Symptoms
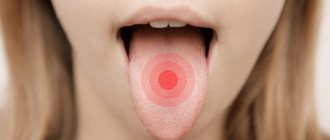
At the initial stage of the disease, swelling and other signs of inflammation are insignificant. Respiratory dysfunction does not develop in patients. Clinically, uvulitis is manifested by a feeling of a foreign object in the throat, a change in voice, and discomfort when swallowing and speaking. The tongue in the throat enlarges and swells slightly.
The general condition of the patients remains satisfactory. Moderate and severe uvulitis manifests itself with more pronounced clinical symptoms. The patient experiences:
- Hyperemia and swelling of the uvula,
- Hanging it to the root of the tongue,
- Swelling and tenderness of the soft palate,
- Fever,
- Weakness, myalgia, arthralgia,
- Dysphonia,
- Hypersalivation,
- The urge to vomit
- Rhinitis.
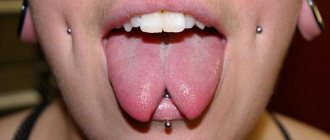
photo of an inflamed tongue in the throat
Symptoms of uvulitis occur when eating food, coughing or sneezing. Persons who have undergone adenoidectomy and tonsillectomy are most susceptible to developing the disease.
The inflamed uvula swells in the throat, becomes red and increases significantly in size. The uvula appears white when coated. In the absence of timely medical care, it can block the airways, which will lead to the development of asphyxia.
Diagnosis of uvulitis involves conducting a pharyngoscopy examination. In patients, the uvula is enlarged, swollen, and hyperemic. If it reaches the root of the tongue, a gag reflex occurs. In severe cases, the tip of the tongue becomes bluish, becomes covered with a false film, or becomes ulcerated.
Tongue diseases
When the organ itself is in a painful state, its appearance, thickness, and size change:
- Glossitis is characterized by swelling of the tongue, the surface becomes smooth, severe redness is observed, pain is felt when moving, and the organ becomes inflamed.
- In geographic language, the symptoms are similar, but their manifestation is spotty, and the lesions can change location.
- Diagnostics establishes macroglossia disease with an abnormally enlarged tongue.
- Sometimes a small ulcer or white raised spot appears on the surface. This is an alarming sign, which in some cases indicates oncology (leukoplakia). A tissue biopsy of the spot is performed; if this is not done, cancer cells will develop in the surrounding gums, cervical lymph nodes and jaw. Timely detection of oncology cures cancer completely.
- Sometimes elongated tubercles appear on the surface, which are called hairiness; the tongue has an unsightly appearance, which indicates insufficient cleaning of the surface.
Causes of tongue diseases
Hairiness of the organ and its unnatural color can be caused by malicious use of tobacco , taking antibiotics or lack of oral hygiene.
For these reasons, bad breath occurs. Sometimes the tongue becomes sick simultaneously with diseases of the body, for example, candidiasis, lupus erythematosus, syphilis or psoriasis. Glossitis occurs as a result of a lack of B vitamins, which is caused by poor diet or impaired metabolism. Glossitis is manifested by superficial or deep tissue inflammation, the magnitude of which depends on the degree of the disease. It can be caused by disruption of the capillaries of the tongue and mucous membrane, which occurs due to organ injuries or burns.
Tongue ulcers , which do not have an oncological nature, appear with scarlet fever, other similar infections, or an overdose of toxic drugs. Herpes simplex entails ulcerative lesions on the surface of the organ.
An increase in size is caused by internal hypothyroidism (cretinism), Down's disease, a surge in growth hormones due to dysfunction of the pituitary gland, and amyloidosis. Glossitis or even leukoplakia can occur when the edges of the organ are irritated from wearing incorrectly fitted dentures, a broken edge of a tooth, cigarette abuse, and sometimes this is a manifestation of HIV. Cancers of the tongue appear most often in smokers, if this is supported by the joint intake of alcoholic beverages.
Symptoms
In addition to the above manifestations of tongue diseases, the following symptoms are observed:
- the abnormal shade may not be clearly expressed, but in some cases the organ has a bluish, brown or almost black color;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- copious uncontrolled secretion of saliva;
- difficulty swallowing due to large size or pain;
- immobility of the tongue.
