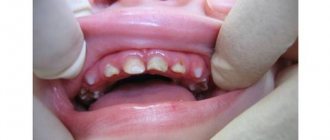
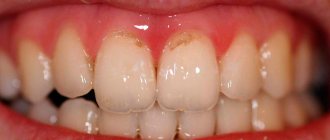
Caries is often localized in the interdental spaces. The reason for this in most cases is insufficient oral hygiene. In order to clean out food debris between the teeth, you need dental floss. Not all people use it. Some people don’t see the need for an additional cleaning product, while others simply don’t know how to use floss.
Poor cleaning of the space between teeth leads to the rapid proliferation of harmful bacteria, which in the process of life produce acid that destroys the enamel structure. This is how one of the most common dental diseases develops.
Signs of caries
As already noted, in the early stages, caries is difficult to recognize; it is asymptomatic. In this case, only a dentist can see the carious lesion. Therefore, it is necessary to undergo preventive examinations with a dentist once every six months. When caries penetrates into the deeper layers of the tooth, the following symptoms occur:
- Painful reaction in the area of the affected tooth to irritants: cold, hot, spicy, salty. After the cessation of exposure to irritants, unpleasant symptoms disappear;
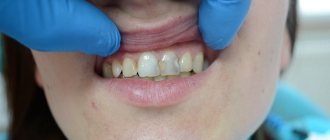
- The enamel color of the affected tooth changes. It may darken or acquire a yellow tint. The space between carious teeth becomes brown or almost black;
- A putrid odor appears from the mouth even after using toothpaste;
- Over time, the side walls break and holes appear in the teeth.
Reasons for the development of interdental caries
To prevent the occurrence of caries, you need to know the reasons that lead to this disease. Among them:
- Insufficient oral hygiene, neglect of additional means of cleaning teeth (dental floss, mouthwash).
- Drinking low-purity water that contains pathogenic microbes.
- Eating a lot of sweets.
- Age. It has been observed that children and adolescents are more susceptible to dental caries than older people.
- Floor. Research shows that women are more likely to develop tooth decay than men. Teeth are especially vulnerable during pregnancy and lactation, when beneficial substances from the woman’s body are transferred to the child.
- Malocclusion, dentition displacement and other physiological characteristics.
- Low quality food.
- Unbalanced diet.
- Decreased immunity.
- Smoking.
Types of caries diagnostics in dentistry
It is very difficult to detect a carious lesion on your own, so it is important to pay attention to the signs described above that indicate its appearance. The earlier caries is diagnosed, the higher the likelihood of successful treatment and prevention of its development on neighboring teeth.
In modern dentistry, there are different diagnostic methods that will help identify the disease and determine its stage.
Types of diagnostics:
- Visual examination of the dentist using a mirror and probe;
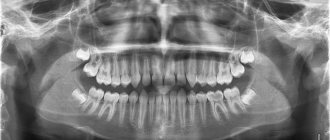
- X-ray diagnostics. The image shows affected areas that are invisible from the outside;
- Use of coloring compounds;
- The use of a special apparatus with pulsed light waves reflected on the surface of the enamel. When the machine sees a carious lesion, it beeps;
- CT scan. Makes it possible to see the structural features of the jaw and the condition of all teeth in a 3D image.
Why is differential diagnosis needed?
The essence of the differential diagnostic method is to use a combination of all of the above methods to establish an accurate diagnosis. An experienced dentist decides on the appropriateness of a particular diagnostic method. The need to use differential diagnosis is due to the fact that in some cases caries can be easily confused with other dental diseases.
For example, to distinguish hypoplasia from caries, a caries marker is used, pulpitis from caries - thermal diagnostics and EOM, non-carious lesions from caries - an x-ray.
It is almost impossible to carry out differential diagnosis using only visual examination methods.
Possible complications
Tooth decay should be treated as early as possible. Otherwise, the disease will penetrate deeper and affect the tooth even more. When caries reaches the nerve, the tooth will begin to hurt and become inflamed. In addition, untimely treatment leads to complications such as:
- Inflammation of internal dental tissues (pulpitis, periodontitis);
- The occurrence and rapid spread of an infection that will extend beyond the tooth and require treatment with antibiotics or surgical intervention;
- Development of chronic infection;
- Removal of a tooth.
What does untreated caries lead to?
Many parents do not pay special attention to the condition of their children’s baby teeth, believing that temporary teeth do not need to be treated. After all, they will fall out, and their place will be taken by beautiful permanent teeth. However, this is a big misconception! If not treated in time, milk caries can affect the health of permanent teeth and general condition in general:
- If a baby tooth decays to such an extent that it cannot be saved by conservative methods and premature extraction must be resorted to, then the permanent tooth may not erupt at all. This occurs because the permanent tooth germ did not have time to complete the formation process. But if it does erupt, it may take an incorrect position in the jaw.
- The carious process can spread from the primary tooth to the permanent tooth germ. Then the permanent dental unit will erupt with a carious defect.
- An advanced carious process leads to the need for dental intervention using a drill. Toothache and the sound of a dental machine can provoke dental phobia in a child. Dentophobia is the fear of dentists.
