Check your bite
There are a number of objective parameters by which the correct, or in other words physiological, bite is determined:
- When closing, the teeth of the upper jaw come into contact with the lower teeth of the same name. The ideal arrangement of teeth is one in which the upper incisors overlap the lower ones by 1/3.
- clear contact of the chewing teeth: molars and premolars,
- no interdental spaces,
- the vertical axis of symmetry of the face passes exactly between the central incisors,
- no problems with diction, chewing and swallowing.
All types of occlusion in dentistry are divided into abnormal and physiological, and within these groups there is a more detailed classification.
Appearance of a smile
The beauty of a smile is determined by the condition and appearance (shape, size, location) of the teeth. This is not the only factor. Teeth are part of the dentofacial system:
- upper jaw (refers to the facial part of the skull);
- lower jaw (connected to the upper, forms the lower part of the facial part of the skull);
- soft tissues;
- muscle tissue.
Each of these elements influences the formation of a smile. When correcting the bite, the orthodontist must take this influence into account so that the face remains harmonious.
Types of correct bite
Let's consider the physiological types of occlusion and their features:
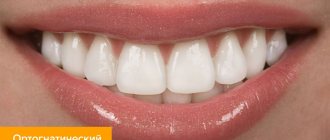
- orthognathic bite - an ideal in which the same 1/3 overlap is observed, which was mentioned above;
- straight - there is no overlap, as in the previous version: the upper and lower incisors are in contact with the cutting edges. This increases the risk of tooth wear, but from the point of view of orthodontics, this case refers to the types of correct bite;
- biprognathic - all incisors are slightly inclined towards the lips, the dentition is pushed forward, but there are no occlusion disorders;
- progenic – the lower jaw is slightly protruded. The closure is tight.
These types of dentition bites do not affect either aesthetics or functionality and are therefore considered the norm.
Types and features of bracket systems
In the past, there were only metal braces - they were not aesthetically pleasing and caused some inconvenience. Today, a huge number of other devices are used for constant wear, and braces have become much more comfortable and aesthetically pleasing.
There are three classifications of systems, which are based on the installation method, mounting location, and material.
Types of braces according to the method of arch attachment
For adult patients, two types of stationary systems are used: ligature and self-ligating (ligature-free). To better understand how they differ from each other, you need to have a good understanding of the design of braces.
Braces consist of an arch and clasps that are located on the teeth. In ligature systems, the clasps are attached to the arch using special rings - ligatures. In self-ligating rings, such rings are not used - the arcs are inserted into a special groove.
Ligature braces
Ligature bracket systems have a classic design and have proven their effectiveness in various pathologies. They will ensure the correction of the bite in the shortest possible time, if we are talking about a relatively strong displacement of the teeth.
Such systems also have a drawback: the patient will have to come to the orthodontist every month for correction.
Self-ligating systems
Ligature-free braces have two key advantages: they are much more aesthetically pleasing and save the patient’s time. You will have to visit the orthodontist every one and a half to two months, and not monthly, as is the case with ligatures.
There is another advantage: such braces provide gentle but constant pressure on the teeth.
Types of braces according to installation site
Classic braces have always been installed on the outside of the teeth. However, in recent years, systems have appeared that can also be worn from the inside. Let's take a closer look at each type.
Vestibular (external) bracket systems
This is a classic version of the system: such braces are located on the outside of the dentition and are visible from the outside. Despite some damage to aesthetics, they are chosen most often due to their high efficiency and relatively low cost.
Lingual systems
Lingual or internal braces are much more aesthetically pleasing. They are simply not visible from the outside: all elements of the system are located on the back side of the dentition.
Lingual systems are more expensive and require some getting used to: they affect diction. However, if you work with people all the time, have a slight malocclusion, and don't want others to see your braces, you can use this option.
Types of braces by material
Once upon a time, only metal braces were available, and many who wanted to correct their bite were embarrassed to go to the orthodontist and wear braces for several years. The situation has changed: now the range of braces has expanded, and they began to be made from different materials - from traditional metal to ceramics and even sapphires. The appearance of the systems has also changed - now they look much more aesthetically pleasing and even look like decoration.
