Each of us knows from an early age about the importance of timely visit to the dentist. However, despite this, many still try to put off going to the doctor. And only when the toothache becomes simply unbearable does the patient decide to make an appointment with the dentist. As practice shows, it is untimely contact with a specialist that is the main factor in the occurrence of caries, which develops into pulpitis. Complications of pulpitis, in turn, can turn into more severe pathologies.
What is pulpitis?
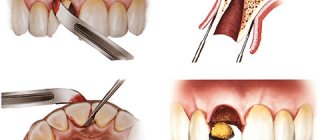
Pulpitis is a pathological disease of the neurovascular bundle. In most cases, this process is the result of untreated caries. There are also cases when pulpitis develops as a result of all kinds of mechanical damage that occurs due to injury or improper treatment. This type of pathology is called “traumatic pulpitis”
In modern medicine, there are two main methods of treating the pathology in question, including:
- biological,
- surgical.
The surgical method is an absolute or partial resection of the neurovascular bundle of the tooth. After conducting all the necessary tests and examining the results obtained, the doctor determines which method of therapy will be the best option. In addition, the final factor may be whether the tooth is permanent or temporary.
What complications can arise from pulp inflammation?
The development of pulpitis due to an advanced form of caries can cause pathogenic bacteria to enter the neurovascular bundle. If you do not visit a doctor in a timely manner to solve this problem, the infection may spread beyond the canal. Quite often, bacteria infect apical periodontal tissue.
Complications of pulp inflammation can cause a number of serious diseases, including:
- periostitis;
- sepsis;
- abscess of the maxillofacial part;
- removal of a tooth;
- Osteomyelitis of the jaw is an acute purulent inflammation of the bone marrow. The disease in question is extremely dangerous when the immune system is weakened, since it can cause the development of all kinds of septic processes;
- phlegmon - the penetration of pus from the affected tooth into the soft tissues; getting rid of this problem is only possible through surgery;
- cessation of functioning of one or more organs due to amyloidosis (systematic intoxication of the body with decay products found in the tooth).
Each of the above diseases is dangerous in its own way, and also has quite serious consequences and requires long-term treatment. Qualified dentists claim that in almost all cases, inflammation of the pulp is the result of the development of caries.
Forms and types
The classification of pulp inflammation divides the disease into two forms according to the nature of the development of the pathology:
- Acute pulpitis is a first-time inflammatory process that lasts from 3 to 5 days and is accompanied by intense symptoms.
- Chronic pulpitis is a long-term inflammation that develops in the absence of treatment for acute pulpitis. Symptoms tend to periodically worsen, and in the intervals between them there is no discomfort or it is very mild.
Both forms have several subtypes, which differ in localization, degree of spread, and the nature of the development of the inflammatory process.
Types of acute pulpitis
There are four types of acute pulp inflammation:
- Focal pulpitis . It is diagnosed during primary inflammation, when the carious cavity reaches the pulp. The localization of the pathological focus is the upper part of the tooth. This type of disease is accompanied by the most intense symptoms and signs of inflammation spreading along the trigeminal nerve and nearby lymph nodes.
- Diffuse pulpitis . Diagnosed 1-2 days after the onset of acute inflammation. The lesion is located throughout the coronal part of the tooth, sometimes down to the neck and root part of the pulp. Attacks of pain last relatively short time and worsen when the patient lies down.
- Serous pulpitis . An advanced form of acute pulpitis, accompanied by painful pain symptoms that do not subside.
- Purulent pulpitis . The final stage of acute inflammation, in which a focus of suppuration forms in the pulp. The process is accompanied by signs of acute intoxication of the body, increased pain when eating warm and hot food. Symptoms weaken when cold is applied to the diseased tooth.
Classification of chronic pulpitis
Chronic pulpitis occurs in three types:
- Fibrous inflammation is the most common variant and lasts about 3 months after the initial inflammation. It is accompanied by bleeding of the pulp when touched, periodic pain in the tooth when it comes into contact with cold or hot food.
- Hypertrophic inflammation is a condition accompanied by the formation of a polyp inside the pulp. It looks like a piece of gum growing out of a tooth. Pain with this type of chronic pulpitis is minimal or absent.