Methods used to treat caries
The choice of treatment for caries depends on the stage of the disease. For superficial carious lesions, gentle procedures are performed:
- Professional cleaning;
- Saturation of tooth enamel with essential minerals (remineralization).
More serious forms are treated using traditional methods:
- Filling (the resulting cavity is filled with filling material);
- Installation of inlays, installation of prostheses.
Prevention of caries
It is quite easy to avoid the development of caries; to do this, you should regularly follow the recommendations of dentists.
- Brush your teeth and use mouthwash after every meal.
- After eating, remove leftover food between your teeth using dental floss.
- Minimize carbohydrate intake.
- Use a professional cleaning service at a dental clinic at least once a year.
- Visit the dentist once every 6 months.
- If unpleasant symptoms and pain occur, consult a dentist immediately.
The Carmen-Med dental clinic in Nizhny Novgorod provides a wide range of services, helping to solve any patient’s problem related to the oral cavity. Our dentistry has modern equipment that allows accurate diagnosis and selection of effective therapy. Painless treatment using modern painkillers will not cause discomfort during the procedures. Experienced and qualified doctors guarantee excellent results.
Question No. 1: EXPOSURE OF THE ROOT BY 1/2 OF ITS LENGTH ALONG V.YU. KURLYANDSKY IS THE DEGREE OF ATROPHY fifth fourth third + second first
Question No. 2: GUM HYPERTROPHY CAN BE CAUSED BY DRUGS + diphenin mexidol ascorbic acid amoxiclav aspirin
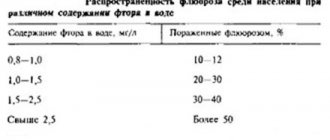
Question No. 3: IN ADDITION TO TEETH, DURING FLUOROSIS, DAMAGES DEVELOP the muscles of the skin, nervous system, blood vessels + bone skeleton
Question No. 4: WHEN TREATING ACUTE PERIODONTITIS AT THE STAGE OF STRONG EXUDATIVE PROCESS, ON THE FIRST VISIT, the canal is filled with permanent filling materials + conditions are created for the outflow of exudate and the tooth is left open, an incision is made along the transitional fold, the tooth is hermetically sealed after medicinal treatment, strong antiseptics are used
Question No. 5: METHOD OF ADDITIONAL RESEARCH WHEN PROVIDING A PRELIMINARY DIAGNOSIS OF CANCER OF THE MUCOUS MEMBRANE OF THE BOTTOM OF THE ORAL CAVITY IN A POLYCLINIC: clinical X-ray + cytological ultrasound tomography
Question No. 6: PART OF THE GINGUM THAT LIES DIRECTLY ON THE PERIOSTUM OF THE VESTIBULAR AND ORAL CIVIL OF THE ALVEOLAR BONE gingival margin marginal gingiva interdental gingiva + attached gingiva mucogingival border
Question No. 7: ADDITIONAL INVESTIGATION METHODS FOR VINCENT ULCERONECROTIC GINGIVITIS correct 1), 3) and 4) + blood test for glucose content bacterioscopy + general clinical blood test + blood test for HIV infection
Question No. 8: ACANTHOLYTIC CELLS ARE FOUND IN CYTOLOGICAL PREPARATIONS IN CASES OF HERPESIS SIMPLE + VULGAR PAMPIGUS, EXUDATIVE erythema multiforme, lichen planus, syphilis
Question No. 9: REMOVAL OF SUBGINGIVAL CALCULUS IS PERFORMED 7 days after curettage before curettage + not carried out during curettage does not matter
Question No. 10: ANTIFUNGAL DRUGS INCLUDED histaglobulsh metronidazole + fluconazole sodium thiosulfate tetracycline
Question No. 11: LOCAL TREATMENT OF CANDIDIASIS hydrocortisone ointment florenal ointment + Canesten ointment oxolinic ointment Solcoseryl ointment
Question No. 12: THE QUANTITATIVE SEVERITY OF CATARHAL GINGIVITIS CAN BE DETERMINED USING THE CPITN INDEX + PMA GreenVermillion PI correct 2) and 3)
Question No. 13: A CONTRAINDICATION TO THE MANUFACTURE OF VENEERS IS diastema, abnormal tooth shape + poor oral hygiene, enamel hypoplasia, fluorosis
Question No. 14: AN ABSOLUTE CONTRAINDICATION TO THE MANUFACTURE OF VENEERS IS fluorosis, acid necrosis, amelogenesis imperfecta + parafunction of masticatory muscles, caries
Question No. 15: WHEN TREATING MODERATE CARIES OF TEMPORARY INCISERS AND FANGS, IT IS POSSIBLE TO APPLY WITHOUT A PLATE + glass ionomer cements silicine evicrol amalgam silidont
Question No. 16: ACHING PAIN, INCREASED WHEN BITING ON A TOOTH, WITHOUT RADIOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE APIKAL PERIODONTAL IS CLASSIFIED AS AN ACHIEVEMENT OF CHRONIC PAINTITIS Acute apical periodontitis (exudation phase) chronic periodontitis + acute apical periodontitis of pulpal origin (intoxication phase ) exacerbation of chronic pulpitis
