Increasingly, parents with young children whose front teeth are badly damaged come to the pediatric dentist for appointments. As you know, caries in baby teeth, especially in young children, develops at lightning speed. While parents, having noticed initial changes in the enamel of their front teeth, decide to consult dentists (according to statistics, parents choose a local clinic for their first visit to a pediatric dentist), who recommend brushing your teeth regularly, or at most coat your teeth with fluoride varnish or silver plate them; precious time is lost.
Dentists in specialized pediatric dentistry already see teeth in the child’s mouth that are destroyed, often down to the gum level.
Naturally, parents want to give their baby back a beautiful and healthy smile; knowing full well that the front teeth are needed not only for beauty, but also for the correct formation of the bite and production of the correct sounds.
There are several treatment options for decayed teeth in children.
Option one.
How are baby teeth different from molars?
Baby teeth appear at the age of six months. First, the central incisors erupt on the lower jaw, then on the upper jaw. By about 2.5 years old, the baby already has a full, white-toothed smile. His mouth contains 20 milk teeth, which will serve the child for several years.
After about six years, temporary teeth begin to be replaced by permanent teeth. When the baby brings the first “trophy” to his parents, it causes sincere joy and tenderness. And also the desire to carefully examine what the baby is holding in his fist. And while studying the tooth, parents can draw several wrong conclusions.
pixabay.co/
The first is that baby teeth have absolutely no roots. This impression is created because the root shoot of a fallen tooth is usually located on only one side, and sometimes it does not exist at all. In fact, primary incisors and molars, of course, have roots, but over time they become smaller.
This occurs in order to ensure a natural and painless process of changing the dentition. When the time comes to change the bite, the roots of the baby teeth gradually dissolve. And thanks to this, the indigenous ones “push out” their predecessors from the gums, taking their place.
The second incorrect conclusion may be related to the size of the tooth. It seems incredible that such a “baby” could have the same structure as an “adult” native.
“The structure of baby teeth is almost the same as permanent teeth,” comments Natalya Terentyeva. “They have roots, root and coronal pulp, root canals through which nerve fibers pass. Milk teeth differ from molars in that their enamel is weakly mineralized, which means it is more susceptible to destruction and the development of carious processes.”
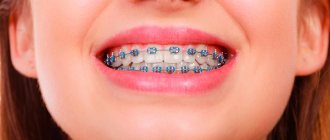
Why do children get braces?
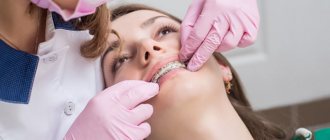
One of the most popular and effective ways to correct a bite is to install braces. What it is?
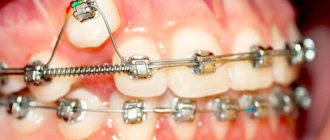
A brace system is an orthodontic structure that consists of a metal arch and small plates that are attached to each tooth. The operating principle of braces is based on shape memory. When braces are attached to crooked teeth, they attempt to return to their original position. As a result, it puts pressure on the teeth and moves them in the right direction. It is the doctor’s task to calculate the position of each bracket on the tooth so that they are aligned when displaced.
Children are usually given braces for several years. The design is non-removable, so it is very important to carefully take care of dental and oral hygiene when wearing braces. Bracket systems may differ in materials, structure and other characteristics. By location, they are external (located on the outside of the teeth) and internal. External braces usually cost less and are easy to install. Modern models are made from transparent materials, so they are almost invisible on the teeth.
Lingual, or internal systems, are attached to the inside of the teeth. They are not visible from the outside, so these braces are suitable for a teenager who is embarrassed to wear any structures on his teeth. It is important for parents to know that internal braces are more expensive than external braces. In some cases, minor problems with diction may appear, which usually go away quickly as you get used to it.
Do baby teeth hurt?
They say that baby teeth have no nerves, so they cannot hurt. This is wrong. Temporary teeth can hurt just like permanent teeth. And the reasons for this are quite adult - injuries or, most often, caries.
The pathological process, which develops first in tooth enamel, causing its destruction, and then “descends” deep into the dental tissues, occurs even faster in children than in adults. There are several reasons for this.
Firstly, babies do not take care of their oral cavity as carefully as their parents. In babies who brush their teeth themselves, without adult supervision, you can often notice a yellow coating on those areas of the enamel where the toothbrush regularly “does not reach.”
