Every person periodically faces such a problem as pain in the gums. Unpleasant sensations can be caused by both temperature exposure and serious inflammatory processes, which can lead to dangerous diseases (including tooth loss). In general, everyone can face this problem, and pregnant women can be classified as a separate risk group. What causes gum inflammation in pregnant women and what treatment methods exist? We will try to answer this question below.
Should I worry if a pregnant woman has sore gums?
If you have problems during pregnancy, you should contact your dentist. You should not hesitate, otherwise health problems may arise for the baby. Dangerous infections can enter his body.
The best time to visit the dentist is the second trimester. And in other periods, you can safely turn to a specialist for help. Only he is able to competently prescribe treatment.
The problem can be identified by symptoms, which include:
- blood during the cleaning process;
- the appearance of plaque;
- redness, swelling;
- there is pain on palpation;
- bad breath;
- discomfort when chewing solid food.
Cause of gum swelling
Swelling of the gums is mainly due to changes in hormonal levels, but there are other reasons.
- Hormones. The restructuring of the body, the formation and development of the baby increases the sensitivity of tissues and mucous membranes. As a result, the mother feels pain in the gum area, especially when exposed to it: from brushing teeth to palpation.
- Toxicosis and change of tastes. The oral cavity is a favorable environment for various types of bacteria, both beneficial and harmful. Pregnant women actively add sweet and salty foods to their diet. Food particles remaining in the oral cavity contribute to the proliferation and development of bacteria, which in turn provokes inflammation. The development of bacteria is also promoted by toxicosis, which increases the acidity of saliva.
- Reduced immunity occurs in many pregnant women. The baby in the womb takes the vitamins and minerals necessary for development from the mother’s body, thereby providing her with hypovitaminosis. Bacteria, which usually do not manifest themselves, begin to provoke diseases when immunity decreases.
- Untreated teeth. Doctors recommend completely curing all teeth before a planned pregnancy or, if urgently necessary, in the early stages (preferably in the second trimester), when treatment is relatively safe for the fetus. Inflammation, tumors, caries and other dental damage not only cause pain, but also affect the developing child, and can sometimes even cause premature birth.
Causes of gum disease
Oral discomfort during pregnancy is often associated with gingivitis. It occurs mainly due to poor oral hygiene - resulting in the formation of plaque. Another reason for the problem is hormonal changes.
Gums begin to hurt from the 3rd month of pregnancy. They change color from red to blue, swell, and bleed less often. Unpleasant sensations in the mouth may occur during eating or at rest. Sometimes ulcers appear. In the second half of the term, the condition of the mouth may deteriorate sharply - the gingival papillae and gum edges become significantly larger.
The gums near the tooth hurt (including after its removal) and for some other reasons.
All of them are complications and require prompt intervention by a specialist:
- Alveolitis is an inflammation of the hole left after tooth extraction. The presented problem arises due to non-compliance with the doctor’s recommendations. After tooth extraction, the problem arises when an infection penetrates the injured tissue, causing swelling and other complications.
- Hematoma is an accumulation of pus in the blood that has accumulated in the soft tissues.
- Trigeminal neuritis. The gums also hurt when the trigeminal nerve is injured. Visually it does not change.
- Remains of cysts, dental roots. In some cases, the pain is due to the fact that the specialist has not removed all the remains. This causes inflammation of soft tissues, headaches, and swelling.
There are cases where women develop periodontal disease due to long-term use of any medications. For example, patients with epilepsy receive special medications that reduce the amount of saliva produced. As a result, their teeth are left with virtually no protection.
What to do if your gums hurt? Seek help from a dentist for medication or surgery.
Gingivitis in pregnant women: impact on the fetus
As noted above, hormonal changes and toxicosis contribute to impaired blood supply to the gums and hypertrophic enlargement of the gingival papillae. But the actual phenomena of inflammation in the gums develop due to insufficient hygiene (against the background of changes in diet) - as a result of which soft microbial plaque accumulates at the necks of the teeth.
If gingivitis occurs in pregnant women, the effect on the fetus will be minimal, because gingivitis is only a superficial form of gum inflammation (although it is clear that some small part of bacterial toxins and inflammatory mediators will still enter the blood of a pregnant woman). And in this case, hypertrophic gingivitis in pregnant women is more of an aesthetic problem. But a completely different situation is when untreated gingivitis transforms into periodontitis, in which periodontal pockets appear between the roots of the teeth and the gums.