Question No. 17: PREPARATION OF A CARIOUS CAVITY INCLUDES pain relief, expansion of the carious cavity, necrectomy, anesthesia, necrectomy, expansion of the carious cavity, necrectomy, finishing, anesthesia, necrectomy, finishing + opening of the carious cavity, necrectomy, formation of the bottom and walls of the carious cavity, finishing
Question No. 18: DISEASE, AS A RULE, CLEARLY ASSOCIATED WITH HIV INFECTION Tappeiner leukoplakia + hairy leukoplakia verrucous leukoplakia flat leukoplakia erosive leukoplakia
Question No. 19: IN INTACT PERIODONTAL DEGAL GROOSE IS DETERMINED by palpation + histologically, radiologically, clinically percussion
Question No. 20: ABSOLUTE GENERAL CONTRAINDICATIONS FOR TEETH WHITENING breastfeeding allergic reaction to hydrogen peroxide + all of the above pregnancy age under 18 years
Question No. 21: DENTAL INCIDENCE IN THE POPULATION OF THE REGION IS ASSESSED WHEN CARRYING out preventive measures: planned sanitation of the oral cavity, preventive examinations, clinical examination of the population + epidemiological dental examination
Question No. 22: AN EARLY CLINICAL SIGN OF PERIODONTAL INFLAMMATION IS poor oral hygiene + symptom of bleeding gums clinical pocket 3 mm deep change in color and shape of the gingival papilla pathological tooth mobility
Question No. 23: THE DIAGNOSIS OF HIV INFECTION IS ESTABLISHED AFTER A STUDY: biochemical blood test, cytological + enzyme-linked immunosorbent test, serological blood test, histological
Question No. 24: NIKOLSKY’S SYMPTOM IS POSITIVE FOR + true pemphigus, erosive form of lichen planus, herpetic stomatitis, 1) and 2) erosive form of leukoplakia are correct
Question No. 25: THE TYPICAL FORM OF LICHEN PLANUS IS DIFFERENTIATED WITH pemphigus, acute mechanical trauma, chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis, medicinal stomatitis + planar leukoplakia
Question No. 26: BEFORE CARRYING OUT THE ADHESIVE FIXATION TECHNIQUE TO IMPROVE ADHESION, THE TOOTH IS PROCESSED with a turbine tip, a cutter for a straight tip, an excavator, a raising tip + an intraoral sandblaster
Question No. 27: PATHOLOGICAL PROCESSES IN THE AREA OF A CHRONIC CRACK OF THE LIP neurodystrophy is true 2) and 3) + inflammatory infiltration + acanthosis ballooning degeneration
Question No. 28: KLEIN'S LINE SEPARATES the red border and perioral skin the red border and attached gingiva mucous membrane and attached gingiva perioral skin and mucous membrane + red border and mucous membrane
Question No. 29: ABSENCE OF CLINICAL SYMPTOMATICS IS CHARACTERISTIC FOR + chronic granulomatous periodontitis acute periodontitis chronic granulating periodontitis acute pulpitis chronic gangrenous pulpitis
Question No. 30: WHEN TREATING CHRONIC CATARHAL GINGIVITIS, gingivectomy + correction of oral hygiene is performed, treatment of gums with resorcinol, gingivotomy, application of proteological enzymes
Question No. 31: REMOVAL OF DENSE CARIOUS DENTIN IS PRODUCED using an excavator with a white-marked diamond bur with a rotation speed of 4500 rpm + a spherical bur with a rotation speed of 4500 rpm, a diamond bur with a speed of 400,000 rpm, a reverse-cone bur with a rotation speed of 4500 rpm
Question No. 32: DENTIN MICROHARDNESS IS 50 N/mm2 280 N/mm2 80 N/mm2 + 180 N/mm2 390 N/mm2
Question No. 33: GLOSALGIA IS DIFFERENTIATED WITH + desquamative glossitis + neuralgia of the lingual nerve + with exudative erythema multiforme Correct 1), 2) and 3) neuropytia of the lingual nerve
Question No. 34: COMPLAINTS OF PATIENTS WITH A SPOTTED FORM OF FLUOROSIS night pain in the teeth radiating pain along the branches of the trigeminal nerve + cosmetic defect pain when biting on a tooth pain from temperature stimuli
Question No. 35: CARRYING OUT THE BIOLOGICAL METHOD IS POSSIBLE WHEN ACCIDENTALLY opening a dental cavity in a 23-year-old patient with type I diabetes, chronic fibrous pulpitis in a 35-year-old patient with acute herpetic stomatitis, acute focal pulpitis in a 16-year-old patient with chronic pyelonephritis, acute focal pulpitis of a multi-rooted tooth in patient 47 years + accidental opening of a tooth cavity during the treatment of caries in a 27-year-old patient
Question No. 36: ETIOLOGICAL FACTORS CAUSING LICHEN PLANUS + taking medications decrease in the height of the lower part of the face is correct 1) and 4) hypothermia + prolonged stress
Question No. 37: A PERIODONTAL POCKET DEPTH OF MORE THAN 5 MM IS CHARACTERISTIC FOR moderate periodontal disease, severe periodontal disease, mild periodontitis + severe periodontitis, moderate periodontitis
