Dentistry has a variety of modern drugs that allow you to cope with toothache efficiently, quickly, safely and for a long time.
But in some cases, remedies that are considered classic treatment methods are still used. One such remedy is arsenic.
Brief information about this tool
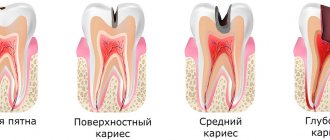
Arsenic is the 33rd chemical element of group 15 from D. Mendeleev’s periodic table, a semimetal, quite brittle, steel-colored with small greenish inclusions. Arsenium is its exact chemical name. This is a toxic substance; the toxic dose for humans is only 5 mg.
It has been used in dentistry since the beginning of the 19th century. It helped to quickly cope with the pain, but killed all the soft tissue. At that time, doctors did not yet know how harmful the substance was to humans and did not calculate its dose.
Arsenic continues to be used to this day in dentistry, but no longer in its pure form. Arsenic anhydride (AS2O3) is used. It is a component of a nerve devitalization paste, in which its amount is minimal.
Symptoms of arsenic poisoning
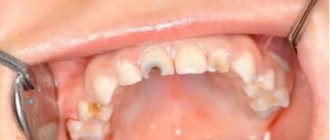
One of the techniques used in dentistry is the use of arsenic in special necrotizing pastes to kill the nerve. This substance is very toxic, so there are special methods for working with it.
Basically this happens in 2 stages. During the first, the doctor opens the carious cavity, removes dead tissue and injects arsenic paste into it, closing it with a special temporary filling. After this, the patient goes home, and after some time he has to return to the doctor to remove the temporary filling and arsenic and complete the treatment.
Indications
In some cases, the use of anhydride in dentistry is justified and completely acceptable. Its use is indicated for:
- impossibility of using another type of anesthesia due to health problems in the patient (for example, hypertension, pathologies of the heart and blood vessels);
- allergies to some components of other anesthetics;
- urgently seeking treatment;
- lack of susceptibility to the action of other drugs due to the patient’s high pain threshold;
- treatment of children's primary teeth, when local anesthesia is impossible.
Despite the fact that there is still debate about the advisability of using arsenic in dental treatment, in these situations only it will help cope with pain.
Contraindications
The main active component of the paste is highly toxic and aggressive, so its use has a number of restrictions:
- children under 2 years old;
- allergy to arsenic itself or one of the components of the paste;
- teeth roots that are not fully formed;
- root perforation or separation;
- the complex structure of the channels, when it is not possible to expand and clean them;
- high eye pressure or glaucoma;
- diseases of the urinary organs;
- pregnancy;
- breast-feeding.
Important: under these circumstances, even a minimal amount of arsenic can be toxic to the body, and its effects can be unpredictable.
Paste composition
Pastes from different manufacturers contain the same ingredients. The concentration of its constituent substances can only change slightly:
- Anhydride (arsenic trioxide) is the main component, occupies 30% of the composition.
- Local anesthetic (up to 27%) - needed to eliminate pain in the inflamed nerve. May be present: novocaine, dicaine or lidocaine.
- Antiseptic (up to 5%) - added to disinfect all tissues. May include: thymol, carbolic acid or camphor.
- The astringent component (1%) is tannin, which slows down the spread of arsenic through the pulp and helps extend the life of the paste.
- Filler – necessary for creating dosage forms of paste (balls).
The composition is designed to minimize the negative effects of arsenic on the body.
Action
Arsenic has a strong necrotic effect. As a representative of protoplasmic poisons, it reacts with sulfhydride (thiol) amino acids. In them, it completely blocks enzyme systems and displaces hydrogen. The result of this effect is the loss of the oxidative properties of amino acids.
This action of the anhydride leads to the development of hypoxia in the tissues. Even a small amount of it, when targeted, causes vasoconstriction in the pulp, the formation of a blood clot and, as a result, cessation of blood circulation.
At the same time, irreversible changes occur in the nerve fibers, leading to blocking of impulses and their subsequent death.
It is precisely this effect of arsenic on a painful pulp that is used in situations where it is impossible to do without eliminating the nerve.
Let's find out how to rinse a wound after tooth extraction. We looked at both medications and folk remedies. And here we will name ways to kill the dental nerve at home.
