Treatment of tooth pulpitis: prices, stages and treatment methods
If your tooth reacts to changes in temperature, hurts at night, or “pulsates,” see a dentist. There may be inflammation of the pulp, the soft tissue inside the tooth. Remember that early on the nerve can be treated.
| Treatment of pulpitis of a single-canal tooth from | 7150 R |
| Treatment of pulpitis of a two-canal tooth from | 9300 R |
Make an appointment
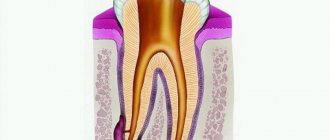
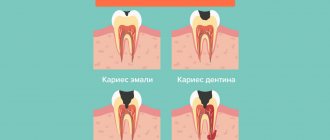
The inflammatory process in the neurovascular plexus of the tooth, which is called pulpitis, can occur for many reasons.
Most often it is provoked by advanced caries, injuries, as well as inconspicuous areas of carious lesions remaining after filling. The pathological process, occurring in acute or chronic form, can be quite dangerous, as it causes various complications. Therefore, when the first signs of the disease appear, you should consult a dentist.
Types of anesthesia for painless dental treatment
Depending on the complexity of the upcoming dental intervention, the doctor can offer the client three options for pain relief:
Application. The anesthetic drug is applied to a gauze pad and applied to the area of the upcoming dental intervention. This method is not able to eliminate severe pain, therefore it is relevant only when helping children, for example, when removing milk units before injecting the medicine.- Infiltration. It is a full-fledged injection, but the medicine is not injected very deeply. The medicine “turns off” peripheral nerve endings. This is enough to painlessly eliminate caries (including deep caries), pulpitis and other diseases.
- Conductor. This type of anesthesia affects both small nerve branches and large clusters, trunks and canals of nerves. Having given an injection, the doctor immediately makes half of the jaw insensitive. This allows you to painlessly perform complex surgical operations, removal, and treat inflammatory pathologies of the oral cavity.
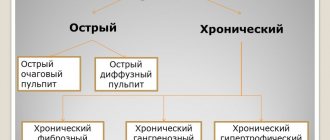
Acute pulpitis
The acute form of the disease causes severe paroxysmal pain, which becomes even more intense at night. Even without an external irritant, attacks of pain increase or decrease, but they usually occur when eating cold or hot food or drinks.
Due to the irradiation of the pain impulse along the nerves, sometimes the patient cannot say exactly which tooth hurts. If the pain becomes more and more intense, this may indicate the development of a purulent process. Its symptom is throbbing and almost constant pain, sometimes shooting and almost never subside.
A clear sign of pulpitis is a prolonged subsidence of pain after removal of the irritant. This takes about 15 minutes. This is its difference from caries, in which the pain disappears immediately if the irritant is removed.
Content:
- Where can you cure caries painlessly?
- Types of anesthesia in dentistry
- When not to use local anesthesia
- Anesthesia and sedation in dentistry
- Anesthetics used in dentistry 5.1. Medicines based on aticaine 5.2. Painkillers containing mepivacaine
Is it painful to treat teeth?
This question worries almost any person planning to undergo dental treatment. In fact, the problem of pain relief in dentistry has always been very acute. Almost all medical procedures performed by a specialist cause severe discomfort. Knowing this, people are afraid to treat caries, pulpitis and other oral diseases. But refusal to seek medical help in a timely manner invariably entails another problem - the progression of the existing pathology. After all, dental diseases do not go away on their own. Over time, they become more pronounced and are less responsive to therapy.
Therefore, it is important to prevent the patient from having a negative experience associated with the lack of adequate pain relief. For this purpose, more and more effective anesthetics are being developed every year. Using them in their work, dentists can offer their clients the most comfortable and completely painless dental treatment.
Chronic pulpitis
In the chronic course of pulpitis, there are no obvious symptoms. Sometimes a slight aching pain may occur, especially after cold or hot drinks or meals. Exacerbations, which are similar in their symptoms to acute pulpitis, are also possible.
When pus accumulates, flux appears. If a person is not provided with proper medical care, this can lead to phlegmon and related complications:
- damage to the jaw bones and facial nerve;
- abscess;
- apical periodontitis;
- sepsis;
- chronic hyperplastic pulpitis (occurs in childhood and adolescence).
Biological method
If the pathological process is still reversible, then the doctor can prescribe therapy that will preserve the pulp and avoid removal of the nerve. For this, it is recommended to carry out physical therapy with a helium-neon apparatus and take certain medications.