Question No. 38: SECONDARY ELEMENTS OF THE LESION INCLUDE a nodule, a spot, a node, a tubercle + a scale
Question No. 39: PROFESSIONAL ORAL HYGIENE MUST BE CARRIED OUT AT LEAST 1 TIME A WEEK + 6 months 2 years month year
Question No. 40: COLORING OF TEETH DURING TRAUMA IS DUE TO THE ACTION OF + iron bilirubin biliverdin silver copper
Question No. 41: LOCAL FACTORS PROVOKING RECURRENCE OF ULCERAL-NECROTIC VINCIENT GINGIVITIS + semi-impacted wisdom tooth + chronic inflammatory periodontal diseases true 1), 2) and 4) + galvanosis unsanitized oral cavity
Question No. 42: SECONDARY SYPHILIS ON THE GUT IS MANIFESTED AS + papular syphilide multiple ulcers gumma chancre cheesy plaque
Question No. 43: THE DEPTH OF DAMAGE TO HARD TISSUES OF TEETH AT III DEGREE OF INCREASED ABRASION REACHES: from 1/3 to 1/2 the length of the crown to 1/3 of the length of the crown from 1/3 to 2/3 of the length of the crown + from 2/3 of the length of the crown to neck of the tooth up to 1/4 of the length of the crown
Question No. 44: PHYSIOTHERAPEUTIC TREATMENT FOR PERIODONTIS hydromassage:, darsonvalization hydromassage, darsonvalization, electrophoresis, UHF therapy + hydromassage, darsonvalization, electrophoresis hydromassage hydromassage, darsonvalization, electrophoresis, UHF therapy, laser therapy
Question No. 45: LOCAL TREATMENT FOR FLAT LEUKOPLAKIA cauterizing therapy antibacterial ointments soda rinses antiviral drugs + keratoplasty agents
Question No. 46: SECONDARY ELEMENT OF DAMAGE IN LICHEN PLANUS + ulcer + plaque + crust correct 1), 2) and 3) erosion
Question No. 47: WHEN THE AMOUNT OF SOFT PLAQUE IN THE ORAL CAVITY INCREASES, THE REACTION OF SALIVA SHIFTES TO THE SIDEWAY: does not change + acidic neutral alkaline variable
Question No. 48: TONGUE PAPILIA + filiform, mushroom-shaped, leaf-shaped, grooved filiform, mushroom-shaped, leaf-shaped, grooved, pear-shaped filiform and mushroom-shaped filiform and leaf-shaped filiform, mushroom-shaped, leaf-shaped
Question No. 49: TERMINAL BRANCHES OF BUSH NERVE ENDINGS PROVIDE REGULATION + distribution of chewing pressure force sensory function trophic function protective function support function
Question No. 50: TREATMENT MEASURES FOR A FOLDED TONGUE AIMED AT improving epithelization + sanitation of the oral cavity, correct 2) and 3) + hygiene correction, increased salivation
Question No. 51: WITH HERPES, THE PATHOLOGICAL PROCESS IN THE EPITHELIA IS CALLED acanthosis parakeratosis hyperkeratosis papillomatosis + ballooning degeneration
Question No. 52: TO CONFIRM THE DIAGNOSIS OF CANDIDIASIS, AN ADDITIONAL RESEARCH METHOD IS USED + bacterioscopic cytological allergological radiological serological
Question No. 53: USING A TOOTHBRUSH AT THE GINGIVECTOMY SITE IS POSSIBLE one month after surgery throughout the entire postoperative period after removal of the bandage after removal of the suture + a week after surgery
Question No. 54: PERIODONT IS A CONNECTIVE TISSUE CONSISTED OF connective tissue, fibers, fiber vessels, cell vessels, fibers, vessels and nerve endings of intercellular substance, cells, fibers, layers of loose connective tissue + connective tissue, blood and lymphatic vessels, nerves, fibers
Question No. 55: THE METHOD OF DEVITAL EXTRACTION IS INDICATED FOR THE TREATMENT OF ALL FORMS OF PULPITIS in any formed temporary teeth only in formed permanent teeth + in formed permanent teeth and in formed temporary teeth in single-root unformed permanent teeth and formed temporary in single-root unformed permanent teeth in case of crown fracture exposing the pulp
Question No. 56: ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK PRIMARILY DEVELOPES AGAINST THE BACKGROUND of chronic pancreatitis, intoxication + a previous allergic reaction, diathesis of atherosclerosis
Question No. 57: ACUTE HERPETIC STOMATITISIS SHOULD BE DIFFERENTIATED WITH desquamative glossitis, atrophic candidiasis, atonic cheilitis + allergic (drug-induced) stomatitis, hyperplastic candidiasis
Question No. 58: IN THE FIBROUS FORM OF HYPERTROPHIC GINGIVITIS, SURGICAL TREATMENT IS PERFORMED: gingivectomy, curettage + gingivotomy, open curettage, flap surgery
Question No. 59: OINTMENT USED FOR TREATMENT OF PIODERMA butadiene + 2% neomycin 2% tebrofen 0.25% oxolinic clotrimazole
Question No. 60: CONCENTRATION OF CHLORHEXIDINE FOR ANTISEPTIC TREATMENT FOR NECROTIZING ULCERATIC GINGIVITIS 1% 0.01% + 2% 0.5% 0.06%
Question No. 61: TO PRODUCE VENEERS, TEETH PREPARATION IS CARRIED OUT with carbide burs + diamond burs, wheel burs, vulcanite discs, carborundum heads.
