Treatment of periodontitis in pregnant women
Periodontitis in pregnant women is treated as follows. First, soft and hard dental deposits are eliminated. This procedure is the basis of all treatment, since these deposits are the cause of periodontitis. Without removing plaque and tartar, all other medical procedures will not give the necessary therapeutic effect. Ultrasound is contraindicated for pregnant women, so tartar is removed using manual instruments. After the procedure is completed, the dentist polishes the tooth surface using special brushes and polishing pastes.
In the first months of pregnancy, dental procedures in the form of anesthesia, treatment of caries and periodontal disease are undesirable. However, this does not apply to the procedure for removing tartar. But even this procedure is postponed to a later date if possible. At the end of pregnancy, it is not forbidden to eliminate tartar. However, during this period the woman quickly gets tired and becomes a little nervous. Therefore, whenever possible, such manipulations are postponed until the postpartum period.
Anti-inflammatory therapy is also indicated for periodontitis. This therapy includes antiseptic rinses and special applications, during which anti-inflammatory gels are applied to the gums. The treatment course is ten days. If the inflammation is not too severe, then therapy is carried out at home. But the effect of such procedures can only be expected if plaque is removed.
The following antiseptics are used for rinsing:
- A solution of five percent chlorhexine (ten days);
- Herbal infusions of chamomile, St. John's wort, eucalyptus and elixirs that do not contain alcohol. There should not be any antibiotic called “triclosan” in these liquids;
- Fluoride rinses. Fluoride is necessary for teeth and gums, as it helps reduce inflammation and produces static caries effects.
Applications are carried out using a gel called “metrogil”. It cannot be used at the beginning of pregnancy, but in the middle and at the end its use is allowed. The use of cholisal gel requires permission from the dentist.
All these gel-like preparations cover the edge of the gums, as well as the papillae located between the teeth. The gel is applied to the frontal and lingual tooth surfaces. After treatment with the gel, you should not eat for a couple of hours. The procedure is carried out in the morning and before resting at night for ten days.
Toothpastes that have anti-inflammatory properties are also useful. A striking example of such products is Parodontax paste, which contains medicinal herbs with a high degree of concentration. The paste also contains salts, which draw out purulent exudate from the gingival tissue and periodontal pockets.
If a pregnant woman has problems with her teeth and gums, then she must not only be treated, but also taught about proper oral hygiene, since all her problems have a “hygienic” reason. The special hormonal status of such patients can provoke an inflammatory process even with a small amount of dental plaque, so they need to be very careful and scrupulous in caring for their teeth and gum tissues.
During this period of life, experts advise purchasing an irrigator, which can be used to wash the interdental space, gum pockets and other hard-to-reach areas of the oral cavity.
It is very important to maintain a correct and adequate diet. You should not have snacks, drink sweet carbonated water, or abuse sweet foods. After a woman enjoys a cake or candy, she must have her teeth brushed. Otherwise, the carbohydrates that make up all the “goodies” will increase the number of harmful microbes in the mouth many times over. If you do not follow all these rules, then the treatment will lose its effect, so it is pointless to carry out it.
Periodontitis: bleeding gums and other symptoms
Among the common diseases of the oral cavity, dentists call periodontitis: what it is, you can look at the photo on the Internet, and at the same time find out what harm it causes to the teeth, how it is treated, etc. This diagnosis is made quite often. A doctor can diagnose the problem already at an initial consultation, but treatment and preventive measures are prescribed only after a thorough examination.
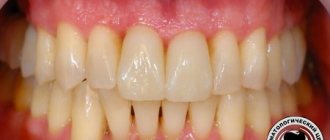
Periodontitis affects the soft tissue that surrounds the teeth. The tissues become inflamed and damaged, which causes discomfort to the person. You should consult a doctor at the first signs: the disease itself is not very pleasant, and its chronic form leads to serious consequences :
- bacterial tissue damage and the appearance of a periodontal pocket (at the junction of the tooth and gum);
- destruction of jaw bones, loosening and loss of teeth;
- chronic infection can harm the entire body: weakened immunity, joint diseases, rheumatism, etc.
At the first signs you should consult a doctor.
The initial appointment is one of the most important steps in treating periodontal disease. Whatever stage of development of gum disease you have, do not delay visiting the doctor. The sooner the work begins, the faster you will get rid of the unpleasant disease and prevent its consequences.
