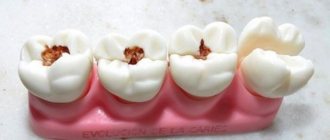
Hyperplasia as the main cause of pathology development
Why does this phenomenon occur when gums grow on a tooth? Most often this is due to the proliferation and enlargement of its cells. Scientifically, this process is called hypertrophy or hyperplasia (i.e. proliferation and increase in volume of tissue). The problem in most cases occurs against the background of an inflammatory process occurring in the oral cavity or metabolic disorders and hormonal imbalances in the body.
On a note! Hyperplasia or hypertrophy is a pathology in which soft tissue cells begin to grow uncontrollably, and the gums themselves can become inflamed and increase in size, they can begin to “crawl” onto the crown, partially or even completely (in the most advanced situations) block it.
Signs that a wisdom tooth is growing
The main symptoms of pericoronitis are accompanied by swelling of the gums, redness, aching pain and fever. These signs are the first signals of complications, and you cannot expect that the problem will go away on its own. There is no point in suffering and numbing the pain with medications; it is better to immediately visit the dentist. Otherwise, an inflammatory process will begin, and this is very dangerous for the oral cavity. The wisdom tooth itself rarely erupts painlessly; in most cases, the help of a specialist is required. Otherwise, the infection may spread beyond the jaw, and then long-term treatment will no longer be possible.
Prerequisites for the development of hyperplasia
Various reasons can serve as prerequisites for accelerated and enhanced cell division:
- excessive accumulation of hard tartar and bacterial plaque above and below the gums,
- malocclusion: in such a situation, some teeth and, accordingly, the soft tissues and mucous membrane that surrounds them are subject to increased stress and pressure, they are constantly injured. The nutrition and blood circulation of tissues is disrupted, as a result of which their cells can begin to grow rapidly,
- endocrine diseases,
- genetic predisposition and heredity,
- long-term use of steroid hormonal drugs, antidepressants, anticonvulsants,
- hormonal imbalance during pregnancy, after childbirth, during menopause in women, changes in hormonal status in adolescents during puberty1,
- acute vitamin deficiency: hyperplasia often occurs due to a lack of vitamin C,
- traumatic damage to the mucous membrane due to incorrectly installed fillings, artificial crowns or braces,
- teething,
- leukemia
Main diseases characterized by tissue hyperplasia
Fibrous or hypertrophic gingivitis
Between the teeth there are gingival papillae, which during the development of fibrous gingivitis begin to gradually increase in size, they become denser and grow. In this case, the mucous membrane remains painless for a long time, and there is no bleeding.
Read more about all types and symptoms of gingivitis in a separate article on the website.
The disease develops against the background of poor oral hygiene and the accumulation of a large amount of plaque; it can appear due to poor-quality prosthetics and constant trauma to the mucous membrane. People who have hormonal imbalances or gastrointestinal diseases also encounter fibrous gingivitis. The disease often occurs in both adults and children.
Important! A growth over a tooth is not always associated with hyperplasia; it can be nothing more than a gumboil, abscess, fistula or cyst, indicating advanced dental diseases. Most often, such manifestations are very painful, they are white in color, because... pus accumulates in them.
Fibromatosis
This is a hereditary disease and therefore often manifests itself in childhood. It is characterized by the growth of individual areas of the gums and proceeds very slowly. The color of the affected tissues is usually no different from healthy ones; they are painless.
The disease occurs mainly in the frontal area of the smile, and soft tissues can grow so much that they cover the crowns by more than 2/3. If fibromatosis is not treated, it is fraught with destruction of interdental septa, osteoporosis, and a severe violation of the aesthetics of the smile.
Fibropapilloma
If the gums have grown onto the crown, then a disease such as fibropapilloma may be to blame. This is a benign tumor. The tumor is hard to the touch, but painless. Its appearance in childhood is more dangerous, because can lead to disruption of the formation, growth and eruption of permanent elements.
Epulis
Epulis, like fibropapilloma, is a benign formation. It has a mushroom shape, because the tumor grows on a stalk. Appears as a result of chronic irritation and tissue injury. The most common location is the area of the incisors or canines. If the tumor is not removed, it can lead to pathological mobility and tooth loss.
Why do the necks of teeth become exposed and how to restore gums?
Quite often, patients come to me with complaints of increased tooth sensitivity. It is impossible to drink cold water in the summer without eating ice cream.