Question No. 62: PATHOLOGICAL PROCESS IN THE ORAL MUCOSA, LEADING TO THE DEVELOPMENT OF NIKOLSKY SYMPTOM parakeratosis acanthosis hyperkeratosis spongiosis + acantholysis
Question No. 63: COMPLAINTS OF A PATIENT WITH CONTACT ALLERGY IN THE ORAL CAVITY TO + bleeding gums itching and burning + bad breath 1) and 3) dryness are correct
Question No. 64: ENZYME PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL TREATMENT OF ROOT CANALS iodinol, betadine dimethyl sulfoxide sodium hypochlorite, chloramine hydrogen peroxide + lysozyme, trypsin
Question No. 65: AT THE FIXATION STAGE, THE CERAMIC VENEER IS TREATED WITH hyaluronic acid self-etching bonding system + hydrofluoric acid, hydrochloric acid, phosphoric acid
Question No. 66: LIMITED PRE-CANCEROR HYPERKERATOSIS OF THE RED BORDER OF THE LIPS CLINICALLY REPRESENTS an aphthae pigmented spot + a focus of keratinization of a polygonal shape; superficial erosion; a hemispherical node
Question No. 67: ULTRASOUND THERAPY AND TRANSCUTANEOUS ELECTRONEUROSTIMULATION ARE USED FOR psychosomatic correction of autotraining for EDI + restoration of the functional state of X-ray diagnostic muscles
Question No. 68: WHEN TREATING HERPES AT THE BEGINNING OF THE DISEASE, MEASURES ARE AIMED AT + blockade of the virus in the nerve trophic endings, sanitation of the oral cavity, identification and elimination of foci of chronic infection, impact on anaerobic microflora, epithelization
Question No. 69: WHEN THE TOOTH ROOT SURFACE IS EXPOSED BY 6 MM AND A PERIODONTAL POCKET IS 5 MM IN, YOU SHOULD ASSUME necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis, gingival fibromatosis, severe periodontal disease, hypertrophic fibrous gingivitis + severe periodontitis
Question No. 70: CONSERVATIVE METHODS FOR TREATING A CHRONIC LIPS + lidocaine blockades + ointment applications + UHF therapy correct 1), 2) and 3) application of proteolytic enzymes
Question No. 71: A FAVORABLE OUTCOME OF TREATMENT FOR CHRONIC GRANULATING PERIODONTITIS IS THE transition to cystogranuloma + transition to the fibrous form, tooth extraction, physiological recovery, chronic pulpitis
Question No. 72: THE LOWER BOUNDARY OF THE FLOOR OF THE ORAL CAVITY IS THE posterior belly of the digastric muscle, the mucous membrane of the floor of the mouth, the base of the tongue + the skin of the submandibular regions, the inner surface of the body of the lower jaw.
Question No. 73: A DRUG WITH ANTI-VIRAL ACTIVITY nystatin tsifran trichopolum dibazole + acyclovir
Question No. 74: TO WASH ONE CANAL DURING ENDODONTIC TREATMENT ANTISEPTIC SOLUTION IS REQUIRED more than 25 ml + 1015 ml 510 ml 2025 ml 15 ml
Question No. 75: CURETAGE OF THE PERIODONTAL POCKET PROVIDES THE REMOVAL of supragingival calculus and gingival epithelium, supragingival calculus and granulations of subgingival calculus and granulations + subgingival calculus, granulations and gingival epithelium of supragingival and subgingival calculus
Question No. 76: DRUGS USED FOR LOCAL TREATMENT OF CHRONIC LIPS + 1% lidocaine solution oil solutions of vitamins A and E + crystalline resorcinol true 1), 3) and 4) + trypsin, chymopsin
Question No. 77: INTERGLOBULAR DENTIN THIS + the main substance between the dentin layers dentin, which arises during the development of the tooth; deposition of dentin during a person’s life; dentin, formed as a result of destruction (erosion, caries, etc.) the part of dentin adjacent to the tooth cavity
Question No. 78: COLLECTION OF MATERIAL FOR BACTERIOSCOPIC STUDY IS CARRIED OUT before meals, 3 hours after meals at any time + on an empty stomach after meals
Question No. 79: LOSS OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE ATTACHMENT OF A TOOTH AT THE DISTANCE FROM THE CEMENTO-ENAMEL BORDER TO THE BOTTOM OF THE PERIODONTAL POCKET - THIS IS the depth of the periodontal pocket clinical gingival groove + loss of periodontal attachment false pocket exposure of the tooth root surface
Question No. 80: COMMUNICATION WITH THE TOOTH CAVITY IS A SYMPTOM OF non-carious lesions of acute pulpitis, acute periodontitis, caries + chronic pulpitis
Question No. 81: LUPUS erythematosus is included in viral diseases, specific infections, benign neoplasms + collagenosis, traumatic lesions