Application diagram
When using arsenic paste, nerve removal always takes place in 2 visits. During the first visit, an x-ray of the diseased tooth is taken, allowing the dentist to see the full picture of its damage from the inside.
Then the cavity affected by caries is opened, cleaned of dead tissue and an arsenic preparation is placed.
In difficult cases, a cotton ball soaked in an anesthetic is additionally placed into the cavity. A temporary filling is placed on top to prevent arsenic from falling out. The tooth may still hurt for some time, but the pain usually subsides after a few hours.
After these manipulations, the patient is allowed to go home for the period specified by the doctor. The time of your next visit depends on several factors:
- patient's age;
- dental conditions;
- type of paste used;
- method of adding the drug.
Typically, the duration of arsenic application is 24 hours. If the tooth is multi-channel, this time is doubled. If baby teeth with formed roots are treated, the duration of exposure may be reduced to 18 hours.
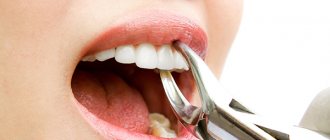
At the 2nd visit, the doctor removes the temporary filling and re-processes the cavity to eliminate the remaining arsenic and dead tissue. Then he begins to depulpate the nerve. The procedure is painless, since the nerve died under the influence of anhydride.
The last stage of treatment is the placement of a permanent filling.
How does the devital pulpectomy procedure occur?
When a patient comes to the clinic complaining of severe tooth pain, doctors immediately suspect pulpitis. But for an accurate diagnosis, in addition to a general and instrumental examination, it is necessary to take an X-ray of the problem area. After making the decision to remove the pulp, everything happens in the following sequence:
- Professional cleaning of a damaged tooth, sometimes the entire dentition.
- Opening a carious cavity.
- A devitalizing paste is applied to the exposed pulp or unopened pulp chamber.
- Using filling material, a temporary filling is installed, and the patient is sent home.
How long can adults and children walk with arsenic in their teeth?
The duration of devitalization depends on what specific drug is applied. The safer the product, the slower it acts, and the longer you will have to walk with it. If the doctor prescribed the latest generation drug, the patient will have to “wear” it for a week or even two.
Also, the following factors influence how long you can keep arsenic in your tooth:
- Patient's health status.
- Nature of the problem and clinical picture.
- Method of applying the drug.
- Patient's age.
Adult patients can keep arsenic in the tooth for one or two days - exactly how long depends on the number of canals. Children should not keep arsenic in their teeth as long as mature patients can, since an unformed body can react differently to the slightest deviations during treatment. If the devitalizing paste is placed on a baby tooth, its action time is reduced to 18 hours.
What happens if arsenic stays in the tooth for a long time?
If arsenic sits longer than prescribed, the risk of the following complications increases:
- Blackening of dentin, which is almost impossible to get rid of with simple or even professional teeth whitening in the clinic.
- The likelihood of periodontitis increases.
- The effect of the poison can spread to bone and periosteal tissue, causing their destruction.
- Not only the pulp tissue, but also the gums can become necrotic.
Signs of deterioration in general health, which may appear if arsenic is in the tooth for a very long time, or the dose of the drug is exceeded:
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Digestive disorder.
- General weakness.
- Change in body temperature.
- The skin turns pale or acquires a bluish tint and becomes sticky to the touch.
- Other signs of intoxication appear.
How to remove a temporary filling with arsenic
After the time for pulp devitalization has expired, the patient comes back to see the dentist. Further treatment is carried out in the following order:
- The doctor removes the temporary filling.
- Removes arsenic paste from the tooth.
- Increases the boundaries of the dental cavity.
- Removes dead pulp.
- Cleanses the tooth cavity.
- Root canals are processed using special instruments and preparations.
- The root canals and dental cavity are filled.
After the procedure, the patient must visit the dentist for some time so that he can monitor the condition of the operated tooth.
Why does the tooth that contains the product hurt?
After applying the paste, the patient usually hopes that it will immediately relieve pain and stop the torment. In most cases, the pain subsides after a few hours, when its analgesic components begin to act and the sensitivity of the nerve endings is blocked.