Secondly, children eat much more sweet food and drink sugary drinks. Sugar is an ideal breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria that actively spread in the oral cavity and cause caries. The longer and more often sweets come into contact with the baby’s teeth, the higher the risk of caries.
pixabay.co/
And thirdly, the reason is in the very structure of the teeth. Children's tooth enamel is less mineralized than adults. It is not as strong and more permeable. Because of this, the bacteria that cause caries need much less time to destroy the outer protective shell and reach its hard tissues. Often caries in childhood develops rapidly. And parents notice it only at the moment when gumboil grows on the gum or the child begins to complain of acute pain in the tooth. All this suggests that the carious process has penetrated very deeply.
“A milk tooth hurts when it is affected by caries or its complications, if the child has not been consulted with a doctor,” notes FAN’s interlocutor. — Children, like adults, can develop pulpitis (inflammation of the internal tissues of the tooth), periodontitis (which affects the tissue around the root). The inflammatory process can also occur in the gums, which also causes pain to the child.”
When should you go to the clinic for dental treatment for your child?
The following symptoms should not be ignored:
- the baby becomes capricious, refuses to eat, spits out the pacifier for no reason;
- body temperature rises sharply without signs of acute respiratory infections;
- gums become red and swollen;
- a white, cheesy coating appears in the mouth;
- reaction to cold and hot foods;
- the teeth are yellowed, dark spots are found on the enamel;
- there was an unpleasant odor from the mouth.
Are baby teeth treated?
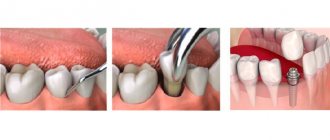
It is believed that if a child’s baby tooth hurts, you shouldn’t fuss with it. Since it will fall out soon, you just need to tear it out and forget it. Indeed, a toothache can be a signal for a doctor to remove a tooth. But only if the doctor sees that there is nothing left to treat: the carious process has completely destroyed the tooth from the inside. Then a decision can be made to remove it.
But if the tooth can be saved, the doctor will do everything necessary for this. As in adulthood, teeth are not simply pulled out in childhood. If only because they have their own purpose in the oral cavity. A child with fewer teeth may have trouble eating. Difficulties may arise with the development of the speech apparatus and the pronunciation of certain sounds, which will subsequently require speech therapy correction. Finally, the beauty of a smile in the future also depends on the quality of care for temporary teeth and timely medical care in childhood.
pixabay.co/
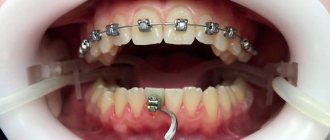
To put it simply, each baby tooth “reserves” a place for a molar one. As a child grows, his jaw becomes larger. And larger permanent teeth occupy the areas reserved for them. Temporary incisors are replaced by permanent ones, and so are temporary molars. If voids appear in the child’s mouth, this can change the dentition and cause bite problems in the future. Temporary teeth may shift to the vacated areas, and molars will erupt out of place. Therefore, children who lose teeth as a result of injury or extraction when treatment is impossible are recommended to be monitored by an orthodontist.
“You need to treat baby teeth,” the doctor clarifies. — For this purpose, painless techniques are used in dentistry. If drilling is necessary, the doctor will use anesthesia. Until the age of four, local anesthesia is not used - only general anesthesia. This eliminates anxiety and pain in the child, and allows him to remain in place while the doctor is working. After four years, local anesthesia can already be used. The treatment is painless, slight discomfort is possible only during the “freezing”.
Types of braces
Modern dentistry offers a huge selection of braces made from different materials:
- Metal ones are suitable for everyone, including teenagers. They are distinguished by their affordable price, durability, and strength. They effectively cope with bite correction, but their aesthetic characteristics leave much to be desired. Therefore, many teenagers do not want to wear metal braces.
- Sapphire ones look more aesthetically pleasing on the teeth and are not as noticeable as metal ones. But they are expensive and cannot cope with all malocclusions.
- Plastic braces have good aesthetic properties, are hardly noticeable on the teeth, but are inferior in strength to metal ones. If the braces break, they will have to be replaced, which delays the orthodontic treatment. Plastic structures may change color due to coloring food and drinks.
- Lingual braces are also suitable for patients of all ages, including children. But for installation you need a sufficient length of teeth. Internal braces are expensive and are not suitable for correcting complex malocclusions. The main advantage is that they are not so noticeable on the teeth.