Question No. 82: OPTIONAL PRECANCERS INCLUDED Atypical FORM OF LICHEN PLANUS + exudative-hyperemic + erosive-ulcerative, correct 2) and 3) hyperkeratotic
Question No. 83: DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF CARIES AT THE STAGE STAGE IS CARRIED OUT WITH focal pulpitis, dentin caries, cement caries, superficial caries + hypoplasia
Question No. 84: HYPERTROPHIC FIBROUS GINGIVITIS IS DIFFERENTIATED WITH herpetic gingivostomatitis, periodontitis + epulis periodontal disease, Vincent gingivitis
Question No. 85: TO DETERMINE THE SEVERITY OF PERIODONTITIS, IT IS NECESSARY TO CARRY OUT A RESEARCH + all answers are correct depth of periodontal pockets tooth mobility loss of periodontal attachment x-ray
Question No. 86: SEVERE FORMS OF RECURRENT APHTHOSIC STOMATITIS Rosenthal syndrome Lyell syndrome + Setton aphthosis StevensJohnson syndrome Sjögren syndrome
Question No. 87: APPLICATION OF CHEMICALLY CURING COMPOSITE IS PRODUCED IN LAYER(S) five three four two + one
Question No. 88: DRUGS FOR LOCAL TREATMENT OF DRUG ALLERGIES + antiviral antihistamines + antifungal painkillers correct 1) and 3)
Question No. 89: BOWEN'S DISEASE IS RELATED TO allergic conditions, viral diseases, facultative precancers + obligate precancerous dermatoses
Question No. 90: THE CAUSE OF DIPHTHERIA IS hemolytic streptococcus coxsackievirus fusospirochetes + Loeffler's bacillus actinomycetes
Question No. 91: FOR ANTI-SCLEROTIC AND VASOTROPIC THERAPY OF PERIODONTAL DISEASE + trental claritin metronidazole amoxiclav nystatin is used
Question No. 92: DURING COLLAPSE SKIN is dry, pale dry, hyperemic moist, hyperemic + moist, pale normal
Question No. 93: MICROHARDNESS OF ENAMEL IS 120N/mm2 + 390N/mm2 80N/mm2 200N/mm2 50N/mm2
Question No. 94: PULP REMOVAL (VITAL, DEVITAL) IS INDICATED FOR chronic gangrenous pulpitis + all forms of pulpitis, acute forms of pulpitis, chronic fibrous pulpitis, chronic hypertrophic pulpitis
Question No. 95: PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC RECURRENT APHTHOSIC STOMATITIS COMPLAINTS OF + pain, bad breath, dry, coated tongue, bleeding gums
Question No. 96: QUARTZING IN A DENTAL OFFICE SHOULD BE CARRIED OUT PER DAY (NUMBER OF TIMES) 5 1 4 + 3 2
Question No. 97: FOR II AND III DEGREES OF INCREASED TEETH ABRASION, THE USE OF stamped crowns, veneers, inlays, stamped-soldered bridges + solid crowns is SHOWN
Question No. 98: THE CHOICE OF THE COLOR OF COMPOSITE MATERIAL SHOULD BE DETERMINED IN daylight in the second half of the day artificial light in the first half of the day daylight artificial light + daylight in the first half of the day
Question No. 99: ETCHING, CONDITIONING OF DENTIN IS CARRIED OUT FOR THE FORMATION OF A HYBRID LAYER, strengthening the marginal fit, maintaining the smear layer + removing the smear layer, enhancing the bactericidal properties of composites
Question No. 100: THE ROOT CANAL IN ACUTE INFLAMMATION OF THE PULP IS FILLED not reaching 2 mm to the apical foramen not reaching 3 mm to the apical foramen + to the physiological apex beyond the apical foramen to the anatomical apex
Question No. 101: MILDLY PAINFUL PROBING OF A WIDELY OPEN TOOTH CAVITY, THE APPEARANCE OF BLEEDING DURING PROBING IS A SYMPTOM OF PULPTIS + chronic hypertrophic acute diffuse acute focal chronic gangrenous chronic fibrous
Question No. 102: TREATMENT MEASURES FOR ATOPIC CHEILITIS desensitizing therapy + antiviral therapy is correct 2) and 3) + antifungal therapy elimination of local neurodystrophy
Question No. 103: ON AN X-RAY DURING PERIODONTITIS OF MODERATE SEVERITY, RESORPTION OF THE INTERALVEOLAR SEPTUM by 3/4 of the length of the tooth root by 1/3 of the length of the tooth root by 2/3 of the length of the tooth root + absent by 1/2 of the length of the tooth root
Question No. 104: THE SECONDARY ELEMENT OF DAMAGE IN ACUTE HERPETIC STOMATISIS IS CALLED aphtha papule + erosion vesicle scale
Question No. 105: FIRST STAGE OF THE “STEP BACK” TECHNIQUE Instrumentation of the apical third of the root canal Formation of an apical stop + passage of the root canal with a small instrument and determination of the working length Instrumentation of the middle and upper parts of the root canal Final alignment with the wall of the root canal
Question No. 106: CREATION OF DRAINAGE BETWEEN THE CARIOUS CAVITY AND THE TOOTH CAVITY PROMOTES THE TRANSITION OF ACUTE FOCAL PULPTIS INTO acute diffuse chronic gangrenous acute periodontitis chronic hypertrophic + chronic fibrous