Is it possible to completely cure gum periodontitis and how? Here, much depends on the form and stage of the disease, as well as on the timeliness of contacting a specialist. In the early stages, achieving the desired result is quite possible.
Diagnosis of periodontitis
The “Good Dentist Clinic” offers comprehensive treatment of gums for periodontitis, which includes various methods of both the treatment program itself and its diagnosis.
Diagnostic procedures begin with an initial examination and also include measuring the depth of the gap between the teeth and gums to determine the form and stage of periodontitis. A periodontal sample may also be taken from the patient and other procedures may be performed.
When all the information has been collected, the doctor draws up a plan that decides how he will treat gum periodontitis (in children and adults): based on the causes, stage and symptoms, complex treatment is prescribed in several stages (drug and/or surgical methods) to prevent exacerbation and unpleasant consequences.
Contraindications for periodontitis
Contraindications are individual intolerance to the components of treatment, allergic reactions. Everything is determined in more detail at the initial stages of treatment.
Prevention of gum disease (periodontitis)
After completing the course of treatment and all operations performed, the doctor prescribes a set of preventive measures based on the stage and form of the disease. As a rule, the prevention of periodontitis includes taking a number of medications and carrying out special procedures for oral hygiene:
- regular rinsing with herbal infusions with an anti-inflammatory effect;
- regular applications of anti-inflammatory gel to the gums and use of anti-inflammatory mouth rinse;
- physiotherapy with the Darsenval apparatus;
- vacuum gum massage and hydromassage;
- brushing teeth with a properly selected paste, brush and floss - the selection should be made by the doctor, based on the condition of the patient’s teeth after treatment.
A well-chosen preventive program allows you to avoid relapse of the disease. All recommendations are given strictly individually.
Symptoms and signs of periodontitis
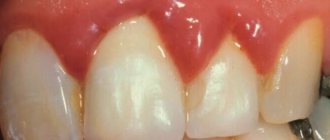
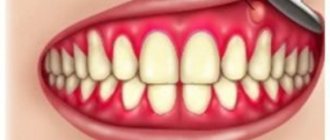
The disease has many different characteristic signs that make it possible to make an almost unmistakable diagnosis, but only a dentist will give complete confirmation. One of the first and most obvious signs is bleeding gums, which can be intermittent or constant, painful or not. You can notice this sign when brushing your teeth, eating solid food (biting an apple, for example). Sometimes the taste of blood in the mouth may appear spontaneously.
What other signs indicate dental periodontitis?
- Bad breath, which is difficult to suppress with any modern means.
- Loosening or displacement of teeth (indicates progression of the disease).
- In severe cases, the gums begin to swell and fester. This can lead to the formation of gumboil, or periodontal cyst.
- Soreness and discomfort in the gums.
- Tooth loss.
- Deterioration in health and general well-being (fever, fatigue, malaise, memory impairment, etc.).
If your gums are bleeding, it's time to make an appointment with your doctor. At the Good Dentist Clinic, specialists will conduct an examination, prescribe a diagnosis (if necessary) and draw up a treatment plan.
Periodontitis: causes of the disease
The appearance and development of the disease is caused by:
- improper or insufficient oral hygiene;
- the presence of subgingival tartar, which threatens the health of the gums and the entire oral cavity;
- poorly installed fillings or dentures, unprofessionally performed restoration, filling material getting into the interdental space, etc.;
- malocclusion, dental anomalies, incorrect position of teeth, etc.;
- some common diseases: gastrointestinal problems, hormonal disorders, cardiovascular diseases, etc.
What is the difference between periodontitis and periodontal disease?
Both periodontitis and periodontal disease are diseases that affect the periodontium (the tissue that supports the tooth). The difference between these diseases is significant :
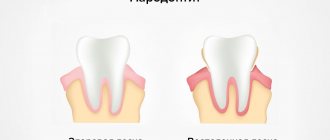
- Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of the gums (periodontal tissue), which is characterized by bleeding, etc. It occurs very often in many adults. Affects either individual areas of the jaw or all teeth;
- Periodontal disease is a systemic periodontal disease that manifests itself in the form of tissue atrophy (tooth cells). It is extremely rare. It affects all teeth of the upper and lower jaws, and there is practically no bleeding.
A more detailed answer in your specific situation can be obtained at a consultation with specialists from the “Good Dentist Clinic” in St. Petersburg and you can find out the exact prices for modern medicinal and therapeutic treatment of various forms of periodontitis (acute generalized, chronic, baby teeth in a child),
Classification of periodontitis
Gum inflammation is classified according to three parameters (minimum), each of which has its own characteristics and characteristics that help determine how severe the gum damage is.
