Orthognathic surgeries (surgeries to correct bite and facial aesthetics)
— a complex of complex surgical procedures, including various types of jaw movements, soft tissue plastic surgery, and elements of aesthetic surgery.
What pathologies can be corrected by such operations, how they are performed and what results they give - we decided to ask a specialist in detail. Our interlocutor is a plastic and maxillofacial surgeon, assistant at the Department of Maxillofacial and Plastic Surgery at Moscow State Medical and Dental University. A.I. Evdokimova, Ph.D. Alexander Vitalievich Glushko
.
— Alexander Vitalievich, what is a dental anomaly and how common is the pathology of malocclusion?
Figuratively speaking, a dental anomaly is a deviation in the development of the jaws, which negatively affects the relationship of the teeth with each other and leads to a violation of the bite and aesthetic parameters of the face.
According to international statistics, about 45% of the population have a malocclusion, characterized by the absence or such a slight violation of the relationship of the jaws that it can only be corrected orthodontically. But nevertheless, from 5% to 15%
people have a dental anomaly, which is characterized by a significant disproportion in the growth of the jaws and to correct it it is necessary to resort to combined (orthodontic and surgical) treatment.
Oral and maxillofacial surgeons deal with the group of patients in whom the anomaly of the dental system has a skeletal form and orthodontists are not able to correct it themselves using orthodontic treatment. At the same time, I would like to note that the interaction between the maxillofacial surgeon and the orthodontist in the treatment of such patients should be maximum.
— Is malocclusion a congenital problem?
In most cases this is true, but not always. In reality this question is more complex and I would answer it as follows.
According to modern concepts, the causes of dental anomalies can be known congenital syndromes, heredity, environmental influences, trauma, as well as tumor processes. All of the above can, to one degree or another, affect the growth of the jaws and thus lead to the occurrence of dental anomalies.
In the case of congenital defects, everything is obvious. Already at the stage of fetal formation, in utero, under the influence of certain terratogenic factors, genetic “errors” occur, which leads to incorrect formation of organs. As a result, children are born with cleft or other syndromes. With tumors, the underlying tissues are involved in the process, which can lead to jaw deformation. In case of injury, the growth zones of the jaws (usually the lower jaw) are disrupted and development slows down. Even significant scars in the maxillofacial area, for example after an extensive burn, can lead to impaired jaw development.
genetic orientation?
But something else is interesting. The fact is that the vast majority of patients with anomalies of the dentoalveolar system have not received any treatment
significant injuries, do not have tumor processes and live in a normal environment.
At the same time, they note the appearance of jaw disproportion in childhood or adolescence. On the one hand, the child is born completely normal, without any signs of anomaly. On the other hand, over time, the jaw abnormality manifests itself. Therefore, most experts are inclined to believe that genetic predisposition
.
This is confirmed by the fact that in some cases, parents who bring their children for consultation themselves have similar problems with bite.
— On which jaw (upper or lower) does the anomaly most often appear?
As a rule, both jaws are always involved in the development of malocclusion. For example, if one is underdeveloped, the other is overdeveloped. A striking example is distal occlusion, when underdevelopment of the lower jaw and chin is combined with the presence of a gummy smile on the upper jaw.
But this doesn't always happen. In some cases, there is little or no evidence of abnormal development of any jaw. In this case, the patient undergoes movement of only one jaw.
— What consequences are accompanied by an anomaly of the dental system?
Of course, the anomaly of the dental system in each individual patient has its own characteristics. But if we look at it as a whole, we can separate two main components: aesthetic and functional.
We can classify the following as aesthetic:
non-closure of lips at rest, constantly tense perioral area and chin, gummy smile, imbalance in facial proportions, sloping or, conversely, pronounced chin, elongated lower third of the face, presence of facial asymmetry (especially in the lower jaw area), insufficient development of the midface and area cheekbones, also an anomaly in the development of the jaws can be combined with a humped nose (often with underdevelopment of the lower jaw, the so-called “bird face” symptom).