Question No. 107: AFFECTED AREAS IN CHRONIC RECURRENT APHTHOSIC STOMATITIS ARE TREATED + with solutions of anesthetic, enzymes, antiseptics, keratoplasty solutions of anesthetic, enzymes and antiseptics solutions of anesthetic, enzymes, antiseptics, Castelpani liquid solution of anesthetic solutions of anesthetic and enzymes
Question No. 108: THE CAUSE OF EXCESSIVE REMOVAL OF FILLING MATERIAL BEYOND THE APICAL HOLE OF THE ROOT IS perforation of the root canal wall + excessive expansion of the apical foramen; formation of a dentinal plug; breakage of the rod instrument in the canal; insufficient medicinal treatment
Question No. 109: MEDICINES FOR THE TREATMENT OF DESEQUATIVE GLOSSITISIS: correct 3) and 4) blockade of the lingual nerve with lidocaine solution antibiotics + analgin 0.5 g 3 times a day + calcium pantothenate 0.10.2 g orally
Question No. 110: THE METHOD OF TEETH CLEANING, IN WHICH THE VESTIBULAR SURFACE OF THE TEETH IS CLEANED WITH CIRCULAR MOVEMENTS, IS CALLED STANDARD G.N. Pakhomov Stillman + circular Fones Bass Leonard
Question No. 111: THE OPTIMUM THICKNESS OF APPLICATION OF A PORTION OF LIGHT CURING COMPOSITE MATERIAL IS (MM) 45 34 23 67 + 7.52
Question No. 112: METHODS FOR REMOVAL OF DENTAL PAPULUS ultrasonic, sonic + manual (mechanical), ultrasonic, sonic, soda jet, chemical mechanical, ultrasonic, sonic manual (mechanical), ultrasonic, sonic, soda jet mechanical, ultrasonic
Question No. 113: IN CHRONIC GRANULATING PERIODONTITIS OF A PERMANENT SINGLE-ROOT IMFORMED TOOTH AFTER REMOVAL OF GRANULATION THE SAME VISIT IS CARRIED OUT + filling the canal with paste the tooth canal is left open physiotherapeutic procedures placing a turunda with proteolytic enzymes anti-inflammatory therapy
Question No. 114: TO DETECT CARIOUS STAINS BY STAINING METHOD, APPLY + 2% solution of methylene blue, potassium iodide solution, Schiller-Pisarev’s reagent, brilliant green caprofer
Question No. 115: MODERATE PERIODONTITIS IS DIFFERENTIATED WITH catarrhal gingivitis + severe periodontitis, periodontal disease, hypertrophic gingivitis, fibromatosis
Question No. 116: DESCUAMATIVE GLOSSITISIS IS THE RESULT OF DISORDERS of psychogenic cardiovascular + neurotrophic hematopoietic venous outflow
Question No. 117: CHRONIC RECURRENT APHTHOSIC STOMATITIS IS DIFFERENTIATED WITH acute herpes, secondary syphilis, necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis, exudative erythema multiforme + chronic herpes
Question No. 118: MEDIO-OCCLUSION-DISTAL CAVITIES ARE FORMED ON THE SURFACES of the anterior contact with an additional platform of the anterior and posterior contact + contact with a common additional platform of the posterior contact with an additional masticatory and vestibular platform
Question No. 119: DEEP CARIOUS CAVITY AND LACK OF COMMUNICATION WITH THE TOOTH CAVITY IS A COMMON SYMPTOM FOR superficial caries and medium caries + deep caries and acute focal pulpitis, chronic gangrenous pulpitis and medium caries, medium caries and carious spots, chronic fibrous pulpitis and chronic periodontitis
Question No. 120: ONE OF THE BASIC REQUIREMENTS FOR TOOTHBRUSHS IS THE PRESENCE OF A power protrusion + artificial fiber bristles, straight handle, natural bristles, indicator bristles
Question No. 121: USING THE API HYGIENIC INDEX, THE severity of dental anomalies is DETERMINED, the degree of inflammation of the gums + the presence of plaque on the contact surfaces of the teeth, the presence of plaque and tartar, bleeding of the gingival sulcus
Question No. 122: CAUSE OF ZINGLES actinomycetes Leffler's bacillus + varicellazoster virus fusospirochete Vincent herpes simplex virus
Question No. 123: PULP CONSISTS OF ground substance, vessels, nerves, cellular elements and vessels + fibrous structures, cells, ground substance, vessels and nerves, cellular and fibrous structures of vessels and nerves
Question No. 124: TO REDUCE HYPERESTHESIA OF HARD TISSUES OF TEETH IN PERIODONTIS, hygienic + remineralizing enzyme-containing salt anti-inflammatory TOOTHPASTES are used
Question No. 125: NORMALLY THE EPITHELIA DOES NOT KERINATE all answers are correct + gingival sulcus papillary gingiva marginal gingiva alveolar gingiva
