, as a result of which the floor of a tooth that is deprived of sensitivity is broken. Also, the clinic may be absent if there is minor damage to the enamel. Such defects can only be determined visually during an independent examination of the oral cavity.
In other cases, when a tooth is fractured, a person experiences pain. A pain syndrome that limits the movement of the lower jaw occurs when a tooth breaks at the root, and the fragments injure the soft tissue of the gums. A tooth broken under the gum often causes loosening of adjacent units, bleeding and speech impairment.
Deputy Chief physician Sergey Evgenievich Brodsky
Sign up for a free consultation
+7
First aid for a fracture
When a tooth breaks and hurts, you should immediately seek help from a dentist. Before examination by a specialist, doctors at the Partner-Med clinic recommend providing first aid, namely:
- rinse your mouth with clean boiled water at room temperature or warm chamomile infusion;
- apply and firmly clamp the application with cotton wool or a bandage in case of bleeding;
- take a pain reliever with an anti-inflammatory effect (Analgin, Paracetamol, Ibuprofen) if there is severe pain;
- apply a cold compress to the sore spot;
- immobilize the jaw with a tight bandage if injury is suspected.
Complications
If the front upper or lower teeth are broken, this causes, first of all, aesthetic discomfort, as the smile changes, articulation and clarity of diction are impaired. It can often provoke the development of psychological problems and complexes. A broken chewing tooth disrupts the food processing process. Large particles of food entering the stomach lead to disruption of its functions. The development of pathological processes is accompanied by a feeling of discomfort in the abdominal area and heartburn. A broken tooth under the crown causes displacement of the prosthesis, deformation of adjacent units, or injury to the gums. There is also a danger of developing infectious and inflammatory processes as a result of the penetration of pathogenic flora into injured tooth and gum tissues.
Ask a question!
8
We'll call you back in 1 minute
Diagnostics
After visiting a dental clinic, a specialist relieves pain and conducts a visual examination of the oral cavity, during which it is possible to determine:
- degree of damage to hard dental tissues;
- dislocation of adjacent teeth;
- tissue necrosis;
- penetration of blood into the tooth cavity.
To obtain a complete clinical picture, assess the condition of the roots of a broken tooth, the degree of displacement and damage to the nerve fibers, an x-ray examination is performed. In case of severe injuries, an orthopantogram or electroodontometry is performed to determine the condition of the dental system and assess the viability of the pulp.
Treatment quality criteria
The main criterion for the quality of an alveolar socket preservation operation is its independent complete healing and maximum preservation of bone tissue, preservation of the natural contour and volume of the alveolar ridge, improvement of the condition of soft tissues and simplification of further stages of treatment. If the operation is successful, there will be enough bone tissue in the socket to install a dental implant. Separately, it is worth highlighting the advantages of condomization for the doctor and the patient - this is improved long-term treatment results, more predictable aesthetics and, of course, saving time for the doctor and the patient.
Complications after tooth root removal and rehabilitation
The body's normal reaction to tissue damage is slight swelling, fever and pain at the surgery site, which should gradually subside within 2-4 days. But if on the 3rd day the temperature rises significantly, the edges of the wound separate, liquid oozes from them, and the pain becomes throbbing, then complications have begun. In this case, you must immediately contact the clinic, where the wound will be cleaned and new stitches applied.
Complications after root cutting can also arise due to medical error. If it touches the nerve of the lower jaw, it will become numb. Getting into the maxillary sinus will cause sinusitis. In addition, the remains of the tooth may become mobile and will still have to be removed.
In order not to mechanically damage the wound and provoke complications, the patient must adhere to certain rules:
- Do not eat in the first hours after surgery;
- Apply cold to the cheek through a cloth;
- Do not rinse or brush your teeth for 24 hours;
- Be sure to change the brush to a softer one and brush your teeth exclusively on the healthy side for at least 10 days;
- Gently rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions from the second day;
- Eat non-irritating foods with a delicate consistency;
- Avoid overheating, severe physical fatigue and emotional stress;
- Quit smoking for at least 3 days.
