A prolonged trip to the doctor sometimes leads to irreversible processes in the body. Most often, patients put off visiting the dentist until the last moment. Meanwhile, oral diseases can cause not only tooth loss, but also spread infection throughout the body, leading to serious consequences. It is better to correctly assess the symptoms in advance and consult the right doctor. In which case you will need an appointment with a periodontist, we consider below.
Who is a periodontist and what does he do?
So, answering the question of who a periodontist is and what he treats, you must immediately indicate that this is a doctor who deals with the oral mucosa, as well as bone tissue and periodontal ligaments. The soft tissues that surround the teeth and securely hold them in place are quite often subject to inflammatory and dystrophic lesions. If not treated promptly, the periodontal ligaments weaken, which can ultimately lead to tooth loss. A specialist in the field in question is engaged in the study, prevention and treatment of diseases that affect the periodontium and sometimes spread to the jaw bone.
A periodontist is a narrower specialist than a dental therapist.
If we talk about how a periodontist differs from a dental therapist, then we need to clarify that we are talking about a more specialized specialist. He treats pathologies such as gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease and other periodontal disorders. To avoid such problems, you need to visit the dentist twice a year. If suspicious symptoms are detected, he will redirect the patient to a specialized expert.
Periostitis is an inflammatory process in the area of the periosteum with the subsequent appearance of purulent foci between the periosteum and the bone.
Periostitis, as a rule, occurs as a complication of periodontitis and manifests itself in the form of significant swelling of soft tissues, characterized by pain and significant changes in the general condition of the body. To eliminate periostitis, emergency surgery is required.
Diseases treated by a periodontist
Now let’s look at what exactly a periodontist does and what he treats. People turn to this specialist primarily for problems with gums. Here are the most common pathologies within his area of expertise:
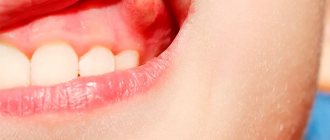
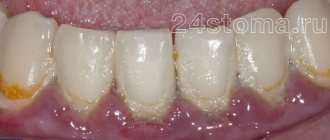
- gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums, which usually precedes any pathological process that penetrates deeper into the soft tissue. In this case, the mucous membrane turns red, swells, pain and bleeding appear,
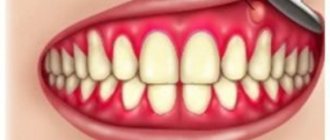
The photo shows gingivitis - Periodontitis is a deeper and more serious inflammatory disease that leads to functional changes in the periodontium, causing severe pain, especially during meals. Bleeding becomes more intense, and in advanced stages teeth begin to loosen, which can ultimately lead to their complete loss,
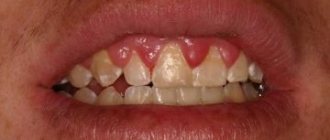
The photo shows advanced periodontitis - periodontal disease - the disease itself is a non-inflammatory pathology in which degenerative processes occur in the soft tissues. The cause of the development of the disease is usually internal disorders, including those related to the functioning of the endocrine system. Gum recession is observed, the necks of the teeth are exposed, and their mobility appears. But in some cases, this term refers to an advanced stage of periodontitis, when, if left untreated, the infection penetrates deeper into the tissue and provokes even more serious structural changes.
This is what periodontal disease looks like
“Based on my life experience, I can only recommend visiting a periodontist at least once a year. All my life I have taken care of my health, brushed my teeth, and never developed caries. And then, at the age of 45, I was diagnosed with periodontal disease! Nothing hurt, my gums didn’t bleed, and the therapist didn’t notice anything. And if I had gone to a periodontist at least once, they could have noticed and slowed down the process...”
Lyudmila V.D., Nizhny Novgorod, from correspondence on the forum www.32top.ru
- root cyst - in this case, the help of a periodontist may also be required, since the pathological phenomenon leads to a pronounced weakening of the ligaments. The neoplasm usually develops without pronounced symptoms, but over time, aching pain occurs in the depths of the gums, swelling appears and the mucous membrane turns red. More often it occurs due to infection entering the tissue, which causes the formation of a cavity with fluid. In the acute stage, it can develop into periostitis, a purulent abscess, and therefore requires mandatory treatment,
- stomatitis is an infectious lesion of the oral mucosa, which is the result of the penetration of a bacterial infection into the tissue, often through wounds and minor injuries. A fungal infection can also cause the development of pathology, and in this case we will be talking about candidal stomatitis. Usually the disease manifests itself in the form of redness and soreness of the mucous membrane, itching and burning, and the formation of ulcers in the mouth.