In periodontal pockets there is always an aggressive pathogenic microflora that destroys the bone tissue around the teeth and maintains a pronounced inflammatory reaction deep in the gums. In inflamed tissues during periodontitis, a large amount of 1) inflammatory cytokines, 2) prostaglandins “PGE-2”, 3) interleukins “IL-6” and “IL-8” are produced. All these inflammatory markers have an extremely negative effect on the course of pregnancy, but in addition they increase the risk of premature birth by 6-7 times.
With periodontitis, increased levels of all of the above inflammatory markers are found in a pregnant woman not only in her blood, but even in the amniotic fluid (in which the fetus is located). Clinical studies have shown that the risk of premature birth in pregnant women with periodontitis is associated with two factors. Firstly, it is associated with the release of PGE-2, which restricts placental blood flow, causing gradual necrosis of the placenta and restriction of intrauterine growth.
Secondly, this is due to cytokines, the production of which promotes contraction of the uterus and dilation of the cervical canal. All this data is taken from clinical studies - 1) Dyortbudak O., Eberhardt R. et al. “Periodontitis - a marker of the risk of premature birth during pregnancy”, 2) Goepfert A.R., Jeffko M.K. et al. “The relationship of periodontal diseases with inflammation of the upper genital tract and early premature birth.”
What to do if your gums hurt and bleed during pregnancy - doctor's advice
Even at the very beginning of pregnancy, the expectant mother should understand that discomfort, bleeding in the mouth and other troubles should be taken seriously. If these symptoms appear, you should contact your dentist to prevent the development of severe pathologies.
If the gums are swollen, the doctor usually prescribes a set of measures:
- Prescribes special anti-inflammatory drugs for external use. Basically these are ointments that should be kept in the mouth for several hours.
- Daily hygiene measures - cleaning, rinsing, etc.
- Professional cleaning in dentistry. Removing plaque is a very important process. The bacteria found in it can cause serious illness.
- Food enriched with microelements and vitamins.
In the early stages of pregnancy, it is important to choose the right medications. They should strengthen the gums, but not harm the child. The best option is decoctions of calendula, medicinal chamomile and sage. Hardware procedures are selected individually.
The use of potent drugs is prohibited.
Among the preventive measures you may be prescribed:
- diet;
- gum massage using a soft brush;
- vitamin complexes;
- reducing consumption of foods high in sugar;
- visiting a specialist once every trimester;
- drinking high-quality clean water.
The best treatment for teeth and gums is prevention. This way you will maintain the health of the mother and fetus. But if pharmaceutical products were nevertheless prescribed, you should make sure that they are not dangerous for pregnant women (made from lidase, acetylsalicylic acid or glucose).
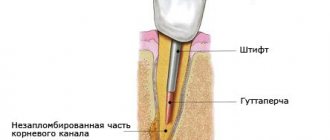
Is it possible to have x-rays and teeth removed in early pregnancy?
Pregnancy is such a crucial period for a woman that any ailment causes fear in them. They don’t want to go to doctors, fearing that the treatment will harm the child. What to do if you have a toothache and the pain becomes unbearable? There cannot be two opinions: only the dentist can make a decision on treatment. If it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis, the woman is offered to take an X-ray of the tooth. According to experts, it is undesirable to do this in the first three months of pregnancy. But at the discretion of the doctor, in exceptional cases, which include acute toothache during pregnancy, it is possible to perform x-rays at low power using a lead blanket.
X-ray of a tooth
Performing dental x-rays in pregnant women in the early stages for their safety requires compliance with a number of conditions, namely:
- the woman’s body is covered with a lead apron that does not transmit x-rays;
- the x-ray beam should be directed strictly at the diseased tooth;
- It is strictly forbidden to expose the gum areas adjacent to the diseased area to rays.
The amount of radiation received during an x-ray is comparable to 2 hours of exposure to the sun.
Application of anesthesia
The composition of modern anesthesia allows for local anesthesia of teeth for pregnant women. Every dental therapist is well aware of the special anesthesia used during treatment. Therefore, there are general recommendations for anesthesia that you should know:
- use anesthetic drugs that do not have a harmful effect on the health of the unborn baby. It is required to warn the dentist about the current month of pregnancy and your general health;
- use only local anesthesia so that the medicine does not enter the circulatory system;
- It is prohibited to use lidocaine as an anesthetic for pregnant women, due to the fact that the medicine can harm the normal development of the fetus: it slows down breathing and causes an increase in blood pressure.
