Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
Remains of food in the oral cavity combine with enzymes in secreted saliva and partially remain on the teeth. These compounds interact with bacteria, dead cells and salts of certain trace elements. Gradually they harden and give the tooth enamel a yellowish tint - this indicates the appearance of plaque or tartar. It is localized in the most difficult to reach places - between the teeth and under the gums. The process of stone formation takes a long time - from several months to several years. The speed of its occurrence depends on the quality of food a person eats, the presence or absence of bad habits, etc.
To prevent tartar, you need to get rid of plaque on time. Asepta Active toothpaste copes well with this task. The natural enzyme papin, which is part of it, effectively breaks down plaque, without leaving it even in places that are difficult to reach with a brush.
What is tartar
Tartar is a hardened soft plaque. When brushing teeth incorrectly or poorly, a soft mass consisting of fragments of the mucosal epithelium, food particles and colonies of bacteria accumulates on their surface and in the interdental spaces. Under the influence of saliva and substances produced by bacteria, this mass gradually hardens, turning into tartar. Hard deposits may be observed on the back surfaces of teeth and between teeth, in which case they are classified as supragingival calculus. Gradually, under the influence of gravity and chewing movements, the stones move under the mucous membrane of the gums and are classified as subgingival.
Causes
The reasons for the occurrence of tartar, which cannot be removed at home, are:
1. Insufficient and poor-quality oral hygiene does not ensure sufficient removal of microbes that begin to actively multiply and “freeze”;
Note! This also includes incorrectly selected toothpaste, brush, brushing teeth “in haste,” and the absence of dental floss, brushes, rinsers, or irrigators in rituals.
2. Hard plaque occurs due to excessive consumption of soft foods and fast carbohydrates (flour and confectionery products). They promote abundant salivation, which provides favorable microflora for the proliferation of bacteria;
3. Bad habits - smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages (especially coloring ones, such as red wine), unhealthy diet;
4. Metabolic disorder, which leads to a change in the composition of saliva and an increase in free salt ions.
A combination of one or more reasons influences the success of tartar removal.
Plaque appears on all teeth, but the most common are the lower teeth on the inside. This is due to its proximity to the large salivary glands.
Symptoms of the disease
If a person is not attentive to the hygiene of his teeth, he is unlikely to examine the oral cavity with a flashlight to assess the degree of neglect of the situation.
Therefore, you can determine the presence of a problem not only visually, but also by indirect signs:
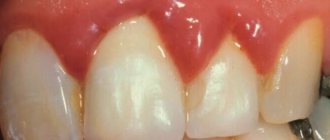
- bleeding gums - often completely painless and occurs only when brushing your teeth (naturally, after the impact of a toothbrush on sensitive gums, unpleasant sensations arise);
- bad breath - if there are no problems with the stomach, but the smell is present, it is worth considering that perhaps an impressive amount of stone has accumulated, since the active activity of microorganisms is associated with the release of sulfur compounds;
- swelling and soreness of the gums - a feature of the accumulation of plaque, which will be discussed below, affects the soft tissues, developing inflammatory processes.
Important! It is very important to remove tartar before gum recession begins - a decrease in soft tissue, “lowering” or “raising” of the gums. This leads to exposure of the tooth root and increased sensitivity.
Types of Tartar
Based on their location, there are two types of plaque:
- Supragingival - visible stone, located above the gum, often found on the lower front teeth on the inside and in the area of the upper molars;
- Subgingival - as the name suggests, plaque, which is located in the periodontal pocket, in the groove between the tooth and the gum, cannot be seen with the naked eye;
- Stone bridge - microbes can cover the enamel of several teeth in a row, the most advanced case.
Cleaning tartar will also depend on the method of its attachment to the surface:
- with the inclusion in the process of organic pellicles on “cement” (this is a specific tissue covering the root part of the tooth);
- with the inclusion of organic pellicles on the enamel in the process;
- synthesis on uneven abrasive surfaces, for example, in the early stages of caries disease, or at chipped sites (and also, as mentioned earlier, during the formation of food plaque);
- attachment in the depressions and ridges between teeth on the enamel or tooth root.
Consequences of dental plaque
Dentists know how to remove tartar to avoid damaging your smile.
What complications threaten?