The photo shows a fungal infection
This is not a complete list of possible pathological conditions in which one cannot do without the help of a professional periodontist - he treats completely independently or involves a therapist/surgeon to help, it all depends on the situation.
But if you discover unpleasant symptoms such as swelling of the gums, pain and bleeding, you can immediately contact a specialized specialist or a dental therapist, who, if necessary, will give the necessary referral.
Gums: what is their role?
First of all, they form the bed of the tooth, which determines its shape, health, and how long it will be safe and sound. The second, no less important function is protective. It is the gums that prevent pathogenic bacteria from penetrating deeper tissues.
When to ask for help
So, we figured out what a periodontist is – what kind of doctor he is in dentistry and what exactly he does. Now let's move on to specific cases in which his help may be required. You need to make an appointment with a specialist if the following symptoms appear:
- the gums “sag”, exposing the necks of the teeth, which is why the crowns seem to lengthen,
- bleeding occurs - traces of blood can be found while brushing your teeth or when biting into hard foods,
- unpleasant odor from the mouth,
- swelling of the mucous membrane, pain,
- the appearance of suspicious neoplasms - wounds, pimples, ulcers, bumps,
- discharge of fluid from the gums,
- increased sensitivity to temperature changes in food,
- pathological mobility of teeth.
If the mucous membrane becomes looser, the tissues turn red and swell, then this is a reason to consult a specialist.
You cannot delay visiting a doctor - the longer you ignore the symptoms, the closer you are to the risk of losing teeth. A timely diagnosis will prevent further development of the disease and its complications.
When to visit a periodontist
Periodontitis and gingivitis occur in patients of any gender and age. Young people under the age of 30 are more often diagnosed with gingivitis, while the older generation often suffers from more severe forms of the disease. This is associated with the body’s resistance, the presence of other diseases, hormonal imbalances, etc. Considering that simple inflammation can quickly turn into serious pathologies, it is better to find out about the symptoms in advance.
The reason for contacting a specialist may be:
- swelling of the gums;
- spotty or widespread redness;
- itching of soft tissues;
- frequent bleeding from the gums;
- pain when chewing food;
- bad breath;
- loosening of the tooth;
- decrease in the gum line (visually the teeth lengthen).
Such phenomena are the reason for a visit to the doctor. When choosing a specialist, you should be very careful, since the health of the oral cavity and the future safety of teeth will depend on his professionalism. It is better to give preference to a trusted doctor with real reviews from patients. Such a doctor can be found not only in expensive private clinics; there are also specialists in public medical institutions. True, most often these end up in private dentistry (new treatment methods, advanced equipment, cooperation with other countries, etc.).
How does an appointment with a specialist work?
As for where the periodontist works, the answer is obvious - in dentistry. We’ll talk about how to choose a good specialist later in this article, but for now let’s move on to the question of what a periodontist does at an appointment. First, the specialist conducts a visual examination and, if necessary, sends the patient for diagnostic procedures.
The degree of tissue damage is assessed, and if in the initial stages the pathology is usually treated with anti-inflammatory therapeutic methods, then in advanced stages more radical measures can be used, including surgery. So what procedures does a periodontist do? Each individual case requires its own technique, so it is quite difficult to come up with a universal treatment plan.
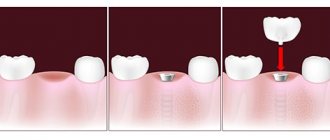
Professional hygiene is mandatory - it is necessary to remove plaque and tartar, which often provoke gum inflammation. If there are periodontal pockets, closed or open curettage (cleaning) is prescribed, depending on the depth. It can be performed using a laser, which facilitates the procedure and increases its effectiveness.
This is how open curettage is performed on the mucous membrane
In case of pronounced structural changes, gum plastic surgery is required: gingivectomy or vestibuloplasty. In the first case, excess overgrown tissue is removed, in the second, part of the mucous membrane taken from other parts of the patient’s oral cavity is “replanted” (in case of gum recession). If pathological mobility occurs, the teeth are splinted using fiberglass, polyethylene or silk thread. If some of the patient’s teeth are missing, you can consider the option of installing a clasp denture with a splinting effect for the remaining mobile teeth.