Functional disorders include
pronounced abrasion of teeth up to their loss, disruption of the normal physiology of the soft tissues of the oral cavity and the development of gingivitis, periodontitis and recessions (including as a consequence of long-term orthodontic treatment and attempts to compensate for the bite); due to malocclusion, pathology of the temporomandibular joints (crunch, clicking or pain in one or both joints up to the restriction of mouth opening), in some cases there is a breathing disorder.
- Breathing? Does it have anything to do with bite?
Yes, sure. In some rather severe cases, an anomaly in the development of the dental system is accompanied by impaired external respiration function, which significantly worsens the quality of life of such patients.
This is due to a pronounced narrowing of the lumen of the upper respiratory tract due to significant underdevelopment of the lower jaw (by the way, this issue is reflected in more detail in my dissertation work). This is especially evident in the 3rd-4th decade of a person’s life, when muscle tone begins to weaken and during sleep the person’s airway narrows at the level of the nasopharynx and oropharynx to a critical level with the occurrence of episodes of nocturnal sleep apnea. Treatment of such patients has its own characteristics and includes functional rhinosurgery (to improve the air-conducting function of the nose), distraction osteogenesis (increasing the length of one or both halves of the lower jaw, sometimes the upper), moving the jaws taking into account the function of external respiration, occlusion and facial aesthetics.
Advantages
The main advantages of the operation as a method of correcting malocclusions:
- Improving the quality of life, confidence in one’s own attractiveness .
After this method of correction, the patient’s self-esteem increases, psychological complexes associated with personal failure and low self-esteem from a not very presentable appearance, in particular the oral cavity, are eliminated. - The time period of therapy is several times shorter than treatment with the same results, which involves partial amputation of organs.
- Formation of the correct lip position, restoration of the correct profile shape.
- With rare exceptions, this procedure involves complete preservation of healthy organs.
- Ease of maintaining the effectiveness of the treatment.
When surgically moving a jaw fragment to a given position, the organs do not try to repeat the trajectory of the jaw. On the contrary, they maintain their original position. In addition, the teeth are trying their best to come back. This effect is achieved only by wearing mouth guards for a long time. - Minimum retention period.
What is tooth enamel hypoplasia and what method can be used to eliminate the pathology?
Let's talk here about methods for correcting an open bite.
At this address https://orto-info.ru/sistemyi-vyiravnivaniya-zubov/breketyi/po-tipu-materiala/keramicheskie/clarity.html you will find a detailed description of the design of Clarity braces.
Indications
The main indications for the operation are:
- pronounced jaw disproportions of an anatomical nature in combination with pathologies of the structure of the dentition;
- a significant violation of the relationship of the jaw fragments relative to each other, excessive development, or, on the contrary, physical underdevelopment of one of them, the inability to fully close the organs or lips (popularly this phenomenon is called the “bird face”). It is distinguished by a large lower jaw;
- a consequence of incorrectly performed surgical treatment of congenital facial abnormalities.
Still have questions? Contact us:
— Does a gummy smile indicate an incorrect bite or not necessarily?
A gummy smile in itself is not a sign of the development of a dental anomaly, and its minor presence may be a variant of the norm and not require any correction. But at the same time, if a pronounced gummy smile is observed, this may indicate excessive vertical development of the upper jaw and as part of dental pathology. In this case, it is worth considering the option of proper treatment (orthodontic and surgical) taking into account all functional and aesthetic aspects with the correction of a gummy smile.
— What if there are no problems with the bite, but the person has a gummy smile?
Most likely this is a variant of the norm. Moreover, such a situation may not fit into the aesthetic canons accepted by society, although anthropometrically everything in a given patient may be conditionally correct.
You ask me: is it worth and is it possible to correct such a gummy smile?