Tooth extraction or prosthetics
In difficult cases, the dentist may recommend the pregnant woman to remove the diseased tooth if it cannot be treated or restored. This procedure does not pose any danger to the fetus. But you should be wary of hypothermia or overheating of the wound after tooth extraction, because... The inflammatory process of an open wound may begin. Therefore, the misconception that tooth extraction during pregnancy is contraindicated is just a misconception. As well as one more thing – dental prosthetics.
Modern dentistry allows for dental prosthetics, provided there are no complications or the presence of disease in the pregnant woman.
What are the dangers of a mother’s bad teeth?
The threat of a mother’s diseased teeth to her child is quite tangible. If a pregnant woman has bad teeth, this can lead to the following diseases in the child:
- The severe pain caused by an untreated tooth has a direct impact on the body of a pregnant woman. This impact has a direct bearing on the future condition of the child. Experts call this threat a psychotraumatic factor.
- Infections that enter the mother's body from a diseased tooth negatively affect the child's body. This can cause a wide variety of complications in the newborn.
- During toothache, intoxication can also occur. This happens due to periodontal damage. Intoxication is determined by elevated temperature, as well as indigestion and toxicosis. This can lead to hypoxia in the fetus, and in the mother to late gestosis.
- The use of prohibited drugs in dental treatment during pregnancy. If doctors give you an anesthetic injection and then offer to perform an application, you should ask what medicine they are going to use. Pregnant women should not use the following drugs:
- Lidocaine is a drug used for anesthesia. The consequence of taking this medicine is weakness in the body, causing dizziness and low blood pressure.
- Sodium fluoride - this drug is used to cure tooth decay. This medicine may cause tachycardia, which may adversely affect the development of the fetus.
- Imudon is a drug used to cure diseases in the oral cavity. The consequences of using this medicine are still unknown.
Traditional methods of treatment
If there is swelling due to a wisdom tooth cutting out or an infection, use special preventive baths. Decoctions of sage, chamomile, and chlorhexidine solution are excellent.
You can also try some other methods if your wisdom tooth is growing:
- Place a few drops of garlic juice on the affected area. Wait a couple of minutes and rinse your mouth.
- Rinse your mouth with a solution of furatsilin or soda.
- Apply ice to the outside of your cheek.
- Perform a massage.
What else to treat? Various applications and masks help a lot. For example, a mask made from raw beets. The grated vegetable is applied to the affected area for 20 minutes.
Another excellent folk option is tar applique. Take a small amount of birch tar and use it to brush your teeth at night. After a couple of days the problem will disappear.
Potato juice can cope with inflammation quickly. Take potatoes, wash them with a stiff brush, and douse them with boiling water. Then all that remains is to grate it and apply it to the problem area for 25 minutes.
An interesting recipe - a mixture of bergenia, galangal, clove spices and tooth powder. All components need to be taken and ground. Then she brushes her teeth in the morning for a couple of minutes.
You can prepare healing gum from lemon juice, mint essential oil, honey and beeswax. The mixture is heated on the stove until it becomes homogeneous. All you have to do is wait until it cools down, make lozenges, and you can chew.
A simple way is to rinse your mouth with 10-day old kefir. The product is diluted in the ratio of half a glass of water per glass of kefir. It is necessary to rinse the affected area with it as often as possible.
In the morning and before bed, you can rinse your mouth with mumiyo (take 3 g of the substance and dissolve in 100 ml of water). The duration of use of the product is about 21 days.
You can get rid of ulcers by rinsing your mouth with infusion of golden mustache. The leaves of the plant are ground and poured with boiling water. Sea salt is added to the mixture, after which you can rinse.
Applying heat to the affected area is strictly prohibited! This will only increase the spread of pathogenic bacteria. There is also no need to apply painkillers to the painful area to prevent irritation.
Dentist's decision
A pregnant woman should visit the dentist regularly, especially if she feels that her gums or teeth are not in order. Dental treatment in the early stages of pregnancy is usually quite safe, but whether it really is up to the doctor to decide. Only a dentist can choose the safest and hypoallergenic method of treatment depending on the trimester:
- In the first trimester, the child’s body develops, so any dental surgery, the use of many medications and anesthesia during this period are not recommended. Fetal development may be impaired. Folk remedies are used as pain relievers. During this period, only dangerous and rapidly developing diseases are treated.
- In the second trimester, the dentist can begin treatment of the oral cavity, but it is still better to postpone complex manipulations to the postpartum period. In the second trimester, you can resort to some types of anesthesia that will not harm the baby.
- The third trimester is the stage during which any intervention can cause premature birth.