During the rehabilitation period, it is recommended to take painkillers, antibiotics and vitamin complexes prescribed by the dentist, and not to self-medicate.
Indications for condom
Preservation of the socket of an extracted tooth is indicated for everyone who in the future wants to install a dental implant in its place. The process of loss and resorption of the jaw bone at the site of the extracted tooth begins immediately after the operation. In the first year, bone tissue resorption will be 25% in volume, and over the next 3 years the loss in width will be 40 - 60%. In the case of socket preservation after tooth extraction, a larger volume of bone tissue in the jaw and the most natural contours of the alveolar process are preserved. And then, subsequently, the likelihood of such a complex operation as alveolar bone augmentation when installing an implant will most likely not be required.
When should you not remove a tooth root?
Removing part of a tooth is not always possible. This is mainly due to anomalies in the structure of the dental system, less often - with the general condition. The surgeon will refuse the operation if:
- All roots are strongly intertwined, fused, short, impenetrable or destroyed;
- The mandibular canal and maxillary sinuses are located too close to the problem area;
- There is thin gum at the site of manipulation;
- The patient has oncology, diseases of the cardiovascular, nervous system or oncology;
- Tissues do not heal well due to blood clotting, diabetes, or radiation therapy.
In these cases, the problematic unit is simply removed.
Contraindications
Preservation surgery is subject to the same restrictions as any osteoplastic surgery. Separately, I would like to note that it is not recommended to preserve a hole after tooth extraction in a state of acute pain, since the risk of complications increases. But in each specific clinical case, the actions of a professional dentist are strictly individual. Sometimes situations arise when you have to take risks, but this is due solely to medical indications. In any case, it is necessary to understand that performing a tooth extraction operation and subsequent preservation on a planned basis is better than as part of emergency care.
Diastema in celebrities
Teeth are the calling card of any famous person, and, according to many, they must be perfect. But there are many stars who have turned the gap between their teeth into their highlight. According to physiognomy, gaps between teeth are a sign of talent and creative potential.
Famous women with diastema
To the list of stars with diastema who became famous in the last century, in addition to Brigitte Bardot and Ornella Muti, you can add Lauren Hutton, who conquered the fashion industry back in the 60s of the 20th century. Among modern models is Georgia May Jagger, who became the face of the Chanel advertising company.
Diastema makes French celebrities even more attractive and is an integral part of their image. In addition to Vanessa Paradis with her pronounced diastema, one can remember the actress Jane Birkin, who considered the gap to be a “funny little thing.” Léa Seydoux, the performer of the role of Belle from Beauty and the Beast, is in no hurry to get rid of this defect.
American women are more conservative in this regard and strive for a Hollywood smile. Fifty Shades of Gray star Dakota Johnson once had a great sense of humor about her diastema. To be convinced of this, just watch a video of a famous American television show with her participation. But over time, the actress got rid of her diastema.
Famous men with diastema
Diastemas and trema in famous men are quite common. Among Hollywood veterans who got rid of the gap between their teeth, we note Arnold Schwarzenegger, Tom Cruise, Nicolas Cage. But the famous director Oliver Stone did not treat the diastema. The gap does not prevent Woody Harrelson, Eddie Murphy, and Laurence Fishburne from smiling widely.
Among the representatives of the younger generation who corrected diastema in their youth, we highlight Zac Efron and Matthew Lewis.
Johnny Depp and the cult director Tim Burton uniquely expressed their “love” for gap teeth by creating the image of the Mad Hatter in the film “Alice in Wonderland.”
You can have different attitudes towards diastema and trema, but you shouldn’t deny that they really suit some of the stars. Diastema can highlight a bright appearance and make it memorable.
Restrictions
It is logical to perform a preservation operation after the removal of permanent molars, within the so-called sevens, second molars (except for wisdom teeth, eights), since when baby teeth fall out, bone tissue does not resorption. There is no upper age limit for performing an operation aimed at preserving the natural contours of the alveolar process.
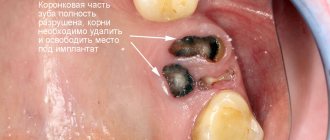
Tooth root removal as a tooth-preserving operation
One type of tooth-preserving surgery is tooth root removal.