Metal bracket systems
These are inexpensive, fairly effective and reliable systems that have gained maximum popularity. Most often, such braces are made of medical steel - it does not cause irritation or allergies, and does not react with saliva and acids that may be in the oral cavity.
In addition to steel systems, titanium systems are used - the most durable and eliminate any reaction in the oral cavity, as well as gold. Gold braces are aesthetically pleasing and effective.
Plastic braces
This is the first type of system to appear as an alternative to metal braces. Plastic systems are aesthetic, almost invisible on the teeth, and are inexpensive. They also have disadvantages: low strength and the possibility of coloring. The first can be eliminated only by completely changing braces, the second can be eliminated by choosing colored systems.
Ceramic braces
Ceramic onlays on the teeth are difficult to notice and provide a good hold. However, like plastic ones, they can collapse under mechanical stress. Coloring is also possible - after strong tea, coffee, cherry juice, red wine.
Sapphire braces
Such systems are made from aluminum oxide. They are almost invisible on the teeth, and in terms of strength they are comparable to ceramic braces. Unfortunately, they also have a drawback - high cost.
Combined bracket systems
Doctors often choose combined braces. They combine the aesthetic appearance of ceramic structures (on the visible upper jaw row) and the strength of metal ones. Also, such designs are relevant if you need to create different tension on the teeth.
Plus this is due to:
- reasonable price for the patient;
- effective and short-term treatment;
- ability to correct complex cases.
Incorrect or abnormal bite
The bite is considered incorrect when there are anomalies in the location of the teeth and occlusion disorders, as a result of which the functions of the dentofacial system are disrupted. All types of malocclusion, to a greater or lesser extent, lead to the destruction and loss of teeth, disorders of the TMJ (temporomandibular joint), as well as facial asymmetry. The consequences of an abnormal bite are discussed in more detail below. Orthodontic treatment in this case is necessary not so much for aesthetics, but for maintaining health.
Is it necessary to restore the correct order of teeth?
In some cases, curvatures and other disorders can be hidden by restoration and other techniques, but in case of pathological abrasion this is not a solution to the problem. Teeth straightening is necessary for:
- restoration of the correct functioning of the dental system, in which all its elements bear normal, uniform loads;
- protection against accelerated abrasion;
- prevention of early tooth loss, the appearance of further deformations;
- prevention of neurological problems (headaches, tics, etc.).
Types of malocclusion
The following types of malocclusion in adults are distinguished:
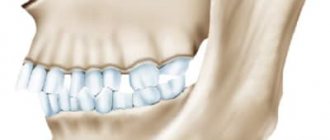
- distal bite
– the upper jaw protrudes forward. The upper incisors can be inclined forward, towards the lips, or backward, into the oral cavity. Often there is no contact between the front teeth of the upper and lower jaws, a sagittal gap and disocclusion (lack of closure) are formed. This type of dental malocclusion is visually manifested in a beveled profile and an upper lip hanging over the lower lip; a “double chin” may form;
- mesial bite
– the lower jaw protrudes forward. Here, a sagittal gap may also be observed and there may be no occlusion, or there may be only a slight overlap of the upper teeth with the lower ones. External signs of mesial occlusion are a protruding lower jaw and a massive chin; the lower lip is usually enlarged;
- deep bite
– the lower incisors are hidden by the upper ones by 50% or more. Depending on the stage, with a deep bite in adults, occlusion may be completely absent and inflammation of the tissues of the upper palate may develop due to injury to the lower teeth. With a deep bite, the so-called gummy smile is common, the lower third of the face looks inharmoniously small, and the chin is sloping;
- open bite
– when the jaws close, there is no contact between the upper and lower teeth. This type of bite causes significant impairment of chewing and speech functions; the facial muscles are usually overstrained and the lower part of the face is elongated;
- crossbite
– vertical asymmetry of the jaws; When closing, an intersection of the dentition is observed. It develops when one of the jaws is underdeveloped and leads to noticeable asymmetry of the face.
The above types of dental malocclusions can be supplemented with dystopia - a malocclusion in which one or more teeth are positioned incorrectly, out of place.
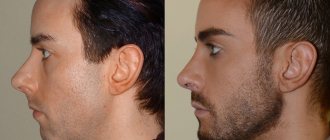
Orthognathic surgery
Orthognathic surgery belongs to the category of complex surgical interventions, which, on the one hand, pursues the goal of maximum restoration of function, and on the other, aesthetics.