My answer is this. Technically, it is possible to correct a gummy smile. But for this, if the patient has a correct and stable bite, it will be necessary to perform surgery on two jaws: on the upper jaw in order to get rid of a gummy smile, in which case it will move upward and the relationship with the lower one will change, and then on the lower one in order to put it into its original, correct relationship with the top. If the patient’s bite is incorrect, then I would advise approaching the issue properly and receiving complete orthodontic and surgical treatment.
But it’s difficult for me to answer the question of whether it’s worth doing this. Here, each patient himself must make a decision after weighing all the benefits and risks, about which he should receive comprehensive information in consultation with the appropriate specialist.
Here you also need to take into account the fact that the cause of a gummy smile can be a short frenulum of the upper lip, a short upper lip, and increased muscle tone.
In this case, it can be compensated for by surgical intervention on the soft tissues of the lip or with the help of butulin therapy.
— What is the optimal age for orthognathic surgery?
Everything determines the severity of the pathology and its impact on the patient’s quality of life.
It is generally accepted that the most favorable time for orthognathic surgery is the period after completion of skeletal growth (girls after 16 years, boys after 18) and before old age, when the body’s reparative processes decrease. According to statistics, the vast majority of patients are in the age group of 20 to 30 years. It is during this period that a person’s self-awareness is fully formed, they are usually fully aware of their problem (anomaly) and are ready to adequately approach treatment.
But at the same time, we should not forget about complex clinical cases when we are talking about children, about a significant violation of their quality of life and, simply, that there is no way to wait for the end of the body’s growth. Here colleagues from “childhood” come to the rescue and the rules of the game change a little. Pediatric maxillofacial surgeons operate on adolescents, young children, and infants. For which I express my great admiration to them! This is a separate surgical world, with its own rules, laws and complexities.
— Why do they put braces on as a preliminary treatment before surgery?
Dental anomaly is not only a violation of the size and relationship of the jaws, but also an incorrect arrangement of teeth on each of them.
To achieve a good and stable result of the operation, it is necessary to create maximum contacts between the teeth of the upper and lower jaws by correctly positioning them relative to each other, in the dentition. This is precisely the task that an orthodontist sets for himself at the preparatory stage of orthodontic treatment.
— Tell us what is the relationship between an orthodontist and a maxillofacial surgeon?
Bite pathology can be divided into dentoalveolar
and
skeletal
. And if in the first case only orthodontic treatment is sufficient, then in the second, orthognathic surgery is almost always inevitable.
Often, patients turn to an orthodontist for malocclusion without suspecting that he or she has an anomaly in the dental system, which requires an integrated approach to treatment. This is where the interaction between the orthodontist and the surgeon begins. Having assessed the clinical situation, the possibilities of orthodontics and the structural features of the dentoalveolar system, the orthodontist makes a very important decision - whether in this case it is possible to manage only orthodontic treatment or whether it is necessary to resort to combined orthodontic and surgical treatment. After this, the patient is explained the advantages of combined treatment, the features of orthodontic preparation, and he is sent to the surgeon. In turn, I, as a surgeon, also evaluate the clinical picture, the structural features of the dental system and the possibilities of surgery. I clearly explain to the patient all the pros and cons and risks of this type of treatment.
After this, I agree on a treatment plan with the orthodontist and treatment begins.
In general, the role of the orthodontist in the treatment of dental anomalies is simply enormous. Ultimately, the result will depend not only on the surgical stage, but also on the orthodontic stage.
A little about the sad. Unfortunately, there are still orthodontists who have no idea about orthognathic surgery or for some reason deny it. Because of this, patients wear braces for years, which do not give the desired result, and in the meantime, periodontal physiology is disrupted and recessions occur, patients become psycholabile and often at first have a negative attitude towards the combined treatment offered to them, which again includes orthodontic treatment.
— What is the preparation for orthognathic surgery?
After the patient has undergone orthodontic preparation for orthognathic surgery, he goes to the surgeon, who plans the surgical stage.
