Bite pathologies are one of the most common reasons for visiting a dentist. People have been engaged in returning teeth “to their place” since ancient times - there is evidence that this issue was of interest in ancient Egypt. However, only in recent decades have doctors come to the conclusion that it is necessary to correct an abnormal bite. Timely orthodontic treatment helps to avoid serious consequences for the entire body in the future. In this article, the leading orthodontist at the ZUUB dental clinic on Lipetskaya in Moscow, Dmitry Anatolyevich Polovkov, talks about the dangers of malocclusion and ways to correct it.
Correct bite - what is it?
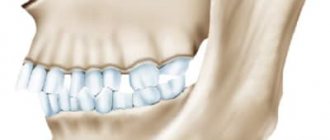
Normal, or physiological occlusion, is characterized by the absence of disturbances in the arrangement of the dentition relative to each other with the jaws fully closed. He can be:
- regular, or orthognathic - in this case, the upper teeth overlap the lower teeth by a third of their height and there are no pronounced gaps between the dentition;
- straight - both jaws clearly close;
- biprognathic - both the upper and lower dentition are slightly tilted forward;
- progenic - only the lower jaw is pushed forward a little, but this does not prevent the cutting edges of the teeth from completely closing.
Correct bite is the absence of pronounced gaps between the teeth when the upper teeth are in contact with the lower ones opposite them. Orthodontists determine a bite without pathologies based on the following characteristics.
- The upper front teeth overlap the lower ones by 1/3 of their height.
- The incisors and canines are arranged in an even, arched line without distortions or crevices.
- The upper teeth protrude slightly outward, the lower teeth “look” slightly inward.
- All teeth are clearly below each other.
- The center of the jaws vertically coincides with the midline of the face, there are no protruding parts of the cheekbones or chin.
It is important to remember that in order to form a correct bite, you need to be careful about teething and caring for them.
Signs of pathology
Incorrect distal bite is conventionally divided into 2 types based on its characteristics. These are facial and intraoral changes. Their most severe severity is observed in adults in the complete absence of treatment.
Facial manifestations of distal occlusion:
- Violation of facial proportions - asymmetrical displacement of the lower jaw back and a small, sloping chin.
- A noticeable state of always half-open mouth.
- Change in the natural shape of the upper lip - reduced in volume, upturned or very short.
- Deformation of the lower lip.
- The teeth of the upper jaw are more developed than the lower jaw, the central upper incisors protrude strongly forward.
- Sharply defined chin fold.
Such changes in the shape of the face negatively affect the appearance, the face becomes bird-like.
Intraoral signs of a distal anomaly are as follows:
- There is no closure between the lower and upper jaw.
- The teeth of the upper frontal group are noticeably moved forward.
- The lateral teeth are located abnormally relative to each other.
In most cases, distal occlusion is formed against the background of other pathologies - diastema, trema, open or crossbite.
Causes of malocclusion
Malocclusion (malocclusion) is due to various reasons: congenital or acquired. An important role is played by genetic factors, as well as insufficient intake of calcium into the mother’s body when carrying a child. Hereditary problems with bite require certain nuances in treatment. Therefore, before carrying out any orthodontic manipulations, the doctor talks with the parents and learns about all the possible factors in the occurrence of pathology.
Acquired malocclusion develops gradually. It appears at different ages due to its own reasons.
In childhood
- Bad habits (finger sucking, pacifiers, chewing on objects).
- Being on artificial feeding.
- Pathological bone formation.
- Teeth grinding (bruxism).
- Lack of sufficient solid food in the child's diet.
- Mouth breathing (formed as a habit or due to respiratory diseases).
- The replacement of baby teeth occurs too sooner or later.
- Pathologies associated with metabolism.
- Calcium and fluoride deficiency.
- Pronounced carious lesion.
- Injuries of the maxillofacial apparatus
In adults
- Installation of unsuitable dentures.
- Diastemas that form as a result of tooth extraction.
- Various types of injuries.
- Lack of space for eights (wisdom teeth).
- Unusual localization of the language.
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Open bite – common in children
It often happens that bad habits in children, characteristic of infancy and younger age, remain with them until the beginning of school and beyond. Naturally, it is very strange for everyone around to look at a first-grader child who still holds foreign objects in his mouth... In our and many other cases, it is the “FINGER”, which simply “remarkably” forms an open bite in children.