Conservative treatment is effective in cases where:
- the patient's age did not exceed 25 years;
- there is a chronic or acute form of focal pulpitis;
- crown spallation occurred with the involvement of root tissues in the inflammatory process;
- carious lesions are in the initial stage.
With biological therapy, a special paste is applied to the inflamed root. If damage to the pulp chamber cannot be avoided during the process of cleaning the bottom of the cavity, then an indirect effect is performed. If the remote control is partially or completely exposed, the paste is applied directly to the pathological tissue.
Timely initiation of therapy allows you to get rid of pulpitis in just one visit to the dentist. Therefore, the symptoms of this disease cannot be ignored, waiting until only surgical therapy is effective.
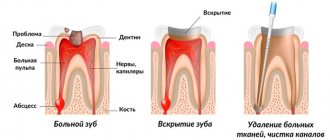
The therapy process is as follows:
- The doctor performs pain relief.
- Then the channels are cleared of harmful microflora. This requires preparation of the carious cavity and removal of the roof of the pulp chamber, which allows access to the instruments that process the canals.
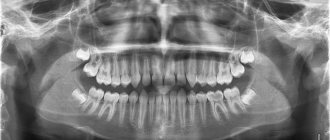
- An X-ray is performed.
- The cavity is disinfected using special disinfectants.
- The dentist puts a filling.
The biological method is recommended for the treatment of pulpitis in children under 12 years of age, since the apex of the tooth has not yet fully formed.
Additional methods of conservative treatment of pulpitis
Physiotherapeutic treatment is used as an addition to the biological treatment method. The following procedures are shown:
- Helium-neon laser - its radiation has an analgesic effect, helps reduce swelling, reduce inflammation.
- Electrophoresis - using this method of electrotherapy, anesthetics are injected into the site of inflammation.
- Ultrasound therapy – low-frequency ultrasound stimulates regenerative processes and accelerates the delivery of medicinal substances to tissues.
After treatment of pulpitis with a biological method, patients must undergo electroodontic diagnostics in order to monitor the condition of the pulp. If the electrical excitability of the pulp is not restored after treatment and pulp death is diagnosed, a depulpation procedure (pulp removal) is performed.
Vital amputation
This procedure involves preserving the pulp in the dental canals, but at the same time it is removed from the crown area. Vital amputation is done in cases where a multi-rooted tooth is affected. It is not used on single-rooted plants due to the lack of a boundary between the root and the coronal pulp zone.
Treatment proceeds as follows:
- Anesthesia (local) is performed.
- The doctor drills out carious lesions.
- The pulp is removed.
- Tissues are treated with drugs.
- The dentist makes an insulating pad.
- A temporary filling is placed.
Subsequently, the specialist may recommend physical therapy and medication.
Causes of the disease
Causes of the disease
Pulpitis occurs due to the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the soft tissues of the tooth. This can happen for several reasons:
- Advanced caries, when bacteria have bypassed the enamel and dentin and begun to destroy the pulp.
- Chips and injuries provide access to the inside of the tooth.
- Errors during treatment - the doctor did not remove all the foci of caries and installed the filling poorly.
- Infection due to infectious diseases - bacteria penetrate the tooth through blood vessels, but in practice this case is quite rare.
Signs of the disease are increased sensitivity to cold, hot, sweet foods, swelling, and fever.
Important! Only a doctor can diagnose pulpitis, since the listed symptoms can also be signs of periodontitis and periostitis.
If symptoms appear, you should contact the clinic as soon as possible. Do not worry about whether it is painful to treat pulpitis . Early detection of the problem will allow the procedure to be carried out with minimal discomfort, preserve maximum healthy tissue, and save time and money.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment involves removing the pulp in several stages. Depulpation is performed in the root and coronal zones in advanced cases. Sometimes it is impossible to cure a tooth without this procedure.
If the tooth is single-rooted, then it will have to be removed in two or even three visits to the dentist. And if this is a multi-channel case, then even more activities are needed. Therefore, the number of visits to the doctor is determined by the complexity of the lesion and the dynamics of treatment.
If a canal has been filled, the filling cannot be placed in one visit, since the material inside the canals must first harden.
Consequences of pulp removal
Unfortunately, the pulp is unable to regenerate, and depulpation of the tooth means that it will forever remain “dead” - it will always lack blood supply and innervation. Therefore, the consequences of removing the tooth pulp only initially seem attractive: the pain in the tooth stops, and it will never return.
But at the same time, the tooth’s ability to restore the deficiency of mineral substances that previously entered it from the pulp will never return. And over time, such a tooth becomes more fragile and weak, and susceptible to destruction.
