A beautiful smile and straight teeth are the calling card of any person. But not all parents know that they need to take care of their child’s beautiful smile already during the formation of baby teeth. How does the primary occlusion affect the formation of the dental system, and what effect does it have on permanent teeth? The article describes the difference between primary and adult occlusions and methods for correcting dental defects.
Features of milk bite
The rudiments of the first teeth appear in the baby long before birth: approximately at the 20th week of intrauterine development. Every pregnant woman should know about this. In order for a child to develop strong teeth, he must receive a diet rich in calcium and phosphorus. Therefore, a pregnant woman’s menu must include these microelements, as well as a complete vitamin complex.
You can see the baby’s first incisors after the fifth month of life: the two lower teeth begin to appear. Then two upper incisors appear, after which canines (16 - 20 months), first and second molars form. The complete set of chewing teeth, canines and incisors ends by the age of three. But the formation of the root system (as well as the bite) continues until 7 - 8 years. And only after the appearance of permanent teeth the formation process is completed.
The signs of correct bite (occlusion) are as follows:
- the upper incisors should be slightly larger than the lower ones;
- the radius of the upper arch of the dentition is slightly larger than the lower one;
- the dental arch has an even semicircular shape;
- the upper incisors should protrude slightly above the lower ones (by a third);
- By the age of three, the baby should have 20 chewing units.
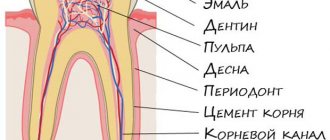
The enamel coating of crowns is very thin, so baby teeth are quickly destroyed by caries. If you do not take care of them, carious teeth provoke improper development of the bite. This, in turn, will negatively affect the formation of permanent molars and occlusion (correct closure of teeth).
Of particular danger is the removal of some milk units due to serious carious lesions. The absence of at least one baby tooth in a row negatively affects the formation of occlusion.
Sequence and pairing of eruption
Milk teeth always erupt in pairs. Otherwise, we can talk about a violation of the morphological norm and atypical development of dental units. The teeth on the lower jaw usually appear first, followed by the upper ones. This applies to the front incisors.
The eruption of lateral incisors, canines and molars occurs in the reverse order. Deviations from this rule indicate improper development of the entire dentofacial apparatus.
The formula for primary occlusion looks like this: 2 * 1 * 0 * 2/2 * 1 * 0 * 0 * 2. In the numerator of this fraction, the first digit means the number of incisors, the second – the number of canines, the third – the number of small molars, the fourth – the number of large teeth molars on one side of the upper jaw. The denominator shows the number of corresponding teeth on one side of the lower jaw.
Stages of bite formation
Dentists distinguish 2 stages of the formation of occlusion - the correct closure of the dentition:
- developing milk bite;
- formed milk bite.
Let's consider these stages in detail.
At the formation stage, the baby’s teeth are “laid” in an arch and then erupt. If there is no reason to worry about an incorrectly formed jaw, then at this stage it is very problematic to determine occlusion defects. Only after all the incisors have appeared can a conclusion be made about the presence/absence of pathology. Thus, by the age of two years of a child’s life, the dentist will be able to determine possible deviations in the development of the dental system. Therefore, it is necessary to immediately show the baby to a specialist.
At two years old, the baby’s incisors are located next to each other, the upper incisors slightly overlap the lower ones (when the teeth are closed), and no abrasions are detected on the enamel. This is with the correct development of the dental system.
At the mature stage, the child has erupted all his teeth. This process is completed by age six. At this time, the milk bite begins to change to a permanent one. If there are developmental defects, parents can independently see them without the help of an orthodontist. For example, with an open bite defect, the child cannot close his teeth tightly: the upper incisors do not overlap the lower ones.
Morphological and functional characteristics
The “father of medicine” Hippocrates called milk teeth because they erupt at a time when the baby is fed with mother’s milk and is not yet able to eat solid food. The crown part of the baby tooth is more convex and sharply demarcated from the root, has a pronounced neck and a bluish-white tint. The configuration of the dentition is almost the same as with a permanent dentition, only they are slightly wider and shorter.
Temporary bite goes through three stages of development:
- The first stage of formation begins at six months and lasts up to 2 – 2.5 years.
- At the second stage, from 2 – 2.5 to 4 years, a stable temporary bite is formed.
- The duration of the third stage is on average two years, and by the age of 6 all milk teeth have grown.
Formation of occlusion
Correct bite is called central occlusion in dentistry. It is formed by proportionally developed jaws and a uniform load on the masticatory muscles. A properly developed dentofacial region promotes thorough chewing of food and uniform distribution of the load on the entire jaw apparatus.
In order for the jaw to form correctly, you need to carefully monitor the timely eruption of teeth. You also need to monitor the health of baby teeth so that they are not affected by caries.