Typically, gum recession is to blame. Let's figure out what it is and what can and should be done to enjoy delicious ice cream without discomfort.
Gum recession is the exposure of the neck of the tooth, which is accompanied by aesthetic discomfort and increased sensitivity.
Why does gum recession occur?
Gum recession occurs for many reasons.
The main reasons for a recession are:
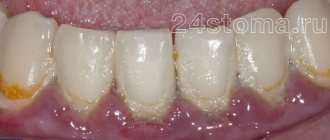
- Hygiene. Plaque and tartar that are not removed in a timely manner lead to “squeezing” of the gums and exposure of the neck of the tooth. Also, overly aggressive poor home hygiene leads to the same consequences.
- Pathological bite. When the tooth is positioned incorrectly, when the tooth is tilted in one direction or another, or when there is severe crowding, the periodontium (the complex of tissues surrounding and holding the tooth) is overloaded, which leads to a reduction in the gums and exposure of the tooth root.
Treatment of gum recession.
A very important point is that during recessions, not only gum loss occurs, but also loss of BONE TISSUE in the tooth area. Based on this, if you do not pay attention to this problem in a timely manner, it can lead to further mobility and loss of teeth.
Surgery is the main treatment for gum recession. Thanks to different techniques, the gingival contour is restored and the tooth root is closed. If the cause of recession is associated with a pathological bite, then in such a situation it is necessary to first carry out orthodontic treatment and, after completion, resort to surgical methods. In some cases, with proper orthodontics, the recession is closed without resorting to surgery.
Gum recession classification.
Depending on the severity of the current, recessions occur
- Mild form - the gums recede no more than 3mm.
- Medium shape - the gums drop by 3-5mm.
- Severe form – the gums recede by more than 5mm.
With regards to the coverage of the oral cavity, the pathology can have both local and generalized distribution.
Treatment of gum recession.
The main essence of the surgical technique is taking your own tissue (from the palate or the tubercle of the upper jaw) and suturing it in the defect area, thereby increasing the volume of soft tissue.
The relevance of this technique remains in both localized and generalized forms. Its advantage is considered to be effective restoration, since the materials are 100% identical. The only drawback of the manipulation is the feeling of slight discomfort for some time at the site of donor tissue collection. There are also cases when the flap does not take root in the transplanted area. As a rule, this happens due to poor hygiene and failure to follow the recommendations given by the doctor.
A favorable prognosis ensures timely seeking qualified help. Therefore, you should not put off your visit to the dentist, since the outcome of treatment depends on this.
How to stop gum recession!
- if there are dental diseases and other injuries to the oral cavity, then it is necessary to treat them in a timely manner - this applies to a greater extent to caries, which patients often bring to an advanced state (becomes complicated forms);
- regularly visit the dentist for a preventive examination: as you know, early diagnosis allows you to quickly eliminate the problem, without radical intervention, without waiting for serious health problems;
- monitor the condition of the gingival margin, avoiding injury and excessive bleeding;
- correct the bite in a timely manner;
- do not forget about strengthening tooth enamel with the help of remineralizing treatment;
- pay special attention to hygiene - effective brushing of teeth, choice of brush and toothpaste.
One of my works:
Preparation (closure of recession) was carried out before orthodontic treatment. After orthodontic treatment, cosmetic removal of remaining recessions is planned.
Why does the problem appear in children and when should you see a doctor?
The situation when gums grow on a child’s tooth most often occurs during the period of teething, as well as the change from a primary bite to a permanent one. During eruption, the mucous membrane swells and increases slightly in size, because it is irritated, blood circulation increases in it, but in this case we are not talking about hyperplasia. However, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the child’s oral cavity over time.
You should consult a doctor in the following situations:
- if 2-3 months after the crown “hatched”, it did not come out completely, and most of it remains under the gum or soft tissue hangs over it, partially covering it,
- the baby tooth did not fall out during the change of bite, but gums are growing on it: perhaps a permanent element is “hiding” under the formed tubercle, which did not have enough space, and it began to make its way in a different direction or into the second row,
- the growth is filled with white contents, and the child has a bad smell from the mouth: perhaps we are talking about the presence of advanced dental diseases, which are complicated by a fistula, abscess or cyst.