- Ceramic. Children are rarely given such braces; they are mainly used to correct the bite of adult patients.
Do baby teeth need to be pulled out?
When the teeth begin to loosen, this indicates that the process of changing the bite has begun. And soon the place of temporary incisors and molars will be taken by permanent ones. But at the same time, parents may worry about whether they need to help their child get rid of a milk bite.
There are different opinions on this matter. Some parents prefer not to interfere, waiting for the teeth to fall out on their own. Others, on the contrary, take the most active part: they advise, tie strings and pull, loosen...
According to Natalya Terentyeva, parents should carefully monitor the process and, if necessary, consult a doctor.
“You need to remove a tooth if there is physiological mobility,” she notes. — It happens that a tooth becomes loose, causes discomfort to the child, causes gum bleeding, but cannot fall out on its own. In this case, you should not try to pull it out yourself, as this could cause injury to the child. It is necessary to contact a dentist who will provide the child with professional medical care.”
pixabay.co/
There is no point in hesitating when the baby tooth is loose and does not fall out, but the molar tooth is already visible under it or next to it. This indicates that the root of the incisor or fang has not resolved. But if it continues to take up space in the gum, the permanent replacement will most likely choose the wrong direction of growth. And then you will have to straighten your bite through orthodontic treatment.
“Sometimes we have to remove healthy and immobile baby teeth,” continues Natalya Terentyeva. “But they do this only for orthodontic indications—when it is necessary to make room in the gums for the proper growth and positioning of molars.”
Correction with crowns
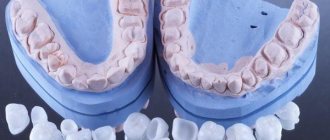
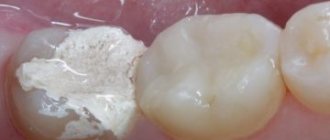
The installation of crowns as tooth extensions is also used in cases where the tooth is not destroyed, but is sufficiently damaged. Installing a crown is one of the effective ways to restore a broken tooth, this applies to both front and chewing teeth. Crowns are also used in cases where it is not possible to fill a chewing tooth, for example, because the cavity left after caries treatment is too large. This type of permanent prosthetics, such as crowns, is an ideal solution in cases where more than 70% of the crown part of the tooth is missing.
In modern aesthetic dentistry, ceramic and metal-ceramic crowns are successfully used. The installation process itself takes place in two stages. First, the doctor prepares the tooth (removes infected tissue, grinds down the walls), then an impression is taken, from which a crown for a chewing tooth or a crown for a front tooth is made in a dental laboratory. The second stage is the fitting and installation of the finished crown. Modern ceramics, used for the manufacture of inlays and crowns, make it possible to perfectly imitate the texture, color and transparency of natural enamel, as well as select a shade in accordance with the color of neighboring teeth.
Should I go to the dentist if my teeth are fine?
Regular preventative dental examinations are needed not only for adults, but also for children. Moreover, in childhood they are required even more often. If adults are advised to visit a doctor every six months, then children, due to the characteristics of tooth enamel and potential risks, should visit a doctor every three months.
In addition, parents should visit an orthodontist when their baby’s teeth begin to change. The specialist will conduct an examination,, if necessary, prescribe an x-ray of the oral cavity and recommend treatment that will help the permanent teeth grow evenly and in their places. This means your child’s smile will be beautiful and healthy.
At what age do children get braces?
Dentists do not have a common view on this issue. Some orthodontists are confident that from the age of 7-8 years it is already possible to begin bite correction with a brace system. The main thing is that by this age the child’s second molars have fully erupted, the teeth are of sufficient length to attach the bracket, and the enamel has good strength. Other orthodontists categorically do not install dental braces before the age of 13.
So when should you put braces on your child? Most experts agree that it is closer to adolescence. It is important to take into account the individual characteristics of a particular patient, the number of crooked teeth, the degree of malocclusion, the strength of the enamel and many other factors. When a child gets braces too early, there is a risk of damage to tooth enamel, root resorption, and even loss of permanent teeth. Therefore, when asked at what age it is better to install braces, most doctors answer - at 13-14 years old. After installation, you can wear braces until you are 18 years old. This age period is considered the most optimal for bite correction. On the one hand, teeth are pliable and easy to straighten. On the other hand, tooth enamel is strong enough to withstand the heavy load of the orthodontic apparatus.