What is the danger?
The uvula protects the respiratory organs from food particles entering them, distributes warm air, activates processes provoked by the gag or cough reflex, and participates in spoken speech. Acute processes of inflammation of the uvula affect the surrounding soft tissues of the oral cavity, which is not just accompanied by unpleasant sensations, but sharply worsens the general physical condition of the patient and provokes breath holding. Ignoring the pronounced symptoms of the disease can cause asphyxia.
Swelling of the throat and tongue can provoke a number of negative changes in the body:
- Sore throat and fever, weakness in the body - what could it be? What to drink for these symptoms
- difficulties in speaking;
- clogging of the respiratory system with food particles (this case requires an immediate response and can lead to respiratory arrest);
- infection and bacteria of the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx;
- constant unpleasant feeling of nausea, gag reflex;
- inflammation of both tonsils.
Important: swelling of the nasopharynx and palatal tongue is life-threatening and therefore requires prompt medical attention.
Preventive and diagnostic measures
Prevention consists of careful treatment of the horizontal and lateral surfaces of the tongue when brushing your teeth. many types of brushes on sale , from which everyone can choose the product at their own discretion.
After eating, it is recommended to rinse your mouth. For a professional examination, you should visit your dentist once a year. Excessive consumption of strong drinks and heavy smoking harms not only the tongue, but the entire body as a whole. To diagnose a particular tongue disease, it is enough to examine the patient and pay attention to the history of his diseases. If it is necessary to exclude the oncological nature of organ changes, a biopsy is performed.
When should you see a doctor? Which one do you need?
If the uvula is very swollen or lengthened, the patient should immediately seek help from a specialized doctor. Such a specialist is an otolaryngologist who will conduct a diagnosis,, if necessary, prescribe additional studies, make a diagnosis and choose a therapeutic tactic.
As a rule, such patients need urgent treatment and can be placed in a hospital, where in case of fulminant asphyxia, qualified medical care will be provided and possible complications of the disease will be prevented.
- Causes of joint pain due to tonsillitis
Most often, the cause of inflammation of the palatine process is an infection, but there are cases when this condition is a symptom of another disease - then the ENT doctor gives the patient a referral to another doctor.
Treatment of tongue diseases
In most cases, the disease goes away if irritating factors that lead to changes are excluded. In other cases, symptoms are relieved when the underlying disease is treated. For example, if there is a lack of vitamins, a comprehensive intake of them is prescribed, and changes in the diet are recommended. After contacting the dentist, the patient adjusts the dentures or files off the rubbing edges of the tooth.
The resulting discomfort is relieved by rinsing with a concentrated salt solution, which helps heal wounds. There are appropriate antiseptic drugs that alleviate the course of the disease. If the infection is infectious, the doctor prescribes antibiotics or antifungal agents; cancerous lesions require surgery and then radiation therapy is prescribed. You should consult a specialist if the symptoms of the disease do not go away within several days or more.
Main causes of uvulitis
In a healthy state, a person does not feel the small tongue. But when it becomes inflamed, it is impossible not to notice it. You should not ignore unpleasant symptoms, because there can be many reasons for such a pathology:
- viral and bacterial infections of the upper respiratory tract,
- dental problems and jaw pathologies, the presence of implants and crowns,
- acute and chronic tonsillitis,
- peritonsillar abscess,
- cystic and tumor formations of the soft palate,
- angioedema,
- sinusitis, rhinitis, sinusitis,
- vegetative-vascular disorders,
- mental pathologies in the acute phase,
- seasonal, household or drug allergies,
- mechanical damage from solid food, sharp objects,
- burns of the mucous membrane of the throat and larynx,
- influence of irritating substances,
- drinking alcoholic beverages and constantly smoking,
- heavy snoring during sleep.
The tongue in the throat may become swollen due to an infection of the ENT organs, when the inflammatory process from the tonsils and throat spreads to all soft tissues.
As you can see, the enlargement of the uvula is not always associated with direct causes, which means that diagnosis is carried out on the basis of many factors. First, the doctor examines the oral cavity to detect a foreign object, as well as the level of swelling. Rapid swelling requires emergency medical attention, otherwise it will lead to suffocation and death in a matter of minutes. This is especially true for children, who cannot always formulate an adequate complaint, and their illnesses progress very quickly and acutely.