Planning of orthognastic surgery includes a whole range of manipulations: anthropometric analysis of the patient’s face taking into account proportions and aesthetic parameters, planning of skeletal movements in a special program, analysis of computed tomography data (measurement of proportion and symmetry, localization of nerves, planning of jaw osteotomy lines), dental engineering part ( production of plaster models and their transfer to the articulator to simulate the true relationship of the jaws, “model surgery” taking into account the planned movements and the production of special positioners that will be used during jaw surgery).
Thus, I would like to emphasize that planning an orthognathic operation is a very important stage, in which the course and outcome of the operation depends on the surgeon.
Contraindications
The operation is not indicated for everyone. This method of treating bite pathologies should be abandoned in the following cases:
- age limit is less than 18 years;
- dentally unprepared organ fragments;
- general contraindications – dysfunction of the circulatory system, heart and vascular failure;
- diabetes;
- the presence of infections and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity until their complete elimination;
- oncological diagnoses.
Varieties
Orthognathic surgery itself is aimed at solving a specific problem, and there are several treatment options.
Which one will be a priority is decided by the doctor based on the clinical picture of the disease.
Maxillary osteotomy
During the manipulation, the surgeon makes incisions in the bony intraoral tissues located in the area of the eye sockets and the upper part of the dentition.
This step allows the doctor to freely move the upper jaw with tooth fragments and the palatal area. The jaw is set in a given position and secured using a special mouthguard.
Mandibular osteotomy
A significant difference from the procedure described above is that the doctor makes an incision in the bone tissue in a place located behind the root organs. Thus, its integral movement becomes possible.
The fragment is given the desired position, secured with durable titanium alloy plates and left in this state until new hard tissue grows.
Signs of mesial occlusion and treatment offered by modern clinics.
In this publication we will discuss the principle of operation of the Derichsweiler apparatus.
Follow the link https://orto-info.ru/sistemyi-vyiravnivaniya-zubov/breketyi/po-raspolozheniyu/lingvalnyie/inkognito.html if you are interested in the design of Incognito lingual braces.
Genioplasty
It is considered a cosmetic procedure that corrects plastic surgery. Its task is to qualitatively reduce or increase the size of the chin, as well as slightly correct its shape.
The duration of the procedure is determined by the degree of development of the anomaly. When changing an organ, the surgeon uses special prosthetic structures, which he inserts into an internal hole prepared in advance.
To prevent a scar from appearing after this, manual distribution of soft subcutaneous tissue fragments is carried out.
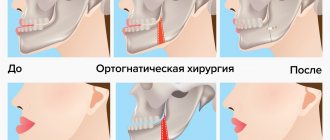
Orthognathic surgery. Osteotomy of the upper and lower jaw. Genioplasty.
In the 21st century, modern orthodontics has enormous potential for solving the problems of malocclusion, which are associated with the incorrect location of the skeletal structure of the upper and lower jaws. Malocclusion can be either congenital or acquired as a result of injuries.
By the age of 16-20, such a jaw anomaly becomes more pronounced, which creates a certain discomfort, both psychological and aesthetic. People become unsure of themselves, and their self-esteem begins to decline. But this is not only a matter of aesthetics; such a pathology contributes to the development of a number of joint diseases, tooth loss, respiratory dysfunction, etc. All problems associated with eliminating such facial disharmony, returning normal occlusion (bite) and facial aesthetics can be solved by orthognathic surgery .
At the Federal State Budgetary Institution Scientific and Clinical Center of Otorhinolaryngology, Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia, orthognathic operations are performed by employees of the scientific and clinical department of maxillofacial surgery. Our Center employs some of the best specialists in Russia in the field of orthognathic surgery - Ph.D. Senyuk A.N., Lyashev I.N., Mokhirev M.A. Nazaryan D.N. , who apply not only the most modern world techniques, but also use their own developments.
“We often have to correct the mistakes of doctors who, with insufficient experience working with such patients, or in the pursuit of profit, corrected malocclusion, which ultimately led to severe complications and patient dissatisfaction with the final result of treatment,” says the head of the department of maxillofacial medicine. Facial and Reconstructive Surgery, Ph.D. Nazaryan D.N.