- inflammation of the gums and gingivitis - tartar, especially the subgingival type, has a direct effect on the tissue, promoting softening and redness, then the pocket between the gum and tooth begins to increase, increasing the formation of new bacteria;
- periodontitis - in which bone tissue is also involved, which gradually begins to break down, which ultimately leads to complete loss of teeth.
Therefore, it is important to pay attention to the formation of tartar in a timely manner and contact a dental clinic to remove it.
Tartar removal
There are several ways to get rid of future diseases.
Ultrasound
Ultrasonic tartar removal is the most common and safe method used in dentistry today.
The principle of operation is small, rapid vibration of the tip of the device - the scaler. When it comes into contact with a tooth, it creates enough resonance to destroy hard plaque.
Additionally, the nozzle treats the tooth surface with a chlorhexidine solution or water, thus polishing the surface to prevent the attachment of new plaque.
The advantage is minimal impact on the native enamel.
Air Flow
In fact, the method is based on the destruction of plaque by a thin jet directed under high pressure, consisting of water and air, non-abrasive particles.
If necessary, additional antiseptic substances are used.
Laser
It is rarely used due to the high cost of the equipment, and the principle of operation is the same as that of ultrasound - a directed beam destroys the stone, and air or water “washes” it out of the dental spaces.
Mechanical cleaning
Sometimes a mechanical, that is, manual cleaning method is used using:
- hand scalers - metal sticks with straight and curved attachments;
- excavators - sticks with attachments, similar to spatulas;
- chisels - so called precisely because of their external resemblance to their larger brother;
- curette - thin metal hooks;
- rasps - the ribbed attachment is designed for scraping.
This type of cleaning is quite unpleasant and painful, but it is the most effective, especially with complex deposits.
However, if the doctor is careless, he can irreversibly damage the tooth enamel, so it is important to choose a dental clinic with professionals in the field of hygienic cleaning.
Which method to choose
The cleaning procedure most often includes several stages, which vary depending on the quantity and quality of plaque. But the standard set of actions looks like this:
- Ultrasound;
- Air-flow;
- Polishing with a brush;
- Remineralizing therapy.
Finally, the doctor will polish the surface of the tooth and coat it with fluoride to prolong the effect of the manipulation.
How tartar is removed in a particular case depends on the diagnosis. It is important that the dentist use a microscope to detect the early stages of plaque.
As a rule, even after improving nutrition and oral hygiene, it is necessary to come for a preventive examination, which includes professional cleaning every six months. This will avoid problems with gums, and will also allow timely detection of caries and other disorders.
In what cases does stone plaque form?
The reason for the formation of tartar is poor quality dental care, in which soft plaque (dental plaque) is not completely removed. High mineral content causes plaque to harden. Using a too soft toothbrush, lack of attention to the interdental spaces and gum margins, irregular oral hygiene, etc. are the main sources of the problem.
But there are factors that increase the likelihood of hard deposits forming on teeth:
- diseases of the digestive system and endocrine system, in which the chemical composition of saliva changes;
- malocclusions and dental defects that form particularly difficult areas to clean;
- wearing dentures, braces, brackets, plates and other structures that make it difficult to properly clean teeth using a traditional brush and paste;
- a large amount of carbohydrate foods in the diet, which facilitates the gluing of soft plaque particles.
Types of Tartar
Plaque is classified into two categories. First, supragingival stone appears, the cause of which is poor oral hygiene. This plaque is formed from food debris and bacteria that stick together into a common mass. Such deposits are located above the upper edge of the gingival crest, so they are easily diagnosed during a routine examination.
Characteristic features of supragingival calculus include:
- Localization on the inner surface of the tooth, from the side of the tongue;
- White or yellowish tint;
- The consistency is hard or clay-like.
The plaque is unstable, so it can be removed mechanically without any problems.
Subgingival calculus appears as a result of the fact that supragingival plaque descends down the root of the tooth and mineralizes. It forms in the gum pocket and is diagnosed only when using special dental instruments. Such deposits are considered age-related and most often appear in people over 40 years of age. If personal hygiene rules are not followed, it can appear at any age.
Signs of tartar:
- Dense and hard consistency;
- Light brown or greenish-black tint;
- Swelling and bleeding gums.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
Tartar happens:
- Subgingival.
- Supragingival.