The tongue in the throat may become swollen due to an infection of the ENT organs, when the inflammatory process from the tonsils and throat spreads to all soft tissues. In this case, the doctor must determine the disease and its nature. After diagnosis, a treatment regimen is selected - at home or in a hospital. It is best to treat a child with uvulitis in a hospital under the 24-hour supervision of a doctor.
What's wrong with your tongue? (10 photos)
Author: ScientaeVulgaris
October 25, 2021 10:12
Community: Facts
Tags: scientae vulgaris history history of medicine medicine popular science rare diseases
2234
10
Why, when there are tests, MRI, and so on and so forth... why do you need to stick your tongue out at a smart and adequate auntie every time and breathe your borscht with garlic and other folk remedies into her?
Stick out your tongue and say “PaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaYYYYYYYYY------.” A tired phrase that seemed outdated and useless. Well, it seems like why all these fetishes - show me, let me smell, take off this, get that, breathe in this, don’t breathe in that. Well, why? In an era when ultrasound of the prostate under VHI is easier than finding salmonella in eggs. Why, when there are tests, MRI, and so on and so forth... why do you need to stick your tongue out at a smart and adequate auntie every time and breathe your borscht with garlic and other folk remedies into her? But chick, it’s necessary! Glossitis (inflammation of the tongue) is not like a cow licking the salt with its tongue. This is science. Medicine. Visual diagnostics and the primary means of determining your speedy end. Meet and lick: a visual guide to glossitis from ScientaeVulgaris.
0
See all photos in the gallery
Sweet strawberry for breakfast. Perhaps the phrase “strawberry” or “raspberry tongue” evokes erotic associations in you, but there is much more hidden behind it than just a beautiful fetish. “Strawberry tongue” or “raspberry tongue” is a type of glossitis when the mushroom-shaped papillae, which are responsible for your sense of sweetness, begin to grow in numbers of up to 1000 pieces. They themselves are terribly interesting guys. They consist of taste buds, and each taste bud consists of supporting cells and taste receptors. When you chew a chocolate bar, it dissolves in saliva, and along with it enters the taste buds through the pores and excites the chemoreceptors. The latter generate a nerve impulse that is transmitted along the afferent nerve fibers of the facial nerve to your brain, which, having received a feeling of sweetness, releases all sorts of endorphins from you, and somewhere at the other end of the body one sweet ass becomes a little happier. The entire bulb lives for 10 days and during this time it completely renews its cell composition.
0
So, strawberry tongue is when the tongue itself turns red, and the papillae, instead of renewing on schedule, begin to divide and divide and grow and divide. And it turns out to be a strawberry. Such beauty can be seen, for example, in early scarlet fever or Kawasaki disease, or in toxic shock syndrome. It could also mean you have a vitamin deficiency. A glossy, bright red tongue is one sign of iron or B12 deficiency. They are necessary for the maturation of these same papillae on the tongue. According to Naomi Ramer, DDS, an oral and maxillofacial pathology specialist at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, “If you don't get enough of these vitamins, you lose those papillae—they thin out, your tongue becomes smoother.” And the remaining papillae are more noticeable. Here's a berry in your mouth. In severe cases, it will cause severe pain when drinking hot liquids and spicy foods. Vegetarians especially often boast of B12 deficiency, since we consume large amounts of this vitamin from meat. If you notice that your entire tongue is strawberry red in color and you are a vegetarian, go to the doctor and try to clarify your diet parameters. Marked vitamin deficiencies can also be associated with an autoimmune gastrointestinal disease in which the stomach does not absorb vitamins. For example, studies of Crohn's disease have shown that about 60% of patients have various oral manifestations of the disease, including cheilitis, oral ulceration, fissures and glossitis, and this may be the first sign of the disease in 5-10% of all cases. Black tongue. If we omit the version with the dialect of Mordor, then, perhaps, this is the most spectacular thing that you can see in the mirror. From coal-black to brown-bear, covered with long hair, frighteningly standing out against the background of a rapidly pale face. Beauty! In fact, it's too early to faint. For the most part, it is such a complex phenomenon that it is generally accepted that it has no clear etiology. Simply put, it could be anything. The most common thing is lack of hygiene. The same papillae, different types of papillae on the surface of the tongue, grow throughout our lives.