You can read more about this case of treating an open bite in a child HERE
Types of malocclusion in adults and children
Dentists usually divide anomalous occlusions into planes.
- Sagittal - characterized by elongated/shortened rows of teeth.
- Transversal - narrowed/expanded dentition is visible.
- Vertical - the presence of shortened/elongated certain areas in the dentition.
In addition, in dental practice it is customary to use the following classification of occlusion.
- Distal.
Sagittal occlusion with the upper jaw pushed forward. - Mesial.
Also a sagittal variety, but with the lower jaw moving forward. - Cross.
Transversal pathology with displacement of the jaws, which can only be partially formed, in one direction or another. - Open.
Vertical occlusion occurs with both partial and complete non-occlusion of teeth. - Deep.
The so-called traumatic, contributing to damage to the enamel. Characteristic is almost maximum overlap of the lower rows with the upper ones. - Vertical occlusal anomaly.
In addition to the above listed occlusion disorders, some experts identify 2 more types of anomalies:
- dystopic bite - displacement of one or more teeth;
- reducing - formed due to damaged and (or) lost teeth.
Constant
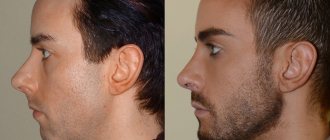
After the eruption of the molars is completed, a permanent bite is formed. This usually occurs around 12–13 years of age. Early disorders, bad habits, injuries and heredity can cause the formation of malocclusion.
photo: malocclusion in adults
Below are described multiple complications of such disorders , which can be avoided by promptly seeking help from an orthodontist.
Decreased chewing activity
Incorrect dentition can affect the ability to chew food normally , significantly reducing chewing activity.
This condition cannot be neglected, as poor chewing affects the absorption of nutrients from food.
In addition, swallowing becomes more difficult and caries and other similar processes begin to develop in the oral cavity.
Temporomandibular joint disease
Most problems with the temporomandibular joint are difficult to treat , especially for advanced cases if the patient has not sought help for a long time.
They provoke:
- headaches and ear pains;
- muscle spasms;
- difficulty opening the mouth;
- crunching and clicking when moving the lower jaw;
- dizziness and much more.
The most common are arthritis and arthrosis of this joint , as well as dislocations that were caused by weakening of the ligaments.
Uneven chewing load on teeth
Due to improper jaw closure, some groups or individual teeth may experience different amounts of load.
This leads to abrasion of enamel, dentin, chips and early adentia.
In addition, the quality of chewing food decreases, which can cause problems in the entire digestive system .
Uneven load can lead to the formation of a wedge-shaped defect, when chips and damage to the enamel first appear at the base of the crown.
Increased enamel wear
The abrasion of hard tooth tissues begins with the top layer – enamel. The longer the bite is not corrected, the more tissue is erased. Most often, the transition to dentin damage occurs much later than 30 years , but the process can begin much earlier.
If the tooth is damaged by more than half, the outline of the face also begins to change - the lower third decreases, which is why folds appear around the mouth.
Damage to bone tissue
Changes in the periodontium and constant improper distribution of pressure on the teeth can provoke destruction and various damage to bone tissue .
Such processes also lead to loss, that is, to a decrease in the volume of bone tissue. At the same time, the teeth themselves suffer - the destructive processes that occur affect the quality of their attachment, so loosening may occur . All this complicates prosthetics and treatment.
Periodontitis
With a deep and crossbite, the tissues surrounding the teeth - the periodontium - are almost always quite severely affected. It is this that serves to hold the roots in the alveoli. The most common periodontal disease – periodontitis – is characterized by the appearance of inflammatory processes in the gums .
In the absence of treatment and the disease progresses to later stages, the process of loosening of teeth begins, which leads to prosthetics and early restorations.
Early tooth loss
Abnormal bite changes also lead to early tooth loss. This occurs because the teeth are subjected to improper stress.
Some areas are more involved in the chewing process - here hard tooth tissues begin to wear off , roots become loose, and destructive processes generally occur. This ultimately causes other multiple disorders.
Impaired diction
Diction disorders of varying degrees occur in people with malocclusion almost always.
This is due to the fact that the full functioning of the speech apparatus is difficult , one of the departments of which is the fixed organs - teeth, palate, alveoli, pharynx, etc.