Question No. 126: LOCAL TREATMENT OF EROSIVE-ULCER FORM OF LICHEN PLANUS correct I), 2) and 3) + elimination of chronic injury + treatment with resorcinol + epithelizing preparations injections of vitamin “PP” under the lesion elements
Question No. 127: ELEMENTS OF DAMAGE IN VINCENT ULCERONECROTIC GINGIVITIS aphtha + ulcer plaque spot erosion
Question No. 128: PMA INDEX FOR PERIODONTIS about 100% to 50% to 70% + does not change less than 30%
Question No. 129: EXCERNSATION OF CHRONIC FORMS OF PULPITIS ALWAYS APPEARS WHEN THE LOAD CHANGES, Lack of irritants + disruption of the outflow of exudate, formation of drainage, exposure to irritants
Question No. 130: THE PRIMARY ELEMENT OF DAMAGE IN ACUTE HERPETIC STOMATISIS IS CALLED aphtha erosion crust + vesicle papule
Question No. 131: A DERIVATIVE OF THE ENAMEL-FORMING EPITHELIA IN THE PERIODONTAL IS periodontal enamel cement periodontal junction + junctional epithelium
Question No. 132: HUTCHINSON'S TEETH IS A MANIFESTATION of + local hypoplasia erasing fluorosis systemic hypoplasia caries
Question No. 133: PERIODONTAL POCKETS IN PERIODONTAL DISEASE up to 5 mm less than 3 mm more than 5 mm up to 4 mm + absent
Question No. 134: DRUG FOR MEDICINE TREATMENT OF CHANNELS WITH STRONG ACTIVITY AGAINST ANAEROBIC MICROORGANISMS sodium hypochlorite diclofenac sodium + metronidazole hydrogen peroxide furacillin
Question No. 135: CARIES AT THE STAIN STAGE DIFFERENTIATE enamel erosion wedge-shaped defect medium caries + fluorosis pathological abrasion of hard tooth tissues
Question No. 136: CHANGES IN THE PULP DURING DEEP CARIES ARE OF THE NATURE of necrosis + acute inflammation, productive changes in pulp aging, chronic inflammation
Question No. 137: THICKENING OF THE CELLS OF THE SLAYER SPINOSUS acanthosis ballooning degeneration spongiosis acantholysis + hyperkeratosis
Question No. 138: WHEN TREATING DENTIN HYPERESTHESIA IN PATIENTS WITH PERIODONTIS, PREFERENCE IS GIVEN TO PREPARATIONS CONTAINING calcium + amorphous calcium phosphate phosphates hydroxyl phosphate all of the above
Question No. 139: SYSTEMIC HYPOPLASTIC CHANGES ARE MORE COMMON IN third molars + permanent incisors, first molars primary molars premolars of the upper jaw premolars of the lower jaw
Question No. 140: FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS, A STUDY IS SHOWN + histological is correct 1) and 2) + cytological bacterioscopic glow in Wood's rays
Question No. 141: THE DIAGNOSIS OF “DEEP CARIES” ACCORDING TO THE MES CLASSIFICATION CORRESPONDS TO THE DIAGNOSIS ACCORDING TO ICD10 cement caries enamel caries + pulp hyperemia recurrent caries dentin caries
Question No. 142: SHRINKAGE OF THE CHEMICALLY CURING COMPOSITE OCCURS TOWARDS the light source, oral, evenly throughout the volume + vestibular cavity of the tooth
Question No. 143: TEETH MOBILITY IN MILD PERIODONTITIS, 1st degree, IIIrd degree, more than IIIrd degree + absent IIIIIIth degree
Question No. 144: SUPERFICIAL PROBING OF THE PULP IS PAINLESS IN PULPITIS + chronic gangrenous chronic hypertrophic chronic in the acute stage chronic fibrous acute focal
Question No. 145: A GENERAL SYMPTOM OF ACUTE FORMS OF PULPITIS IS PAIN from hot food, which goes away after the irritant is eliminated from sour from cold, which goes away after the irritant is eliminated + spontaneous from sweets
Question No. 146: AN ACTIVE METHOD OF DENTAL EDUCATION IS television advertising, publication of popular scientific literature, publication of advertising booklets for oral hygiene products, holding exhibitions of oral hygiene products + classes on teaching oral hygiene in a kindergarten group.
Question No. 147: WITH A BLACK HAIRY TONGUE, THE PAPILIA ARE SUBJECT TO INCREASED KERINATION AND HYPERTROPHY: mushroom-shaped, pear-shaped, leaf-shaped + filiform, grooved.
Question No. 148: THE FORM OF INCREASED ABRASION OF HARD TISSUES OF THE TEETH DEPENDS ON the age of the patient, the shape of the dentition + the type of bite, the size of the teeth, the size of the jaws
Question No. 149: SUPPRESSES SALIVARY iodolipol chlorhexidine + atropine potassium iodide potassium chloride
Question No. 150: Zoster CAN CAUSE COMPLICATIONS IN THE FORM of chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis, foot and mouth disease, allergies, chronic recurrent herpetic stomatitis + trophic disorder of the affected area