Since dental interventions are not always welcome, many women turn to traditional medicine. Folk remedies based on herbal ingredients can indeed be safe during pregnancy, but not all recipes are so, and they are used more for pain relief than for treatment. Be careful when choosing and if your gums are swollen, first visit your doctor and ask him about contraindications.
Painkillers during pregnancy - how not to harm the baby
Experts prescribe various antiseptic solutions to pregnant women suffering from inflammation and pain. They perfectly eliminate various types of suppuration.
It is recommended to use such drugs as:
- Iodinol;
- Furacilin;
- Trachisan;
- Chlorhexidine;
- Tantum Verde, etc.
In some cases, various antiseptic and antibacterial tablets are prescribed, for example, Grammidin, Septolete, Hexalize and others. Using them several times a day will avoid rinsing. Doctors recommend using analgesics with caution. Meloxicam, Ibuprofen, Ketorol are selected individually.
Why do almost all experts not recommend using aspirin? It thins the blood and, accordingly, can increase bleeding.
Finlepsin should also be treated with caution. Tantum Verde and Tenflex should not be taken for more than a week.
Paracetamol is prescribed by almost all specialists. The presented drug is able to penetrate the placenta, but it does not harm the fetus. The tablets have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Nurofen is prescribed in moderate doses. The product is not used in the third trimester. It can reduce the amount of amniotic fluid.
Riabal and No-shpa do no harm. They reduce pain and spasms.
As for antibiotics, they are used only if there is a pronounced inflammatory process. It is not allowed to take the presented products for longer than a week. If the nerve is damaged and there is no pain, antibiotics are not prescribed.
Why do gum problems occur during pregnancy?
Gums can begin to bother a pregnant woman for many reasons, but the main ones include:
- Restructuring of hormonal levels - a decrease in the number of enzymes makes mucous tissues more vulnerable to the effects of microbes.
- Toxicosis is a change in microcirculation. It can have a negative effect on gum tissue.
- Vitamin deficiency , calcium, magnesium and iron deficiency has the most negative effect on the health of bone tissue.
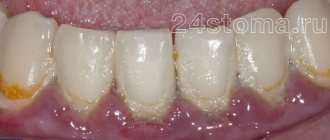
- Poor oral care can cause plaque accumulation, tartar growth, and the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
Many pregnant women refuse to use a toothbrush due to toxicosis and nausea, preferring rinsing. This does not completely clean the oral cavity and can lead to the development of inflammatory processes!
Features of gum treatment after childbirth
If a woman has a wisdom tooth coming out after childbirth or her gums are swollen for other reasons, she needs comprehensive treatment. First, you should visit your dentist. He will prescribe anti-inflammatory and antiseptic medications.
If there is no improvement, problems with the immune system can most likely be diagnosed. Then the specialist prescribes general strengthening medications that will not harm the baby.
After giving birth, you should definitely go on a special diet.
It is recommended to eat foods rich in vitamins:
- in the morning you can drink carrot juice;
- Corn, peas, beans, and bread should be included in the diet (they contain vitamin E);
- It is very important to eat cabbage, spinach, tomatoes and citrus fruits. They are high in vitamin C;
- Milk, rye flour and apples contain vitamin B.
For severe bleeding in the mouth, you can use special pastes and decoctions. They should contain sage, oak bark or chamomile.
Causes of gum pain during pregnancy
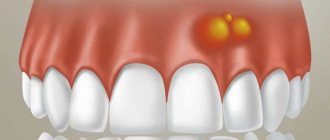
Pain in the gums in a pregnant woman can be caused by the following diseases:
- Stomatitis can affect several teeth or the entire oral cavity. It is expressed by tissue swelling, rash and redness.
- Periodontal disease is expressed by exposure of the tooth root, sensitivity to temperature changes and mechanical stress. The gums may itch and cause aching pain in the jaw.
- Periodontitis affects all tissues surrounding the tooth with inflammation. The gums are swollen and very painful, and periodontal pockets form. Plaque and hard deposits of tartar appear on the teeth. The bone structure is disrupted.
- Periodontitis is a consequence of untreated caries or pulpitis. The disease affects both gums and teeth. In the acute form, eating becomes difficult due to acute toothache when biting. In the chronic form, the gums ache and ache. If the disease has progressed to the granulating stage, then a fistula forms above the tooth, from which pus is released, which causes a lot of discomfort.
Also, toothache can occur due to insufficient oral hygiene or gum injuries, which can be divided into several categories:
- Mechanical - appear as a result of traumatization of the mucous membranes with solid food or any other harsh impact on the soft tissue of the gums.