If all requirements for oral hygiene, balanced nutrition and careful treatment of teeth are met, a pulpless tooth can last for several decades. But in practice, its lifespan is most often limited to 5-8 years, since it is more vulnerable to stress and can be irreversibly damaged even when chewed.
In addition, a pulpless tooth may darken over time and begin to stand out among healthy teeth. This complication especially often develops when filling with cheap materials, which themselves are susceptible to pigmentation.
Category: Tooth extraction Published by Mister stomatolog
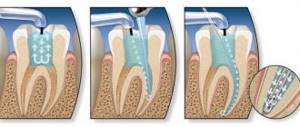
How is the treatment carried out?
First visit:
- The doctor performs anesthesia. Thanks to painkillers, all manipulations performed by the dentist will be comfortable for the patient. Mandibular anesthesia is sometimes required for mandibular molars.
- Carious and partially healthy dental tissues are drilled out. The latter are used to open the mouth of the root canal and provide access to them for working with instruments.
- A rubber dam is placed to protect the canals from saliva, which may contain pathological microflora.
- A pulp extractor (a very thin barbed needle) is used to remove the nerve.
- A special devitalizing paste without arsenic is applied to the treatment site (it is not used in modern products due to toxicity).
- The doctor determines the length of the root canal using radiography with an apex locator. In cases where there are several canals, a K-file is inserted into them one by one, which, when penetrating deeper, indicates that the instrument has reached the apex of the tooth root. This is done with each channel separately, since their depth is not the same.
- The canals are widened for subsequent filling. At the same time, washing with antiseptic agents is carried out constantly.
- Placement of turundas into the canals and installation of a temporary filling.
Second visit:
- The doctor removes the temporary filling.
- The canal is washed with antiseptics and then dried.
- The canal is sealed. To do this, the dentist uses a gutta-percha point and paste. The pin is used to compact the filling compound.
- Finally, you need to take an x-ray to make sure that all actions were performed correctly and that the filling is tight to the top of the canal.
- A temporary filling is placed again. After this, painful sensations may persist for some time. To eliminate them, it is allowed to take ibuprofen, ketanov, nimesil and other drugs that the dentist should recommend.
Third visit:
- A permanent light-polymer filling is placed.
Types of treatment for dental pulp infection
Treatment of pulpitis
there are two types. At the very beginning of the development of pulpitis, you can do without removing the nerve. In this case, the inflammation in the pulp is reversible and has not turned into a purulent form. After removing the softened dentin and medicinal treatment, special pads are applied to the pulp. They have a bactericidal, anti-inflammatory effect, protect the nerve from the harmful effects of infection and promote the development of replacement dentin, which will cover the nerve from the hole in the tooth. Such treatment does not always give the desired result and sometimes after it a procedure for completely removing the nerve from the tooth is still required.
The second method of treating pulpitis is to remove the pulp. It can be complete or partial. Partial removal of the inflamed pulp is a coronal pulp amputation. With this method, the root pulp is not removed, but is covered with special pastes that mummify and disinfect the pulp. This method is used for acute forms of pulpitis. And also in children in baby teeth, when resorption of the roots is expected, or in permanent teeth, which have not yet formed roots after eruption.
Complete removal is carried out on a living (vital) pulp or after devitalization of the pulp. Devitalization (killing) of the pulp is carried out by applying pastes with arsenic or parafolmadehyde to the pulp for a period of one day to two weeks. In such cases, treatment is carried out over several visits.
The pulp is removed from the tooth using special hand instruments (files) or using an endodontic handpiece. Then the tooth root is washed generously with antiseptics and filled. After filling, there may be minor pain when pressing on the tooth, which quickly passes.
Doctors from the dental department of Dr. Jacques always advise to carry out preventive dental treatment at least 2 times a year in order to avoid such complications of dental disease as inflammation of the dental pulp.
| Prices for pulpitis treatment: |
| Treatment of canals of a single-rooted tooth | — | 6500 rub. |
| Treatment of canals of a double-rooted tooth | — | 7000 rub. |
| Treatment of canals of a three-rooted tooth | — | 8400 rub. |
Progressive therapies
In modern dentistry, innovative treatment methods are increasingly being practiced:
- Laser. Thanks to it, the root remains viable and inflammation is effectively eliminated. The procedure is suitable for children and does not require multiple visits. The patient's condition improves the very next day.
- Using depophoresis. This procedure is aimed at relieving inflammation in the root canal and is suitable for the treatment of retrograde pulpitis. It involves the use of copper and calcium hydroxide, which is exposed to a weak electric field.