They are used to support the movable and have the greatest influence on the technique of speech itself.
Diction disorders may vary, depending on the specific clinical picture.
Aesthetic violations
First of all, the smile itself becomes unattractive. In addition, the proportions of the face change, which greatly affects aesthetics .
- With a distal bite and protrusion of the upper jaw, the chin becomes disproportionately small.
- When diagnosing a mesial bite, a protruding lower jaw and, accordingly, the chin are observed.
- An open bite is characterized by a constantly slightly open mouth and a general asymmetry of features.
Gastrointestinal diseases
In order for the digestive system to function properly, all stages of digestion are very important. The first of these is sufficient grinding of food with the teeth.
With malocclusion, food is chewed poorly, and, consequently, an increased load is placed on the organs of the gastrointestinal tract . This happens constantly over a long time and leads to natural disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract.
Difficult oral hygiene
The unnatural arrangement of teeth makes it difficult to clean them properly.
The number of places in the oral cavity that can be classified as hard to reach increases significantly. Food debris constantly accumulates in these areas , which are an excellent breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria. Because of this, people with orthodontic conditions are more likely to suffer from tooth decay and many other dental diseases.
Difficult prosthetics and restoration
Several factors come into play here. Incorrect distribution of loads during chewing leads to premature failure of artificial crowns.
The installation of bridges also becomes more complicated - often twisted or out-of-row teeth cannot serve as a reliable support for installing the structure . And some aesthetic restorations, for example, installation of veneers, are contraindicated for malocclusions.
Breathing problems
Normally, a person should breathe through the nose. Some structural disorders of the dental system prevent this, such as an open bite.
In this case, there is a non-closing of the jaws (usually in the anterior section), due to which the mouth is constantly slightly open.
Also, breathing problems, and subsequently malfunctions of the ENT organs, can be caused by a distal or deep bite.
Bruxism
Bruxism is the involuntary grinding of teeth. It occurs due to too strong and uncontrolled contraction of the masticatory muscles.
Most often, symptoms of this disease occur during sleep , but sometimes bruxism also occurs during the day. Subsequently, this can lead to diseases of the temporal joint, abrasion and loosening of teeth, headaches and neck pain.
ENT diseases
Numerous diseases of the ENT organs can also be provoked by orthodontic abnormalities . This happens not only due to frequent mouth breathing. Problems also occur due to the atypical structure of the entire dental system.
Many people learn about malocclusion only after numerous sinusitis, otitis and other diseases, when the otolaryngologist gives them a referral to an orthodontist.
Traumatization of soft tissues of the oral cavity
Protruding parts of the dentition when chewing or simply closing the lower and upper jaws can constantly injure the oral mucosa and soft tissues . Similar damage is often caused by protruding sharp edges formed due to chips due to malocclusion.
Chronic soft tissue injuries, in addition to discomfort, can provoke the appearance of non-healing ulcers , stomatitis, inflammation and swelling caused by infection.
How to correct a child's malocclusion
- Children under 7 years of age
are shown a set of gymnastic exercises and massage that will help solve the problem. - Children under 10 years of age
are already prescribed trainers, with the help of which they can set the desired direction for their teeth. They must be worn for a certain number of hours during the day. But, if the pathologies are more advanced, removable plates and mouthguards are used. Correction of the anomaly takes approximately 2 years. - For children aged 10-12
years, braces are used to correct their bite - special orthodontic structures consisting of a power arch and clasps that set an individual direction for each tooth. They cannot be placed at an earlier age; it is necessary that all milk teeth be replaced by permanent ones. How long to wear braces for malocclusion is determined by the treating orthodontist.
How to correct malocclusion in an adult
A very common treatment method for adults is wearing braces. Transparent aligners (aligners) are also very popular now. They are made of transparent plastic material. Aligners are effective in correcting impaired occlusion, are easy to use and look very aesthetically pleasing. All details about this technique can be found here.
In cases where the patient is not in the mood for long-term bite correction with aligners or braces, there is another solution - microprosthetics. In this case, special overlays are installed on the teeth - veneers, with the help of which you can correct uneven teeth and gaps between them. But if there are serious malocclusions, this technique is not used.
There are bite defects for which only surgical treatment is indicated. Examples include: severe malocclusion, facial asymmetry due to trauma or hereditary causes, and chin dysplasia.