In their practice, our specialists carry out complex treatment, which includes orthopedic and orthodontic interventions, to achieve functional and aesthetic goals. Only an experienced specialist can determine that braces and orthodontic wires will not be able to relieve a patient with a skeletal jaw deformity from a protruding chin or a “ gummy smile ”, but on the contrary, they can lead to tooth dislocation and the development of the temporomandibular joint. We take a comprehensive approach to solving such problems, the essence of which lies in preliminary stage-by-stage preparation and preliminary 3D planning. Computed tomography, photography, plaster and STL models allow us to perform a complete preoperative analysis and simulated surgery. Orthognathic surgery allows you to move one or both of the patient's jaws back and forth, up and down. The treatment procedure takes place according to a pre-planned scheme, which involves moving the jaws, chin, soft tissues, eliminating dentoalveolar compensation, and aligning the dentition in relation to the main bone.
Orthognathic surgery is performed with maxillary osteotomy , where intraoral bone incisions are made above the teeth and below both eye sockets, allowing the upper jaw, including the palate and upper row of teeth, to be repositioned. This movement is positioned using a pre-made special splint, which will reliably guarantee its correct position of the lower jaw in relation to the soft tissues.
A mandibular osteotomy involves making bone cuts behind the molars, along the jaw, and downward so that the mandible can move as a single unit. As a result of this manipulation, the lower jaw, with the help of a titanium plate, smoothly moves to a new location.
The genioplasty operation is aimed at leveling the midline of the patient’s face, during which the chin part of the lower jaw is cut off and moved in the correct, harmonious direction.
All orthognathic operations are performed using intraoral access and do not have external incisions or scars. Such operations, in order to avoid relapses associated with continued jaw growth, can be performed on patients over 18 years of age, since it is believed that by this age the growth of a person’s jaws is completed. Orthognathic operations are performed under general anesthesia and, depending on the planning of the treatment requiring correction, can last from one to six hours.
In our Center, using specially made titanium plates, specialists fix all detachable parts of the jaw. After surgery, the following temporary symptoms are possible: postoperative swelling, bruising in the lips and cheeks, difficulty communicating in the first week after surgery, limited oral hygiene, numbness in the operated area, and a feeling of nasal congestion. In order to minimize risks and complications after surgery, the patient should follow the doctor's recommendations during the recovery period. After surgery, patients are recommended to eat semi-liquid food; there are no special dietary restrictions.
Thanks to Andrey Nikolaevich Senyuk in Russia, orthognathic surgery began to be carried out entirely using intraoral approaches, using preliminary preoperative planning in such a way that a precisely planned result in advance is achieved, coinciding with the final one both in terms of aesthetics and occlusion. It was he who organized the first international conference of orthofacial surgery in Russia.
Many years of experience in orthognathic surgery and deep knowledge of the problem will allow our highly qualified specialists to work wonders, as noted by the patients themselves), restoring self-confidence to patients and leading a fulfilling lifestyle. The surgical team of the department, headed by Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Karayan A.S., develops an individual treatment program for each patient, and attention and warmth from the treating staff are guaranteed to everyone!
Clinical cases
Example 1
| Diagnosis: combined deformation of the jaws, asymmetrical deformation horizontally. Planned: osteotomy of the jaws according to Le_Fort 1 and sagittal of the lower jaw. |
| On the 7th day: |
Other examples:
| BEFORE | AFTER |
Preparation
Before surgical intervention, a set of general preparatory measures is indicated:
- Bringing the oral cavity back to normal – eliminating plaque and calculus, eliminating caries manifestations. Amputation of the root part of organs and removal of decayed teeth.
- Leveling manipulations are a long period and involve the use of braces. After the course of treatment, the specialist, based on the results obtained, plans to correct the bite through surgery.
- Computer preparation - using modern programs, they plan a treatment regimen aimed at correcting the defect and calculate the expected result.
This is possible using 3D technologies that project a panoramic image. Based on the results of such forecasting, a template layout of the future face is drawn up.