Sometimes it takes much longer to completely relieve pain - up to 2 days. This is considered normal.
But this is not always the case. Often the tooth continues to hurt severely even if there is arsenic in it. There are several explanations for this:
- Its dose is calculated incorrectly; it is less than the required norm.
- The patient has a high pain threshold.
- Inflammation from the pulp spread to neighboring tissues.
- Necrosis of the periosteum developed.
- An allergic reaction to one of the components of the paste occurred.
- Incorrect paste insertion.
Many people try to relieve pain with a large dose of painkillers, applying heat to the cheek, or chewing food on the side of the problem tooth. This is not recommended. But you can’t continue to endure the pain! To avoid complications, you should consult a doctor.
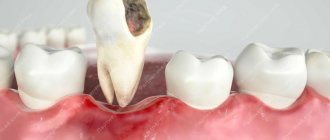
What is pulp?
The pulp, or dental nerve, is a bundle of nerve endings and capillaries in the internal cavity of the tooth. It is protected from external irritants and infection by the tissue that is located in the root and crown.
After removal of the nerve, the blood supply and mineralization of the tooth deteriorate significantly. In addition, its sensitivity decreases, the enamel becomes dull and weakens. In other words, pulp removal negatively affects the structure and strength of the tooth, but makes it possible to preserve it.
Indications for the procedure:
- exposure of the nerve as a result of tooth trauma and damage to the crown;
- consequences of improper dental treatment;
- the presence of caries-affected tissues;
- preparation for prosthetics;
- chronic inflammation of the pulp (pulpitis);
- inflammation of the root membrane of the tooth (periodontitis);
- low placement of crowns;
- extensive pulp area;
- bactericidal infection of the apex of the tooth root.
Patient Safety Rules
A patient who has had arsenic used to kill a nerve should follow these recommendations:
- Preserve the integrity of the placed filling: 2 hours after placing the drug you cannot drink or eat anything. This time is enough for the filling to harden.
- If the paste falls out, the patient will feel a sour taste.
In this case, doctors recommend rinsing your mouth with a soda solution and drinking 1 tbsp. milk. They neutralize the effect of all substances in the paste, prevent them from burning the mucous membrane, bind all toxic compounds and remove them from the body. - It is not recommended to wear a temporary filling for longer than the period specified by the dentist. You should not put off visiting a doctor, even if toothache does not bother you.
- Don't drink alcohol. It increases the effect of anhydride on the body, which can lead to poisoning.
First aid for poisoning
If there is a suspicion of arsenic poisoning through the mouth, you should immediately drink a glass of clean water in which three grams of citric acid and one tablespoon of vinegar are diluted. It is worth noting that the usual activated carbon is ineffective in this case, and laxatives should not be taken. If a person starts vomiting, they should drink warm milk.
It is important to understand that in case of arsenic poisoning, emergency medical attention is needed. Toxicologists treat arsenic intoxication in the body.
Before treatment, laboratory tests are prescribed. Urine and blood tests can reveal the amount of arsenic in the body. It is worth noting that in urine it should not exceed 100 mcg per 1 liter of urine, and in blood 30 mcg per 1 liter. Also in the blood there is a decrease in hemoglobin and red blood cells, and an increased ESR. An increase in protein levels is observed in the urine.
After a few months, it can easily be detected in the victim’s hair and nails. There are special drugs that act as an antidote. They are administered intramuscularly and prescribed strictly by a doctor. If there is no antidote, the person is given an antidote and then the stomach is washed. If there is pain in the abdominal area, then injections of morphine and atropine are prescribed.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
To prevent dehydration of the body, saline solution, reamberin and glucose solution are prescribed, calcium chloride and sodium thiosulfate are administered. If renal failure occurs, hemodialysis is performed.
Possible dangers and complications
Arsenic, although present in small quantities in the paste, can lead to discomfort and poisoning if it enters the stomach with saliva. Such a development of events occurs extremely rarely and is associated only with a violation of the integrity of the filling and individual susceptibility to this substance.