How to check for closure pathology? To do this, a method called occlusion key was developed. It was created by doctor Andrews. In fact, checking the bite is simple: the patient’s 6th tooth in the upper jaw must be in contact with the same one in the lower jaw.
Central (correct) occlusion can be static and dynamic. With dynamic teeth, the teeth close together only when chewing food or during a conversation. With static occlusion, the teeth are always closed correctly: while eating, while talking, at rest.
The formation of occlusion is influenced by:
- timing of the eruption of milk units;
- cutting order;
- pairing of units;
- quantity.
Timing of baby teeth eruption
Each baby's tooth erupts at a time strictly determined by nature. Parents should monitor this process and write everything down in a diary. At the age of six months, parents rejoice at the appearance of the first (lower) incisors. According to tradition, it is customary to give a silver spoon so that teeth grow beautiful and healthy. Dentists have compiled a table of the timing of teething in babies. But a deviation of 3-4 months in one direction or another is not a pathology.
If by the age of one year the baby has not erupted teeth, this is a developmental pathology - primary adentia. Some children lack the rudiments of teeth, and the jaw system is underdeveloped. To prevent the development of pathology, you need to immediately take your child to an orthodontist. Timely correction can prevent problematic development.
Order of appearance of baby teeth
It is important to monitor not only the eruption of milk units, but also the order in which they appear. The lower incisors appear first, followed by only the upper ones. Then come the lower lateral incisors, followed by the upper ones. Fangs appear only after the molars have formed. The order of appearance of temporary units is reflected in the formation of the occlusion height. The child’s lower part of the face begins to stretch out: this is due to the formation of the lower jaw.
The second molars are the last to form. They form a full chewing function.
There are cases of violation of the order of eruption of molars and incisors. The pediatric dentist should be notified about this. Perhaps the issue is not developmental pathology at all.
Eruption pairing
The appearance of milk units occurs synchronously or with a lag of a month. The antagonist teeth are located strictly opposite each other, appearing in their own time. Pathology may be indicated by the absence of antagonists at the appropriate time.
For example, if the lower incisors have erupted, and instead of the upper incisors, lateral units begin to appear, this is already evidence of pathology. Parents should urgently show the baby to an orthodontist, because the incisors may not erupt due to a defect in the alveolar ridge.
Number of teeth
By the age of three, a child has erupted 20 temporary units; more will not fit in the jaw. If instead of 20 units more have erupted, you need to take the child to an orthodontist. The usual number 32 appears only when the baby teeth are replaced by permanent ones. By this time, the jaw develops and expands: it is already capable of accommodating more molars.
What is the difference between a milk bite and a permanent bite?
The main difference is the number of teeth. The milk bite has only 20 of them, while the permanent bite has all 32.
Milk teeth differ from permanent teeth in the following ways:
- the shape of the crown is more convex;
- the enamel is snow-white because it is very thin;
- the root system is underdeveloped: the roots are short and narrow.
The formation of a correct bite is influenced by the development of the chewing muscles, so it is necessary to give the child solid vegetables/fruits. The more he chews hard foods (carrots, apples, pears), the better his chewing muscles develop. They, in turn, affect the development of the jaw and dentition.
Prevention measures
At each stage of the development of a child’s jaw system, important rules must be followed that will help prevent problems. Here's what experts recommend in this regard:
- during feeding, the nipple or nipple should be positioned at a right angle to the baby’s mouth,
- it is better to abandon nipples with an opening that is too wide, since the development of chewing muscles and the sucking reflex is important for the proper growth and formation of the baby’s jaws,
- it is necessary to ensure proper prevention of rickets, and in this regard it is imperative to consult a pediatrician,
- Make sure that your child does not develop the habit of thumb sucking during sleep or constantly holding the pacifier in his mouth,
- try to control the position of the baby's head during sleep. When the baby sleeps, his head should not be thrown back too much or pressed to the chest,
- timely wean yourself from falling asleep with a pacifier in your mouth.
Timely weaning from the pacifier is the key to a correct bite.
You should make an appointment with the dentist immediately after the appearance of the first tooth. Subsequently, it is advisable to show the child to a specialist once every six months, and if there are any problems, it is better every three months. On baby teeth, caries and other pathological processes develop many times faster, and their condition has a direct impact on the health of the oral cavity in the future. Therefore, at the first suspicious symptoms, you should immediately take your baby to the doctor.
- Farrell K. Correction of harmful myofunctional habits in children, 2003.
Causes of pathology
The most common occlusion defects are open or cross bite. Also common defects include a large distance between units, a sagittal gap. The reasons for the development of anomalies can be various factors. But more often, defects originate at the stage of intrauterine development of the baby. A genetic predisposition cannot be ruled out.
Pathologies in the development of the dental system can appear as a result of bad habits: prolonged pacifier sucking, thumb sucking in sleep.
Sometimes the shape of the pacifier and improper grip of the nipple by the lips of the newborn are directly related to the incorrect formation of occlusion. Timely diagnosis of the cause will allow you to find optimal methods for correcting the defect.