During the operation, many structures of the facial skeleton are affected, which has a direct impact on the surrounding soft tissues. Taking into account the totality of planning stages, the need for special technical equipment and the peculiarities of the operation, it becomes obvious that the likelihood of an error and subsequent complications is simply enormous. But this does not mean that something will definitely happen in every patient. Not at all!
In this section, I want to convey to you, as a patient, information that orthognathic surgery is associated with risks that you simply must be informed about. Some of the things described below are rare, some do not occur at all, but concern you as a patient.
Damage to the mandibular nerve. When moving the lower jaw, damage to the mandibular nerve on one or both sides almost always occurs. In rare cases, its complete intersection is possible. This is due to the technical features of mandibular osteotomy and the anatomy of this area. The mandibular nerve is a powerful trunk, which, entering through the mandibular foramen into the mandibular canal, passes through the thickness of the branch and body of the lower jaw together with the artery and vein of the same name and emerges from the mental foramen to the surface of the face. It is completely sensitive and is not responsible for facial muscles, and its damage is accompanied by numbness of part of the lower lip, subcollective area and oral mucosa on the side of the injury. Almost always, during movement of the lower jaw, an injury to the above nerve occurs, which is accompanied by a loss of sensitivity in the postoperative period for up to 4-12 months.
Damage to the infraorbital nerve (when moving the upper jaw). This nerve is completely sensitive, and its damage is accompanied by numbness in part of the infraorbital region and upper lip on the side of the injury. With the correct surgical technique, damage to this nerve occurs extremely rarely and most often due to its atypical location. If it is damaged, restoration of sensitivity lasts up to 4-12 months.
Damage to the facial nerve. Should we be afraid? The facial nerve innervates the facial muscles and forms five branches, each of which is “responsible” for a specific area of the face. If the operation is performed correctly technically, it is not possible to damage any of the branches of the facial nerve. / According to a study by Dr. Choi BK, who in 2010 analyzed 3,105 patients after orthognathic surgery and found facial nerve damage in only 0.1% of cases.
Scar formation. The entire operation is performed through approaches from the oral cavity. The oral mucosa has good regeneration properties. As a rule, scars are barely noticeable and do not cause discomfort.
Damage to teeth. In some cases, when performing osteotomy of the jaws, damage to the roots of any teeth may occur. They can also be damaged when the displaced jaws are fixed with titanium screws. In this case, in the postoperative period it will be necessary to open the tooth pulp, sanitation and filling its canals.
Unexpected bone osteotomy. When performed technically correctly, it is extremely rare. In some cases, the occurrence of this complication is facilitated by the anatomy of the jaws. If this happens, all necessary measures are taken to fix the incorrectly osteotomized fragment in its required position.
Deformation and asymmetry. Titanium plates and screws are used to fix the displaced jaws. Very rarely, in the early postoperative period, their deformation may occur, which may require refixation. In some cases, patients note a feeling of their “presence” in the oral cavity. This is possible when the metal structure is close to the relatively thin mucous membrane of the oral cavity. In this case, it is recommended to remove them, but not earlier than a year after the operation.
Relapse of jaw position. With the use of modern surgical techniques and rigid fixation, the occurrence of relapse (partial change in the position of the jaws relative to the initial state) is a rare phenomenon. However, bone remodeling in the area of the osteotomy lines and in the area of the heads of the condylar processes of the mandible can lead to relapse of varying severity.
Facial asymmetry. Normally, a person's face is asymmetrical. Asymmetry can be expressed in different ways, it can be in the middle and/or lower area of the face, it can be formed by the facial skeleton or soft tissues, or a combination of both. In any case, orthognathic surgery aims to achieve maximum aesthetic results, but can never guarantee a high degree of symmetry. It is possible that after orthognathic surgery, additional interventions may be necessary on the bony structures of the facial skeleton or soft tissues of the face in order to achieve higher aesthetic values.