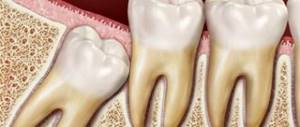
Gum growth on wisdom teeth
There are situations when gums have grown on a wisdom tooth. And this is not related to the phenomenon of hyperplasia. If the third molar has only recently begun to erupt outward, one of its cutting edges has already appeared, and suddenly you feel pain, bad breath appears, and upon examination, inflammation, swelling of the soft tissues and their overhang over the tooth are discovered, then you probably have pericoronitis began.
Pericoronitis is an inflammation of the gingival hood over the third molar. The disease develops due to the fact that small pieces of food begin to get into the gap between the gum and the “eight” that has not fully penetrated, which rot because they are difficult to remove.
For more information about what pericoronitis is and how it is treated, read the feature article on the website.
Main features of teething
The average age when wisdom teeth come in is from 17 to 23 years. Of course, there are exceptions when this happens at the age of forty. For each person, this process occurs differently: for some, the tooth erupts without any complications, for others - incorrectly and with complications, and for others it does not erupt at all. It all depends on the anatomical features. There are four types of wisdom teeth position:
- Buccal-angular. This situation is common - the tooth grows with an inclination towards the cheek.
- Lingual-angular. It is also quite a common occurrence that a tooth grows with an inclination towards the tongue.
- Vertical. Or eight. This is the most correct position for the growth of wisdom teeth.
- Horizontal. And this position is the most incorrect and is fraught with complications.
The last type is very difficult, since the horizontal position interferes with free eruption. As the tooth grows, it grows into its “neighbor” and begins to destroy it. Trauma and inflammation of the gums occur, which causes a lot of suffering to the person. In this case, only surgical intervention will help, that is, removal of the wisdom tooth.
If a broken tooth is healed
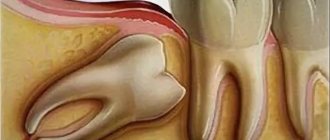
Situations where a tooth broken at the very root is overgrown with gums are not uncommon. It can break due to injury or collapse due to advanced dental disease. After this, many people are in no hurry to remove the root, and in some cases it gradually grows over from above (this process can last several years), and then does not bother or hurt for a long time. However, sooner or later, unpleasant sensations still appear: it becomes painful to chew, overgrown tissues swell and are constantly injured.
“My gums have grown on my back tooth, which broke off three years ago. I completely forgot about him, because... It didn’t give me any trouble, only sometimes after cleaning it would scavenge, but I didn’t attach any importance to it. All this was revealed during an examination at the dentist, when I went there with a completely different problem. In principle, the doctor decided everything quickly: he opened this growth and removed the root, then put stitches, but then it healed for a very long time and painfully. It was also very disappointing to hear that if I had contacted him immediately after the tooth was chipped, it could have been restored, but I immediately decided for myself that it was lost. That’s it!”
Varvara, review from 32top.ru
Remember that if a tooth is broken, then either its timely removal or restoration and prosthetics is necessary, because a serious inflammatory process can begin under the overgrown tissues or at the root, which can spread to the jaw, cheek, can develop deep into the body, lead to periostitis and osteomyelitis.
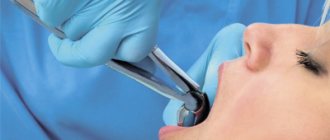
How is an overgrown tooth removed?
Root extraction is a fairly common dental operation. It is performed under local anesthesia and, as a rule, does not cause complications. An overgrown root cannot be removed using traditional methods, since it is completely covered with gum tissue and there is no access to it. Treatment is carried out in several stages:
- Examination by a dentist, x-ray examination. X-ray allows the doctor to see the size, position, and depth of the root. The dentist assesses the risk of damage to adjacent teeth during surgery.
- The operation is performed under anesthesia. First, the doctor makes an incision in the gum, providing himself with access to the root. After this, the root is removed and sutures are applied.
- During the rehabilitation period, the doctor selects anti-inflammatory drugs and agents that accelerate wound healing.
The process of removing an overgrown root is individual in each case. The complexity of the operation is influenced by many factors:
- Tooth location. Removal of roots on the upper and lower jaws has its own characteristics and is carried out using various dental instruments.
- The degree of damage to the root and nearby tissues, the presence of fragments. Sometimes, for a successful and as painless removal for the patient as possible, the root is destroyed by a drill into several parts. Separation is required in cases where the tooth has several strong, deep roots. As a rule, after destruction, individual parts are easily removed using ordinary tools.