Signs of supragingival calculus include yellow or dark brown formations on the walls of the tooth. The patient can independently detect them during a visual examination of the oral cavity in the mirror.
Subgingival formations are invisible at first glance. They are detected during an examination by a dentist using special diagnostic methods. Characterized by the following features:
- Density and hardness.
- Adjacent to tooth roots.
- They have a dark brown (closer to black) or dark green tint.
Symptoms of Tartar
The first symptoms of tartar are a change in the color of the enamel on the upper molars and lower incisors. Soft yellow or gray plaques appear. First of all, tartar forms in areas where there is no self-cleaning of the surface during the process of chewing food or rinsing: the interdental space, the inner walls of the tooth.
Primary symptoms:
- Bad breath;
- Mild itching of the gums;
- Slight bleeding.
If no measures are taken to remove plaque, it begins to mineralize, becoming harder. As a result, the gums may become inflamed and there will be severe swelling and redness. Detachment of the gingival margin is possible, which leads to the appearance of a periodontal canal.
What are the dangers of tartar?
In cases where tartar has already formed, treatment should be carried out immediately. Otherwise, it moves under the gums and leads to severe disorders of tissue metabolism in soft tissues.
As a result, acute or chronic gingivitis develops, the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth becomes inflamed and, as the most severe complication, periodontal disease develops - atrophy of the tissues that provide support to the tooth. As a result, a person who has developed subgingival tartar in the future faces the need to remove teeth that have lost stability and are no longer able to perform their functions.
Treatment methods
It is not possible to treat tartar on your own. Tartar removal is performed using practical and painless methods in the dentist’s office:
- Ultrasonic cleaning. This is the treatment of tartar with a scaler. The equipment generates low-frequency ultrasonic vibrations that destroy dental plaque. After this, the dentition is washed with a stream of water, and the enamel is ground and polished.
- Air Flow whitening system. In this case, cleaning is performed with an abrasive compound supplied under pressure through a special nozzle. The composition includes air, water and sodium carbonate. The equipment does an excellent job of cleaning the interdental space and effectively removes stubborn plaque.
- Laser cleaning. This is a non-contact technique that does not cause discomfort or pain. Tartar cleaning is performed with a directed laser beam, the remaining particles are washed out of the oral cavity with a water-air jet.
How does an irrigator help with tartar?
One of the most frequently asked questions about whether an irrigator removes tartar can be answered this way: the irrigator helps with the prevention of tartar. It can only help if deposits have just begun to form and they have not yet formed stone. Regular and thorough brushing with a toothbrush and toothpaste, flossing, and completing your oral care with a irrigator can greatly reduce the risk of tartar.
But even in this case, tartar cleaning should be completed in the dentist’s office: the doctor will grind the enamel to eliminate roughness that facilitates the formation of plaque.
Ultrasound cleaning
Cleaning teeth from stone using the ultrasonic method (removing deposits under the gums, on the neck of the tooth and the root) involves using an ultrasonic scaler as the main equipment. This device has a gentle effect on enamel and is safe for periodontal disease.
Using this technology, stone is removed, and preventive tasks are also implemented. Targeted action on bacteria and their destruction prevents carious processes and solves other dental problems. The cost of teeth cleaning at the dentist is affordable for everyone.
How to prevent the formation of tartar
The only reliable and effective means of prevention is control over the quality and regularity of dental and gum care.
Be sure to brush your teeth at least 2 times a day (morning and evening), ending each procedure with the use of an irrigator. This will help remove soft plaque from areas that traditional oral hygiene products cannot reach.
In addition, it is important to monitor your overall health, promptly seek bite correction and minimize the consumption of fast carbohydrates such as baked goods, sweets, etc.
More detailed information is presented in the catalog of oral irrigators.
Clinical researches
Clinical studies have proven that regular use of professional toothpaste ASEPTA REMINERALIZATION improved the condition of the enamel by 64% and reduced tooth sensitivity by 66% after just 4 weeks.
Sources:
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” GENTLE WHITENING” Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” COFFEE and TOBACCO Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky. First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: Asepta toothpaste used in combination with Asepta mouthwash and Asepta gum balm Head. Department of PFS Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor S.B. Ulitovsky St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova. Faculty of Dentistry. Department of Preventive Dentistry.