0
For example, the most numerous are filiform papillae, scattered throughout the tongue. In front, by the way, they are the longest - up to 2.5 mm. They do not feel anything and are a protrusion of the mucous membrane of the nipple, covered with keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium. Why do we need them? Well, for example, they function as organs of touch and help retain food on the tongue. You will understand this principle if you catch your cat and force him to lick something. In carnivorous and ruminant animals, such nipples are much more pronounced - they are visible visually, and if the cat starts licking you, you will quickly understand the species difference between your papillae and his.
0
As a rule, papillae wear out on their own from chewing and drinking, but sometimes they grow faster than they wear off, making them targets for various types of bacteria or pigmentation from food. This, in turn, can cause bad breath or impaired taste perception. Blackening can be caused by smoking, coffee and tea, or poor dental hygiene, says Jack Krikor Der-Sarkissian, MD, in Los Angeles, California. In order to get rid of such a special effect, you don’t have to run like a deer into the first grove and lick stones, erasing your nipples, no matter what you imagine now. The simplest thing is to clean your tongue with a tongue scraper. Snow-white curd. As a rule, this option is quite predictable. A lumpy, white-coated tongue, like snow that suddenly fell in November or half-eaten cottage cheese. Both in fact, thrush is the same Candida. The condition is often associated with antibiotics. Your tongue, like your mouth itself, and in general your entire mortal carcass, is home to hundreds of species of bacteria and fungi. They fight for space under your tongue and fight to the death on the back of your cheeks. Your saliva supplies the good guys, but the bad guys constantly come from outside. This battle is endless. But when you take antibiotics, for example, they selectively kill bacteria, allowing yeast to temporarily take over.
0
Thrush may cause loss of taste or pain. It can also be caused not only by antibiotics, but also by a weakened immune system and other disorders. When your body can't support the good guys, the bad guys come out. Typical of young children, thrush also affects people with autoimmune diseases, diabetics, chemotherapy patients, and senior citizens awaiting death or retirement or what have you. If you suspect that you may have thrush, consult a doctor, and do not suffer from bullshit, scraping and do not lick salt, reindeer moss or whatever else Yandex Zen advises. Leopard white. Stylish spotted tongue. Beautiful, but useless. Most likely this means irritation. Painless white spots are called leukoplakia - this is what your mucous membrane looks like when it reacts to something it doesn’t like. In 90% of all cases, we are talking about gastrointestinal pathology, sometimes about a lack of vitamin A.
0
If this is so, then most likely you can find such spots on the mucous membrane of the lips, corners of the mouth, oral cavity, cheeks, and on the mucous membrane of the genital organs. It usually occurs at the age of about 30 years. External irritants that can cause leukoplakia are mechanical injuries, hot tobacco smoke, and exposure to ultraviolet rays. In short, if you are a hipster and like to sleep with your mouth open, vape, and all that, then your mouth is at risk. Leopard red. Scarlet spots, like in zombie horror films. Not to be confused with ulcers or small wounds. Red, inflamed spots with bleeding that don't heal for more than two weeks are serious symptoms no matter where you get them. Any doctor will tell you that you should have been in the hospital with such things yesterday.
0
We usually learn about diseases such as tongue cancer from Google when we try to diagnose ourselves and look for some bullshit like “what does the taste of aluminum mean in the morning” or associate them with elderly and seriously ill people. Both this and that are complete nonsense. Such pathologies can occur at any age. Unless it is something hereditary, like Rendu-Osler disease, a familial hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia expressed in abnormalities of blood vessels and their bleeding. If this is her, then you most likely have known everything about her for a long time. Here she is.
0
“Why would tongue cancer appear?” you ask in surprise, nervously licking your lips. As a rule, it is associated with tobacco use, but its appearance is often associated with the human papillomavirus. Google the rest yourself: Wrinkles, crevices, cracks and other jagged craters in the body of your pink friend.