Before the procedure itself, you must adhere to certain requirements:
- 7-8 hours before the expected start of the manipulation, do not eat or drink water;
- give up alcohol and smoking one day before;
- If you have any viral or inflammatory diseases or general malaise, immediately inform your doctor and reschedule the procedure.
Orthognathic surgery
September 12, 2016
No matter how much we repeat the hackneyed phrase that “one is guided by the mind,” a pleasant appearance, in particular the face, plays a significant role in success in life. What if you were unlucky with your face from birth? Or, God forbid, was it damaged as a result of injury? In many cases of malocclusion and severe disharmony of facial shapes, it is worth turning to maxillofacial correction, and specifically to orthognathic surgery. This relatively young field of medicine, thanks to the latest advances in science and technology, not only restores correct bite and other vital functions of the dental system, but also restores patients’ self-confidence and joy of life. Improvement in appearance, as a rule, pleases even more than comfort and health.
Let's take a closer look at this section of surgery. Moving the upper or lower jaws during surgery, correcting malocclusions and facial shape - this is what orthognathic surgery is all about. This is general information. But in what cases of malocclusion is it worth considering surgical intervention, what are the stages of preparation for the operation, how it happens and how to go through the rehabilitation period without complications - it is better to ask a practitioner about this.
Andrey Nikolaevich Senyuk, a maxillofacial and aesthetic surgeon with more than twenty years of experience, candidate of medical sciences, chief physician and director of the maxillofacial surgery clinic “Face Smile Center,” is ready to answer these and other questions.
Does malocclusion always imply the need for orthognathic surgery?
It depends on the nature of the defect. Malocclusion is distinguished as dentoalveolar and skeletal. And if in the first case the correct relationship of the teeth is corrected by an orthodontist, then only orthognathic surgery can restore the desired relationship of the jaws. This is where the most important stage of treatment begins—the interaction between the orthodontist and the surgeon. Achieving complete success in this process is always the result of a combination treatment. Indications for surgical intervention are: open bite, asymmetry of facial proportions, strongly protruding lower jaw, the so-called gummy smile, pronounced chin slope. This is aesthetics. Physiological disorders include difficulties with chewing food, speech impediment, breathing problems, and the development of chronic pathology of the temporomandibular joint.
Obviously, the type of defect leads to differences in the types of surgical operations?
Yes. There are three main types of orthognathic operations: maxillary osteotomy, mandibular osteotomy and chin osteotomy. In the process of maxillary osteotomy, it becomes possible to move the entire jaw as a single unit. Then it is given the correct position in relation to the lower one. With a mandibular osteotomy, bone cuts are made behind the molars (hence the need to first remove all wisdom teeth) and the jaw is set in the desired position. To secure the jaws, special plates made of medical titanium are used. Osteotomy of the chin is part of a set of measures for surgical correction of the chin in order to improve its aesthetic appearance.
What do you need to know before deciding to undergo orthognathic surgery?
First of all, you need to clearly understand that this process is very slow, since orthodontic preparation for surgery alone can take about a year. All this time the patient wears a brace system. This is the specificity of the treatment. In addition, wisdom teeth must first be removed, because... The saw line of the jaw usually falls on these places. Further. Orthognathic surgery can only be performed upon reaching the age of 18, when active skeletal growth ceases. Statistically, an age group of 20 and 30 years can be distinguished. It is at this age that formed self-awareness and an adequate approach to the treatment process are most characteristic. Finally, individual response to anesthesia is also taken into account when deciding whether to undergo orthognathic surgery.
Are there any peculiarities in the preoperative period?
After orthodontic preparation, the patient moves to the surgeon's group. Here, too, a number of manipulations are required: facial anthropometry taking into account individual parameters, computed tomography and its analysis, planning the necessary movements of the jaws in a special program. Before the operation itself, several conditions must be met: stopping food intake 12 hours before the appointed time, including water; it is strictly forbidden to perform the operation in case of illness: a cold or even just a fever, as well as problems with digestion. In this case, the operation is postponed until complete recovery. If the patient is routinely taking any medications, the doctor should be aware, since some of them may be incompatible with anesthesia or affect blood clotting.