The method allows you to preserve the remaining roots and crown, which can perform the functions of the whole tooth: they can be chewed, and the aesthetics of the smile will also be preserved. If the crown has to be removed along with the damaged root, the remaining part is used as a base for the prosthesis. In this article on Stom-Firms.ru we look at how tooth root removal operations are carried out, indications and limitations for manipulation, and what complications may arise after the intervention.
Price
According to the classifier of surgical interventions in the oral cavity, condomation is not among the standard surgical interventions and this, of course, affects the cost of its implementation. In addition, the price of osteoplastic materials and related products is quite high. Some materials are used only in conjunction with a special membrane to avoid ingrowth of soft tissue into the alveolar socket. The price is also affected by the method of tooth extraction. Removal of a tooth or tooth root is sometimes still a traumatic procedure, leading to direct loss of alveolar bone and soft tissue. With atraumatic removal, the alveolar bone is preserved in a larger volume, which reduces the final cost of the operation.
Preservation of the socket after tooth extraction is an important procedure when planning the installation of an implant. Timely preservation of the socket will allow you to preserve such valuable bone tissue and avoid a much more complex and expensive operation to build it up - augmentation, as well as significantly reduce the overall treatment time. The cost of preserving the natural contours of the alveolar socket pays off, because you thereby provide the teeth surrounding it with a reliable position, and as a result, during implantation, you get an imitation of the removed tooth root. This procedure applies even to those patients who do not intend to restore or replace a lost tooth with an implant, because in this case the gingival contour will have the most aesthetic appearance, without failures, and will allow for the most aesthetic bridge prosthetics. Therefore, reservation is gaining increasing popularity in dental dentistry.
According to antiplagiat.ru, the uniqueness of the text as of October 16, 2018 is 90.3%.
Key words, tags: tooth extraction, wisdom tooth, bone tissue, implant installation, augmentation, implantation.
*Images: Astra Tech Dentsply Implants; Principles of hard tessue regeneration and implant therapy.
Is it easy or difficult to remove a tooth?
In fact, there are only two categories of complexity for tooth extraction - simple and complex, which, in turn, also has its own degrees of complexity - second and third - depending on the location of the tooth.
Simple removal includes the removal of teeth of the 3rd and 4th degree of mobility (most often, mobile teeth occur in periodontal diseases, for example, periodontitis). This operation does not entail any serious manipulations or complications and can be done by almost any, even not very experienced, dentist.
Complex teeth (teeth of the second category of complexity) include fixed teeth. I would especially like to highlight the so-called “red” or resorcinol teeth. These teeth are absolutely motionless and attached to bone tissue, so they are sometimes quite difficult to remove. They are also fragile, like glass, and often break and crumble during removal. Moreover, it is very important to carefully, accurately and carefully separate (separate) the tooth so as not to injure the bone tissue and so that later you do not have to replant an artificial one (say, in the case of implantation). In addition, the damage to bone tissue itself is considered quite traumatic and can lead to a number of postoperative complications: pain, swelling, temperature. In case of careful, non-traumatic removal, the healing of the surgical wound will be faster, and all these symptoms will disappear quite quickly, and may not even appear at all. This is the art of tooth extraction.
A special category of complexity (third) includes the removal of wisdom teeth, or “eights,” especially impacted ones (that is, unerupted ones). Among wisdom teeth, the lower wisdom teeth are considered the most “stubborn” - at first they do not want to be born, and then they are difficult and difficult to remove. By the way, the above postoperative complications – pain, swelling, etc. – are very typical for them and are considered normal. And this is due to their anatomical location, which contributes to more difficult and prolonged healing.
Difference in time
“How long can it take to remove a tooth?” — doctors have to hear from their patients. In general, all cases are individual. It is almost never possible to estimate the exact time that removal may take. The operation can take from a few seconds to 4-5 hours. Of course, when it comes to simple removal, we can say that the operation will take a split second.