As a rule, it is associated with tobacco use, but its appearance is often associated with the human papillomavirus. Google the rest yourself: Wrinkles, crevices, cracks and other jagged craters in the body of your pink friend.
0
It looks unpleasant, but the explanation is very simple - you are getting older (yes, even your tongue can age). Cracks in the surface of the tongue are usually harmless, but they can become problematic if you have difficulty with oral hygiene - this will then lead to infection within your wrinkled folds. Well, actually, the same thing will happen if you don’t wash the sand out of other wrinkles on your body in time. As a rule, such infections are fungal in nature. If it appears, you will feel pain, an unpleasant odor and sometimes a burning sensation. Often the infection is treated with a topical antifungal medication. Old age in this regard is not the only threat, although it is inevitable. You can get a gap in your mouth either at the dentist or by scratching your tongue while wearing a denture. In any case, to prevent anything unnecessary from getting into the cracks, maintain oral hygiene. Sometimes a folded or scrotal tongue is a congenital pathology, as a result of which the entire tongue suffers in its shape and size. But in this case, you know about this problem from birth. It may manifest itself as one of the symptoms of Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome, during which, in addition to lesions of the tongue, facial paralysis may develop. The etiology of the syndrome is still unknown, but usually they try to associate it with Crohn's disease or Sarcoidosis. In half of all cases, the folded tongue is paired with a geographic tongue. So to speak, two for the price of one. Geographical language. It's a very popular thing. Recognizable, fashionable, you can look for continents in the morning and look for familiar cities. Geographical language can mean absolutely anything. If you have a unique language, in the center of which is an archipelago, name it after yourself and don’t be upset - this does not mean that you have some kind of language disease. Typically harmless, geographic tongue affects 1% to 2.5% of the population, according to the American Academy of Oral Medicine. Although the reason is not entirely clear, it may also have something to do with taste buds. They, like all parts of the epithelium, die and regenerate. But if you have stress or menstruation, or some other unpleasant state of the body, or you ate something bad or have problems with hormones, the areas of regeneration do not keep up with the death, and wandering glossitis appears. Continents walk, meet and separate. No one knows exactly what causes this, but there are guesses that it may be some kind of specific infection. It is sometimes said to be associated with parafunctional habits, such as tongue biting or teeth scratching.
0
Geographic tongue usually does not require treatment or examination, but if it becomes painful, you may be prescribed an anti-inflammatory steroid paste or antihistamine rinse. In any case, excessive changes in the tongue - whether it is a map, with or without continents, horror with drops of blood, lumps of drool or foam in the corners of the mouth - a change in the pattern of white coating indicates a violation of the natural biome of the mucous membrane. And it is affected by many things - from possible increased acidity and rapidly progressing gastritis, to autoimmune disorders, such as Crohn's, or disorders in the absorption of sugar, or something else... It is unlikely that a precise diagnosis can be made based on one type of your mouth, unless it is caries , but you can at least narrow down your search and understand from which end to look for the rest. Thank you for reading to the end, your SV 
Source:
subscribe to the “Facts” community
Tags: scientae vulgaris history history of medicine medicine popular science rare diseases
Did you like the post? Support Chips, click:
33 8 25
Liked
25 1
5
Partner news
What kind of disease is this?
Glossitis is a severe inflammatory process that occurs on the tongue.
The onset of the disease can be triggered by both third-party factors (for example, a cut of the tongue or constant smoking) and various diseases, including infectious ones (glossitis often accompanies herpes).
There are several forms of glossitis, some of which can be transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person. The disease requires high-quality treatment, since it can progress and affect third-party organs.
What does a perfectly smooth tongue tell?
With atrophy of the taste buds, their number sharply decreases, or they completely disappear, and the surface of the tongue becomes perfectly smooth and shiny. Doctors call this phenomenon a varnished tongue. This symptom may indicate that the human body does not absorb vitamin B2, there is a chronic form of colitis or stomach cancer.
When a smooth tongue is additionally covered with a dense dark coating, and it is quite difficult to remove it; in addition, diagnostics in the tongue reveals cracks, this may indicate a disease such as pellagra - a lack of vitamin B and nicotinic acid.