Anesthesia and sedation in dentistry
If a patient asks for general anesthesia due to panic, then he can be offered sedation. This is an alternative to "deep sleep". Thanks to it, during therapy the person is half asleep and does not feel pain.
Anesthesia is used very rarely in dentistry, only if a serious and complex maxillofacial operation is to be performed. Its use is also relevant if the patient has a low pain sensitivity threshold and is allergic to all local painkillers.
Possible consequences
If pulpitis is advanced and nerve removal is already required, then after 3-4 months the pathological process will make itself felt by darkening of the teeth. In addition, they will become brittle and dull. If the enamel has acquired a bluish tint, the dentist may have made a mistake when filling. This happens if there were traces of blood in the canal at that moment.
It is worth remembering that it is impossible in principle to cure pulpitis using traditional methods. Moreover, there is no single medicine that a doctor can prescribe to a patient for this diagnosis. Each case is individual, so treatment methods are selected taking into account the characteristics of the clinical picture: the degree of tooth damage, the presence of caries, purulent contents, diseases of the oral cavity, etc. Therefore, if signs of this disease occur, be sure to consult a doctor.
Symptoms of tooth pulpitis
How can you determine that your tooth hurts precisely because of the development of pulpitis? This disease has its own characteristic symptoms and the first sign of the development of pulpitis may be pain that occurs when a diseased tooth comes into contact with cold/hot, sweet/sour foods. Unlike pain during caries, these sensations do not go away immediately after the irritant that caused them is eliminated: they persist for longer than 15 minutes. If you are bothered by such sensations during and after eating, you need to urgently contact your dentist for diagnosis and treatment of pulpitis.
It is important to understand that without proper treatment, pulpitis will not go away: the inflammatory process will continue to develop and this will lead to the transition of pulpitis to an acute form. In acute pulpitis, pain can occur suddenly and on its own, without external influence. Pus collects in the pulp, and if there is no natural outlet for its outflow, it begins to put pressure on the bundle of nerves, and severe pain occurs.
At first, this pain can be eliminated by taking tablets from the pharmacy, but if treatment for pulpitis is not carried out, pharmacy painkillers will no longer help. The pain will be excruciating and constant, moreover, it can spread along the nerve endings to different parts of the oral cavity. For this reason, people who go to the doctor for treatment of acute pulpitis often cannot pinpoint exactly which tooth is hurting. In acute pulpitis, swelling of the gums and increased body temperature may be observed.
Pulpitis is not only acute - it has its own fairly extensive classification into various forms, and each form of pulpitis has its own symptoms. Accurate determination of the form of pulpitis is of fundamental importance for choosing an effective method of treating it. Below we will look at all seven main forms of pulpitis and their main symptoms.
Fibrous pulpitis of the tooth
The development of a fibrous form of pulpitis may be indicated by mild, aching pain, which occurs most often when a tooth comes into contact with hot/cold food during chewing. The pain is usually localized quite clearly - in one tooth. If fibrous pulpitis is not treated in time, then as the disease develops, pain may appear on its own and not stop for 24-48 hours.
Hypertrophic form of pulpitis
With this form of pulpitis, patients who go to the doctor for treatment complain of a viscous, aching pain, which often occurs when eating. This pain causes people to avoid chewing on the side of the jaw where the painful tooth is located. Another sign of hypertrophic pulpitis may be bleeding gums that appear when brushing teeth in the area of inflammation.
Gangrenous pulpitis and its symptoms
This form of pulpitis is also characterized by aching pain that occurs under the influence of chewing load on the teeth or from contact of the diseased tooth with temperature irritants. A person with the development of gangrenous pulpitis may experience the appearance of extremely unpleasant odor from the mouth, which cannot be removed by the standard procedure of brushing teeth and rinsing with balms. When, when treating gangrenous pulpitis, the dentist opens the tooth cavity, thick gray pus with a fetid odor is found in the area of inflammation.
Chronic pulpitis and signs indicating its development
This form of pulpitis is insidious in that it may not show itself for a long time.
Chronic pulpitis can be detected only after diagnostic measures are carried out or when it transforms into an acute form, which has bright and pronounced symptoms. Acute pulpitis, which has not been treated, can become chronic. But you shouldn’t think that you can continue to calmly live with a bad tooth and not take any measures to treat it. Chronic pulpitis sooner or later turns into acute and then a person is simply forced to see a doctor, because the pain becomes unbearable and pills from the pharmacy cannot save it.
To choose an effective treatment method, you need to conduct a high-quality diagnosis that allows you to determine the form of pulpitis and the stage of development of inflammation.