How is the operation performed?
The operation itself lasts from 1 to 6 hours, depending on the volume and complexity of the surgical intervention. There are no reserves left on the facial tissues outside, because... All surgical procedures are performed in the oral cavity. To fix the displaced jaw, plates made of special medical titanium are used. The wounds are then sutured. From this moment, an equally important rehabilitation period begins.
What symptoms of the postoperative period are considered normal?
Unfortunately, it is not possible to avoid a number of unpleasant but inevitable symptoms after such an operation, such as: temporary swelling and bruising in the cheeks and lips, nausea, sore throat, nasal congestion, difficulties with proper oral hygiene, and minor weight loss.
What are the possible complications with such operations?
I want to say that if all stages of orthognathic surgery are carried out correctly, then complications occur extremely rarely. However, when performing an osteotomy of the lower jaw, due to its anatomical structure, a decrease in the sensitivity function of the ternary nerve is possible. This manifests itself in the form of partial numbness in the area of the lower lip and has practically no effect on facial expressions. Complications such as bleeding and inflammation depend on the individual characteristics of the body and on compliance with the doctor’s recommendations.
How long does the rehabilitation period generally last?
The early stage of rehabilitation lasts 3 weeks, after which the patient returns to his professional activities. Further restoration of the body is the work of the body itself. This implies a gentle regimen of exercise, both physical and vitamins and physiotherapy.
What to take with you to the hospital
The clinic will definitely need:
- passport, referral for surgery and outpatient card;
- personal clothing and footwear;
- Personal hygiene products, optional, towel and bed linen;
- a special sippy cup with a spout, since during the rehabilitation period, especially in the first days, the process of drinking in traditional ways will cause physical difficulties and pain.
You will learn what orthognathic surgery means from the video.
Possible complications
If the operation is performed correctly, complications are the exception rather than the rule. But, nevertheless, they sometimes happen. The most common:
- Rupture of the nerve of the lower jaw - occurs during osteotomy. Since the nerve is completely exposed during the operation, there is a risk of damage or complete rupture. Externally, the defect does not appear in any way.
- Damage to the infraorbital nerve affects the inhibition reflexes of nerve impulses. It provokes expansion of the infraorbital canal, which is normally somewhat narrowed. It goes away gradually and spontaneously.
- Damage to the facial nerve is fraught with fragmented numbness of the labial region. Doesn't affect facial expressions.
- Blood loss during manipulation depends on the individual characteristics of the body, and the quality of functioning of the circulatory system, in particular, blood clotting. The complication does not pose a serious threat to the patient’s health.
- Scar formation depends on the sensitivity and structural content of the skin. It can be eliminated with special creams with a wound-healing effect. Not dangerous.
- Damage to teeth occurs due to poor quality of manipulation and lack of professionalism of the doctor. The only solution in this situation is artificial restoration of organs.
- Unexpected bone osteotomy - another operation will most likely be required to eliminate the pathology. The complication arises due to the anatomical features of the patient’s jaw structure and the mobility of bone tissue.
- Deformation and asymmetry are a temporary phenomenon; as the source of inflammation heals, it goes away spontaneously; in severe cases, it is corrected surgically.
- Inflammation - occurs when the oral cavity becomes unintentionally infected.
- A jaw fracture is the result of extreme unprofessionalism of the surgeon. Requires urgent surgical correction.
Still have questions? Contact us:
— Do I need to remove any teeth during the preparation stage?
Yes, wisdom teeth. This is carried out according to orthodontic and surgical indications. Sometimes their absence makes it easier or even necessary for the orthodontist to work, and they themselves refer patients to have their eighth teeth removed before starting orthodontic treatment. This is important for surgery for two reasons: if on the upper jaw the osteotomy (cut) line can pass through the area where the eighth tooth is located, then on the lower jaw the osteotomy line always passes through the eighth tooth. Therefore, as planned, 2-3 months before surgery, all eighth teeth are removed.