But the time it will take for a complex removal is quite difficult to predict, especially if we are talking about resorcinol teeth (on average, this operation takes from an hour to an hour and a half, which makes it possible to remove a tooth in the least traumatic way, without damaging bone tissue) and wisdom teeth (from 15 minutes to 4-5 hours). And teeth of the second category of complexity can sometimes take several hours.
In many ways, the time frame depends not only on the complexity of the tooth, its anatomical location, but also on the skill of the doctor - different doctors will take different times to remove the same tooth. And if a complex tooth is removed in 5-10 minutes, then this indicates the professionalism of the doctor.
By the way!
There is no concept of “time” in medical protocol. Each doctor spends as much time as he needs to follow this protocol, that is, perform all stages of removal. After all, it is important that quality does not suffer.
Price issue
Of course, the easier it is to remove a tooth, the less effort spent on it, the cheaper the operation will cost. However, the time spent on the operation does not affect the price in any way. Firstly, as we have already said, different doctors need to spend different amounts of time to remove a tooth of the same degree of complexity. Secondly, no matter how long the operation lasted, what is important is how the tooth was removed: how non-traumatic the removal was, and whether possible post-operative complications were avoided (or minimized).
In our clinic, for the convenience of the patient and transparency of the pricing policy, we have simplified the degree of complexity of tooth extraction, dividing them into two categories - simple and complex. The only exception is wisdom teeth, or “eights.”
For example, if we talk about a tooth of the first degree of complexity, then removal will cost approximately 1,500 rubles*. However, if the patient has periodontitis and, as a result, complications may develop after removal, then in some cases it is necessary to suture the soft tissues or apply medication. Of course, this will slightly increase the cost of the operation. Complex removal (second category of complexity) costs 2800 rubles*. But the necessary additional manipulations will also have to be paid in addition to this amount.
A separate degree, a separate level of complexity, as we said earlier, this is the third degree. It usually refers to wisdom teeth. The cost of removing “eights” starts from 3800 rubles* (this is a simple “eight”). A wisdom tooth of average complexity will cost 5,200 rubles, and the cost of removing a complex “eight” tooth can reach up to 7,500 rubles*.
*I would like to immediately note that the above prices are approximate and current at the time of writing, they do not include the cost of anesthesia, suturing, medications used during surgery, etc. However, we don’t have “surprises”. When a patient comes to the clinic, we draw up a treatment plan in advance and negotiate its price. We always indicate the maximum cost that can be charged if removal for one reason or another turns out to be more difficult than we initially expected.
By the way!
In the case of tooth extraction, the patient pays for the process - for the professionalism of the doctor, for his hands. However, medical skill is only one of the undoubtedly important “components of success.” The final result also largely depends on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, his reactions to surgical intervention, as well as on the patient’s compliance with all the doctor’s recommendations.
What is atraumatic tooth extraction?
The essence of atraumatic tooth extraction is to saw the crown under local anesthesia into a certain number of parts (this depends on the number of roots in the tooth) and carefully remove each part along with its root. With this method, the interradicular bone septa are preserved and the walls of the socket are not damaged, which is extremely important for good healing and further prosthetics.
One of the stages of atraumatic tooth extraction is the infusion of platelet mass into the socket, which promotes tissue regeneration and accelerates healing. Thus, a basis is formed for further prosthetics using dental implants.
After atraumatic tooth extraction, the wound heals quite quickly and without problems such as swelling, bruising and other troubles familiar to many. It goes without saying that the patient must strictly follow all the recommendations of the attending physician for several days.
Recommended sections on the topic
In these sections you will find more information on how to solve the problem of removing part of a tooth:
- Consultation with a dental surgeon
- X-ray diagnostics
- Restoring part of a tooth
Literature used for the article:
- Surgical dentistry and maxillofacial surgery. National leadership / Ed. A. A. Kulakova, T. G. Robustova, A. I. Nerobeeva. ― M.: GOETAR-Media, 2010.
- Therapeutic dentistry of children / Ed. L.A. Khomenko. ― Kyiv: Kniga Plus LLC, 2007.
Author of the article: Natalya Aleksandrovna Kozlova
Copywriter of the information portal Stom-Firms.ru. Specializes in medical and dental texts.