- The presence of pathology in the surrounding bone tissue, inflammation of the gums.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
If there is no inflammation, the gum is carefully separated from the alveolus and the tooth is removed using suitable dental forceps. The inflammatory process “melts” the surrounding tissue, so for successful removal it is enough to provide access to the root by making an incision in the gum. Application of forceps does not require labor, and there is no need to additionally separate the gingival tissue from the alveoli. In difficult cases, elevators are used.
How long does the gum “grow” and the stages of development of hyperplasia
Pathology can develop slowly if it is caused by fibromatosis, epulis or fibropapilloma. And it can develop more rapidly if it occurs against the background of gingivitis.
As for the stages of development of hyperplasia, doctors identify the following:
- first stage: the gingival papillae thicken and thicken, while there are no other alarming signs,
- second stage: soft tissues grow and can cover up to half of the crown. Due to the volume, tissues are easily injured during oral hygiene and when chewing food, they can begin to bleed,
- third stage: the most rare stage. The tissues grow so much that they can even cover the cutting area of the crown. Granulations appear on the affected areas.
If you break off a tooth, gum growth may take several years.
What complications do impacted teeth cause and why do they need to be “extracted”?
It is difficult for the patient to immediately understand what danger “hidden” teeth can pose, but it is really serious.
Semi-retinated teeth cause inflammation of the “hood” with which they are covered and adjacent tissues, and this provokes purulent inflammation.
Fully impacted teeth that lie in the jaw can behave like a foreign body; they put pressure on neighboring teeth, causing their displacement and a number of other problems.
In this case, the patient experiences pain and fever in case of inflammation, a feeling of pressure and discomfort in the jaw, neuralgia or numbness of part of the face.
If we list the diseases that can result from impacted teeth, it will become clear that this is a real “time bomb” that can detonate at any moment.
What diseases can be caused by an impacted tooth:
- periodontal cyst,
- caries of neighboring teeth and their roots,
- pulpitis,
- pericoronitis,
- periostitis,
- periodontitis,
- purulent lymphadenitis,
- inflammation of the trigeminal nerve,
- odontogenic sinusitis,
- abscess,
- phlegmon,
- resorption (resorption) of the roots of adjacent teeth,
- bad habits: mouth breathing, infantile swallowing, inserting the tongue into a dental defect,
- problems with biting food,
- malocclusion, displacement of interdental contacts, crowding of teeth.
Signs and symptoms of hyperplasia
Those who have this problem rarely experience pain right away. But almost all patients notice a visual violation of the aesthetics of a smile, because the gums become voluminous and loose, which, as a rule, is the reason for visiting a doctor.
Discomfort and pain appear after the tissues have grown significantly, and they involuntarily have to be constantly injured during hygiene procedures and eating food. Another sign is the appearance of bad breath, which does not go away after careful hygiene or quickly returns again.
Consequences and complications if the pathology is not treated
Many patients see overgrown gums as only one problem – a significant disruption to the aesthetics of their smile. However, this is not so: if the pathology is not eliminated and it is allowed to progress further, then this is fraught with serious complications for the health of the oral cavity and the body as a whole.
If left untreated, the patient may develop degenerative diseases of periodontal tissues, leading to the destruction of the interdental septa and supporting ligaments that hold the teeth in the sockets. You may lose your teeth much earlier than you would like.
Hypertrophied tissues are subject to constant trauma, which is why any benign formation can sooner or later become malignant. Another common complication is osteoporosis.
For children, the lack of treatment is fraught with disruption of the formation, as well as the timing of the loss of milk and the eruption of permanent elements.
If a single growth appears on the gum, this may not always indicate hyperplasia or hypertrophy. Some people mistake the growth for a fistula, cyst, or abscess. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner for these pathologies, the purulent contents from these neoplasms can spread throughout the body, causing damage to the cardiovascular and circulatory systems, gastrointestinal diseases, sepsis and even a brain abscess.
Methods of treating pathology in dentistry
The most common method of removing overgrown tissue is surgical excision using a scalpel or laser. Scientifically, this surgical operation is called gingivectomy. The procedure is performed under anesthesia.
About the indications, types and complications after gingivectomy - in the feature article on the website.
If there are few damaged tissues, then doctors may suggest their removal using cryodestruction, when under the influence of low temperatures they die off on their own over time.