By process diffusion
- Localized periodontitis
The inflammatory process occurs in individual areas (in the area of one or more teeth). Localized periodontitis occurs as a result of trauma, for example, with an oversized filling or an incorrectly installed prosthesis. Most often it begins suddenly and with rapidly manifesting clinical symptoms.
- Generalized periodontitis
It is also called diffuse, and it is characterized by damage to almost all teeth in a row or in the entire jaw. The emergence and development of generalized periodontitis occurs as a result of bacterial damage. It is mostly asymptomatic and painless, most often taking a chronic form.
By severity
- Mild periodontitis
At this degree, the tooth root is exposed a little, and a small periodontal pocket (up to 3.5 mm) is formed, which is detected upon examination. The teeth remain motionless.
- Moderate periodontitis
The periodontal pocket reaches 5 mm, the tooth root is half exposed. Also, a distinctive feature of this stage is slight mobility of the teeth.
- Severe degree
It is characterized by a large depth of pockets (more than 5 mm), with significant exposure of the root, and the teeth are very loose.
According to the process
- Acute form
The acute form is characterized by sudden sharp pain, bleeding gums, swelling, purulent discharge, etc.
- Chronic form
The inflammatory process in periodontal tissues occurs constantly, but is cyclical in nature, that is, there is a change in relapses and remissions of periodontitis. At the same time, the chronic form also has its own subcategories or forms with characteristic features:
- Chronic generalized periodontitis
It affects all or almost all periodontal tissues and is characterized by a change in conditions (relapses and remissions) and manifestations of clinical signs.
- Purulent form
A pathological form, when there are already significant sized gum pockets where purulent discharge accumulates. This form cannot be allowed to develop; it can lead to the development of an abscess.
- Abscess form
This is the very stage when a serious complication appears in the form of an abscess (purulent focus). For any form and individual characteristics of the patient, its own form of treatment is selected.
Surgical methods of treatment
After examination and diagnosis, the doctor comes up with a treatment plan, which may include surgery.
- Closed curettage
Closed curettage of periodontal pockets is a procedure that involves using special dental instruments to remove all deposits (plaque or tartar) that have accumulated under the gums. The peculiarity of closed curettage is that it is performed without cutting the gums.
- Open curettage
To perform an open operation, the doctor must determine the depth of the resulting pockets. If the pockets exceed 1-2 mm, then food debris accumulates in them and cannot be cleaned out yourself, which means that there is an ideal place for the development of microbes. Only open curettage will allow you to completely clean the periodontal gum pocket.
- Flap operations
This is a surgical procedure, the main purpose of which is to clean the pockets as with curettage, as well as to reduce them. Flap surgery for periodontitis is performed under local anesthesia and involves a vertical incision in the gum followed by the formation of a flap.
The doctor cleans all deposits under the gum and sometimes performs bone grafting. When the operation is completed, the doctor sutures the flap and applies a special bandage.
Dental implantation for periodontitis
Installing implants is one possible solution to the problem, but it must be carefully considered. First of all, the possibility of using the implantation method depends on the individual case.
What are the benefits of dental implantation for periodontitis? The operation allows you to stop further development and worsening of the situation. It is carried out only at the stage of remission of periodontitis, and only after consultation and examination of the patient by several specialists (periodontist, orthopedist, implantologist, etc.).
Dental prosthetics for periodontitis
Prosthetics must be carefully prepared depending on the individual characteristics of each specific situation. It makes it possible to preserve teeth if they are healthy and strengthen them if they are loose.
Periodontitis in children
The pediatric form of the disease is much less common than the adult form, and most often these are patients aged 9–10 years. Periodontitis in children is an inflammation of those areas of the gums where tissue restructuring and development is still underway.
Any, even minor damage to such periodontal tissue can lead to the development of the disease. Periodontitis in children occurs in different forms. For example, in chronic or acute, and also has its own classification - prepubertal and pubertal.
Periodontitis during pregnancy
Periodontal inflammation occurs quite often in pregnant women. Lack of treatment for periodontitis during pregnancy leads to serious complications not only for the teeth and gums, but also for the entire body of the expectant mother as a whole, which can affect the child. If this diagnosis has been made, then treatment is carried out taking into account all the individual characteristics of the patient and the course of pregnancy. If there are no problems, then expectant mothers need to be very careful about preventing the disease.