Each method of orthodontic treatment has both indications and contraindications. Only an orthodontist can determine the method of treatment after a thorough examination and full diagnosis.
Treatment and correction of distal bite
Treatment methods for prognathia depend on its degree, the form of the disorder and are selected only after diagnosis.
What is prescribed to the patient:
- radiography;
- teleradiography;
- CT;
- MRI;
- rheography;
- electromyography.
These diagnostic procedures allow you to determine the correct shape of the jaw, as well as identify any complications caused by the distal anomaly. During the examination, the entire temporomandibular joint and masticatory muscles are checked.
Correction of prognathism in adult patients takes several years. Sanitation of the oral cavity is first required, that is, complete cure of diseases of the gums and teeth, for example, caries.
Correction of distal occlusion without surgery is possible if the deformation affects only the dentition. In this case, braces are effective, after which you will have to wear retainers or mouth guards for a long time or constantly to keep the teeth in the desired, correct position. Complex therapy includes special myogymnastics.
In more complex cases, special devices are used to correct the bite or surgery is performed. During treatment, all consequences obtained during the development of the deformity are eliminated.
Application of braces
Correction of distal pathology using braces in adult patients requires at least 2 years. They are selected individually, which depends on the degree of deformation, the reasons that caused the development of the pathology, and financial capabilities.
To correct the bite, braces are used:
- metal;
- ceramic;
- sapphire.
Such materials do not harm the body and do not provoke the development of allergic reactions.
Some people prefer lingual braces when correcting distal occlusion. These are devices that are fixed on the inner surface of the teeth and are invisible to others. But they are not suitable for correcting all forms of prognathic deformity.
With the help of a braces system, not only the bite is corrected, but also the function of proper chewing is normalized. To do this, it is necessary to perform special gymnastics.
When using braces on your teeth, you must constantly visit your doctor, follow all his recommendations and take the most careful care of your oral cavity. The duration of wearing braces is determined by the degree of prognathism.
Myogymnastics
If a distal bite is corrected using braces, correction after them or while wearing them involves performing myogymnastics. This is a special set of exercises for developing facial muscles.
What effect does regular exercise have?
- secures the jaws in the desired position;
- eliminates tooth alignment disorders;
- corrects the position of the upper and lower lips;
- develops tongue and chewing muscles.
Devices for correcting bite
In severe forms of deformation, treatment is carried out with the fixation of frame devices; they help move the first molars to normal. For this purpose, non-removable devices Forsus and Powerscope are used, which must be worn for up to six months.
A facebow with palatal traction helps eliminate deformation of the upper jaw. This device is worn for about 10 hours every day.
To bring the lower jaw into a normal position, intermaxillary elastics are used. With their help, the lower bone moves forward over a period of 3 to 4 months.
Alternative Methods
Orthodontists also use alternative methods to correct bite:
- Veneers. Only minor deformations of the dentition are hidden.
- Aligners. They are removable plastic mouth guards. In case of distal damage, they are ineffective, so they will have to be changed every month.
- Trainers. Removable silicone structures to correct malocclusion. At the beginning of therapy, soft ones are used, at the end - more stringent ones.
Consequences of malocclusion
It is a mistake to think that a pathological bite concerns only appearance and only leads to an unattractive smile. This is where the problems arise that are more serious. For example, in 90% of people with abnormal occlusion, incorrect posture is also detected. There is a logical explanation for this: with a broken bite, the center of gravity of the head shifts. This in turn affects the compensation mechanisms of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus of the maxillofacial system. The result of all this is an increase in the pathology of teeth closure.
Aesthetically, occlusion abnormalities lead to facial asymmetry. A weak-willed chin becomes pronounced, and lips protrude unattractively.
The next malocclusion is severe inclination of the front teeth
But the most interesting thing is that the teeth were positioned this way after previous treatment with braces. Braces were unable to simulate the final result of bite treatment and, in fact, it was carried out blindly. It turns out that you are a little over 20 years old, in the recent past you straightened your teeth at the orthodontist with braces and thought that a beautiful smile is now with you forever, BUT... Unfortunately, sometimes we have to admit that the doctor’s incorrect recommendations for correcting the bite or the patient’s arrogance leads to relapses and spoils everyone's mood.
Read more about this treatment case HERE
What is the danger of malocclusion?