Failure to follow the dentist’s recommendations and keeping the paste in the tooth cavity for a long time can lead to the development of complications. If the maximum permissible time of presence of the product is exceeded, the following are observed:
- change in dentin color;
- swelling of the pulp;
- periodontitis;
- development of inflammation of the tissues around the tooth;
- burn of the mucous membrane and gum tissue;
- death of tissue in the periosteum and healthy neighboring ones;
- malaise, weakness.
You can see photos of inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth, and also familiarize yourself with methods of its treatment. And here you can learn about treating tongue tip at home.
By clicking on the following link: https://dentist-pro.ru/xirurgiya/udalenie-zubov/posle-bolit-desna-chto-delat.html, you will find the most complete information about what to do if your gums hurt after tooth extraction. You can also read reviews from patients who have encountered the same problem here.
The high professional level of the dentist and the patient’s compliance with all his instructions will reduce the development of these consequences to a minimum.
We recommend watching the following video, which will tell us how to prevent arsenic poisoning:
Is arsenum dangerous?
The use of arsenic always carries little danger, since the substance has an aggressive toxic effect. As a rule, after using it, the tooth may hurt for several hours, but over time the pain subsides.
In some cases, even after a few days, the painful sensations do not disappear, but become more intense. The most harmless reason that can cause such manifestations is an insufficient dose of a substance that is not capable of killing the nerve .
What to do after resection of the apex of the tooth root if pain occurs.
Experts shared information about the best way to rinse your mouth after tooth extraction.
Follow the link https://zubovv.ru/hirurgiya/udalenie-zubov/kak-mozhno-ostanovit-krov-posle.html tips on how to stop bleeding at home after tooth extraction.
Serious causes of danger include:
- inflammation of the periodontium of a diseased tooth, which can lead to the formation of granuloma;
- localized gum necrosis , gradually developing into periodontitis;
- intolerance to the components of the drug. Additionally, it is manifested by swelling and redness of the mucous membrane;
- an incorrectly placed filling that puts pressure on the tooth cavity and pulp.
The only correct option in such a situation is to consult a dentist as quickly as possible.
Pregnancy
The use of arsenic-based paste during pregnancy and breastfeeding is contraindicated . Despite the minimum dosage used for treatment, a toxic effect of the drug on the fetus and infant is not excluded.
Therefore, when contacting a doctor, first of all, you need to inform him about your situation of future or present motherhood. For treatment during this period, other drugs with a similar but less toxic effect will be used.
Childhood
Just as during pregnancy, arsenic is prohibited for the treatment of pulpitis in young children. The main reasons for refusing the drug are:
- The inability to calculate the exact dosage , which can lead to negative effects on adjacent tissues.
- There is a high probability of ingestion of a substance that causes severe poisoning of the body of a small patient.
- Aggressive impact on not fully formed dentin, which leads to its rapid destruction.
Despite good reasons, arsenic is still used to treat children's teeth, but only with formed roots. Neglect of this factor often leads to the development of periodontitis.
Most often, devitalizing paste is used as a gentle measure when a child has a strong fear of injections.
The period that a child must wear this product is much shorter than for adults. Generally the period is 16-24 hours.
Nuances of use during pregnancy and lactation
The use of arsenic paste during pregnancy and breastfeeding is prohibited! Even though the anhydride content in the product is minimal, its toxic effect on the intrauterine development of the fetus and the condition of the infant cannot be ruled out.
When visiting a dentist during this period, it is important for a woman to warn him about her motherhood.
There are many other arsenic-free drugs that have a similar effect, but are safe for the baby and the health of the mother.
Alcohol compatibility
Doctors usually recommend not drinking alcohol while taking any medications, and arsenic is no exception. The pastes that contain it have many chemical components, and drinking can become a catalyst for them and this often causes serious complications.
Therefore, whether it is possible to drink alcohol or not while arsenic is in the tooth, each person decides for himself independently, but it is still better to listen to the opinion of doctors, especially since you can endure it for 2-3 days.
Nuances of use in children
In pediatric dentistry, an arsenic drug is used in extremely rare cases when the use of another drug is not possible due to the following circumstances:
- allergic reaction to components of another anesthetic;
- the child’s fear of injections necessary to administer pain medication.
When using arsenic, the dentist also takes into account the degree of formation of tooth roots. The drug can be used when the roots are fully formed. Failure to comply with this condition can lead to the development of periodontitis.