If tissue proliferation is accompanied by an inflammatory process, then electrophoresis and darsonvalization may additionally be prescribed.
In addition to excision of excess tissue, treatment should be carried out aimed at eliminating the cause that provoked the development of the pathology. If the cause is a malocclusion, then the patient needs to see an orthodontist, who will prescribe devices to correct the position of the dentition. If there is a fragment of a tooth inside the overgrown gum, then it is necessary to remove it or use prosthetics, if the situation allows. In case of internal diseases of the body, the patient will be referred to specialized specialists - endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, cardiologist, etc.
Dentists are required to sanitize the oral cavity and remove hard and soft bacterial plaque.
Treatment
How to get rid of a lump that appears on the gum? Treatment is based on eliminating the causes and symptoms of the underlying disease.
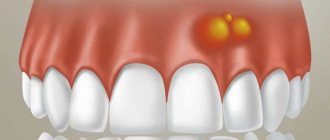
Fistula.
When a fistula occurs, the main goal is to eliminate the source of infection and remove the pus. To do this, rinse the mouth with a solution of soda and salt in a 1:1 ratio (half a teaspoon per glass). The procedure is repeated daily every 1.5-2 hours until the seal completely disappears.
Exostosis.
Exostosis is treated only surgically if there are indications for removal of the lump: pain, rapid growth, or the presence of a cosmetic defect.
During surgery, overgrown areas of tissue are removed with a chisel, then the bone is smoothed out. Worth knowing!
In children, exostoses often disappear on their own over time, so there may be no need for surgery.
Epulis.
Treatment of epulis begins with eliminating the causes that caused it - removing tartar, treating caries, adjusting prosthetic structures. Then observation is carried out and, if necessary, surgical excision of the cones to healthy tissue.
Periodontitis.
To treat periodontitis, the filling is removed from the diseased tooth, the canals are sanitized and widened (to allow pus to escape) and the affected periodontal tissues are removed. Antiseptic treatment is carried out and antibiotics are prescribed. Then a temporary filling is placed, which is later replaced with a permanent one.
Periostitis.
Treatment for periostitis is similar to the sanitation of periodontitis, with a difference in the duration of the procedure due to the more serious consequences of the disease. The tooth is unfilled, the canals are cleaned and expanded. Medicine is placed under the temporary filling and it is removed after 2 months. The tooth is washed with antiseptics, then the temporary filling procedure is repeated again. When the symptoms of the disease are eliminated, a permanent filling is applied; if there is no result, the tooth is removed.
Periodontitis.
Treatment takes place on an outpatient basis. The doctor removes tartar and performs antiseptic treatment of dental pockets. For serious lesions, treatment is performed surgically.
Gingivitis.
Gingivitis can be treated at home, using ointments, gels and rinses prescribed by your doctor.
But the main thing is proper oral hygiene. Important!
Treatment of diseases, depending on their complexity and nature, can be carried out on an outpatient basis or at home. One thing is certain: only a specialist should make a diagnosis and prescribe procedures (even at home!)!
Recovery period after surgery
If the gum has grown on the tooth, then now you know what to do - you need to contact a dentist who will prescribe adequate treatment.
Since treatment for hyperplasia involves surgical manipulation, there will be a recovery period after it, taking from 5-7 to 10-14 days. At this time, you need to follow all the doctor’s recommendations: take prescribed anti-inflammatory and wound-healing agents, rinse with antiseptics, and use painkillers as pain occurs.
During the rehabilitation period, it is important to exclude “irritating foods” from the diet: spicy and salty, cold and hot, solid foods. And, on the contrary, you need to diversify your diet with foods rich in vitamins C, E, B, A, calcium and phosphorus.
To care for the oral cavity, you need to use a brush with soft bristles and a non-abrasive toothpaste; you should avoid using an irrigator for a few days.
Is it possible to get rid of the problem on my own?
Some people use decoctions of medicinal herbs and plants (chamomile, oak bark, sage and others), as well as solutions to relieve gum inflammation (such as Chlorophyllipt or Stomatophyte) to get rid of the problem. However, you need to understand that hyperplasia cannot be cured by rinsing. This measure will not reduce the volume of overgrown tissue, but will help relieve signs of the inflammatory process and alleviate the condition during teething, and is also well suited as a concomitant therapy after surgical excision of excess gum tissue, which is carried out in a dental office.