Stages of diagnostics
Diagnosis and identification of the disease by language (photos will help you navigate) will be more effective if you follow all the stages of its implementation:
- Study the structure and density of the tongue. All changes in shape, color and mobility are taken into account. All these criteria help to correctly assess the functional state of all body systems, and especially the blood.
- Study of plaque. It is graded by color, thickness, shape and appearance. It is also important to determine whether the tongue is dry or wet.
- Stains. The main thing is to exclude those that appeared after taking medications or food. All other changes should indicate the development of a particular pathology.
- Roughness and other criteria.
And now - in more detail about all stages of diagnosis, so that you can better determine which organ has failed.
Zones of the tongue: correspondence to their internal organs
To determine diseases by the condition of the tongue, you need to take into account that it is conventionally divided into several zones that are responsible for certain organs within the body. During a tongue diagnosis, the doctor will definitely look at the location of the changes. Ancient practices divided all areas of language into five primary elements:
- back - Water;
- center - Earth;
- sides – Tree;
- the area between the tip and the center is Metal;
- tip – Fire.
Kinds
The following types of glossitis are distinguished:
- Desquamative type of pathology develops due to gastrointestinal diseases or the presence of viral infections, most often observed in women.
- Candidal glossitis is a consequence of the increased presence of Candida fungi in the oral cavity.
- The folded appearance is considered a congenital pathology, characterized by the appearance of folds on the tongue.
- Rhomboid is a chronic disease, the symptoms of which appear periodically, while the patient only occasionally feels discomfort.
- Gunterovsky is a consequence of a lack of vitamins.
- The catarrhal form of the disease is the initial stage of glossitis, the main reason for the development of the disease is improper oral care.
- Atrophic glossitis develops with an infectious lesion of the oral cavity.
- The ulcerative form of the disease occurs when the tongue is injured or there is an infection in the oral cavity.
- Herpetic glossitis is caused by the herpes virus. Recognized as one of the most contagious types of the disease.
- Mycotic glossitis is not an independent disease, but is a consequence of fungal infections.
- Allergic glossitis is caused by intolerance and allergy to products used to treat the oral cavity.
- Interstitial glossitis causes syphilitic lesions of the tongue.
Roughness of the tongue: what does it mean?
The surface of the tongue in a healthy person is velvety, and all because of the pronounced taste buds. If the tongue becomes rough and coarse, then this phenomenon is considered from the perspective of linguodiagnostics. So what does roughness indicate:
- dehydration;
- malfunction of the salivary glands;
- overdose of vitamins A and D;
- drug overdose;
- biliary dyskinesia;
- complicated pathologies of the stomach and intestines: appendicitis, peritonitis, ulcers and others;
- cracks in the tongue, dryness and roughness - all this indicates thyroid disease or diabetes.
When conducting a more accurate diagnosis of a person’s tongue, cracks in the tongue, swelling, spots and other changes in the organ should also be taken into account.
Diagnosis of internal diseases by tongue color
Characteristic colors , studied over many years, characterize the beginning pathologies of important organs of the human body:
- Red color signals improper functioning of the heart, lungs and other respiratory organs of the system, diseases of the hematopoietic system, and various infectious diseases.
- Raspberry speaks of severe infectious lesions, poisoning with symptoms of chills, complicated pneumonia.
- Dark red characterizes the same diseases as the red color, but they occur in a more severe form or are advanced. Toxic disorders and severe renal pathology occur.
- Alternating red and white areas on the surface of the tongue indicate scarlet fever, a red lacquered organ indicates the development of pellagra.
- A light bluish tint indicates impaired blood circulation and cardiac or pulmonary failure.
- The coloring of the lower area of the tongue in a bluish color indicates heart failure long before the onset of the disease. This indicator is especially typical for middle-aged people who do not expect such changes in the cardiac system, while older people have the opportunity to seriously take preventive measures.
- Purple color indicates severe disorders of the hematopoietic system and pulmonary diseases.
- Black color suggests cholera infection.
- A pale and bloodless tongue indicates anemia and severe general exhaustion of the body. In this case, tooth marks on the lateral surfaces indicate insufficient absorption through the intestinal walls. If discoloration appears only in certain areas of the tongue, then the disease threatens those organs that correspond to the anatomical distribution of surface zones.