Tips for choosing a good periodontist
In your search for a good, experienced specialist, reviews from real patients will help you - you can find them on the Internet or ask your friends for recommendations. When choosing a doctor, you should pay attention to the following points:
- length of service and work experience,
- status of the dental clinic,
- availability of modern equipment in the institution,
- variety of services offered.
It’s good if the specialist has a certificate of advanced training in “periodontology”, and it’s better than the state standard. This is confirmation that the doctor has completed specialized courses lasting at least 144 hours and has a specialized education.
Choose a specialist responsibly
It is important that the doctor is able to find a common language with the patient, win him over, and inspire confidence. To do this, you should pay attention to his communication skills, sincere interest in the problem and its solution. The psychological aspect actually plays an important role when choosing a doctor, although many do not attach much importance to it.
How is diagnostics carried out?
As part of the diagnosis, a visual examination of the oral cavity is first performed. Next, the doctor refers the patient to the necessary examinations. Let's look at the activities that may be required to make an accurate diagnosis:
- interviewing the patient regarding complaints, current condition, past and possible chronic diseases,
- examination of the oral cavity, search for foci of caries and inflammation, assessment of the volume of dental plaque. By palpation, that is, feeling, the doctor assesses the condition of the gums and lymph nodes,
- examination of inflamed areas - assessment of the degree of bleeding and swelling, possible signs of atrophic processes,
- cytological and microbiological analyzes of microflora,
- determining the depth of periodontal pockets - allows you to identify the stage of periodontitis (mild - up to 3.5 mm, medium - up to 4-5 mm, severe - more than 5 mm),
- X-ray examination, functional diagnostics,
- collection of blood tests if necessary.
For examination, you may need to take blood tests.
In each individual clinical case, a set of diagnostic procedures is selected individually. The periodontist must carefully examine the current condition of the oral tissues and take into account all associated factors in order to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Prices for services
Prices for periodontist services depend on the type and stage of the disease, the scope of treatment, the qualifications of the doctor, the location of the clinic and some other factors.
Approximate tariffs for some types of services
| Service | Price, rub |
| Consultation with a periodontist. | 500-00 |
| Hygiene training. | |
| Professional hygiene of PR (ultrasonic removal of dental plaque, remineralization, caries prevention). | 3000 |
| Treatment of periodontal pockets. | 1000 |
| Curettage of periodontal pocket (1 tooth). | 600 |
| Cable splinting. | 1600 |
| Gum retraction. | 600 |
| Bone tissue regeneration (Bio-Oss grafting). | 6000 |
How are some periodontal diseases treated?
The main thing that a periodontist does is examine periodontal tissues, prescribe and carry out treatment procedures. Moreover, the methods are selected strictly individually. To get a clearer understanding of this process, consider what measures are usually used to combat the most common diseases of the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
Gingivitis – inflammation of the gums
The pathology extends to the upper layer of the mucosa, so treatment is usually quick and painless. The main thing is to start it on time to prevent the development of more serious diseases. In addition, if the acute form can be cured in 10 days, then the chronic stage requires much more time and effort.
First of all, the doctor performs a professional teeth cleaning.
To begin with, the periodontist prescribes professional cleaning to remove plaque and tartar. You will also have to adjust your diet, replace your toothbrush and, possibly, toothpaste - a specialist will help you choose the right product. To restore the mucous membrane, a gel is usually prescribed - Metrogyl Denta or, for example, Sorcoseryl. As a restorative therapy, rinsing with decoctions of medicinal herbs - sage, eucalyptus, chamomile - is recommended. Before carrying out the procedures, you should definitely consult your doctor.
Anti-inflammatory and drug therapy is carried out, vitamin complexes with a high content of vitamin C are prescribed, which helps strengthen blood vessels and the immune system in general.
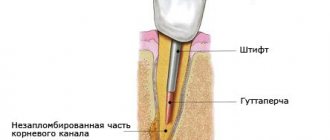
Treatment of periodontitis
In this case, an integrated approach is required: taking medications orally, using antibacterial drugs, gels, rinses and baths. But first, the periodontist must remove the foci of inflammation. To do this, hardware cleaning of teeth and gum pockets is carried out using ultrasound and water-abrasive solutions (“Vector”, “Varios”). All carious lesions are eliminated. In order to restore the mucous membrane and stimulate blood circulation, special injections are performed in it, and physiotherapy is prescribed.