Temporomandibular joint. The effects of orthognathic surgery on the function of one or both TMJs are always specific and cannot be completely predicted. If you already have joint pathology (crunching, clicking or pain), then no one can guarantee relief from these symptoms after surgery, since the structures of the joint have already been irreversibly changed by the time of treatment. But at the same time, it is statistically significant that restoration of the normal anatomy of the dental system and physiological occlusion has a positive effect on the TMJ and, in most cases, significantly reduces or even prevents its possible subsequent degenerative changes. It is possible that at the stage of preparation for orthognathic surgery, you will need additional interventions on the TMJ (arthrocentesis, arthrolavage or arthroscopy). The likelihood of such interventions depends on the initial clinical situation.
Nasal breathing and intervention on the internal structures of the nose. The development of dental anomalies may be accompanied by impaired nasal breathing. Moreover, the peculiarities of the movement of the upper jaw can also negatively affect nasal breathing. In such cases, I always perform intervention on the nasal septum. It consists of a slight correction along the base to prevent displacement into one of the nasal passages in the postoperative period. In some cases, I perform a more extended plastic surgery of the nasal septum and plastic surgery of the inferior turbinates (when moving the jaw upward).
Aesthetic rhinoplasty. In itself, rhinoplasty is a separate and rather complex operation. But in some cases I perform simultaneous operations combining orthognathic surgery and rhinoplasty. The possibility of performing this surgical volume is determined in each specific case.
Significant blood loss during surgery. Today, during orthognathic surgery, blood loss does not exceed 100 ml - an excellent indicator. / For reference: the incidence of massive intraoperative bleeding during orthognathic surgery in 1972 was 38%, in 2005 - 1%, today - 0.3%.
The occurrence of infection (inflammation). For the purpose of prevention, you are prescribed antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy. However, after orthognathic surgery, infection and local inflammation may occur. In this case, you will have to adjust your postoperative care plan, for example: changing antibiotics, washing the wound, and so on.
After the operation, any general surgical complications may develop: wound suppuration, bleeding, thrombophlebitis, thromboembolism and others. These phenomena are rare, but I must warn you.
Consequences of malocclusion
All types of malocclusion cause a complex of problems, both dental and more general:
- the development of caries and gingivitis is caused by ineffective oral hygiene. Even with regular and thorough brushing of teeth, due to malocclusion, hard-to-reach areas remain where food debris accumulates and bacteria multiply;
- accelerated tooth decay, abrasion and chipping of enamel - caused by uneven load on the teeth;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract that occur due to insufficient chewing of food;
- diseases of the respiratory system due to improper development of the dental system;
- problems with the TMJ, causing pain in the head, ears, back, overstrain of the facial muscles, bruxism, poor posture, etc.;
- violations of facial aesthetics: asymmetry, nasolabial folds, sagging skin of the chin and neck - these and other defects caused by malocclusion can be effectively corrected only with the coordinated work of a cosmetologist and an orthodontist.
Make an appointment
What causes teeth to become out of order?
This is an evolutionary problem. The volume of mental activity increases from generation to generation, which is why the cerebral part of the skull increases in size. The dental system experiences less load, which causes the jaws to become smaller and there is not enough space for the normal (correct) formation of the dentition. Additionally, bone pathologies have an impact - they are among the most stable in inheritance, so the disorders become a genetically fixed problem.
Types of bite correction
Orthodontic and surgical types of bite correction depend on the nature of the pathology. In case of skeletal abnormalities, surgical intervention is necessary to correct the bite. In other cases, with dental anomalies, only orthodontic treatment is sufficient. In our clinic, we use aligners for this - invisible mouth guards that allow you to correct all types of dental bites in a person of any age. The technology allows you to achieve a guaranteed result within a predetermined period, and even before the start of treatment you will see what your smile will look like after the bite is corrected.
Correction methods
Dental restoration is carried out by orthodontists at DentoSpas Dentistry. The set of methods used in a particular case is selected individually:
when all teeth are in normal condition and intact, corrective orthodontic systems are used;- in the complete absence of one or more teeth, prosthetics are used. Correcting the bite without it is impractical: the teeth will gradually continue to move towards each other where there is free space in the row. Their position will not be stable, and correction will not produce results;
- if the teeth are too densely spaced and therefore tilted, it is possible to remove those that do not have functional, aesthetic value (usually the fourth from the center). The resulting gaps are completely closed by the end of the bite correction.