- Gangrenous inflammation is the most dangerous pathological process, which is accompanied by active necrosis of tooth tissue. Accompanied by an unpleasant putrid odor from the mouth.
Good to know! In addition to the listed types of acute and chronic pulpitis, dentistry distinguishes deep root, two- and three-channel inflammation, as well as pulpitis under a filling.
Complications during and after treatment
Unfortunately, even professional dentists can make mistakes when treating pulpitis. Let's look at the most common ones among them.
Breakage of a needle or instrument in a tooth canal
Tool breakage occurs, as a rule, in cases where penetration into narrow and rather tortuous channels is required. Several factors influence the occurrence of such a problem. First of all, incorrect selection of a tool that does not fit the size of a certain channel.
There are cases when the breakage of a part of a tool is caused by the use of a worn-out device or a violation of the operating technique of working tools.
This problem can be solved in certain ways. In some cases, quick and painless removal of the instrument from the canal is possible, even when the tooth has a filling.
If the remainder is too deep, the doctor fills the canal with filling material, after which the filling is removed along with the broken section of the instrument. At the same time, the doctor must explain to his patient the need for such a procedure. If the broken part of the instrument is combined with a perforation, tooth extraction is required.
Perforation of the tooth root
In most cases, tooth perforation is the result of an error by a dentist or endodontist. However, there are cases when the process of demineralization of tooth walls develops quite quickly, which causes holes to appear in the walls of the tooth. Moreover, the occurrence of the pathology in question is not in all cases a purely medical error, since it can occur as a result of probing. Of course, this is not the dentist’s fault.
Prerequisites for tooth perforation
As practice shows, tooth perforation can be caused by several factors:
- during treatment, the doctor does not take into account the placement of the pulp chamber;
- the dentist is not sufficiently familiar with the anatomy of the mouths of all root canals;
- the patient has narrowed or curved canals, during the mechanical treatment of which the doctor may unintentionally perforate the walls of the tooth.
Classification of pulpitis, symptoms
According to the type of course of the disease, chronic and acute pulpitis are distinguished.
In acute pulpitis, the pulp chamber is closed, and the infection enters the pulp through the thin wall of the tooth, destroyed by the carious process. Initially, acute pulpitis is focal in nature, then, against its background, purulent pulpitis develops, which is accompanied by the appearance of purulent discharge.
Symptoms of acute pulpitis: severe shooting and bursting pain. Pain appears not only during chemical and temperature exposure, but also bothers (and even increases) for some time after the removal of the irritant. Sometimes the tooth hurts all day, and the pain intensifies at night. The pain can spread along the trigeminal nerve, radiate to the temple, and involve the entire jaw. When tapping on a tooth, it is insensitive or not sensitive at all (with periodontitis, the opposite picture is observed). If acute pulpitis is not treated, it will progress to the chronic stage.
Chronic pulpitis is dangerous because many of its forms occur with virtually no pain, so patients are in no hurry to see a doctor. Only with gangrenous chronic pulpitis (when tissue decay has already taken place) are pains disturbing, and sensitivity to hot especially increases.
Symptoms of tooth root perforation
The pathology in question has several primary symptoms:
- during the examination, a feeling of “instrument failure” is formed;
- during the treatment of pulpitis, carried out without the use of local anesthesia, painful sensations are created during probing,
- the occurrence of bleeding from the perforation site.
In order to avoid such a problem, it is recommended to refer the patient for an x-ray before starting treatment. A competent analysis of the obtained research will help to clearly determine the characteristic features of the structure of the canals, as well as their inclination and placement. It is worth noting that if there is a lack of proper treatment, a complication of pulpitis can develop into a chronic form.
Removal of material beyond the apex
Today, such a pathology as the removal of material beyond the boundaries of the root apex is quite common. However, serious complications that can bring pain to the patient can only be provoked in cases where filling material enters the upper sinus, which often occurs during treatment of molars and other teeth located in the upper part.
Excess material can provoke the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the sinus mucosa (sinusitis). The only way to get rid of the problem under consideration is through surgery - resection of the apex of the tooth root, followed by cleaning the sinus from the resulting infection.
If a patient with this type of complication resulting from treatment does not have pain or any unpleasant symptoms, additional procedures are not necessary. The only thing is that it is necessary to monitor the tooth for a certain period of time.