The duration of stay of the product in a child’s tooth is much less than in adult patients. If the paste was applied to a bare pulp, then the child’s second visit should take place after 14-16 hours. When applying the drug to an unopened pulp, this time increases to 24 hours.
Why is it not necessary to remove the nerve to install crowns?
The need to remove the nerve arises primarily when the tooth is completely destroyed. It can also be dictated by the qualifications of the doctor: when heating or deeply removing the top layer, there is a risk of damage to the nerve endings, and this is very painful. That is why many dentists prefer a safer route, that is, preliminary removal of the nerve. Especially in the presence of the initial stage of caries.
In addition, depulpation can be performed in a number of cases before prosthetics: with increased sensitivity, with small sizes and in the presence of more than 15-degree inclination of the teeth. The pulp may also be removed for aesthetic reasons.
It is not necessary to perform depulpation before installing crowns, since the nerve can always be removed through the top of the crown.
After depulpation, the hole is filled. The main disadvantage of this procedure is the exposed tooth root, which can cause complications in the future.
Analogs
Today, the use of arsenic paste has become rare. Several modern products have been developed that are highly effective and completely safe.
Modern analogues are:
- Paraformaldehyde pastes - in addition to the main necrotizing effect, they have antibacterial properties, have a milder effect and do not lead to periodontal irritation. Their only disadvantage is the prolonged death of the nerve (it takes up to 6 days).
- Arsenic-free pastes – the most popular are the “Devit” group of products. The duration of nerve killing can be up to 10 days, but these remedies are completely safe for health.
Available in 3 forms:
- "Devit-A" - it contains a powerful antiseptic substance - paraform. Used for anesthetic and antiseptic compresses;
- "Devit-P" - used in the treatment of temporary teeth in cases where dead pulp will not be removed;
- “Devit-S” is intended for removing dead pulp after treatment in adults.
Which drug will be used to kill the nerve depends on many factors.
How to remove medicated paste from a tooth yourself?
Doctors do not recommend removing the medicine yourself, especially since it is quite problematic, but there are situations when there is no other way out. This happens when emergency treatment is needed, and dental clinics are closed due to weekends or holidays. Finding yourself far from civilization, you also have to get rid of arsenic yourself. Arsenic should also be removed if the temporary filling has fallen out. So how can this be done?
Read also: Inflammation of the nerve of the tooth If there is a filling, it can be removed with a regular sewing needle or a syringe attachment.
As a rule, compositions for temporary fillings are not particularly hard. If the filling comes out on its own, you need to remove the arsenic paste with the same needle or tweezers pre-treated with alcohol. It is advisable to rinse your mouth with a soda solution with the addition of iodine or hydrogen peroxide .
The open cavity must be covered with a cotton swab. There is no need to delay visiting a doctor. In the absence of qualified dental care, the risk of developing inflammatory processes and the possibility of complications increases sharply.
Reviews
Arsenic is a dangerous and highly toxic substance. But it is still used in dental treatment, even though safer drugs already exist.
In many cases, it is the only possible and affordable way to get rid of severe toothache. But the feasibility of its use must be accurately calculated by the dentist.
You can share your impressions about the experience of dental treatment using arsenic by leaving a comment on this article.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Should a tooth hurt during treatment, and what to do if it hurts?
How long does a tooth hurt after installing a temporary filling with medicated paste? If arsenic paste is applied correctly, the tooth should not hurt. Firstly, because the drug contains anesthetic components. Secondly, necrotization of the nerve contributes to the complete loss of sensitivity in the tooth.
Why does a tooth on which arsenic was placed hurt?
- the drug is applied to the closed pulp;
- allergic reactions;
- insufficient concentration of the drug;
- inflammation of periodontal tissues;
- overexposure of the drug.
Under no circumstances should toothache be tolerated during treatment. The presence of pain indicates serious problems that can have unpleasant consequences for the patient. It is not recommended to use anesthetic drugs on your own.
Firstly, it is difficult to determine their compatibility with the components of arsenic paste. Secondly, the arsenic drug itself is a powerful anesthetic, and if it does not work, then you should not look for an even stronger painkiller, but identify the problem that toothache is signaling.