Possible reasons for the formation of a pathological bite:
- maxillofacial injuries;
- absence of a large number of molars;
- musculoskeletal disease;
- presence of bad habits;
- foreign objects in the baby's mouth;
- breathing through the mouth;
- infantile type of swallowing.
Malocclusion is also directly affected by untimely eruption of permanent molars.
Consequences
What are the consequences of incorrect occlusion, and why is it important to correct a child’s bite in a timely manner? Proper closure of the dentition promotes high-quality chewing of food and evenly distributes muscle load (so that the temporomandibular joint does not suffer).
Correct closure depends on:
- straight posture;
- correct articulation;
- blood circulation of the brain;
- symmetrical facial features;
- gastrointestinal health.
Also, the health of the mucous membranes and soft tissues of the oral cavity depends on proper closure. With uneven chewing load, those parts of the periodontium that are most loaded suffer.
Correction methods
Early identification of the problem and timely correction is the path to successful correction of occlusion. The correction technique is selected individually.
Correction methods:
- special gymnastics;
- removable plates;
- aligners, aligners;
- braces;
- trainers;
- surgical correction.
With the help of special gymnastics, minor occlusion defects can be leveled. The child also breaks the habit of bad habits that led to improper closure: thumb sucking, addiction to a pacifier.
Removable plates are installed for children under 14 years of age. These are special orthodontic devices made of polymer materials that are attached to the teeth using hooks. The purpose of the plate is to form the jaw. If a child has a naturally narrow jaw, the plate stimulates its growth. If the jaw is wide, the plate prevents it from expanding even more.
Aligners are custom orthodontic appliances made from an impression of the patient's jaw. Modern aligners can also be worn by adult patients; they are a successful alternative to braces. If mouth guards are prescribed to children, parents should constantly monitor them. Children do not realize the importance of the issue and may secretly remove the aligners.
Braces are prescribed only to children over 14 years of age, as well as adults. This is an effective way to correct occlusion, but is quite inconvenient. Caring for your mouth while wearing braces is difficult. The method also causes pain at the initial stage of addiction.
Trainers correct occlusion and also correct other defects of the dental system. First, the patient wears soft silicone trainers, then puts on a more rigid structure.
Surgical intervention is prescribed for severe anomalies when hardware methods do not produce results. This happens in rare cases.
Is it worth fixing or is it better to wait?
The health of the oral cavity in the future directly depends on how correctly the temporary bite is formed and the condition of the baby teeth. Therefore, if there are indications for orthodontic treatment, they cannot be ignored. Correction can begin from an early age - with removable corrective plates and other gentle techniques. Fixed braces can be installed from the age of 13-14, that is, after a complete change in bite.
It also happens that a child loses a baby tooth, for example, as a result of a fall on the playground. In another case, it may be removed due to severe destruction by caries. If this happened at the age of about 6 years, then the entire row will form asymmetrically, and the adjacent rows of the crown defect will begin to noticeably tilt towards the free space. As a result, the growth of the alveolar process will be inhibited, which will lead to a distortion of the proper functioning of the jaw system. To avoid all these troubles, temporary prosthetics are performed.
The photo shows prosthetics for baby teeth
It’s another matter if the tooth had to be removed at the age of 8-9 years - in this case, the risk of distortion of the occlusion will be much less. An interesting fact is that in a similar situation, closer to 12-14 years, that is, by the time the formation of permanent occlusion ends, the likelihood of its curvature increases sharply again1.
Bottom line
A correct bite is not only about a beautiful smile. Health, symmetry of facial features, and psychological comfort depend on it. The baby bite differs from the adult bite in the number of teeth (there are only 20), but the formation of the entire dental system depends on it. It is in childhood that it is easiest to correct occlusal defects, so parents should show their child to an orthodontist as early as possible.
Sources used:
- Guide to prosthetic dentistry, ed. A. I. Evdokimova, M
- Handbook of Dentistry, ed. A. I. Rybakova and G. M. Ivashchenko, M.
- Klineberg I., Jaeger R. Occlusion and clinical practice. - 2nd ed. - M.: MEDpress-inform, 2008.
- Academy Of Prosthodontics
Price
The cost of correcting a bite is not limited to the installation of orthodontic structures. The therapy consists of successive stages, for each of which the patient is forced to pay:
- consulting a doctor and choosing the appropriate treatment method;
- diagnostic measures to identify contraindications to the procedure and measure jaw parameters;
- installation of devices selected in advance by the orthodontist;
- adjustment of orthodontic systems and their replacement;
- removal of fixed structures.
The cost of installing each orthodontic system should be considered separately:
- plates – 6,000–7,000 rubles;
- trainers – 7,000–10,000 rubles;
- mouthguards – from 15,000 rubles per set;
- braces from 16,000.