- Chemical - occur as a result of a burn to the oral cavity with aggressive medications or an alcohol-based mouthwash.
- Thermal is a tissue burn that can be caused by carelessly consuming too hot drinks or food.
Unexpected pain in your gums can be caused by an incorrectly placed or ill-fitting dental filling or a crown that is too large.
For young expectant mothers between 20 and 30 years of age, the pregnancy period may coincide with the eruption of wisdom teeth. This can provoke the development of pericoronitis and swelling. To eliminate pain and discomfort, you should visit the dentist, where the doctor will take all necessary measures.
Prevention of oral diseases
To prevent inflammation of the gums around the tooth, various preventive measures should be taken.
The following measures will help prevent bleeding:
- Performing a gum massage using a soft brush;
- Taking vitamins for expectant mothers;
- Reducing intake of sugary foods;
- Timely treatment of caries;
- Treatment of mouth diseases;
- Visiting the dentist once every trimester;
- Drinking high-quality clean water;
- Diet;
- Regular dental care.
If you follow the rules presented, you will not have to look for information on forums on how to deal with the problem. In addition, you will prevent the occurrence of diseases both in yourself and in your baby.
Diseases that require treatment during pregnancy
Once in the dentist's chair, if you are taking medications, let them know. This will help you choose the safest treatment tactics.
During pregnancy, adhere to hygiene, use toothpastes containing fluoride, and no toothpastes with a whitening effect!
If you have tooth decay?
Caries can be treated simply, without painkillers, but the process should not be started, even if the pain is tolerable, otherwise tooth decay will reach the pulp and then removal of the nerve cannot be avoided, therefore, more serious treatment. In the process of treating caries, there are no restrictions on the fillings used; you can use conventional or photopolymer fillings.
Often one of the reasons for the development of caries during pregnancy is frequent toxicosis. For example, using toothpaste with flavoring additives when brushing your teeth can provoke vomiting. And the acid contained in vomit is dangerous for tooth enamel. Therefore, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with plain water as often as possible.
Gingivitis or stomatitis
Inflammation of the gums (gingivitis) during pregnancy can occur in a hypertrophied state due to constantly occurring hormonal imbalances in the pregnant body. If gingivitis occurs, you must immediately seek professional help from a dentist; under no circumstances should you self-medicate or use folk remedies.
. Ignoring the problem will lead to a complex form of periodontitis, which will negatively affect not only the health of the mother, but also the health of the child. Thus, recent studies have shown that periodontitis poses a threat of miscarriage or even the occurrence of pathologies in newborns.
In case of a quick visit to the dentist, a mouth rinse will be prescribed, an application to gradually relieve inflammation, and the doctor will carry out professional cleaning of the oral cavity.
The weakened immunity of a pregnant woman contributes to the occurrence of stomatitis in the oral cavity. Swelling and small ulcerative lesions bring discomfort in the oral cavity, so it is better to consult a dentist. Most likely, he will recommend a spray that is harmless during pregnancy.
Some statistics...
45% of pregnant women come into contact with a problem such as gingivitis. Their gums swell and bleed, discomfort and bad breath appear. For most of them, these problems go away on their own after childbirth if they followed the recommendations of specialists.
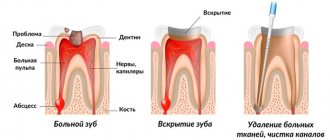
Periodontitis or pulpitis
Pulpitis is a direct consequence of advanced caries, which leads to inflammation of the nerves, and periodontitis is the process of inflammation around the root tissues. In both cases, the resulting inflammation must be treated using anesthesia and x-rays. True, modern devices have low-power radiation, which allows treatment to be carried out practically without causing harm. In such cases, it is better to contact paid dental clinics, or clinics that have modern equipment and consumables.
Etiology of the disease
The reasons for the development of the disease are hormonal changes in the body. Symptom: “the gums are swollen” during pregnancy indicates gingivitis, which is a consequence of changes in the levels of progesterone and gonadotropin.
These hormones are synthesized by the fetus or placental tissues. Only immediately before childbirth the hormonal levels are normalized, which has a beneficial effect on the condition of the gums. A slight exacerbation of oral diseases can also be observed during breastfeeding.
Dentists identify the following risk factors:
| Predisposing factors for the development of gingivitis for pregnant women | Clinical picture |
| Activation of pathogenic microflora that is part of dental plaque. |
|
| Chronic vitamin deficiency. |
|
| Early toxicoses. |
|
The first symptoms of the pathology, as a rule, form already in the first trimester and bother the patient until the birth of the child.