Do you have questions about correcting your bite?
We will call you back within 30 seconds
+7
Diagnostics
The correctness of the bite is determined by the orthodontist at the appointment. Such a specialist is available in any dental clinic - both for children and for adults.
He determines the correct position of the teeth and also selects a method for correcting it. Already during the initial examination, large gaps between bone formations, their crowding, extra teeth or knocking them out of the general row are noticeable.
For more accurate diagnosis, X-ray equipment is used. Such an image allows you to clearly determine the distance between the teeth, the location of the jaws relative to each other, the presence or absence of large gaps between bone formations. Also, an x-ray will show how best to correct the bite in the presence of pathologies.
How are orthognathic surgeries performed?
Any modern orthonic procedure is performed using internal access to the oral cavity. This means that there will be no external cuts, wounds, or scar tissue. The type of anesthesia is also selected in each specific case - it all depends on the type of operation. The average duration of the procedure is from 30 minutes to 5 hours, respectively.
Benefits of jaw surgery:
- “Turnkey” harmonization – the operation allows you to eliminate both functional and aesthetic problems;
- Monitoring the condition after surgery - the doctor monitors the recovery process until the patient is completely satisfied with the result;
- Modern surgical intervention is as gentle as possible, on an outpatient basis, without the need for a long break from work.
What to do in the postoperative period
In addition to following all the instructions of the attending physician, you need to pay attention to several important points.
- You need to apply ice to the jaw area and apply ointment or gel for swelling.
- Strictly observe daily routine and hygiene: get up, walk around, do not smoke, eat.
- Avoid heavy objects, do not bend over, avoid sudden movements.
- Do not hesitate to seek help if there is any discomfort.
The second most popular question concerns nutrition during the postoperative period. Contrary to expectations, the straw does not always help. According to reviews from people who have undergone this operation, it is better to use a small spoon. The only difficulty with eating usually is that it takes longer. In the hospital, during the postoperative period, patients are prescribed a gentle diet, in which dishes are served pureed.
Immediately after returning home, you can choose your usual menu, guided by your preferences. However, at first, the food should still be pureed. If necessary, you can consult a gastroenterologist.
What is the cost of orthognathic surgery?
An accurate calculation of the cost of surgical intervention can only be done individually after consultation with an orthodontist and a surgeon in the clinic of your choice. Plus, you will always additionally need to take a panoramic image or computed tomography of the maxillofacial region, condylography. In addition, correcting the bite may require the participation of related specialists.
When searching for a suitable dentist, pay attention to the clinic’s special offers: in some cases, you may be offered to pay for services in installments or in parts.
In what cases may treatment be required?
Typically, treatment by an orthodontist is not for those who have a physiologically correct orthognathic bite. However, the structural features of the dentofacial system in some cases may require a certain correction even with this type of bite:
- Sometimes, with an orthognathic bite, a problem may arise with teeth that are uneven in relation to the rest in the row .
Treatment in this case requires changes in appearance - this situation can greatly spoil the impression of a smile and cause psychological discomfort. - One of the possible problems is that the incisors are too large in relation to the rest of the row . In this case, the closure remains correct in all respects, but a discrepancy occurs in the position of the teeth.
The structure of the dentofacial apparatus is characterized by individual characteristics for each patient, so there may be other cases that require the intervention of an orthodontist.
Do I need to prepare for orthognathic surgery?
The preparatory period can last more than one week. As mentioned above, orthognathic surgery is completely predictable. Therefore, at the first stage, the specialist decides what results should be after treatment:
✔
determines the necessary future parameters;
✔
finds the maximum possible number of closures between opposing teeth;
✔
monitors how the results of the operation will affect the patient’s appearance.
In most cases, when preparing for surgery, surgeons use special 3D modeling tools for the result. Thanks to the software, a template is obtained and the paths that will lead to the expected effect of orthognathic treatment are found.
Then orthodontic treatment with braces or aligners begins. This can take from several months to a year and a half. Once the dentition is aligned, orthognathic surgery can begin.
Orthognathic intervention takes 4-6 hours. Then the patient remains in the clinic for another 3-4 days under the supervision of the attending physician. Afterwards you can return home, and after 3 weeks you can go back to work.