In addition to visual problems, more serious dysfunctions often occur, including internal organs.
- Due to increased and uneven load on the teeth, periodontal disease develops and teeth begin to decay.
- Inadequate chewing of food leads to disruption of the digestive system.
- The functioning of the temporomandibular joint is impaired.
- The respiratory system also begins to malfunction.
- Slow metabolism.
- Increased risk of developing caries, especially with cross-closing teeth.
- Problems with pronunciation of sounds.
In addition, with malocclusions, daily dental care becomes much more difficult, which contributes to the constant accumulation of plaque on them.
Make an appointment
right now!
Polovkov Dmitry Anatolievich
Orthodontist
What complications can there be?
If an adult or child has developed a distal bite, treatment will help avoid the consequences of pathology. In the absence of correction, the following complications are possible, which are dangerous to health:
- problems with diction, speech defects arise, correctly constructed speech becomes impossible;
- dysfunction of chewing and swallowing food;
- disruption of the proper functioning of the respiratory system;
- the appearance of dental diseases - caries and stomatitis develop;
- rapid wear of teeth, which leads to their premature loss;
- the formation of complexes due to unsightly appearance.
Malocclusion affects a person’s entire life, causing psychological problems and the development of an inferiority complex. People with this problem are often unhappy and lack self-confidence. Only correction will help improve your condition and appearance.
What to do to avoid malocclusion.
The consequences of malocclusion can be avoided by taking measures in time, namely in childhood. Here the responsibility falls largely on parents, who can promptly pay attention to problems and carry out prevention. It is important to take into account the risk of congenital disorders, hereditary predisposition, and also eliminate unfavorable factors:
- prevent the development of rickets and other diseases that impair bone growth;
- bottle feed your baby correctly;
- monitor the position of the child’s body during sleep (posture without tension, head not tilted back, etc.);
- maintain correct posture;
- timely wean your child off the pacifier, thumb sucking habit, toys and other objects;
- treat baby teeth immediately, because their early loss (as well as too late) can negatively affect the bite;
- to prevent nasal breathing disorders, namely to treat diseases of the ENT organs and ARVI.
When anomalies in the development of teeth are identified in childhood, timely assistance from an orthodontist will help solve problems faster than in advanced cases in adults. In children, as a rule, there is no need for surgical intervention yet, and even a complex of therapeutic exercises for the facial muscles can significantly help in correcting the bite.
Publisher: Expert magazine about dentistry Startsmile.ru
Stages of bite formation
Malocclusion manifests itself already in childhood, and its symptoms may include teeth moving forward or backward, gaps between teeth, rotation of teeth, etc.
In general, dentists identify five main stages of child development that affect the formation of the bite:
- 1. The period from the birth of the child to six months;
- 2. 6 months-3 years – formation of a temporary bite, during which the eruption of temporary teeth occurs;
- 3. 3-6 years – the period of formed temporary occlusion, when the jaws are actively growing and preparation for the eruption of permanent teeth begins;
- 4. 6-12 years – period of mixed dentition, eruption of permanent teeth;
- 5. 12-15 years – the period of formation of a permanent bite, during which milk teeth are replaced by permanent ones.
Virtual 3D setup from Star Smile - see your restored bite
A special feature of bite correction using Star Smile aligners is the ability to see the result of your treatment BEFORE it begins using a special computer program. See how this happens in case of crowded teeth:
The video shows how the 3D setup is done. In the Star Smile company, or more precisely in the clinics of its partners (which are more than 70 cities in Russia), any treatment
begins with diagnostics and drawing up a virtual setup. The doctor takes photographs of the patient’s face, dentition, as well as x-rays and dental casts. Using special software, the obtained data is processed and a three-dimensional model of the patient’s dental system is obtained. And this already allows you to calculate the trajectory of tooth movement, treatment time, and the required number of sets of aligners. Also, the final result of the treatment will be visualized - the patient will be able to evaluate the aesthetics of the smile after treatment. Patients really like this approach - they can see their future smile, their straight teeth. The 3D setup forecast for correcting malocclusion with aligners comes true in almost 100% of cases. You see, this is completely different from correcting a “blind” bite. Everything is clear here, without any guesswork or assumptions.
“Okay,” you say, “but in my case, can you help me?” — this is a question patients ask our orthodontists every day. See for yourself.