Using the Vector ultrasonic device, a specialist cleans gum pockets
In advanced cases, periodontitis leads to severe tooth mobility. In such a situation, they are splinted, that is, securely fixed in the desired position using the finest threads or a clasp design. If the teeth are severely damaged, the best solution would be to remove them and then implant them with prosthetics. There are one-stage technologies that involve installing a crown or prosthesis immediately after implantation of artificial roots (within 7 days), which can significantly reduce treatment.
Periodontal therapy
In this case, treatment is aimed at eliminating symptoms, since it is impossible to completely cure the disease. At the initial and middle stages, the following activities are usually carried out:
- removal of plaque and deposits, including from under the gums,
- elimination of foci of caries - with periodontal disease they are usually localized in the root region,
- splinting with threads or clasp construction,
- restoration of gums using hardware techniques, laser, physiotherapy, special massage and electrophoresis,
- flap surgery to restore the aesthetics of the gingival contour,
- rinses and baths,
- increasing the level of oral hygiene,
- treatment of concomitant diseases of the body.
Splinting is used to fix mobile teeth.
An advanced form of pathology often leads to violations of the periodontal ligaments and tooth loss. The optimal way out of the situation would be implantation with immediate loading. The prosthesis is fixed on the same day or within a week after surgery, which provides the ability to quickly restore the appearance and functionality of the jaw apparatus.
Drug treatment of periodontitis
The next stage of treatment is to relieve inflammation and eliminate bleeding gums to prevent further development of the disease. This goal is achieved through drug therapy.
Medicines for the treatment of periodontitis are divided into local and general:
- local remedies are used to treat the affected areas. This includes rinses, antiseptic solutions, anti-inflammatory gels and balms. Local treatments also include therapeutic and prophylactic toothpastes, which can be used as an addition to the main therapy;
- general drugs, which are combinations of antibiotics in the form of tablets or intramuscular injections.
Non-invasive treatment for periodontitis may also include physical therapy. Auxiliary procedures using laser or electrophoresis will help eliminate inflammation faster.
Specifics of children's specialists
Children also experience periodontitis. The disease is diagnosed in approximately 3-5% of young children and adolescents, although most often it develops at the age of 9-10 years1. The problem is that the tissues of the oral cavity are still immature, constantly changing and rearranging, which is why they can react sharply to the slightest inflammation. In this case, the therapy will be little different from the treatment of an adult patient. Professional hygiene and physiotherapeutic measures will be required. Sometimes the lip frenulum is corrected if it has become one of the prerequisites for the development of periodontitis. In general, an integrated approach to diagnosis and treatment is required, since the causes may also lie in systemic pathologies.
Recently, lasers have been increasingly used to correct frenulums.
Gums are bleeding - contact a periodontist
If you notice the slightest symptoms of periodontitis, immediately go to the doctor. The first sign is regular bleeding of the gums after mechanical impact.
If there is a single bleeding, there is no reason for serious concern: to strengthen the gums, you can change the toothpaste to a special product for the treatment and prevention of periodontitis, or use a strengthening gel or balm. But if bleeding becomes regular, you need to see a specialist.
If the disease progresses, some teeth may need to be removed. Therefore, the earlier the diagnosis is made and treatment is started, the greater the chances of completely getting rid of periodontitis without negative consequences.
What do periodontist surgeons do?
Specialists in this profile perform operations on the soft tissues of the oral cavity. There are many types of surgical interventions, and here are just some of the possible options for flap operations:
- resection of the gum pocket,
- removal of the gum edge,
- soft tissue transplantation - “replanting” soft tissues in the area of absorbed periodontal tissues,
- restoration of bone tissue for subsequent implantation,
- gum grafting to give an aesthetically pleasing smile,
- plastic surgery of the frenulum, etc.
A periodontist deals with all kinds of gum surgery.
To avoid serious gum diseases, it is enough to carefully monitor their condition and maintain a high level of hygiene. No one is immune from problems with teeth and gums, but we can reduce any risks to the bare minimum. Remember to brush your teeth twice a day, rinse your mouth after meals, and floss. In order to be able to recognize the pathology in time and immediately begin its treatment, it is important not to miss scheduled preventive examinations at the dentist, at least twice a year.
- According to WHO.