— How is orthognathic surgery performed?
The patient is hospitalized in the clinic's inpatient unit, where he is prepared for surgery. The operation itself is performed in a full-fledged operating room under endotracheal anesthesia. All manipulations are carried out through the oral cavity and there are no incisions or punctures on the outside. The technical part of the operation is carried out with instruments specially created for various stages of orthognathic surgery (sets for moving the upper and lower jaws). After moving, the jaws are rigidly fixed. The wounds are sutured and the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit for personal observation.
— How do you secure the displaced jaws?
For this purpose, plates and screws made of special purified medical titanium are used. They stay for life. But if desired, a year after the operation, all metal structures can be removed.
— How large is the operating team for orthognastic operations?
The optimal composition is a surgeon and two assistants or 6 hands. Resident doctors or graduate students assist. In addition, operating nurses and a team of anesthesiologists participate in the operation.
— How long does the operation take?
It all depends on the extent of the surgical intervention. Orthognathic surgery is a collective concept. Here we can talk about moving only one lower jaw, or maybe about segmental osteotomy of the upper jaw (its separation and division into several fragments), moving the lower jaw, chin and zygomatic bones. As you understand, the difference is colossal. Moreover, during the operation, along with moving the jaws, various surgical techniques are performed (plasty of the nasal septum, suturing the base of the nose, excision of fragments of the jaws, etc.), which also consumes time resources. But on average, moving both jaws and the chin (the most common scope of surgery) takes about 4-5 hours.
— How much blood does the patient lose during such large-scale operations?
Blood loss - 100 ml.
For many this will seem surprising, but during orthognathic surgery, blood loss does not exceed 100 ml. Such low blood loss is achieved due to well-developed surgical techniques, correctly selected instruments, coherence of the operating team and, of course, the high professionalism of our anesthesiology service.
— How long does the patient spend in the hospital after surgery?
About seven to ten days. During this period, he is given dressings and receives anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy. The patient eats liquid food and, of course, he has a number of restrictions. Already from 3-5 days after surgery, the patient is sent to an orthodontist to begin postoperative orthodontic management.
In general, postoperative management of patients after orthognathic surgery is the final, but very important stage. If, say, you operate on a patient and send him home without any observation, then, I think, in almost 50% of cases certain problems will arise. Therefore, after discharge, I schedule frequent follow-up visits with my patients. It is necessary to control the newly created jaw relationship (bite).
— What complications occur during such operations?
I would like to note that with proper preparation, surgical technique and postoperative management, complications are very rare.
Nevertheless. Perhaps one of the most common complications concerns the technical part of the operation - rupture of the mandibular nerve. Occurs during osteotomy of the lower jaw. This nerve (left and right) runs deep into the ramus and body of the lower jaw and is always exposed when moving it. Unfortunately, depending on the anatomy of the jaw, there is always a risk of damage and complete intersection. The nerve is sensitive, so the facial muscles do not suffer from its rupture and this does not manifest itself in any way on the face, only a partial loss of sensitivity in the area of the lower lip.
Complications also include various deformities as a result of incorrect osteotomy and unsatisfactory fixation, relapse, bleeding and inflammation.
— What recommendations and restrictions exist for the postoperative period?
For the first week, the patient eats only liquid food (baby food, juices, broth). To improve recovery, you can prescribe a complex of vitamins and conduct physical therapy. In the early postoperative period, the patient should not engage in physical activity. You can’t go to the gym, pool, etc. for about a month. After the specified period, the restrictions are lifted.
During hospitalization, we give the patient a memo that describes many issues that concern them and the rules of behavior after the operation.
Alexander Vitalievich, thank you for the interesting conversation! You revealed to us not only all the variety of possibilities of orthognathic surgery, but also told us a lot of useful nuances that only a doctor can convey.