Complications during treatment of pulpitis
No doctor, regardless of qualifications, is immune from accidents when treating a disease. Let's look at common mistakes and explain why they happen.
Tool breakage
Pulpitis is treated with very thin instruments, and the canals in which the vascular bundles are located are surrounded by hard walls, but are narrow and tortuous. As a result of accidental jamming or pressure, the thin metal breaks. This is also possible due to metal “fatigue” from frequent use.
Three ways to solve the problem:
- Get a piece, even if you have to destroy the newly created filling;
- Leave in place if the apical canal is already tightly sealed. The fragment is carefully filled with filling material, making it impossible for the metal to move. The patient must be informed of what happened;
- If a broken instrument causes perforation of the canal, the cause is removed; the consequence requires repeated endodontic treatment.
Perforation of the canal wall
Perforation of the tooth wall can be the result of a medical error, and sometimes occurs because the strength of the tooth was already questionable due to progressive demineralization. The thinned partition could not resist the pressure of the tool, and a breach appeared. In the latter case, the doctor is innocent.
The moment of perforation is always noticeable to the doctor and sometimes to the patient. If the canal examination is performed without anesthesia, the patient will feel pain. But such an experience is rare, because pulpitis is practically not treated without pain relief.
The doctor is able to feel the instrument sinking during probing - this indicates a breakthrough in the tooth wall. An additional symptom is bleeding.
Most often, this situation occurs for the following reasons:
- Insufficient examination by the dentist of the x-ray, which indicates the location and shape of the root tubules, or complete neglect of the preliminary x-ray procedure;
- The presence of tooth canals of complex shape, which makes it difficult to perform high-quality probing.
A timely noticed error in the form of perforation during the treatment of pulpitis complicates therapy, but does not prevent the tooth from healing.
Removal of material beyond the apex of the tooth canal
Treatment of pulpitis involves repeated visits to the clinic by the patient. According to technology, it is impossible to fill the canals and place a light-hardening filling on the crown of the tooth in one visit. The material used to seal the root tubules must first harden and dry out. Otherwise, there is a high risk of so-called canal overfilling, when the gutta-percha pin is squeezed out from the apex and penetrates into the surrounding tissue.
This material is perceived by the body as foreign. Inflammation develops. It is especially dangerous to remove material beyond the apical parts when treating upper teeth. There is a high risk of perforation into the maxillary sinus and the development of complications in the form of sinusitis. This will entail an operation to clean out the sinus with the permanent removal of the tooth itself.
The doctor is obliged to check the correct filling of the root canals and re-treat the tooth canals. Occasionally, however, this happens: material falls out beyond the boundaries of the root canal, but this does not bother the patient. Then the dentist observes the patient for some time and intervenes only if alarming changes begin.
Post-filling pain
In almost all cases, patients experience pain of a post-filling nature, which is caused by various prerequisites:
- reaction of periodontal tissues to foreign invasion;
- poor-quality filling;
- removal of the filling material beyond the boundaries of the apical foramen.
The most common is the first reason. In addition, pain after filling can last quite a long time and even reach two weeks. In the case when the filling procedure is carried out correctly, and the installed filling is of high quality, painful sensations arise in the canal only when biting it. In most cases, the pain goes away on its own after some time, but painkillers can be taken.
Let's sum it up
As already mentioned, complications of pulp inflammation can be caused by various reasons, but it is very important to promptly contact qualified specialists who can prescribe and carry out the correct treatment. Otherwise, this pathology can lead to a lot of undesirable consequences that will require long-term and serious treatment.
The best option to protect against any oral diseases is periodic visits to the dentist and preventive procedures for professional oral hygiene.
Symptoms
Inflammation of the pulp is not difficult to differentiate already at the stage of examining the oral cavity and interviewing the patient. This disease is characterized by:
- sudden onset of pain and its intensification at night;
- a gradual increase in pain intensity and duration in the first 3-5 days from the onset of the disease;
- irradiation (spread) of pain to the ear, eye, chin, depending on the location of the diseased tooth.
A characteristic feature of pulpitis, which makes it possible to distinguish it from caries and other dental pathologies, is a sporadic increase in pain, which is not associated with thermal, mechanical or other effects on the tooth.